中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (36): 5806-5811.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.36.012
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
不同位置脑损伤模型大鼠坐骨神经的再生
马建军1,何新泽2,王浩琪1,孙 勃1,高云峰1,付士杰1,王 培1
- 1承德医学院附属医院手足外科,河北省承德市 067000;2滨州市中心医院,山东省滨州市 256600
Sciatic nerve regeneration in a rat model of brain injury at different locations
Ma Jian-jun1, He Xin-ze2, Wang Hao-qi1, Sun Bo1, Gao Yun-feng1, Fu Shi-jie1, Wang Pei1
- 1Department of Hand and Foot Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Chengde Medical University, Chengde 067000, Hebei Province, China; 2Binzhou Central Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
创伤性脑损伤:美国康复医学会定义创伤性脑损伤为:外力引起脑的创伤性结构损伤和/或脑功能障碍。出现以下4项异常或原有1项加重,4项包括:①任意时间段出现意识丧失或降低;②损伤后出现一过性记忆力丧失;③损伤即刻出现精神状态改变(如意识模糊、定向力障碍及思维迟缓);④一过性或持久性神经功能障碍(如平衡失调、行为异常、不全麻痹、下肢麻痹或截瘫、视力改变、其他感觉异常、失语)。
周围神经再生:损伤神经近侧断端残留的施万细胞分裂增生,并向远瑞生长形成细胞索,受伤的近端轴突以出芽的方式向远端生长,伸入新生的施万细胞索内,在施万细胞的诱导下,轴突沿细胞索生长直至伸到原来轴突终末所在部位,新生轴突终末可分支与相应细胞组织建立联系,使靶器官再神经化的过程称为神经再生。
文题释义:
创伤性脑损伤:美国康复医学会定义创伤性脑损伤为:外力引起脑的创伤性结构损伤和/或脑功能障碍。出现以下4项异常或原有1项加重,4项包括:①任意时间段出现意识丧失或降低;②损伤后出现一过性记忆力丧失;③损伤即刻出现精神状态改变(如意识模糊、定向力障碍及思维迟缓);④一过性或持久性神经功能障碍(如平衡失调、行为异常、不全麻痹、下肢麻痹或截瘫、视力改变、其他感觉异常、失语)。
周围神经再生:损伤神经近侧断端残留的施万细胞分裂增生,并向远瑞生长形成细胞索,受伤的近端轴突以出芽的方式向远端生长,伸入新生的施万细胞索内,在施万细胞的诱导下,轴突沿细胞索生长直至伸到原来轴突终末所在部位,新生轴突终末可分支与相应细胞组织建立联系,使靶器官再神经化的过程称为神经再生。
.jpg) 文题释义:
创伤性脑损伤:美国康复医学会定义创伤性脑损伤为:外力引起脑的创伤性结构损伤和/或脑功能障碍。出现以下4项异常或原有1项加重,4项包括:①任意时间段出现意识丧失或降低;②损伤后出现一过性记忆力丧失;③损伤即刻出现精神状态改变(如意识模糊、定向力障碍及思维迟缓);④一过性或持久性神经功能障碍(如平衡失调、行为异常、不全麻痹、下肢麻痹或截瘫、视力改变、其他感觉异常、失语)。
周围神经再生:损伤神经近侧断端残留的施万细胞分裂增生,并向远瑞生长形成细胞索,受伤的近端轴突以出芽的方式向远端生长,伸入新生的施万细胞索内,在施万细胞的诱导下,轴突沿细胞索生长直至伸到原来轴突终末所在部位,新生轴突终末可分支与相应细胞组织建立联系,使靶器官再神经化的过程称为神经再生。
文题释义:
创伤性脑损伤:美国康复医学会定义创伤性脑损伤为:外力引起脑的创伤性结构损伤和/或脑功能障碍。出现以下4项异常或原有1项加重,4项包括:①任意时间段出现意识丧失或降低;②损伤后出现一过性记忆力丧失;③损伤即刻出现精神状态改变(如意识模糊、定向力障碍及思维迟缓);④一过性或持久性神经功能障碍(如平衡失调、行为异常、不全麻痹、下肢麻痹或截瘫、视力改变、其他感觉异常、失语)。
周围神经再生:损伤神经近侧断端残留的施万细胞分裂增生,并向远瑞生长形成细胞索,受伤的近端轴突以出芽的方式向远端生长,伸入新生的施万细胞索内,在施万细胞的诱导下,轴突沿细胞索生长直至伸到原来轴突终末所在部位,新生轴突终末可分支与相应细胞组织建立联系,使靶器官再神经化的过程称为神经再生。摘要
背景:课题组前期研究发现创伤性脑损伤可促进周围神经损伤的修复再生,这可能与减少神经断端胶原瘢痕形成有关。
目的:观察不同位置脑损伤对大鼠同一侧坐骨神经损伤后修复的影响。
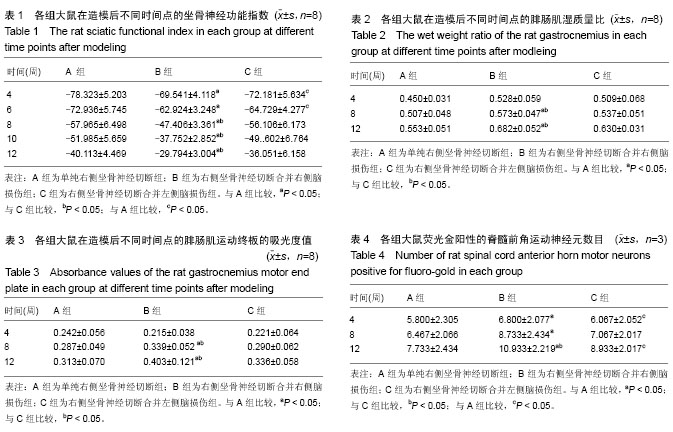
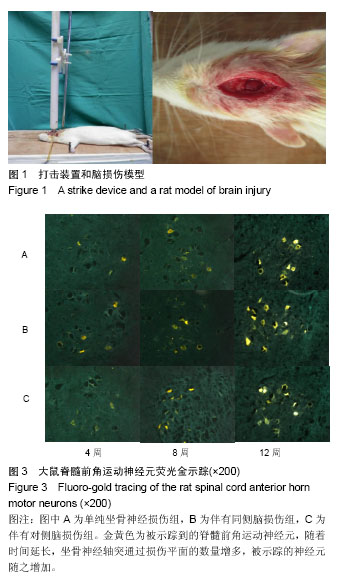
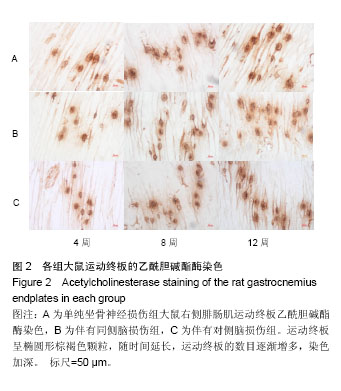
方法:将99只SD雄性大鼠,按照完全随机分组原则,分为单纯右侧坐骨神经损伤组(A组)、右侧坐骨神经损伤并右侧脑损伤组(B组)、右侧坐骨神经损并左侧脑损伤组(C组)。全部大鼠右侧坐骨神经完全切断,显微镜下吻合,B组同时采用Feeney方法建立右侧大脑皮质损伤模型,C组建立左侧大脑皮质损伤模型,于造模后4,6,8,10和12周各时间点踩足印并测量数值,计算坐骨神经功能指数;于造模后4,8和12周,取每组大鼠双侧腓肠肌,称湿质量并计算腓肠肌湿质量比;随后取右侧腓肠肌进行运动终板的乙酰胆碱酯酶染色,分析平均吸光度值;于造模后4,8和12周进行右侧坐骨神经处荧光金逆行示踪,示踪1周后取脊髓L4、L5节段做冰冻切片,荧光显微镜观察并计数被荧光金标记的脊髓前角运动神经元。
结果与结论:①随时间延长,各组大鼠坐骨神经功能指数逐渐恢复,造模后4、6周时B和C组均优于A组(P < 0.05);自8周起,B组坐骨神经功能指数恢复明显优于A组与C组(P < 0.05);②在造模后4周,3组大鼠的腓肠肌湿质量比无明显差异(P > 0.05);自8周起,B组明显高于A和C组(P < 0.05);③腓肠肌运动终板乙酰胆碱酯酶染色后,在造模后4周,3组间腓肠肌运动终板吸光度差异无显著性意义。自8周起B组吸光度值明显高于A和C组(P < 0.05);④在造模后4周时,B组与C组的荧光金阳性脊髓前角运动神经元的数目均明显多于A组(P < 0.05); 12周时B组荧光金阳性神经元数量明显较A和C组多(P < 0.05);⑤结果提示,伴有同侧脑损伤可促进大鼠坐骨神经损伤修复再生,这为进一步揭示创伤性脑损伤可促进周围神经损伤的具体机制提供理论依据。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-4510-9435(马建军)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
创伤性脑损伤:美国康复医学会定义创伤性脑损伤为:外力引起脑的创伤性结构损伤和/或脑功能障碍。出现以下4项异常或原有1项加重,4项包括:①任意时间段出现意识丧失或降低;②损伤后出现一过性记忆力丧失;③损伤即刻出现精神状态改变(如意识模糊、定向力障碍及思维迟缓);④一过性或持久性神经功能障碍(如平衡失调、行为异常、不全麻痹、下肢麻痹或截瘫、视力改变、其他感觉异常、失语)。
周围神经再生:损伤神经近侧断端残留的施万细胞分裂增生,并向远瑞生长形成细胞索,受伤的近端轴突以出芽的方式向远端生长,伸入新生的施万细胞索内,在施万细胞的诱导下,轴突沿细胞索生长直至伸到原来轴突终末所在部位,新生轴突终末可分支与相应细胞组织建立联系,使靶器官再神经化的过程称为神经再生。
文题释义:
创伤性脑损伤:美国康复医学会定义创伤性脑损伤为:外力引起脑的创伤性结构损伤和/或脑功能障碍。出现以下4项异常或原有1项加重,4项包括:①任意时间段出现意识丧失或降低;②损伤后出现一过性记忆力丧失;③损伤即刻出现精神状态改变(如意识模糊、定向力障碍及思维迟缓);④一过性或持久性神经功能障碍(如平衡失调、行为异常、不全麻痹、下肢麻痹或截瘫、视力改变、其他感觉异常、失语)。
周围神经再生:损伤神经近侧断端残留的施万细胞分裂增生,并向远瑞生长形成细胞索,受伤的近端轴突以出芽的方式向远端生长,伸入新生的施万细胞索内,在施万细胞的诱导下,轴突沿细胞索生长直至伸到原来轴突终末所在部位,新生轴突终末可分支与相应细胞组织建立联系,使靶器官再神经化的过程称为神经再生。