| [1] Zhao DW, Yu M, Kai H, et al. Prevalence of nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head and its associated risk factors in the chinese population: results from a nationally representative survey. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128(21): 2843-2850.[2] Ito H, Matsuno T, Omizu N, et al. Mid-term prognosis of non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Bone Joint J. 2003;85(6):796-801.[3] 曹衍玉,梁海,刘毅.加强生物力学结构治疗股骨头坏死的临床研究[J].中华损伤与修复杂志:电子版,2013,8(3):293-294.[4] 葛辉.同种异体腓骨移植术治疗股骨头坏死的生物力学与临床疗效研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2016.[5] 梅荣成,杨述华,杨操,等.同种异体骨支撑架结合自体骨和脱钙骨基质植入强化力学结构修复股骨头坏死[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(19):3620-3624.[6] 裴福兴.加强基础与临床研究,努力提高中国股骨头坏死总体诊治水平[J].中华骨科杂志,2010,30(1):3-5.[7] 马信龙,李海涛,马剑雄,等.股骨近端主压力骨小梁生物力学特性[J].生物医学工程与临床,2012,16(2):118-122.[8] 马剑雄,高峰,马信龙,等.不同角度载荷下股骨头骨小梁的生物力学特性[J].医用生物力学,2015,30(6):521-527.[9] 常文举,丁海.股骨近端解剖与生物力学研究进展[J].医用生物力学,2016,31(2):188-192.[10] 赵德伟,傅维民,王本杰,等.带旋股外侧血管蒂大转子骨瓣转移重建股骨头的临床随访研究[J].中华显微外科杂志,2015,38(3):218-221.[11] Zienkiewicz OC, Taylor RL, Zhu JZ. The Finite Element Method: Its Basis and Fundamentals. Butterworth- Heinemann. 2013.[12] Courant R. Variational methods for the solution of problems of equilibrium and vibrations. Bull New Ser Am Math Soc. 1943; 49(1943):1-23.[13] Bae J Y, Kwak D S, Park K S, et al. Finite element analysis of the multiple drilling technique for early osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Ann Biomed Eng. 2013;41(12):2528-2537.[14] Shi J, Chen J, Wu J, et al. Evaluation of the 3D finite element method using a tantalum rod for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Med Sci Monit. 2014;20(4):2556-2564.[15] Bae JY, Kwak DS, Park KS, et al. Finite element analysis of the multiple drilling technique for early osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Ann Biomed Eng. 2013;41(12):2528-2537.[16] Peng-Fei LI, Hui GE, Pang ZH, et al. Research progress in predicting the collapse of the femoral head osteonecrosis based on radiology. Med Recapitulate. 2016.[17] 何海军,陈卫衡,鲁超,等.基于CT图像建立可供动态力学模拟分析的股骨头坏死有限元模型[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2016, 25(9):5-10.[18] Brown TD, Fergson AB, Mechanical property distribution in the cancellous bone of the human proximal femur. Acta Orthop Scand. 1980;51:429-437.[19] Brown TD, Way ME, Fergson AB, Mechanical characteristics of bone in femoral capital aseptic nerosis. Clin Orthop. 1981;156(5):240.[20] Brown TD, Hild GL. Pre-collapse stress redistributions in femoral head ostconecrosis a three-dimensional element analysis. J Bionech Eng. 1983;105(2):171. [21] Brown TD, Hild GL. Pre-collapse stress of subchondral bone involvement in segmental osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Res. 1992;10(1)79. [22] Etienne G, Mont MA. Ragland PS Instr Course Lect. 2004; 53:67-85. [23] Ueo T, Biomechanical aspects of the development of aseptic necrosis of the femoral head. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1985;104:145. [24] 刘安庆,张银光,王春生,等.人股骨生物力学特性的三维有限元分析[J].西安医科大学学报,2001,22(3):242-244.[25] 汪金平,杨天府,钟风林,等.股骨生物力学特性的有限元分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2005,7(10):931-934. [26] 陆晴友,吴岳嵩,王成焘.股骨近端解剖形态的CT三维重建分析[J].第二军医大学学报,2005,26(9):1029-1033. [27] Xue W, Wang KZ, Ling W. Three-dimensional finite element analysis on the treatment of adult femoral head necrosis using different graft. Shengwu Yixue Zazhi. 2006;20(1):55-58.[28] Zhang YY, Feng EY, Chen RQ. Biomechanical study and three-dimension finite element analysis on the treatment of the iscbemic necrosis of the femoral head using pieces of tantalum in adult. Orthop Biomechanics Mater Clin Study. 2012.[29] Xiao D, Ming Y, Xiong L, et al. Biomechanics analysis for the treatment of ischemic necrosis of the femoral head by using an interior supporting system. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(3): 4551-4556.[30] Shi J, Chen J, Wu J, et al. Evaluation of the 3D finite element method using a tantalum rod for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Med Sci Monitor Int Med J Exp Clin Res. 2014;20(4): 2556.[31] 赵德伟,傅维民,王本杰,等.带旋股外侧血管蒂大转子骨瓣转移重建股骨头的临床随访研究[J].中华显微外科杂志, 2015,38(3): 218-221.[32] 赵德伟,田丰德,郭林,等.带血管蒂大转子骨瓣转移治疗股骨头缺血坏死的生物力学研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2009,27(5): 580-583.[33] Taira T, Nayak A, Brenguier F, et al. Monitoring reservoir response to earthquakes and fluid extraction, Salton Sea geothermal field, California. Sci Adv. 2018. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1701536. [34] Liu J, Chen C, Feng Y, et al. Ultralow-Carbon Nanotube-Toughened Epoxy: The Critical Role of a Double-Layer Interface. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b14767. [35] Knapik JJ, Reynolds K, Hoedebecke KL. Stress fractures: etiology, epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. J Spec Oper Med. Summer 2017;17(2):120-130.[36] Zahn D, Duchstein P. Multi-Scale modelling of deformation and fracture in a biomimetic apatite-protein composite: molecular-scale processes lead to resilience at the μm-scale. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0157241. [37] Malekipour F, Oetomo D, Lee PV. Equine subchondral bone failure threshold under impact compression applied through articular cartilage. J Biomech. 2016;49(10):2053-2059. [38] Torres AM, Matheny JB, Keaveny TM, et al. Material heterogeneity in cancellous bone promotes deformation recovery after mechanical failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(11):2892-2897. [39] Hoyt AJ, Yakacki CM, Fertig RS 3rd, et al. Monotonic and cyclic loading behavior of porous scaffolds made from poly(para-phenylene) for orthopedic applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2015;41:136-148. [40] Tang T, Ebacher V, Cripton P, et al. Shear deformation and fracture of human cortical bone.Bone. 2015;71:25-35. |
.jpg)
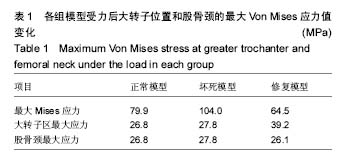
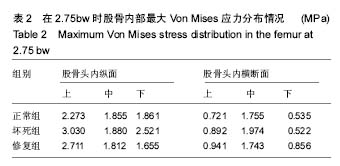
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)