| [1] Howlader D, Vignesh U, Bhutia DP, et al. Hydroxyapatite collagen scaffold with autologous bone marrow aspirate for mandibular condylar reconstruction. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2017; 45(9): 1566-1572.[2] Tuukkanen J, Nakamura M. Hydroxyapatite as a Nanomaterial for Advanced Tissue Engineering and Drug Therapy. Curr Pharm Des.2017;23(26):3786-3793.[3] Kamalaldin N, Jaafar M, Zubairi SI, et al. Physico-Mechanical Properties of HA/TCP Pellets and Their Three-Dimensional Biological Evaluation In Vitro.Adv Exp Med Biol.2018. doi: 10.1007/5584_2017_130. [Epub ahead of print][4] Tohamy KM, Mabrouk M, Soliman IE, et al. Novel alginate/hydroxyethyl cellulose/hydroxyapatite composite scaffold for bone regeneration: In vitro cell viability and proliferation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Biol Macromol.2018; 112: 448-460.[5] Tanaka M, Haniu H, Kamanaka T, et al. Physico-Chemical, In Vitro, and In Vivo Evaluation of a 3D Unidirectional Porous Hydroxyapatite Scaffold for Bone Regeneration. Materials(Basel). 2017;10(1). pii: E33. doi: 10.3390/ma10010033.[6] Tamaddon M, Samizadeh S, Wang L, et al. Intrinsic Osteoinductivity of Porous Titanium Scaffold for Bone Tissue Engineering. Int J Biomater.2017;2017:5093063.[7] Huang B, Caetano G, Vyas C, et al. Polymer-Ceramic Composite Scaffolds: The Effect of Hydroxyapatite and beta-tri-Calcium Phosphate. Materials(Basel).2018; 11(1). pii: E129. doi: 10.3390/ ma11010129.[8] Meskinfam M, Bertoldi S, Albanese N, et al. Polyurethane foam/nano hydroxyapatite composite as a suitable scaffold for bone tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018; 82:130-140.[9] Zang S, Zhu L, Luo K, et al. Chitosan composite scaffold combined with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for bone regeneration: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Oncotarget. 2017;8(67):110890-110903.[10] Varoni EM, Vijayakumar S, Canciani E, et al. Chitosan-Based Trilayer Scaffold for Multitissue Periodontal Regeneration. J Dent Res.2017:1335507775.[11] Li Y, Zhang Z, Zhang Z. Porous Chitosan/ Nano-Hydroxyapatite Composite Scaffolds Incorporating Simvastatin-Loaded PLGA Microspheres for Bone Repair. Cells Tissues Organs. 2018; 205(1):20-31.[12] Zhou T, Wu J, Liu J, et al. Fabrication and characterization of layered chitosan/silk fibroin/nano-hydroxyapatite scaffolds with designed composition and mechanical properties. Biomed Mater. 2015;10(4):45013.[13] Iqbal H, Ali M, Zeeshan R, et al. Chitosan/hydroxyapatite (HA)/hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose (HPMC) spongy scaffolds-synthesis and evaluation as potential alveolar bone substitutes.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;160:553-563.[14] Chen BQ, Kankala RK, Chen AZ, et al. Investigation of silk fibroin nanoparticle-decorated poly(l-lactic acid) composite scaffolds for osteoblast growth and differentiation. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017; 12:1877-1890.[15] Oftadeh MO, Bakhshandeh B, Dehghan MM, et al. Sequential application of mineralized electroconductive scaffold and electrical stimulation for efficient osteogenesis. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(5):1200-1210.[16] Dhivya S, Keshav NA, Logith KR, et al. Proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on scaffolds containing chitosan, calcium polyphosphate and pigeonite for bone tissue engineering. Cell Prolif. 2018;51(1). doi: 10.1111/cpr.12408. Epub 2017 Nov 21.[17] Shahbazarab Z, Teimouri A, Chermahini AN, et al. Fabrication and characterization of nanobiocomposite scaffold of zein/chitosan/ nanohydroxyapatite prepared by freeze-drying method for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018; 108:1017-1027.[18] Lu Y, Li M, Li L, et al. High-activity chitosan/nano hydroxyapatite/zoledronic acid scaffolds for simultaneous tumor inhibition, bone repair and infection eradication. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2018;82:225-233.[19] Moraes PC, Marques I, Basso FG, et al. Repair of Bone Defects with Chitosan-Collagen Biomembrane and Scaffold Containing Calcium Aluminate Cement. Braz Dent J. 2017;28(3):287-295.[20] Li J, Wang Q, Gu Y, et al. Production of Composite Scaffold Containing Silk Fibroin, Chitosan, and Gelatin for 3D Cell Culture and Bone Tissue Regeneration. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23: 5311-5320.[21] Kaczmarek B, Sionkowska A, Kozlowska J, et al. New composite materials prepared by calcium phosphate precipitation in chitosan/collagen/hyaluronic acid sponge cross-linked by EDC/NHS. Int J Biol Macromol.2018;107(Pt A):247-253.[22] Lu Y, Li L, Zhu Y, et al. Multifunctional Copper-Containing Carboxymethyl Chitosan/Alginate Scaffolds for Eradicating Clinical Bacterial Infection and Promoting Bone Formation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2018;10(1):127-138.[23] Ruan SQ, Deng J, Yan L, et al. Composite scaffolds loaded with bone mesenchymal stem cells promote the repair of radial bone defects in rabbit model. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;97:600-606.[24] Shalumon KT, Lai GJ, Chen CH, et al.Modulation of Bone-Specific Tissue Regeneration by Incorporating Bone Morphogenetic Protein and Controlling the Shell Thickness of Silk Fibroin/ Chitosan/Nanohydroxyapatite Core-Shell Nanofibrous Membranes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2015;7(38):21170-21181.[25] Qi X N, Mou Z L, Zhang J, et al. Preparation of chitosan/silk fibroin/hydroxyapatite porous scaffold and its characteristics in comparison to bi-component scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(2):366-372.[26] Ruan SQ, Yan L, Deng J, et al. Preparation of a biphase composite scaffold and its application in tissue engineering for femoral osteochondral defects in rabbits. Int Orthop. 2017;41(9): 1899-1908.[27] Ruan SQ, Deng J, Yan L, et al. Composite scaffolds loaded with bone mesenchymal stem cells promote the repair of radial bone defects in rabbit model. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;97:600-606.[28] Raina DB, Isaksson H, Teotia AK, et al. Biocomposite macroporous cryogels as potential carrier scaffolds for bone active agents augmenting bone regeneration. J Control Release. 2016;235:365-378.[29] Ran J, Hu J, Sun G, et al. A novel chitosan-tussah silk fibroin/nano-hydroxyapatite composite bone scaffold platform with tunable mechanical strength in a wide range. Int J Biol Macromol.2016;93(Pt A):87-97.[30] Bhuiyan DB, Middleton JC, Tannenbaum R, et al. Bone regeneration from human mesenchymal stem cells on porous hydroxyapatite-PLGA-collagen bioactive polymer scaffolds. Biomed Mater Eng.2017;28(6):671-685.[31] A A, Menon D, T B S, et al. Bioinspired Composite Matrix Containing Hydroxyapatite-Silica Core-Shell Nanorods for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(32): 26707-26718.[32] Hernandez I, Kumar A, Joddar B. A Bioactive Hydrogel and 3D Printed Polycaprolactone System for Bone Tissue Engineering. Gels.2017;3(3).pii: 26.doi:10.3390/gels3030026. Epub 2017 Jul 6.[33] David N, Nallaiyan R. Biologically anchored chitosan/gelatin-SrHAP scaffold fabricated on Titanium against chronic osteomyelitis infection. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018; 110: 206-214.[34] Chen CK, Chang NJ, Wu YT, et al. Bone Formation Using Cross-Linked Chitosan Scaffolds in Rat Calvarial Defects. Implant Dent.2018;27(1):15-21.[35] Stepniewski M, Martynkiewicz J, Gosk J. Chitosan and its composites: Properties for use in bone substitution. Polim Med. 2017;47(1):49-53.[36] Casagrande S, Tiribuzi R, Cassetti E, et al. Biodegradable composite porous poly(dl-lactide-co-glycolide) scaffold supports mesenchymal stem cell differentiation and calcium phosphate deposition. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2017:1-11.[37] Garcia-Gonzalez CA, Barros J, Rey-Rico A, et al. Antimicrobial Properties and Osteogenicity of Vancomycin-Loaded Synthetic Scaffolds Obtained by Supercritical Foaming. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(4):3349-3360.[38] Lin HY, Chang TW, Peng TK. 3D plotted alginate fibers embedded with diclofenac and bone cells coated with chitosan for bone regeneration during inflammation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018; 106(6):1511-1521.[39] Sommer MR, Vetsch JR, Leemann J, et al. Silk fibroin scaffolds with inverse opal structure for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2017;105(7):2074-2084.[40] Jo YY, Kim SG, Kwon KJ, et al. Silk Fibroin-Alginate- Hydroxyapatite Composite Particles in Bone Tissue Engineering Applications In Vivo. Int J Mol Sci.2017;18(4). pii: E858. doi: 10.3390/ijms18040858.[41] Farokhi M, Mottaghitalab F, Samani S, et al. Silk fibroin/hydroxyapatite composites for bone tissue engineering. Biotechnol Adv.2018;36(1):68-91.[42] Sangkert S, Kamonmattayakul S, Chai WL, et al. Modified porous scaffolds of silk fibroin with mimicked microenvironment based on decellularized pulp/fibronectin for designed performance biomaterials in maxillofacial bone defect. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(6):1624-1636.[43] Bhattacharjee P, Naskar D, Maiti TK, et al. Non-mulberry silk fibroin grafted poly (capital JE, Ukrainian-caprolactone)/nano hydroxyapatite nanofibrous scaffold for dual growth factor delivery to promote bone regeneration. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2016;472: 16-33.[44] Mclaren JS, White LJ, Cox HC, et al. A biodegradable antibiotic-impregnated scaffold to prevent osteomyelitis in a contaminated in vivo bone defect model. Eur Cell Mater. 2014;27: 332-349.[45] Lu M, Liao J, Dong J, et al. An effective treatment of experimental osteomyelitis using the antimicrobial titanium/silver-containing nHP66(nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide-66) nanoscaffold biomaterials. Sci Rep.2016;6:39174.[46] Mostafa AA, El-Sayed M, Mahmoud AA, et al. Bioactive/Natural Polymeric Scaffolds Loaded with Ciprofloxacin for Treatment of Osteomyelitis.AAPS Pharm Sci Tech.2017;18(4):1056-1069.[47] Zhou J, Zhou XG, Wang JW, et al. Treatment of osteomyelitis defects by a vancomycin-loaded gelatin/beta-tricalcium phosphate composite scaffold.Bone Joint Res. 2018;7(1):46-57.[48] Pacheco H, Vedantham K, Aniket, et al. Tissue engineering scaffold for sequential release of vancomycin and rhBMP2 to treat bone infections. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(12):4213-4223.[49] Dorati R, Detrizio A, Modena T, et al. Biodegradable Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration Combined with Drug-Delivery Systems in Osteomyelitis Therapy. Pharmaceuticals(Basel).2017; 10(4). pii: E96. doi: 10.3390/ph10040096.[50] David N, Nallaiyan R. Biologically anchored chitosan/gelatin-SrHAP scaffold fabricated on Titanium against chronic osteomyelitis infection.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;110: 206-214.[51] Jr Sanchez CJ, Prieto EM, Krueger CA, et al. Effects of local delivery of D-amino acids from biofilm-dispersive scaffolds on infection in contaminated rat segmental defects. Biomaterials. 2013;34(30):7533-7543.[52] Cao ZD, Jiang DM, Yan L, et al. Biosafety of the Novel Vancomycin-loaded Bone-like Hydroxyapatite/Poly-amino Acid Bony Scaffold. Chin Med J(Engl).2016;129(2):194-199.[53] Hassani B N, Mottaghitalab F, Eslami M, et al. Sustainable Release of Vancomycin from Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles for Treating Severe Bone Infection in Rat Tibia Osteomyelitis Model. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2017;9(6):5128-5138.[54] Hess U, Hill S, Treccani L, et al. A mild one-pot process for synthesising hydroxyapatite/biomolecule bone scaffolds for sustained and controlled antibiotic release. Biomed Mater.2015; 10(1):15013.[55] Huang TY, Su WT, Chen PH. Comparing the Effects of Chitosan Scaffolds Containing Various Divalent Metal Phosphates on Osteogenic Differentiation of Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth. Biol Trace Elem Res.2018; 185(2):316-326.[56] Pipattanawarothai A, Suksai C, Srisook K, et al. Non-cytotoxic hybrid bioscaffolds of chitosan-silica: Sol-gel synthesis, characterization and proposed application.Carbohydr Polym. 2017;178:190-199.[57] Drampalos E, Mohammad HR, Kosmidis C, et al. Single stage treatment of diabetic calcaneal osteomyelitis with an absorbable gentamicin-loaded calcium sulphate/hydroxyapatite biocomposite: The Silo technique. Foot(Edinb).2017;34:40-44.[58] Posadowska U, Brzychczy-Wloch M, Pamula E. Gentamicin loaded PLGA nanoparticles as local drug delivery system for the osteomyelitis treatment.Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2015;17(3):41-48.[59] Rumian L, Tiainen H, Cibor U, et al. Ceramic scaffolds enriched with gentamicin loaded poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microparticles for prevention and treatment of bone tissue infections. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2016;69:856-864.[60] Wang Q, Chen C, Liu W, et al. Levofloxacin loaded mesoporous silica microspheres/nano-hydroxyapatite/ polyurethane composite scaffold for the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis with bone defects. Sci Rep.2017;7:41808. |
.jpg)

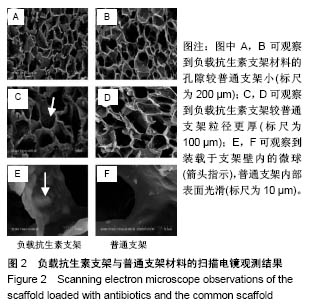
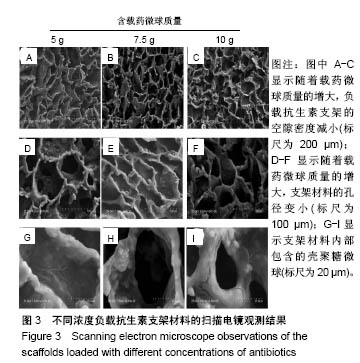
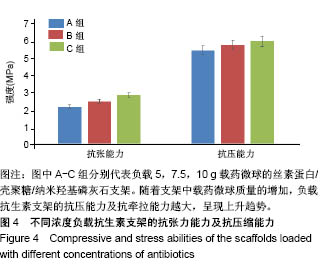

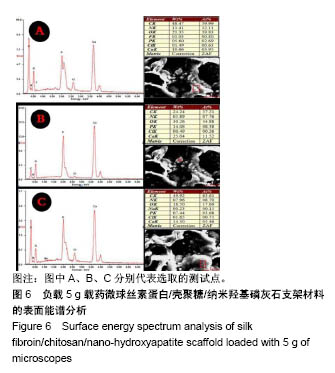
.jpg)