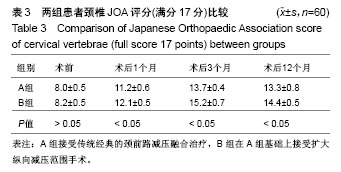
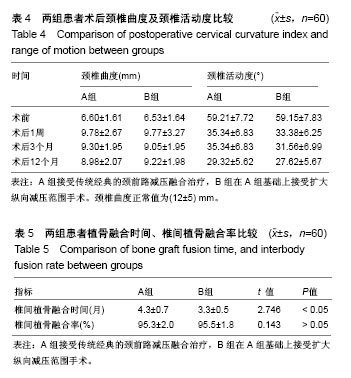
| [1] Luo J, Cao K, Huang S, et al. Comparison of anterior approach versus posterior approach for the treatment of multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Eur Spine J.2015;24(8):1621-1630.[2] Wang H, Ma L, Yang D, et al. Incidence and risk factors of postoperative adjacent segment degeneration following anterior decompression and instrumented fusion for degenerative disorders of the cervical spine. World Neurosurg.2017;105:78-85.[3] Wang T, Wang H, Liu S, et al. Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion versus anterior cervical corPectomy and fusion in multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) .2016;95(49) :e5437.[4] Park JH, Kim JH, Roh SW, et al. prognostic factor analysis after surgical decompression and stabilization for cervical spinal-cord injury. Br J Neurosurg.2017;31(2):194-198.[5] 周非非,孙宇,张凤山,等. 颈椎前路椎间盘切除、植骨融合内固定术治疗脊髓型颈椎病术后轴性症状的前瞻性研究[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2014,24(6):505-509.[6] Kouyoumdjian P, Guerin P, Schanelderle C, et al. Fracture of the lower cervical spine in patients withankylosing spondylitis: retrosPective study of 19 cases. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2012; 98(5):543-551.[7] 任志伟,杜恒,杨益民,等.颈椎前后路手术治疗多节段脊髓型颈椎病疗效对比观察[J].山东医药,2018,58(23):85-88.[8] 马原,高帅,阎朝辉,等.多节段颈椎病前路减压植骨内固定临床效果评价[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2012,20(17):1576-1579.[9] 石磊,陈德玉,史建刚,等. 颈椎前路手术中硬膜损伤的预防与治疗[J]. 脊柱外科杂志,2017,15(3):156-160.[10] Qi Q, Chen Y, Ling Z, et al. Modified laminoplasty Preserving the Posterior deep extensor insertion into C2 improves clinical and radiological results compared with conventional laminoplasty: A meta-analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018;111:157-165.[11] Kimura A, Shiraishi Y, Inoue H, et al. Predictors of Persistent axial neck Pain after cervical laminoPlasty. Spine. 2018;43(2) :10-15.[12] Lian XF, Xu JG, Zeng BF, et al. Noncontiguous anterior decompression and fusion for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a prospective randomized control clinical study. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(5):713-719.[13] 侯铁胜,严宁,虞舜志,等.前路手术治疗4节段脊髓型颈椎病的疗效分析[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2015, 35(11): 1129-1135.[14] 赖超博,刘斌.多节段脊髓型颈椎病前路手术治疗进展[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2017,14(6):64-68+72.[15] 张德生,董芳.椎间高度和颈椎曲度的变化对颈椎前路手术患者神经功能及轴性症状的影响[J].颈腰痛杂志, 2017,38(6):602-603.[16] 何达,赵经纬,田伟.下颈椎前路间盘切除融合术与椎体次全切除融合术[J].骨科临床与研究杂志,2018,3(1):52-56.[17] 林栋,陈长青,林东,等.保留与切除钩椎关节在颈前路手术的临床效果比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(1):11-16.[18] 王荣生,石裕明,刘雄业,等.颈前路手术后出现早期并发症的相关因素分析[J].颈腰痛杂志,2018,39(3):269-272.[19] Okamoto A, Shinomiya K, Furuya K, et al. Reduced neck movement after operation for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Int Orthop.2015;19: 295 -297.[20] 张年春,任先军,张峡,等.保留与未保留终板的颈椎前路减压植骨融合术对融合节段高度的影响[J].脊柱外科杂志, 2003,1(3):141-144 [21] Shou F, Li Z, Wang H, et al. Prevalence of C5 nerve root palsy after cervical decompressive surgery: a meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2015; 24(12):2724-2734.[22] Alonso F, Voin V, Iwanaga J, et al. potential mechanism for some postoperative C5 Palsies: an anatomical study. Spine. 2018;43(3): 161-166.[23] 关立,汪文龙,海涌,等.颈椎前路非融合术与前路融合术治疗颈椎病的中期疗效比较[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2016, 96(25):1991-1996.[24] Gu Y, Shi J, Cao P, et al. Clinical and imaging predictors of surgical outcome in multilevel cervical ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament: An analysis of 184 patients. PLoS One.2015;10(9): e0136042.[25] 甘立猛,鲁世保,孙文志,等. 前路椎体次全切与椎间盘切除减压植骨融合内固定术治疗双节段颈椎病的临床疗效比较[J]. 北京医学, 2016, 38(7):631-637.[26] Eicker SO, Steiger HJ, Elkathib M. Transtubular microsurgical approach to treat lateral cervical disc herniation.World Neurosurg.2016;88:503-509.[27] Hartman J. Anatomy and clinical significance of the uncinate pro?cess and uncovertebral joint: a comprehensive review. Clin Anat. 2014;27 (3):431-440.[28] 刘长安,张卫平,王凌云,等. 颈椎前路多节段椎体次全切减压植骨融合内固定术治疗多节段脊髓型颈椎病[J]. 解放军医药杂志,2015, 27(4): 24-27.[29] 姚高文,汪卫,周永强. 前路不同手术方式治疗脊髓型颈椎病疗效分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2015, 30(6):1-2.[30] Rieger A, Holz C, Marx T, Sanchin L, et al. Vertebral autograft used as bone transplant for anterior cervical corpectomy technical note. Neurosurgery. 2003;52(2):449-453.[31] Tetreault L, Ibrahim A, Côté P, et al. A systematic review of clinical and surgical predictors of complications following surgery for degenerative cervical myeloPathy. J Neurosurg SPine. 2016;24(1): 77-99.[32] 陈德玉,贾连顺,赵定麟,等.颈椎病前路减压术后再手术[J].中华骨科杂志,2002,22(3):134-137.[33] Woods BI, Hohl J, Lee J,et al. Laminoplasty versus laminectomy and fusion for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(3):688-695.[34] Liu JM, Peng HW, Liu ZL, et al.Hybrid decompression technique versus anterior cervical corpectomy and fusion for treating multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy: which one is better. World Neurosurg. 2015;84(6):2022-2029.[35] Shi JS, Lin B, Xue C, et al. Clinical and radiological outcomes following hybrid surgery in the treatment of multi level cervical spondylosis: over a 2 year follow Up. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:185.[36] 许良,孔鹏,徐展望.颈前路椎体次全切减压钛网植骨融合联合钛板固定治疗多节段脊髓型颈椎病[J].中国骨伤, 2016,29(3):211-215. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)