| [1] Ankrum JA, Ong JF, Karp JM. Mesenchymal stem cells: immune evasive, not immune privileged. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32(3):252-260.[2] Yu B, Zhang X, Li X. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(3):4142-4157. [3] Sahoo S, Klychko E, Thorne T, et al. Exosomes from human CD34(+) stem cells mediate their proangiogenic paracrine activity. Circ Res. 2011;109(7):724-728.[4] Sun L, Xu R, Sun X, et al. Safety evaluation of exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cell. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(3):413-422.[5] Taverna S, Amodeo V, Saieva L, et al. Exosomal shuttling of miR-126 in endothelial cells modulates adhesive and migratory abilities of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Mol Cancer. 2014;13:169. [6] Xiao J, Pan Y, Li XH, et al. Cardiac progenitor cell-derived exosomes prevent cardiomyocytes apoptosis through exosomal miR-21 by targeting PDCD4. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(6):e2277.[7] Hu X, Xu Y, Zhong Z, et al. A Large-Scale Investigation of Hypoxia-Preconditioned Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Myocardial Repair in Nonhuman Primates: Paracrine Activity Without Remuscularization. Circ Res. 2016;118(6): 970-983.[8] Wang X, Yin X, Sun W, et al. Intravenous infusion umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell in primary immune thrombocytopenia: A two-year follow-up. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13(5):2255-2258.[9] Wang Y, Han ZB, Ma J, et al. A toxicity study of multiple-administration human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in cynomolgus monkeys. Stem Cells Dev. 2012; 21(9):1401-1408.[10] Majore I, Moretti P, Stahl F, et al. Growth and differentiation properties of mesenchymal stromal cell populations derived from whole human umbilical cord. Stem Cell Rev. 2011;7(1): 17-31. [11] 雷鑫,陈彦,张建林,等.评价脐带间充质干细胞移植前细胞活性的指标[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(32):5847-5854.[12] 崔蕾,雷鑫,牛玉虎,等.人脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗大鼠急性肺损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(14):2563-2569.[13] 郭莹,王秀伟,牛玉虎,等.人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体提取方法的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(9):1382-1388.[14] Khong SML, Lee M, Kosaric N, et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomics of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reveal Age-Related Cellular Subpopulation Depletion and Impaired Regenerative Function. Stem Cells. 2018. doi: 10.1002/stem.2934. [Epub ahead of print][15] Hendijani F, Sadeghi-Aliabadi H, Haghjooy Javanmard S. Comparison of human mesenchymal stem cells isolated by explant culture method from entire umbilical cord and Wharton's jelly matrix. Cell Tissue Bank. 2014;15(4):555-565.[16] Taghizadeh RR, Cetrulo KJ, Cetrulo CL. Wharton's Jelly stem cells: future clinical applications. Placenta. 2011;32 Suppl 4:S311-315. [17] Prabhu SD, Frangogiannis NG. The Biological Basis for Cardiac Repair After Myocardial Infarction: From Inflammation to Fibrosis. Circ Res. 2016;119(1):91-112.[18] Carreau A, El Hafny-Rahbi B, Matejuk A, et al. Why is the partial oxygen pressure of human tissues a crucial parameter? Small molecules and hypoxia. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(6): 1239-1253.[19] Zhou P, Tan YZ, Wang HJ, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning-induced autophagy enhances survival of engrafted endothelial progenitor cells in ischaemic limb. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(10):2452-2464.[20] Santos Nascimento D, Mosqueira D, Sousa LM, et al. Human umbilical cord tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate remodeling after myocardial infarction by proangiogenic, antiapoptotic, and endogenous cell-activation mechanisms. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(1):5.[21] Ohnuki M, Takahashi K. Present and future challenges of induced pluripotent stem cells. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015;370(1680):20140367.[22] Zhang Y, Hu YW, Zheng L, et al. Characteristics and Roles of Exosomes in Cardiovascular Disease. DNA Cell Biol. 2017; 36(3):202-211.[23] Charoenviriyakul C, Takahashi Y, Nishikawa M, et al. Preservation of exosomes at room temperature using lyophilization. Int J Pharm. 2018;553(1-2):1-7.[24] Li RC, Tao J, Guo YB, et al. In vivo suppression of microRNA-24 prevents the transition toward decompensated hypertrophy in aortic-constricted mice. Circ Res. 2013;112(4): 601-605.[25] Bernardo BC, Gao XM, Winbanks CE, et al. Therapeutic inhibition of the miR-34 family attenuates pathological cardiac remodeling and improves heart function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(43):17615-17620.[26] Ibrahim AG, Cheng K, Marbán E. Exosomes as critical agents of cardiac regeneration triggered by cell therapy. Stem Cell Reports. 2014;2(5):606-619.[27] Feng Y, Huang W, Meng W, et al. Heat shock improves Sca-1+ stem cell survival and directs ischemic cardiomyocytes toward a prosurvival phenotype via exosomal transfer: a critical role for HSF1/miR-34a/HSP70 pathway. Stem Cells. 2014;32(2):462-472.[28] Hu GW, Li Q, Niu X, et al. Exosomes secreted by human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate limb ischemia by promoting angiogenesis in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:10.[29] Kogure T, Yan IK, Lin WL, et al. Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Transfer of a Novel Long Noncoding RNA TUC339: A Mechanism of Intercellular Signaling in Human Hepatocellular Cancer. Genes Cancer. 2013;4(7-8):261-272.[30] Mohankumar S, Patel T. Extracellular vesicle long noncoding RNA as potential biomarkers of liver cancer. Brief Funct Genomics. 2016;15(3):249-256.[31] Xu LF, Wu ZP, Chen Y, et al. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) regulates cellular proliferation, invasion, migration, and apoptosis by targeting PTEN, RECK and Bcl-2 in lung squamous carcinoma, Gejiu City, China. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e103698.[32] Lin J, Li J, Huang B, et al. Exosomes: novel biomarkers for clinical diagnosis. Scientific World Journal. 2015;2015: 657086.[33] Diaz G, Wolfe LM, Kruh-Garcia NA, et al. Changes in the Membrane-Associated Proteins of Exosomes Released from Human Macrophages after Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection. Sci Rep. 2016;6:37975.[34] Zhang J, Ma J, Long K, et al. Overexpression of Exosomal Cardioprotective miRNAs Mitigates Hypoxia-Induced H9c2 Cells Apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(4): E711. |
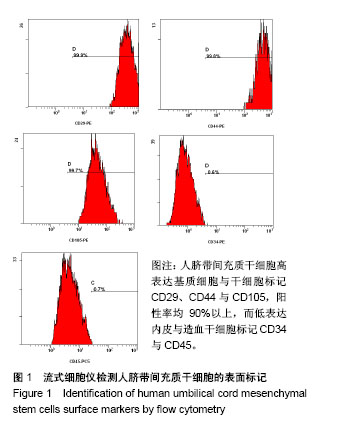
.jpg)
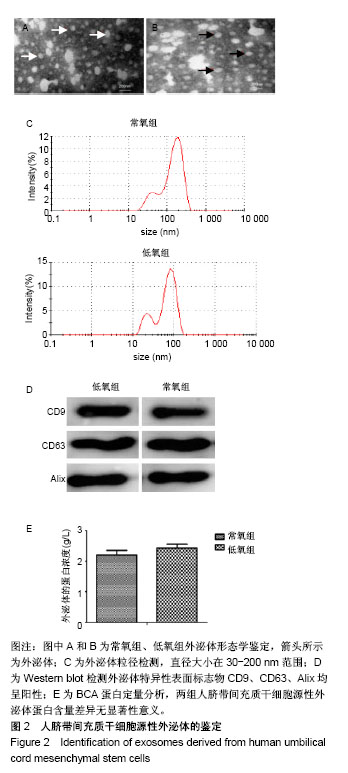
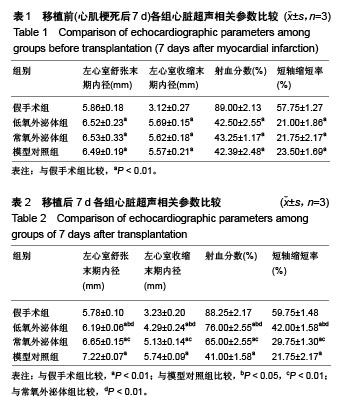
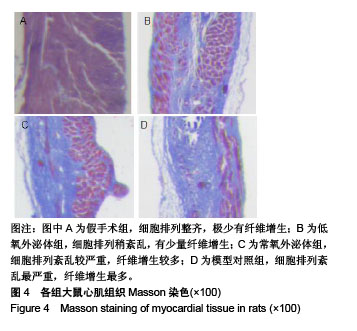
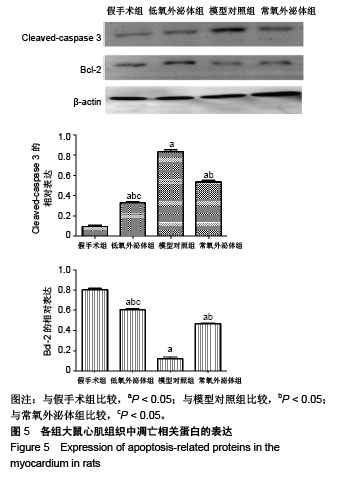
.jpg)
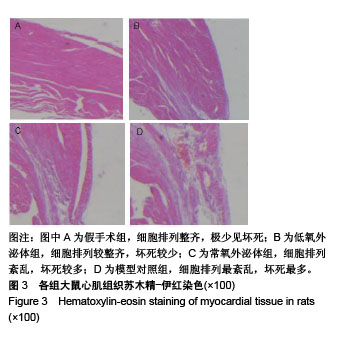
.jpg)