| [1] 陈现乐.美国脑卒中中心认证制度及对我国的借鉴意义[J].中国中西医结合急救杂志,2016,23(2):115-116.[2] 王学义,马承君,王莹莹,等.亚低温治疗方案的临床应用[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2012,21(7):741-745.[3] 张儒有,郑永日,胡韶山,等.神经干细胞移植治疗脑卒中后遗症50例临床效果分析[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(9):138-139.[4] Sravanthi KN, Rao NR. Cerebroprotective activity of Pentapetes phoenicea on global cerebral ischemia in rats. Indian J Pharmacol. 2016;48(6):694-700.[5] Bai S, Sun Y, Wu L, et al. Tripotolide ameliorates inflammation and apoptosis induced by focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016;45(5): 493-500.[6] Gekht AB, Kanaeva LS, Avedisova AS, et al. Possible applications of rac-hopantenic acid in the treatment of anxiety and depressive disorders in patients with chronic cerebral ischemia. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2016; 116(11):45-57.[7] Gritti A, Vescovi AL, Galli R. Adult neural stem cells: plasticity and developmental potential. J Physiol Paris. 2002;96(1-2): 81-90.[8] 彭超华,戴冀斌,田毅浩,等.小鼠胚胎大脑皮质与中脑神经干细胞培养与分化比较的研究[J].解剖学报, 2005,36(6):660-664.[9] Laterza C, Wattananit S, Uoshima N, et al. Monocyte depletion early after stroke promotes neurogenesis from endogenous neural stem cells in adult brain. Exp Neurol. 2017;297:129-137.[10] Zhang F, Duan X, Lu L, et al. In Vivo Targeted MR Imaging of Endogenous Neural Stem Cells in Ischemic Stroke. Molecules. 2016;21(9): E1143.[11] Kokaia Z, Darsalia V. Human Neural Stem Cells for Ischemic Stroke Treatment. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2018;66:249-263.[12] Yu X, Wang X, Zeng S, et al. Protective effects of primary neural stem cell treatment in ischemic stroke models. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(3):2219-2228.[13] Bierer S, Herrmann E, Kopke T, et al. Lymphangiogenesis in kidney cancer: expression of VEGF-C, VEGF-D and VEGFR-3 in clear cell and papillary renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2008;20(4):721-725.[14] Zhao J, Li H, Wang M. Acute renal failure in a patient receiving anti-VEGF therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2009;4(9):1185-1187.[15] Xu Z, Han K, Chen J, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor is neuroprotective against ischemic brain injury by inhibiting scavenger receptor A expression on microglia. J Neurochem. 2017;142(5):700-709.[16] Liu M, Wu Y, Liu Y, et al. Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Protects Astrocytes Against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Upregulating the Caveolin-1/VEGF Signaling Pathway. J Mol Neurosci. 2018;64(2):211-223.[17] 万鲁虹,张伟丽,孙凯,等.VEGF 2型受体基因多态与脑卒中易感性和脑卒中复发相关[J].中国分子心脏病学杂志, 2009,9(4): 204-208.[18] Anuncibay-Soto B, Santos-Galdiano M, Fernandez-Lopez A. Neuroprotection by salubrinal treatment in global cerebral ischemia. Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(11):1744-1745.[19] Duan K, Wang X, Yang Z, et al. Therapeutic effect of GDNF gene-modified mesencephalic neural stem cell transplantation in a rat model of Parkinson disease. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2016;36(1):32-38.[20] McGinley LM, Kashlan ON, Bruno ES, et al. Human neural stem cell transplantation improves cognition in a murine model of Alzheimer's disease. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):14776.[21] Zhou CL, Zhao L, Shi HY, et al. Combined acupuncture and HuangDiSan treatment affects behavior and synaptophysin levels in the hippocampus of senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 after neural stem cell transplantation. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(3):541-548. [22] Chen M, Takano-Maruyama M, Pereira-Smith OM, et al. MRG15, a component of HAT and HDAC complexes, is essential for proliferation and differentiation of neural precursor cells. J Neurosci Res. 2009;87(7):1522-1531. [23] Bieberich E, MacKinnon S, Silva J, et al. Regulation of cell death in mitotic neural progenitor cells by asymmetric distribution of prostate apoptosis response 4 (PAR-4) and simultaneous elevation of endogenous ceramide. J Cell Biol. 2003;162(3):469-479. [24] Braga A, Maestá I, Rocha Soares R, et al. Apoptotic index for prediction of postmolar gestational trophoblastic neoplasia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;215(3):336.e1-336.e12.[25] Szweda M, Rychlik A, Nowicki M, et al. The effect of budesonide on the expression of Ki-67 and PCNA and the apoptotic index in dogs with inflammatory bowel disease. Pol J Vet Sci. 2017;20(4):743-750.[26] Shi X, Yan C, Liu B, et al. miR-381 Regulates Neural Stem Cell Proliferation and Differentiation via Regulating Hes1 Expression. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0138973. [27] Zheng J, Yi D, Liu Y, et al. Long nonding RNA UCA1 regulates neural stem cell differentiation by controlling miR-1/Hes1 expression. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(8):3696-3704. [28] Bao H, Song J. Treating Brain Disorders by Targeting Adult Neural Stem Cells. Trends Mol Med. 2018;24(12):991-1006.[29] Wang C, Lu CF, Peng J, et al.Roles of neural stem cells in the repair of peripheral nerve injury.Neural Regen Res. 2017; 12(12):2106-2112.[30] Vogel S, Aswendt M, Nelles M, et al. Initial graft size and not the innate immune response limit survival of engrafted neural stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(3):784-793.[31] Thermet A, Robaczewska M, Rollier C, et al. Identification of antigenic regions of duck hepatitis B virus core protein with antibodies elicited by DNA immunization and chronic infection. J Virol. 2004;78(4):1945-1953.[32] 冯娜,戴冀斌,陈龙菊,等.不同低氧浓度对神经干细胞增殖与凋亡的影响[J].解剖学研究,2011,33(5):327-330.[33] Zhao C, Sun G, Li S, et al. MicroRNA let-7b regulates neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation by targeting nuclear receptor TLX signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107(5):1876-1881. [34] Edlich F. BCL-2 proteins and apoptosis: Recent insights and unknowns. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;500(1): 26-34.[35] Cianciulli A, Porro C, Calvello R, et al. Resistance to apoptosis in Leishmania infantum-infected human macrophages: a critical role for anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein and cellular IAP1/2. Clin Exp Med. 2018;18(2):251-261.[36] Peña-Blanco A, García-Sáez AJ. Bax, Bak and beyond - mitochondrial performance in apoptosis. FEBS J. 2018; 285(3):416-431.[37] Schwingshackl A, Lopez B, Teng B, et al. Hyperoxia treatment of TREK-1/TREK-2/TRAAK-deficient mice is associated with a reduction in surfactant proteins. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017;313(6):L1030-L1046.[38] Pan L, Yang F, Lu C, et al. Effects of sevoflurane on rats with ischemic brain injury and the role of the TREK-1 channel. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(4):2937-2942.[39] QiNan W, XiaGuang G, XiaoTian L, et al. Par-4/NF-κB Mediates the Apoptosis of Islet β Cells Induced by Glucolipotoxicity. J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:4692478.[40] Zhang DX, Ma DY, Yao ZQ, et al. ERK1/2/p53 and NF-κB dependent-PUMA activation involves in doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016; 20(11):2435-2442. [41] Zhuang C, Huo H, Fu W, et al. Aluminum chloride induced splenic lymphocytes apoptosis through NF-κB inhibition. Chem Biol Interact. 2016;257:94-100. |
.jpg)
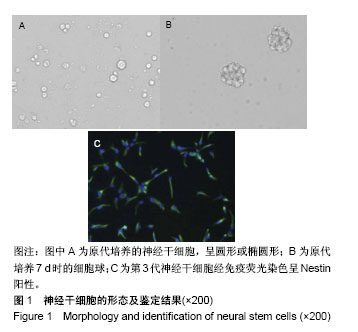
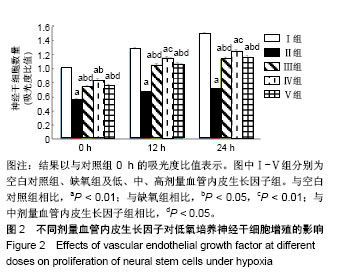
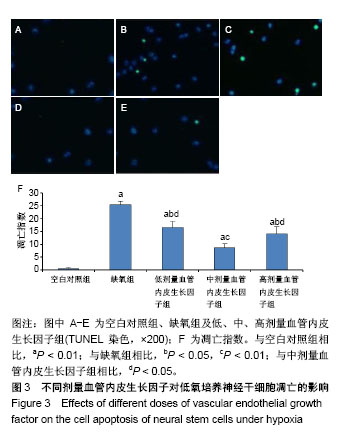
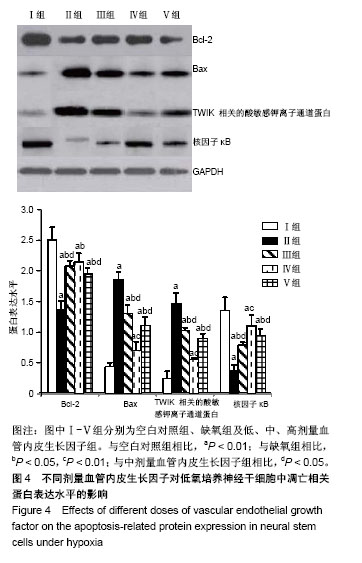
.jpg)
.jpg)