中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (8): 1223-1228.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0825
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
开放性胫骨骨折感染新西兰模型兔的建立
耿 芳1,潘礼存1,周孜辉2
- 1上海微创骨科医疗科技有限公司研究发展部,上海市 201203;2上海交通大学附属第一人民医院,上海市 200080
Establishment of an animal model of open tibial fractures with infection in New Zealand rabbits
Geng Fang1, Pan Li-cun1, Zhou Zi-hui2
- 1Department of Research and Development, Shanghai MicroPort Orthopedics Co., Ltd., Shanghai 201203, China; 2Shanghai First People’s Hospital of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200080, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
动物模型:是指各种医学学科中建立的具有人类疾病模拟表现的动物。主要用于实验生理学、实验病理学和实验治疗学的研究,避免了人体实验造成的伤害。借助于动物模型的间接研究,可以有意识地改变在自然条件下不可能或不易排除的因素,以便更准确的与人类疾病比较研究,更有效的认识疾病的规律。
核左移:正常时外周血中中性粒细胞的分叶以3叶居多,杆状核与分叶核之间的正常比值为1∶13,如杆状核粒细胞增多,或出现杆状以前幼稚阶段的粒细胞,称为核左移。核左移伴有白细胞总数增高者称再生性左移,常见于感染,尤其是化脓菌引起的急性感染。
文题释义:
动物模型:是指各种医学学科中建立的具有人类疾病模拟表现的动物。主要用于实验生理学、实验病理学和实验治疗学的研究,避免了人体实验造成的伤害。借助于动物模型的间接研究,可以有意识地改变在自然条件下不可能或不易排除的因素,以便更准确的与人类疾病比较研究,更有效的认识疾病的规律。
核左移:正常时外周血中中性粒细胞的分叶以3叶居多,杆状核与分叶核之间的正常比值为1∶13,如杆状核粒细胞增多,或出现杆状以前幼稚阶段的粒细胞,称为核左移。核左移伴有白细胞总数增高者称再生性左移,常见于感染,尤其是化脓菌引起的急性感染。
.jpg) 文题释义:
动物模型:是指各种医学学科中建立的具有人类疾病模拟表现的动物。主要用于实验生理学、实验病理学和实验治疗学的研究,避免了人体实验造成的伤害。借助于动物模型的间接研究,可以有意识地改变在自然条件下不可能或不易排除的因素,以便更准确的与人类疾病比较研究,更有效的认识疾病的规律。
核左移:正常时外周血中中性粒细胞的分叶以3叶居多,杆状核与分叶核之间的正常比值为1∶13,如杆状核粒细胞增多,或出现杆状以前幼稚阶段的粒细胞,称为核左移。核左移伴有白细胞总数增高者称再生性左移,常见于感染,尤其是化脓菌引起的急性感染。
文题释义:
动物模型:是指各种医学学科中建立的具有人类疾病模拟表现的动物。主要用于实验生理学、实验病理学和实验治疗学的研究,避免了人体实验造成的伤害。借助于动物模型的间接研究,可以有意识地改变在自然条件下不可能或不易排除的因素,以便更准确的与人类疾病比较研究,更有效的认识疾病的规律。
核左移:正常时外周血中中性粒细胞的分叶以3叶居多,杆状核与分叶核之间的正常比值为1∶13,如杆状核粒细胞增多,或出现杆状以前幼稚阶段的粒细胞,称为核左移。核左移伴有白细胞总数增高者称再生性左移,常见于感染,尤其是化脓菌引起的急性感染。摘要
背景:开放性骨折有着很高的感染率,是临床上非常棘手的问题。建立可靠的开放性骨折感染动物模型,能有利于指导药物及器械在该方面的研究及临床应用。
目的:建立小动物新西兰大耳白兔的开放性骨折感染模型,确定可使用的能导致开放性骨折感染的最适合细菌数量。
方法:通过建立开放性骨折结构及调节菌群的浓度来确定感染所需的可确认用菌量,取新西兰大耳白兔30只,建立1个对照组和4个实验组,在胫骨中段形成胫骨横断骨折模型,分别注入生理盐水及浓度分别为1×105,1×106,5×106,1×107 CFU/mL的金黄色葡萄球菌悬液1 mL。造模后通过大体观察、体温体质量分析、血白细胞和C-反应蛋白检测及细菌培养和病理组织切片分析,确定1 mL用量导致机体感染的最佳使用细菌浓度。
结果与结论:①5×106 CFU/mL组所有兔子感染并且存活率高;1×105 CFU/mL,1×106 CFU/mL 2组部分动物未发生感染;1×107 CFU/mL组有1只新西兰兔因感染而死亡;②使用5×106 CFU/mL浓度的金黄色葡萄球菌1 mL,可建立稳定的新西兰兔开放性骨折感染模型,可用于指导其他药物及器械等治疗手段在治疗感染过程中作为治疗感染有效性的模型使用。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-7660-6576(耿芳)
中图分类号:
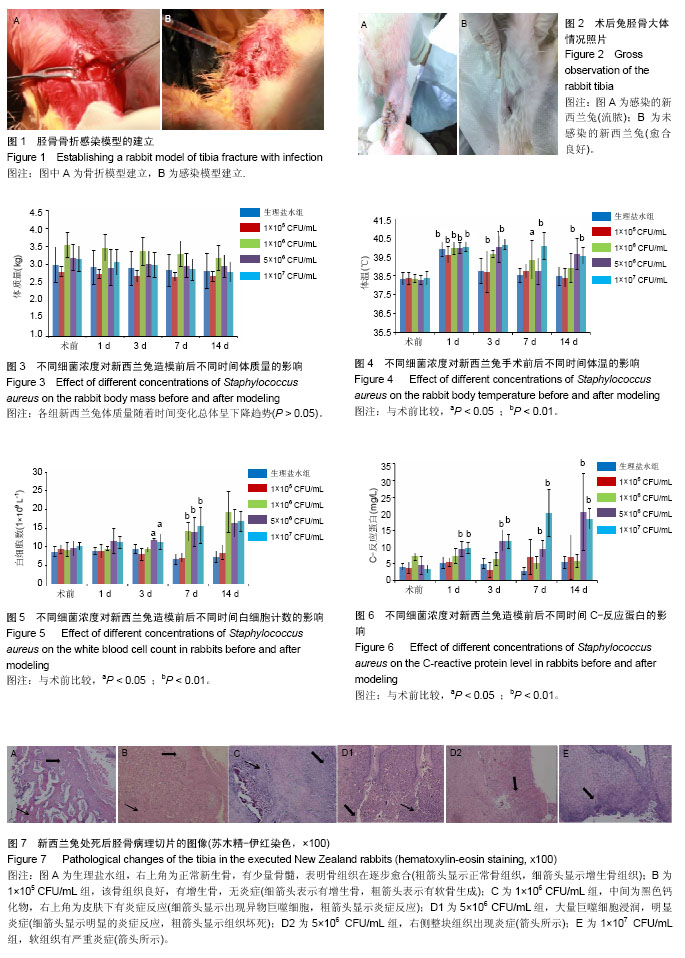

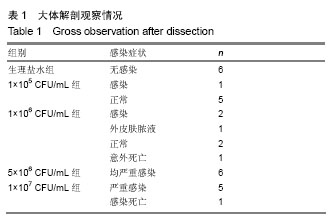
.jpg) 文题释义:
动物模型:是指各种医学学科中建立的具有人类疾病模拟表现的动物。主要用于实验生理学、实验病理学和实验治疗学的研究,避免了人体实验造成的伤害。借助于动物模型的间接研究,可以有意识地改变在自然条件下不可能或不易排除的因素,以便更准确的与人类疾病比较研究,更有效的认识疾病的规律。
核左移:正常时外周血中中性粒细胞的分叶以3叶居多,杆状核与分叶核之间的正常比值为1∶13,如杆状核粒细胞增多,或出现杆状以前幼稚阶段的粒细胞,称为核左移。核左移伴有白细胞总数增高者称再生性左移,常见于感染,尤其是化脓菌引起的急性感染。
文题释义:
动物模型:是指各种医学学科中建立的具有人类疾病模拟表现的动物。主要用于实验生理学、实验病理学和实验治疗学的研究,避免了人体实验造成的伤害。借助于动物模型的间接研究,可以有意识地改变在自然条件下不可能或不易排除的因素,以便更准确的与人类疾病比较研究,更有效的认识疾病的规律。
核左移:正常时外周血中中性粒细胞的分叶以3叶居多,杆状核与分叶核之间的正常比值为1∶13,如杆状核粒细胞增多,或出现杆状以前幼稚阶段的粒细胞,称为核左移。核左移伴有白细胞总数增高者称再生性左移,常见于感染,尤其是化脓菌引起的急性感染。