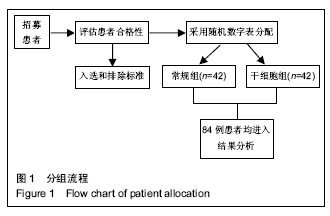
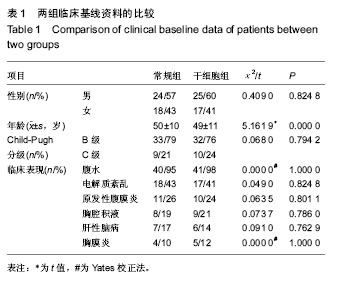
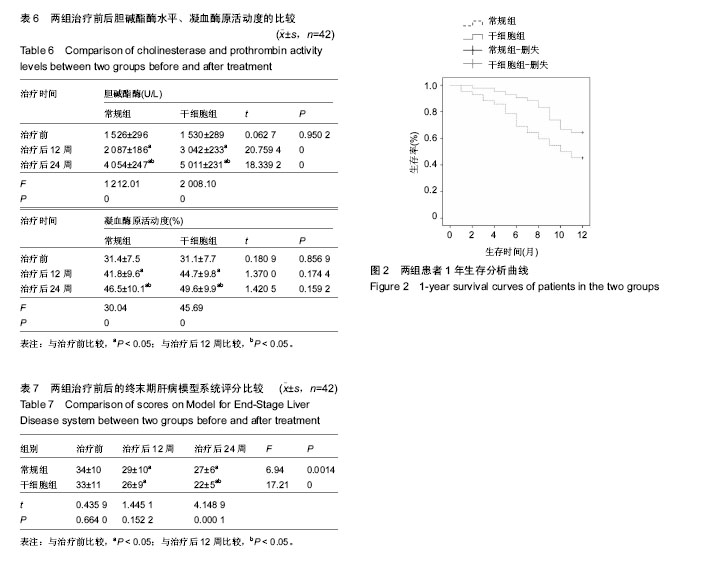
| [1] 中华人民共和国卫生部.2006-2010年全国乙型病毒性肝炎防治规划[J].中国实用乡村医生杂志,2006,13(8):1-4.[2] Fattovich G, Bortolotti F, Donato F. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B: special emphasis on disease progression and prognostic factors. J Hepatol. 2008;48(2):335-352.[3] Fitzpatrick E,Wu Y,Dhadda P,et al. Coculture with mesenchymal stem cells results in improved viability and function of human hepatocytes. Cell Transplant. 2015; 24(1): 73-83.[4] 中华医学会肝病学分会,中华医学会感染病学分会.慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2015年版)[J].中国肝脏病杂志(电子版),2015,7(3): 1-18.[5] 李海军,杨新英,李东,等.乙型肝炎肝硬化失代偿期临床指标与预后关系研究[J].人民军医,2008,51(4):222-223.[6] 耿明凡,高方媛,谷莉莉,等.终末期肝病的模型与评价指标的研究进展[J].中国肝脏病杂志(电子版),2014,6(3):98-100.[7] 杨方,魏倪.乙型肝炎肝硬化失代偿期预后因素分析及预后模型的建立[J].中华传染病杂志,2008,26(12):750-753.[8] Jang JW,Choi JY,Kim YS,et al. Long-term effect of antiviral therapy on disease course after decompensation in patients with hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis.Hepatology. 2015; 61(6):1809-1820.[9] Liaw YF,Raptopoulou-Gigi M,Cheinquer H,et al.Efficacy and safety of entecavir versus adefovir in chronic hepatitis B patients with hepatic decompensation: a randomized, open-label study.Hepatology.2011;54(1):91-100.[10] Ye XG,Su QM.Effects of entecavir and lamivudine for hepatitis B decompensated cirrhosis: meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol.2013;19(39):6665-6678.[11] Wong GL,Chan HL,Mak CW,et al.Entecavir treatment reduces hepatic events and deaths in chronic hepatitis B patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology,2013,58(5): 1537-1547.[12] Liaw YF,Sheen IS,Lee CM,et al.Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), emtricitabine/TDF,and entecavir in patients with decompensated chronichepatitis B liver disease. Hepatology. 2011;53(1):62-72.[13] 胡晓平.扶正化瘀胶囊对肝硬化失代偿期的临床疗效[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2007,16(15):2038-2039.[14] 张先俊,杨力,胡建国.恩替卡韦联合扶正化瘀胶囊治疗失代偿期乙型肝炎肝硬化临床观察[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2010, 24(12):1217-1219.[15] Kim SS,Hwang JC,Lim SG,et al.Effect of virological response to entecavir on the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B viral cirrhotic patients: comparison between compensated and decompensated cirrhosis.Am J Gastroenterol.2014;109(8):1223-1233.[16] Salama H,Zekri AR,Medhat E,et al.Peripheral vein infusion of autologous mesenchymal stem cells in Egyptian HCV-positive patients with end-stage liver disease.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(3):70.[17] Uccelli A,de Rosbo NK.The immunomodulatory function of mesenchymal stem cells: mode of action and pathways.Ann N Y Acad Sci.2015;1351:114-126.[18] Volarevic V,Nurkovic J,Arsenijevic N,et al.Concise review: Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of acute liver failure andcirrhosis.Stem Cells.2014; 32(11):2818-2823.[19] El-Ansary M,Abdel-Aziz I,Mogawer S,et al.Phase Ⅱ trial:undifferentiated versus differentiated autologous mesenchymal stem cells transplantation inEgyptian patients with HCV induced liver cirrhosis.Stem Cell Rev.2012;8(3): 972-981.[20] Amer ME1,El-Sayed SZ,El-Kheir WA,et al.Clinical and laboratory evaluation of patients with end-stage liver cell failure injected with bonemarrow-derived hepatocyte-like cells.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol.2011;23(10):936-941.[21] 焦煜全,李雪丽,吕杰,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞肝移植治疗代偿期肝硬化疗效观察[J].中国继续医学教育,2016,8(4):105-106.[22] 于双杰,陈黎明,吕飒,等.人脐带间充质干细胞治疗失代偿性乙型肝炎肝硬化的安全性与疗效[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2016,24(1): 51-55.[23] 吴锋,蒲春文,张勇.自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗失代偿期肝硬化的临床疗效观察[J].中国肝脏病杂志(电子版),2015,7(3): 130-134.[24] 方雪晴,张骏飞,宋海燕,等.间充质干细胞移植及其在失代偿期肝硬化中的研究进展[J].中华传染病杂志,2016,34(8):509-512.[25] Xuan J,Feng W,An ZT,et al.Anti-TGFβ-1 receptor inhibitor mediates the efficacy of the human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells against liver fibrosis through TGFβ-1/Smad pathway.Mol Cell Biochem.2017.doi: 10.1007/s11010-017-2940-1.[Epub ahead of print][26] Chen L,Zhang C,Chen L,et al.Human Menstrual Blood-Derived Stem Cells Ameliorate Liver Fibrosis in Mice by Targeting Hepatic Stellate Cells via Paracrine Mediators.Stem Cells Transl Med.2017;6(1):272-284.[27] Ezquer F,Bahamonde J,Huang YL,et al.Administration of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells restores liver regeneration and improves liver function in obese mice with hepatic steatosis after partial hepatectomy.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):20.[28] Fang XQ,Zhang JF,Song HY,et al.Effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on immune function and prognosis of patients with decompensated hepatitis B cirrhosis.Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2016;24(12): 907-910.[29] Liu Y,Xiong Y,Xing F,et al.Precise Regulation of miR-210 is Critical for the Cellular Homeostasis Maintenance and Transplantation Efficacy Enhancement of Mesenchymal Stem Cell in Acute Liver Failure Therapy.Cell Transplant.2016.doi: 10.3727/096368916X694274. [Epub ahead of print][30] Zhang YC,Liu W,Fu BS,et al.Therapeutic potentials of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells for ischemic-type biliary lesions following liver transplantation. Cytotherapy.2017;19(2):194-199.[31] Jin S,Li H,Han M,et al.Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Enhanced Bcl-2 Expression Promote Liver Recovery in a Rat Model of Hepatic Cirrhosis.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;40(5): 1117-1128.[32] Fitzpatrick E,Wu Y,Dhadda P,et al.Coculture with mesenchymal stem cells results in improved viability and function of human hepatocytes.Cell Transplant.2015; 24(1): 73-83.[33] Liu H,Kim Y,Sharkis S,et al.In vivo liver regeneration potential of human induced pluripotent stem cells from diverse origins. Sci Transl Med.2011;3(82):82ra39.[34] 郑盛,杨涓,刘琼,等.经肝固有动脉自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗肝硬化失代偿期患者[J].中华移植杂志(电子版),2015,9(4): 165-169.[35] Kharaziha P,Hellström PM,Noorinayer B,et al. Improvement of liver function in liver cirrhosis patients after autologous mesenchymal stem cell injection: aphase I-II clinical trial.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol.2009;21(10):1199-1205.[36] Peng L,Xie DY,Lin BL,et al.Autologous Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation in Liver Failure Patients Caused by Hepatitis B: Short-Term and Long-Term Outcomes.Hepatology.2011;54(5):1891-1892.[37] Kim G, Eom YW, Baik SK, et al. Therapeutic Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Patients with Chronic Liver Diseases: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Korean Med Sci.2015;30(10):1405-1415.[38] Xue HL,Zeng WZ,Wu XL,et al.Clinical therapeutic effects of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells transplantation in thetreatment of end-stage liver disease. Transplant Proc.2015;47(2):412-418. |
.jpg)

.jpg)