中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (23): 3687-3691.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0323
• 骨与关节临床实践 clinical practice of the bone and joint • 上一篇 下一篇
血小板/淋巴细胞比值对髋关节炎严重程度预测的分析:横断面研究及预试验结果
矫 秀1,朱爱青2
- 滨州医学院烟台附属医院,1检验科,2皮肤性病科,山东省烟台市 264100
Predictive analysis of severity of hip arthritis using platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio: study protocol for a cross-sectional study and preliminary results
Jiao Xiu1, Zhu Ai-qing2
- 1Department of Clinical Lab, 2Department of Dermato-Venereology, Yantai Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Yantai 264100, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
血小板计数:指单位体积血液中所含的血小板数目。血小板是血液中最小的细胞,可保护毛细血管的完整性。
淋巴细胞:是白细胞的一种,由淋巴器官产生,是机体免疫应答功能的重要细胞成分。
摘要
背景:炎症改变在髋关节炎的发病过程中占有重要地位,但目前在髋关节炎严重程度的预测上尚缺少有效的有诊断价值的炎性标志物。目前已有研究发现,血小板/淋巴细胞比值在类风湿性关节炎、银屑病性关节炎、结肠癌中与疾病的严重程度存在相关性。
目的:试验假设血小板/淋巴细胞比值与髋关节炎严重程度具有相关性,可成为一个预测髋关节炎严重程度的标志物。
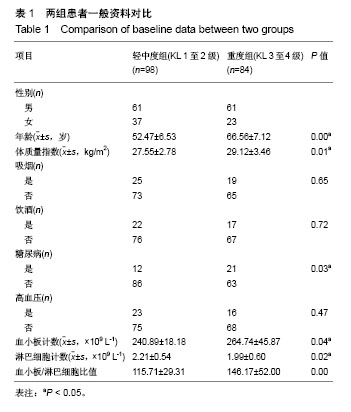
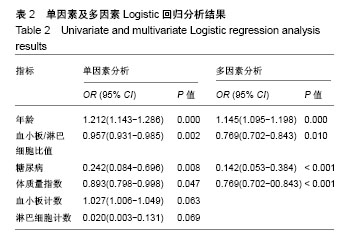
方法:试验设计将纳入滨州医学院烟台附属医院髋关节炎住院患者260例,根据髋关节炎K-L分级将患者分为2组,K-L 1至2级为轻中度组130例,K-L 3至4级为重度组130例,同时选取健康正常人130例设为对照组。各组入院后当天收集患者临床资料,进行血液生化检查及髋关节X射线检查。研究的主要结局指标为各组血小板/淋巴细胞比值。研究的次要结局指标为血小板计数,淋巴细胞计数;髋关节X射线形态;髋关节炎严重程度危险因素Logistic回归分析结果;血小板/淋巴细胞比值对髋关节炎严重程度预测的ROC曲线下面积、截断值、敏感度及特异度。稿件提交时作者已完成试验方案的设计,并完成了该项目前期的预试验:选取2014年1月至2017年6月于滨州医学院烟台附属医院住院治疗的髋关节炎患者182例,根据K-L分级分为轻中度组98例,重度组84例,Logistic回归分析显示,患有糖尿病、年龄及体质量指数增高、血小板/淋巴细胞比值增高与髋关节炎加重有关,是髋关节炎加重的独立危险因素。试验经滨州医学院烟台附属医院医学伦理委员会批准(审批单位:滨州医学院烟台附属医院,审批时间:2018年6月,审批号:20180601001)。研究符合世界医学会制定的《赫尔辛基宣言》的要求。参与者对试验方案和过程均知情同意,并签署知情同意书。试验设计时间为2018年4月,试验于2018年10月开始招募患者及数据收集,2019年3月完成对象招募,2019年4月进行结果指标分析,2019年5月完成试验。文章结果将以科学会议报告,或在同行评议的期刊上发表传播。试验已在中国临床试验注册中心注册(注册号:ChiCTR1800016820),注册方案版本号1.0。
讨论:试验旨在进一步验证如下问题:①血小板/淋巴细胞比值与髋关节炎严重程度的相关性;②血小板/淋巴细胞比值预测髋关节炎严重程度的敏感度、特异度、诊断正确率较高;③试验拟同时根据ROC曲线筛选最佳截断值,从而得出血小板/淋巴细胞比值预测髋关节炎严重程度的最佳诊断界值。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID:0000-0002-2435-2452(矫秀)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)