| [1]Khojasteh A, Behnia H, Naghdi N, et al. Effects of different growth factors and carriers on bone regeneration:a systematic review. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2013;116(6):e405-423.[2]Hassani A, Khojasteh A. The anterior palate as a donor site in maxillofacial bone grafting:a quantitative anatomic study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005,63(8);1196-1200.[3]Khojasteh A, Behnia H, Dashti SG. Current trends in mesenchymal stem cell application in bone augmentation: a review of the literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 70(4): 972-982.[4]Khojasteh A, Behnia H, Shayesteh YS, et al. Localized bone augmentation with cortical bone blocks tented over different particulate bone substitutes: a retrospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012;27(6):1481-1493.[5]Kübler N, Reuther J, Kirchner T, et al. Osteoinductive, morphologic, and biomechanical properties of autolyzed, antigen-extracted, allogeneic human bone. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1993;51(12):1346-1357.[6]Fu E, Tseng YC, Shen EC, et al. Effects of low-dose cyclosporin on osteogenesis of human demineralized bone grafts in a surgically created mandibular defect in rats. J Periodontol. 2003;74(8):1136-1142.[7]Kaigler D, Pagni G, Park CH, et al. Stem cell therapy for craniofacial bone regeneration: a randomized, controlled feasibility trial. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(5):767-777.[8]Wang RE. Ridge preservation after tooth extraction. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;23(Suppl 6):147-156.[9]Pang C, Ding Y, Zhou H, et al. Alveolar ridge preservation with deproteinized bovine bone graft and collagen membrane and delayed implants. J Craniofac Surg. 2014;25(5):1698-1702.[10]Sbordone C, Toti P, Martuscelli R, et al. Evaluation of volumetric dimensional changes in posterior extraction sites with and without ARP using a novel imaging device. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2017;19(6):1044-1053.[11]Vignoletti F, Matesanz P, Rodrigo D, et al. Surgical protocols for ridge preservation after tooth extraction A systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res.2012;23(Suppl 5):22-38.[12]Alzahrani AA, Murriky A. Influenceof platelet rich fibrin on post-extraction socket healing: A clinical and radiographic study. Saudi Dent J.2017; 29(4):149-155.[13]王芳,孙乐刚,张惠芹.PRF 植入兔拔牙创内的实验研究[J].滨州医学院学报,2014,37(1):15-18.[14][胡杨,马莹,何惠宇.β-磷酸三钙支架材料即刻植入对保存剩余牙槽嵴的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(16): 2905-2910[15]王艳,尼加提•吐尔逊,李淑慧,等.2种材料复合用于犬上前牙拔牙位点保存的实验研究[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2014,28(1): 10-14.[16]王宇,车彦海,于东升,等.Choukroun富血小板纤维蛋白对兔拔牙窝愈合修复的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2011,6(27):456-459.[17]李洋,喻健,张文云.植物血球凝集素(PHA)在拔牙位点保存中的可行性研究[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2014,19(4):169-172,179.[18]Maki K, NishiokaT, Shioiri E. Effects of dietary consistency on the mandible of rats at the growth stage: Computed X-ray densitometric and cephalo-metric analysis. Angle Orthod. 2002;72(5):468-475.[19]杨明德.拔牙后牙槽嵴位点保存在口腔种植学中的应用[J].国际口腔医学杂志. 2012,39(2):211-213.[20]Mardas N, Chadha V, Donos N. Alveolar ridge preservation with guided bone regeneration and a synthetic bone substitute or abovine-derived xenograft: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;21(7): 688-698.[21]Mardas N, D’Aiuto F, Mezzomo L, et al. Radiographic alveolar bone changes following ridge preservation with two different biomaterials. Clin Oral Implants Res.2011;22(4):416-423.[22]Chackartchi T, Stabholz A. Ridge preservation after tooth extraction: what do we know today. Refuat Hapeh Vehashinayim (1993).2013;30(2):65-75,83.[23]Hannuerle CH, Araujo MG, Simion M, et al. Evidence-basal knowledge on the biology and treatment of extraction sockets. Clin Oral Impl Res. 2012;23(Suppl5):80-82.[24]Jamjoom A, Cohen RE. Grafts for ridge preservation. J Funct Biomater. 2015;6(3):833-848.[25]周玉琴.噬菌体随机肽库技术在细胞特异性多肽筛选中的研究进展[J].安徽医科大学学报,2013,48(12):1549-1551.[26]杜明亮,钱海燕.钛种植体表面固定生物素的实验研究[J].安徽医科大学学报,2015,50(4):463-465.[27]钱海燕,陈慧敏,杜明亮,等.成骨细胞特异性识别多肽对人成骨细胞增殖和矿化影响的实验研究[J].安徽医科大学学报, 2016, 51( 3):337-40.[28]陈慧敏,宋婷婷,吴齐越,等.海藻酸钠壳聚糖支架复合成骨细胞特异性多肽修复兔颅骨缺损[J].安徽医科大学学报, 2017,52(4): 504-507.[29]Laffargue P, Hildebrand HF, Rtaimate M, et al. Evaluation of human recombinant bone morphogenetic protein-2-loaded tricalcium phosphate implants in rabbits' bone defects.Bone. 1999;25( Suppl2):55S-58S.[30]Pelletier MH, Oliver RA, Christou C, et al. Lumbar spinal fusion with β-TCP granules and variable Escherichia coli-derived rhBMP-2 dose. Spine J.2014,14(8):1758-1768.[31]Ono M, Sonoyama W, Yamamoto K, et al. Efficient bone formation in a swine socket lift model using Escherichia coli-derived recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 adsorbed in β-tricalcium phosphate. Cells Tissues Organs. 2014,199(4):249-255. |
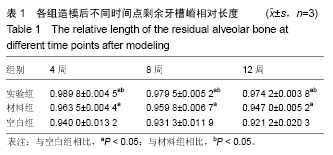
.jpg)

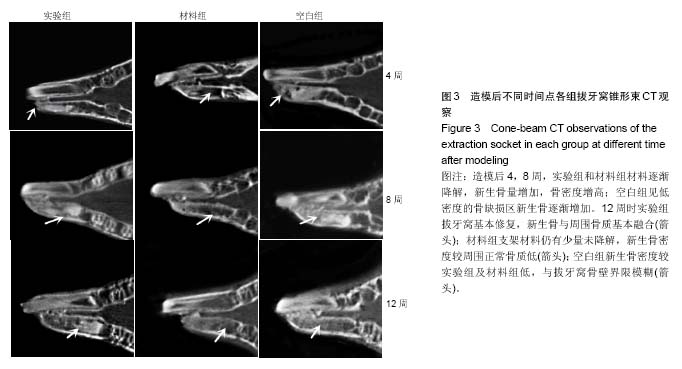
.jpg)
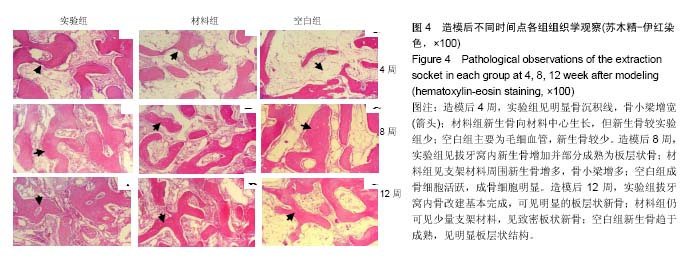
.jpg)