中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (10): 1506-1510.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0707
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
钛材料和纳米羟基磷灰石修复大鼠骨缺损:对免疫调控的影响
刘 锋1,梁载明2
- 1四川省宜宾市第一人民医院骨一科,四川省宜宾市 644000;2西南医科大学附属医院,四川省泸州市 646000
Titanium and nano-hydroxyapatite for bone defect repair in rats: effects on immune regulation
Liu Feng1, Liang Zai-ming2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, First People’s Hospital of Yibin, Yibin 644000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
理想的骨缺损修复材料:应该具备以下特性:具备良好的生物相容性;具有足够的力学性能及良好的生物学适应性;骨传导性能良好且具备诱导性;能为细胞提供足够的增殖空间,具有良好的骨组织界面;可塑性较好。
免疫调节:是指免疫系统中的免疫细胞和免疫分子之间,以及与其他系统如神经内分泌系统之间的相互作用,使得免疫应答以最恰当的形式维持在最适当的水平。免疫调节可比喻为机体的交响乐队,配合好—识别和清除抗原,对自身成分产生免疫耐受,维持内环境的稳定;配合差—病原微生物感染、肿瘤、自身免疫病、免疫缺陷病、超敏反应。
背景:研究表明,钛材料具有良好的生物学性能,能调控成骨细胞的黏附、增殖和分化,但有关钛材料在大鼠骨缺损中的修复效果及对机体免疫调控影响的研究较缺乏。
目的:探讨钛材料在大鼠骨质疏松性骨缺损中的修复效果及对机体免疫调控的影响。
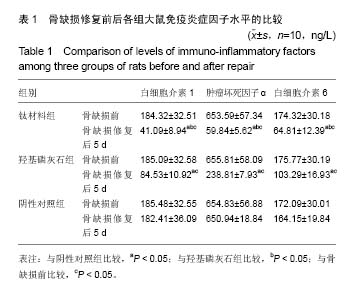
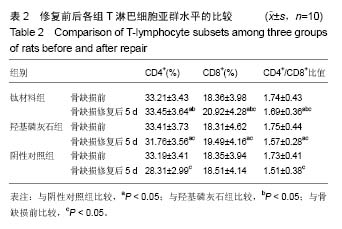
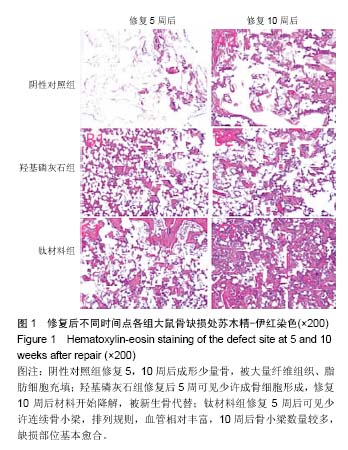
方法:摘除30只Wistar大鼠双侧卵巢,建立骨质疏松模型。3个月后,在30只大鼠股骨远端制备直径为2.5 mm的穿通骨缺损,随机分3组干预,每组10只:阴性对照组不进行任何干预,羟基磷灰石组在骨缺损处填充纳米羟基磷灰石,钛材料组在骨缺损处填充钛材料。干预5 d后,采用酶联免疫吸附实验检测血清白细胞介素1、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平,采用流式细胞仪检测血清T淋巴细胞亚群水平;干预5,10周后,苏木精-伊红染色观察缺损部位组织形态。
结果与结论:①干预5 d后,钛材料组白细胞介素1、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平明显低于阴性对照组、羟基磷灰石组(P < 0.05);②干预5 d后,钛材料组CD4+、CD8+、CD4+/CD8+比值均明显高于羟基磷灰石组、阴性对照组(P < 0.05);③苏木精-伊红染色显示,阴性对照组干预5,10周后形成少量骨,被大量纤维组织、脂肪细胞充填;羟基磷灰石组干预5周后可见少许成骨细胞形成,干预10周后材料开始降解,被新生骨代替;钛材料组干预5周后可见少许连续骨小梁,排列规则,血管相对丰富,10周后骨小梁数量较多,缺损部位基本愈合;④结果表明,将钛板材料修复大鼠骨质疏松性骨缺损的效果理想,能调节骨缺损修复中引起的免疫反应。
中图分类号:
.jpg)