| [1] Kalichman L, Kim DH, Li L,et al. Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis: prevalence and association with low back pain in the adult community-based population. Spine. 2009;34(2):199-205. [2] Wiltse LL, Winter RB.Terminology and measurement of spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983; 65(6):768-772.[3] Labelle H,Roussouly P,Berthonnaud E,et al. Spondylolisthesis, pelvic incidence and sagittal spino-pelvic balance: a correlation study. Spine. 2004;29(18): 2049 -2054. [4] Roussouly P, Gollogly S, Berthonnaud E,et al. Sagittal alignment of the spine and pelvis in the presence of L5-S1 isthmic lysis and low-grade spondylolisthesis. Spine. 2006;31(20):2484-2490. [5] 张奎渤,刘辉,王建儒,等. L_5轻度峡部裂型滑脱患者脊柱-骨盆矢状面参数与椎间盘退变的关系[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2015, 23(7):605-609.[6] 吴华荣,吴占勇. 椎间盘退变在成人峡部裂性腰椎滑脱病理进展中的作用[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2007, 15(17):1287-1289.[7] Vialle R, Ilharreborde B, Dauzac C, et al. Is there a sagittal imbalance of the spine in isthmic spondylolisthesis? A correlation study. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(10): 1641-1649.[8] 杜长志,孙旭,王斌,等. 青少年L5/S1发育不良性滑脱患者的骶骨矢状面形态[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2016,26(11):991-998.[9] Lafage V, Schwab F, Skalli W, et al. Standing balance and sagittal plane spinal deformity: analysis of spinopelvic and gravity line parameters. Spine. 2008;33 (14):1572-1578.[10] Taillard W. Spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. Acta Orthop Scand.1954;24(2):115-144.[11] Griffith JF, Wang YX, Antonio GE, et al. Modified Pfirrmann grading system for lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine. 2007; 32(24):708-712.[12] 李危石,孙卓然,陈仲强,等. 正常脊柱-骨盆矢状位参数的影像学研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2013, 33(5):447-453.[13] 何守玉,朱锋,邱勇,等. 成人峡部裂性腰椎滑脱患者脊柱-骨盆矢状面参数变化及其临床意义[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,24(2):109-115.[14] 刘勇,刘臻,朱锋,等. 成人腰椎峡部裂性滑脱症与退变性滑脱症患者脊柱骨盆矢状面形态学研究[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2013, 23(4):307-311.[15] Mac-Thiong JM, Berthonnaud E, Betz RR, et al. Sagittal alignment of the spine and pelvis during growth. Spine. 2004;29(15):1642-1647.[16] Ferrero E, Ould-Slimane M, Gille O, et al. Sagittal spinopelvic alignment in 654 degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2015; 24(6):1219-1227.[17] Wang T, Wang H, Liu H,et al. Sagittal spinopelvic parameters in 2-level lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis. Medicine. 2016;95(50): 5417. [18] Boos N, Weissbach S, Rohrbach H, et al. Classification of age-related changes in lumbar intervertebral discs: 2002 Volvo Award in basic science. Spine. 2002;27(23):2631-2644.[19] Weiler C, Nerlich AG, Zipperer J, et al. 2002 SSE Award Competition in Basic Science: Expression of major matrix metalloproteinases is associated with intervertebral disc degradation and resorption. Eur Spine J. 2002;11(4): 308-320.[20] Yang SH, Lin CC, Hu MH, et al. Influence of age-related degeneration on regenerative potential of human nucleus pulposus cells. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(3): 379-383.[21] Cheung KM, Chan D, Karppinen J, et al. Association of the Taq I allele in vitamin D receptor with degenerative disc disease and disc bulge in a Chinese population. Spine. 2006;31(10):1143-1148.[22] Siemionow K, An H, Masuda K, et al. The effects of age, sex, ethnicity, and spinal level on the rate of intervertebral disc degeneration: a review of 1712 intervertebral discs. Spine. 2011;36(17):1333-1339.[23] Akeda K, Yamada T, Inoue N, et al. Risk factors for lumbar intervertebral disc height narrowing: a population-based longitudinal study in the elderly. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16(1):1-9.[24] Hukins DW. A simple model for the function of proteoglycans and collagen in the response to compression of the intervertebral disc. Proc Biol Sci. 1992;249(1326):281-285.[25] 顾韬,阮狄克. 生物力学因素对椎间盘退变的影响及机理[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2011, 21(6):523-526.[26] Lotz JC, Colliou OK, Chin J R, et al. Compression-induced degeneration of the intervertebral disc: an in vivo mouse model and finite-element study. Spine. 1998;23(23):2493.[27] Hanson DS, Bridwell KH, Rhee JM, et al. Correlation of pelvic incidence with low- and high-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis. Spine. 2002;27(18):2026-2029.[28] Barrey C, Jund J, Noseda O, et al. Sagittal balance of the pelvis-spine complex and lumbar degenerative diseases. A comparative study about 85 cases. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(9):1459-1467.[29] 姚欣强,程勇泉,郑明辉,等.不同节段腰椎峡部裂对腰椎间盘退变程度的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(9):785-789.[30] Toy JO, Tinley JC, Eubanks JD, et al. Correlation of sacropelvic geometry with disc degeneration in spondylolytic cadaver specimens. Spine.2012;37(1): 10 -15.[31] 许勇,郭昭庆,云才. 合并椎间盘突出的退变性腰椎滑脱椎间盘形态改变及其意义[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2012, 22(5):398-400.[32] 马泓,吕国华.腰椎滑脱患者脊柱-骨盆参数改变的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,24(3):271-274.[33] 张忠民,金大地,陈建庭,等. 重度腰椎滑脱脊柱序列功能重建[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2008, 28(4):302-306.[34] 吕国华,王正光,王冰,等. 重度腰椎滑脱术后骨盆-脊柱参数与临床症状的相关分析[J]. 中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志, 2013,5(4):207-213.[35] 吕国华,王正光,王冰,等. 重度腰椎滑脱患者脊柱-骨盆参数改变与症状的关系[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2013, 93(15):1133-1137.[36] 李亮,隋海涛,于学忠,等. 轻度峡部裂性腰椎滑脱症融合前后脊柱-骨盆矢状位参数及临床疗效分析[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2013,27(11): 1338-1344. |
.jpg)
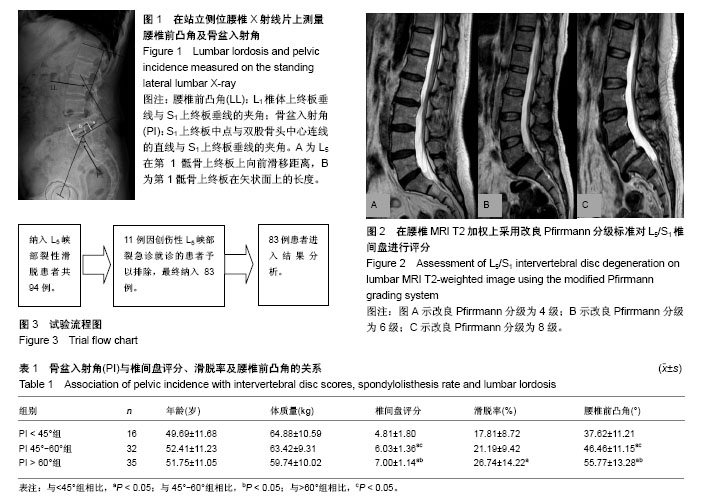
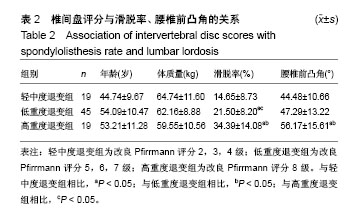

.jpg)