中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (9): 1313-1318.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0458
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 下一篇
骨形态发生蛋白2联合基因转染骨髓间充质干细胞复合同种异体骨修复极限骨缺损
王小志1,杨 桦1,张 辰2,何惠宇1,巴娇娇3
- 1新疆昌吉回族自治州人民医院口腔科,新疆维吾尔自治区昌吉市 831100;2中国南方航空股份有限公司新疆分公司医务室,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830002;3新疆生产建设兵团总医院口腔科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830000
Bone defect repair using allogenic bone carrying bone morphogenetic protein-2 and gene transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Wang Xiao-zhi1, Yang Hua1, Zhang Chen2, He Hui-yu1, Ba Jiao-jiao3
- 1Department of Stomatology, People’s Hospital of Changji Hui Autonomous Prefecture, Changji 831100, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Infirmary of the Xinjiang Branch of China Southern Airlines, Urumqi 830002, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 3Department of Stomatology, General Hospital of Xinjiang Construction Corps, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义: 骨涎蛋白:主要由成骨细胞分泌,在骨改建过程中,伴随成骨细胞从前体细胞逐渐向成熟形态分化的同时,骨涎蛋白的表达呈正相关性,说明骨涎蛋白是骨大量形成的标志物,检测成骨实验研究中局部骨涎蛋白的表达量,可直接反映成骨细胞已处于分化成熟阶段。因此,骨涎蛋白多分布在趋向钙化的软骨组织附近或已钙化的骨基质中。同时骨涎蛋白也是一种作用优良的血管形成分子,还能触发成骨样细胞,使其在与Ⅰ型胶原的α-2链相结合时具有优先权,后者沉淀形成羟基磷灰石结晶,加速矿化的完成。 骨形态发生蛋白2:属于转化生长因子β超家族,具有诱导未分化间充质干细胞向成软骨细胞和成骨细胞定向分化与增殖的能力,是骨组织形成过程中最关键的调节因子,可促进成骨细胞分化成熟,在调节骨和软骨生长发育的同时,也参与骨组织重建过程,诱导骨内、外膜及骨髓基质细胞向骨母细胞分化成熟,加强骨床再生能力,同时活化并诱导血管周围间充质细胞分化为软骨和成骨细胞。 碱性成纤维细胞生长因子:是一种强力的促细胞分裂原,在成骨过程中至关重要,因此对骨损伤的修复发挥重要作用。成骨细胞的胞膜表面存在碱性成纤维细胞生长因子受体,成骨细胞合成的碱性成纤维细胞生长因子以自分泌或旁分泌形式释放到胞外与受体结合,可促进骨原细胞分化为成骨细胞,诱导成骨细胞分裂、增殖,并促使其合成骨基质、钙结合蛋白及含有羟基磷灰石颗粒的基质小泡,加快基质钙化。
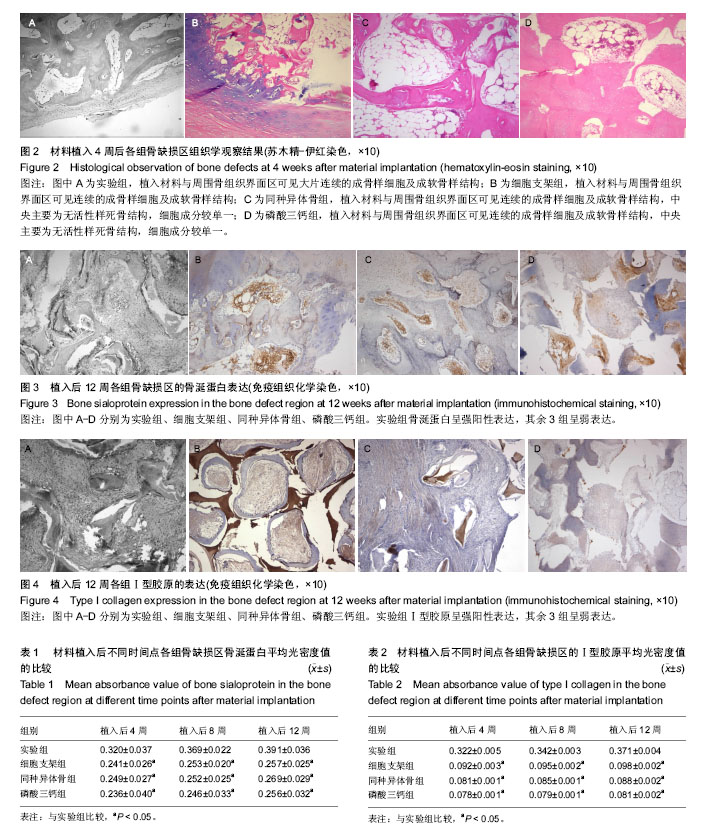
摘要 背景:组织工程技术为骨缺损带来新的治疗路径,生物基因转染优化了组织工程骨修复骨缺损的效果。 目的:观察骨形态发生蛋白2与碱性成纤维细胞生长因子基因转染骨髓间充质干细胞/同种异体骨修复绵羊极限骨缺损的效果。 方法:取9只阿勒泰大尾绵羊,制作双侧髂骨极限性骨缺损模型,左侧植入骨形态发生蛋白2与碱性成纤维细胞生长因子基因转染骨髓间充质干细胞/同种异体骨复合材料(实验组),其中3只右侧植入骨髓间充质干细胞/同种异体支架骨复合材料(细胞支架组),3只右侧植入同种异体支架骨材料(同种异体骨组),3只右侧植入β-磷酸三钙材料(磷酸三钙组)。植入后4,8,12周进行组织学、免疫组织化学染色观察。 结果与结论:①组织学观察:植入12周时,实验组同种异体骨材料大范围吸收,破骨样细胞逐渐减少,成骨样细胞增多,骨小梁周围骨纤维基质逐渐致密,可见大面积成片状新骨,骨小梁结构清晰,骨改建明显,术区始终未见炎性细胞浸润;其余3组支架骨材料降解,但无明显骨改建;②免疫组织化学观察:植入12周时,实验组骨涎蛋白与Ⅰ型胶原呈强阳性表达,其余3组骨涎蛋白与Ⅰ型胶原呈弱表达;③结果表明:骨形态发生蛋白2联合碱性成纤维细胞生长因子基因转染的骨髓间充质干细胞复合同种异体骨,可完全修复羊极限骨缺损。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程 ORCID: 0000-0002-4852-2700(王小志)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)