| [1] Zeng J, Gao X. A prospective CBCT study of upper airway changes after rapid maxillary expansion. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;77(11):1805-1810.[2] Machadojúnior AJ, Zancanella E, Crespo A. Rapid maxillary expansion and obstructive sleep apnea: A review and meta-analysis. Medicina Oral Patologia Oral Y Cirugia Bucal. 2016;21(4):e465-e469.[3] 郭婧,邹淑娟.上颌快速扩弓的生物力学研究进展[J]. 国际口腔科学杂志, 2008, 35(s1):311-314.[4] 彭易坤.鼻腔扩容术在OSAHS治疗中的应用及临床疗效评估[J]. 山东大学耳鼻喉眼学报, 2017, 31(1):13-17.[5] Hass AJ.The treatment of maxillary deficiency by opening the midpalatal suture. Angle Orthod.1965;35:200-217.[6] Hass AJ.Rapid expansion of the maxillary dental arch and nasal cavity by opening the midpalatal suture. Angle Orthod. 1961; 31(2):73-90.[7] 邱严力,杜凤芝,Kapika Faustin,等. 上颌快速扩弓联合前牵引对安氏Ⅲ类患者上气道和舌位置的影响[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2011, 27(3):365-368.[8] 赵健,张宗德,赵昊,等. 上颌快速扩弓在伴有上颌狭窄的儿童OSAHS治疗中的应用[J]. 中国医学创新, 2014, 11(17):41-44.[9] Angell EC.Treatment of irregularities of the permanent or adult teeth.Dental Cosmos.1860;1:540-544.[10] Almuzian M, Ju X, Almukhtar A, et al. Does rapid maxillary expansion affect nasopharyngeal airway? A prospective Cone Beam Computerised Tomography (CBCT) based study. Surgeon. 2016. pii: S1479-666X(15)00125-0.[11] Baccetti T, Franchi L Jr. The Cervical Vertebral Maturation (CVM) Method for the Assessment of Optimal Treatment Timing in Dentofacial Orthopedics. Semin Orthod. 2005;11(3):119-129. [12] El H, Palomo JM. Three-dimensional evaluation of upper airway following rapid maxillary expansion: a CBCT study. Angle Orthod. 2014;84(2):265-273.[13] 骆英.上颌铸造式Hyrax快扩后鼻上颌复合体三维形态变化的锥体束CT观察[J]. 中华口腔正畸学杂志, 2014, 21(3):128-131.[14] 冯妍,张良,陈文静,等. 快速扩弓前方牵引矫治替牙期骨性反合效果的CT观察[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2015,15(31):6074-6077.[15] Park JJ, Park YC, Lee KJ, et al. Skeletal and dentoalveolar changes after miniscrew-assisted rapid palatal expansion in young adults: A cone-beam computed tomography study. Korean J Orthod. 2017;47(2):77-86. [16] Weissheimer A,de Menezes LM,Mezomo M,et al.Immediate effects of rapid maxillary expansion with Hass-type and hyrax-type expanders:a randomized clinical trial.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop.2011;140:366-367.[17] Ghoneima A,Abdel-Fattah E,Eraso F, et al. Skeletal and dental changes after rapid maxillary expansion:a computed tomography study. Aust Orthod J. 2010;26(2):141-148.[18] 张茜,李洪发,刘俊玲,等.快速扩弓后牙齿及牙槽骨变化的锥体束CT研究[J]. 天津医科大学学报, 2014, 20(1):57-60.[19] Majourau A, Nanda R. Biomechanical basis of vertical dimension control during rapid palatal expansion therapy. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1994;106(3):322-328.[20] de Almeida AM, Ozawa TO, Alves AC, et al. Slow versus rapid maxillary expansion in bilateral cleft lip and palate: a CBCT randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Investig. 2016. [Epub ahead of print][21] Doruk C,Sokucu O,Sezer H,et al.Evaluation of nasal airway resistance during rapid maxillary expansion using acoustic rhinometry. Eur J Orthod. 2004;26(4):397-401.[22] Ghoneima A, Albarakati S, Jiang F, et al. Computational fluid dynamics analysis of the upper airway after rapid maxillary expansion: a case report. Prog Orthod. 2015;16(1):85.[23] Starchjensen T, Blaehr TL. Transverse Expansion and Stability after Segmental Le FortⅠOsteotomy versus Surgically Assisted Rapid Maxillary Expansion:a Systematic Review. J Oral Maxillofac Res. 2016;7(4):e1. [24] Matsushita K, Inoue N, Kobori Y, et al. New device for palatal expansion in conjunction with the Le Fort I osteotomy. British J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;53(10):1038-1039.[25] Stokbro K, Aagaard E, Torkov P, et al. Surgical accuracy of three-dimensional virtual planning: a pilot study of bimaxillary orthognathic procedures including maxillary segmentation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016;45(1):8-18.[26] Guilleminault C, Monteyrol PJ, Huynh NT, et al. Adeno- tonsillectomy and rapid maxillary distraction in pre-pubertal children, a pilot study. Sleep Breath. 2011;15(2): 173-177.[27] Cistulli PA,Sullivan CE.Influence of maxillary morphology on nasal airway resistance in Marfan’s syndrome. Acta Otolaryngol.2000;120:410-413.[28] Zhao Y, Nguyen M, Gohl E, et al. Oropharyngeal airway changes after rapid palatal expansion evaluated with cone-beam computed tomography. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010;137: S71-S78.[29] Ozbek MM, Memikoglu UT,Altug-Atac AT, et al. Stability of maxillary expansion and tongue posture. Angle Orthod. 2009; 79(2):214-220.[30] Izuka EN, Feres MF, Pignatari SS. Immediate impact of rapid maxillary expansion on upper airway dimensions and on the quality of life of mouth breathers. Dent Press J Orthod. 2015; 20(3):43-49.[31] 李磊,齐素青,王宏伟,等. 上颌快速扩弓对颅颌面骨及上气道影响的锥形束CT分析[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2015, 50(7):403-407.[32] 易红良,焦晓. 体位相关性OSAHS的临床特征与治疗策略[J]. 山东大学耳鼻喉眼学报, 2017, 31(1):8-12.[33] 孙念,叶京英,倪鑫,等. 体位相关性阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征患者临床特征分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016, 51(11):801-805.[34] Hong JS, Park YH, Kim YJ, et al. Three-dimensional changes in pharyngeal airway in skeletal class III patients undergoing orthognathic surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;69(11): e401-e408.[35] 唐倩,方志欣,周嫣,等. Ⅰ类和Ⅱ类矢状骨面型青年男性上气道形态差异的X线头影测量研究[J]. 中国临床新医学, 2016, 9(11): 975-978.[36] Morin O,Gillis A,Chen J,et al.Megavoltage cone-beam CT: System description and clinical applications. Med Dosim. 2006; 31(1):51-61. [37] 王国杰,刘春丽,杨晓瑞,等. 锥形束CT在反牙合正畸治疗中的应用[J]. 中国医疗设备, 2016, 31(3):118-120.[38] 付鼎,厉松,马玉洁,等.上颌快速扩弓对小型猪后牙颊侧骨板改建影响的锥体束CT研究[J].中华口腔正畸学杂志,2013,20(1):8-12. [39] 唐顼晶,李晅.锥束CT在正畸治疗中上气道研究的应用[J]. 生物医学工程学进展,2012,33(2):97-100. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
上颌快速扩弓:临床矫治上颌横向发育不足的常用方法。其原理是在短期内对上颌骨施加较大的矫形力,即在牙周支持组织来不及发生改建时,这种应力在腭中缝迅速堆积,导致骨缝处的纤维连接被拉开甚至部分断裂,骨缝扩开,从而使上颌宽度得到扩展。
鼻上颌复合体:是由上颌骨、颧骨、鼻骨、鼻甲组骨、上牙列及部分颅骨组成的骨性结合体,各个骨块间以骨缝连接,存在上颌窦、鼻腔、筛窦等空腔结构。
文题释义:
上颌快速扩弓:临床矫治上颌横向发育不足的常用方法。其原理是在短期内对上颌骨施加较大的矫形力,即在牙周支持组织来不及发生改建时,这种应力在腭中缝迅速堆积,导致骨缝处的纤维连接被拉开甚至部分断裂,骨缝扩开,从而使上颌宽度得到扩展。
鼻上颌复合体:是由上颌骨、颧骨、鼻骨、鼻甲组骨、上牙列及部分颅骨组成的骨性结合体,各个骨块间以骨缝连接,存在上颌窦、鼻腔、筛窦等空腔结构。.jpg) 文题释义:
上颌快速扩弓:临床矫治上颌横向发育不足的常用方法。其原理是在短期内对上颌骨施加较大的矫形力,即在牙周支持组织来不及发生改建时,这种应力在腭中缝迅速堆积,导致骨缝处的纤维连接被拉开甚至部分断裂,骨缝扩开,从而使上颌宽度得到扩展。
鼻上颌复合体:是由上颌骨、颧骨、鼻骨、鼻甲组骨、上牙列及部分颅骨组成的骨性结合体,各个骨块间以骨缝连接,存在上颌窦、鼻腔、筛窦等空腔结构。
文题释义:
上颌快速扩弓:临床矫治上颌横向发育不足的常用方法。其原理是在短期内对上颌骨施加较大的矫形力,即在牙周支持组织来不及发生改建时,这种应力在腭中缝迅速堆积,导致骨缝处的纤维连接被拉开甚至部分断裂,骨缝扩开,从而使上颌宽度得到扩展。
鼻上颌复合体:是由上颌骨、颧骨、鼻骨、鼻甲组骨、上牙列及部分颅骨组成的骨性结合体,各个骨块间以骨缝连接,存在上颌窦、鼻腔、筛窦等空腔结构。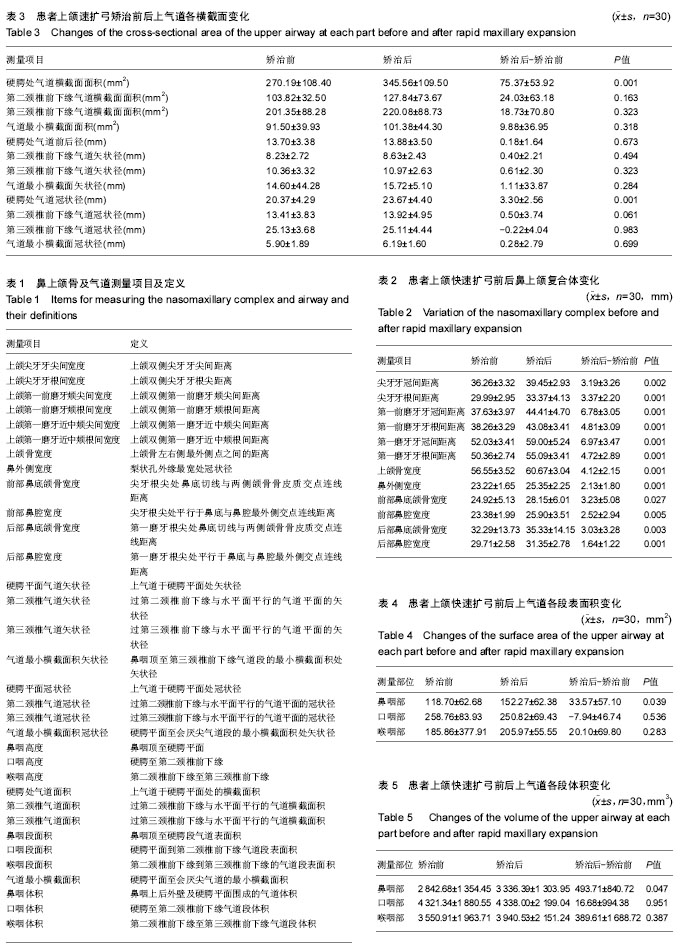
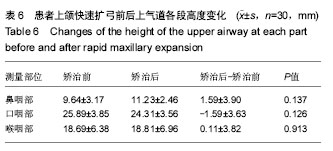
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
上颌快速扩弓:临床矫治上颌横向发育不足的常用方法。其原理是在短期内对上颌骨施加较大的矫形力,即在牙周支持组织来不及发生改建时,这种应力在腭中缝迅速堆积,导致骨缝处的纤维连接被拉开甚至部分断裂,骨缝扩开,从而使上颌宽度得到扩展。
鼻上颌复合体:是由上颌骨、颧骨、鼻骨、鼻甲组骨、上牙列及部分颅骨组成的骨性结合体,各个骨块间以骨缝连接,存在上颌窦、鼻腔、筛窦等空腔结构。
文题释义:
上颌快速扩弓:临床矫治上颌横向发育不足的常用方法。其原理是在短期内对上颌骨施加较大的矫形力,即在牙周支持组织来不及发生改建时,这种应力在腭中缝迅速堆积,导致骨缝处的纤维连接被拉开甚至部分断裂,骨缝扩开,从而使上颌宽度得到扩展。
鼻上颌复合体:是由上颌骨、颧骨、鼻骨、鼻甲组骨、上牙列及部分颅骨组成的骨性结合体,各个骨块间以骨缝连接,存在上颌窦、鼻腔、筛窦等空腔结构。