中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (4): 512-517.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1031
• 脊柱植入物 spinal implant • 上一篇 下一篇
多节段腰椎后路椎体间及后外侧融合椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗老年骨质疏松骨折合并胸腰椎后凸畸形
李青松1,2,刘少喻3,尹宗生1
- 1安徽医科大学第一附属医院骨科,安徽省合肥市 230022;2安徽省第二人民医院脊柱外科,安徽省合肥市 230011;3中山大学附属第一医院脊柱外科,广东省广州市 510080
Multiple posterior lumbar interbody fusion and posterolateral fusion instrumentation for thoracolumbar kyphosis and osteoporotic fracture in older adults
Li Qingsong1, 2, Liu Shaoyu3, Yin Zongsheng1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230022, Anhui Province, China; 2Department of Spinal Surgery, Anhui No. 2 Provincial People’s Hospital, Hefei 230011, Anhui Province, China; 3Department of Spinal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
脊柱后凸畸形:由各种原因造成脊柱异常后凸,使脊柱本身及其附属结构发生改变的一种疾病。绝大多脊柱后凸畸形是继发性的,例如可继发于椎体骨折、感染或肿瘤以及医源性如多节段椎板切除减压造成等。
脊柱融合术:是脊柱外科最常采用的基本手术方法。在1991年Hibbs和Albee分别提出了脊柱后路融合的基本原则和方法,并获得融合成功。适应证包括治疗脊柱感染、畸形、创伤、各种退变性疾病。
摘要
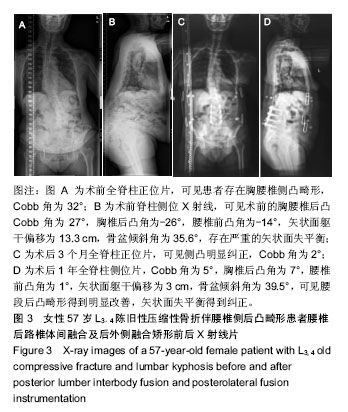
背景:随着中国人口老龄化程度不断加重,骨质疏松性骨折合并后凸畸形发病率逐渐增高。对该病的手术方式是否需要截骨矫形尚存在争议。
目的:探讨多节段腰椎后路椎体间融合及后外侧融合椎弓根螺钉内固定矫形对老年骨质疏松骨折合并胸腰椎后凸畸形患者的临床疗效和矢状位平衡的改善情况。
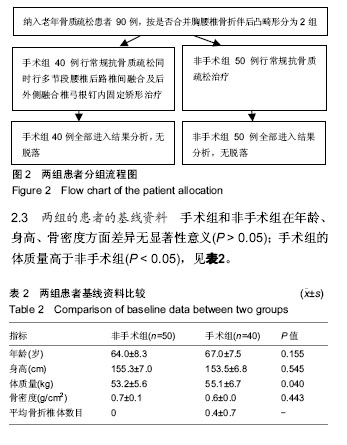
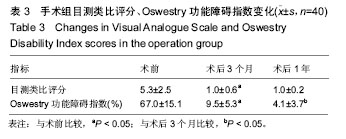
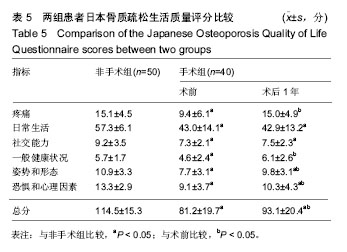
方法:回顾性研究共纳入90例老年骨质疏松的患者,其中手术组40例为合并胸腰段后凸畸形的患者,在抗骨质疏松治疗基础上,通过多节段腰椎后路椎体间融合及后外侧融合椎弓根螺钉内固定进行矫形;非手术组50例存在骨质疏松,但无后凸畸形。通过对患者术前和术后随访,观察手术组Oswestry功能障碍指数、目测类比评分变化;对比2组间脊柱骨盆矢状位参数如胸椎后凸角、腰椎前凸角、矢状面躯干偏移、骨盆倾斜角和骨盆入射角,评估患者矢状面平衡的改善;通过日本骨质疏松生活质量评分对患者的生活质量进行评估。
结果与结论:①手术组患者术后目测类比评分,Oswestry功能障碍指数均较术前明显改善;②手术组术后胸椎后凸角、矢状面躯干偏移和骨盆倾斜角均较术前明显改善;③生活质量方面,手术组术后姿势和形态评分、恐惧和心理评分较术前有明显改善,但仍低于非手术组(P < 0.05);手术组术后的疼痛评分、一般健康评分与非手术组之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);④通过多节段腰椎后路椎体间融合及后外侧融合椎弓根螺钉内固定矫形能有效改善老年骨质疏松合并胸腰椎后凸畸形患者的矢状面平衡,并提高患者的生活质量。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-0150-0109(李青松)
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)