中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (15): 2372-2377.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.15.014
• 骨科植入物 orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
股骨近端防旋髓内钉与股骨近端锁定板修复不稳定型老年骨质疏松股骨转子间骨折
王江静,胡思斌,孙宏辉,崔路宽
- 河北省沧州中西医结合医院骨三科,河北省沧州市 061001
Proximal femoral nail anti-rotation versus locking proximal femoral plate for osteoporotic unstable intertrochanteric fractures in senile patients
Wang Jiang-jing, Hu Si-bin, Song Hong-hui, Cui Lu-kuan
- Third Department of Orthopedics, Hebei Province Cangzhou Hospital of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, Cangzhou 061001, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
不稳定型股骨转子间骨折:股骨转子间骨折系指股骨颈基底至小转子水平之间的骨折,属于关节囊外骨折。骨折分为4型Ⅰ型:同大转子至小转子沿着转子间线所发生的骨折,稳定无移位,没有粉碎,复位简单(占21%);Ⅱ型:骨折位于转子间线,同时伴有皮质骨的多处骨折,为粉碎性骨折,伴有移位,复位较困难,一旦复位可获得稳定,其中有一种特殊骨折——转子间前后线型骨折,骨折线只能在侧位片上看到(占36%);Ⅲ型:基本属于转子下骨折,至少有一骨折线横过近端股骨干小转子或小转子以远部位,有大的后内侧粉碎区域,并且不稳定,复位比较困难,手术期、恢复期并发症较多(占28%);Ⅳ型:转子区和近端股骨干至少2个平面出现骨折,股骨干多呈螺旋形斜形或蝶形骨折,骨折包括转子下部分,不稳定。Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅵ型均为不稳定型。
螺旋刀片的位置:传统观念认为股骨头内拉力钉应位于正位片的中下1/3 ,侧卧位于股骨头颈的中央,这样可以使螺钉的上方保留更多的骨质。而到1995年耶鲁大学学者Baumgaertner等提出尖顶距(Tip-Apex Distance,TAD)的概念,是通过标准正侧位片上螺钉尖与股骨头中轴线顶点之间的距离评价螺钉在股骨头颈内的位置,预测螺钉切出股骨头颈的发生率。
摘要
背景:老年股骨转子间骨折具有老年化、不稳定性、并发症多、病死率高等特点,选择合适的内固定方式对治疗效果起重要作用。
目的:比较股骨近端防旋髓内钉与股骨近端锁定板微创治疗不稳定型老年骨质疏松股骨转子间骨折的临床疗效。
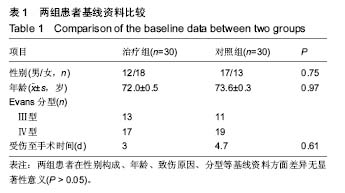
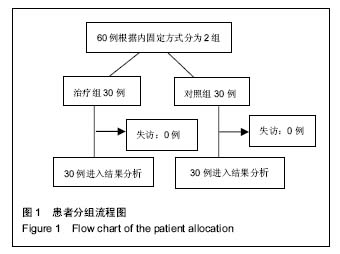
方法:对60例不稳定型股骨转子间骨折患者的临床资料进行分析,将其随机分为治疗组和对照组。治疗组30例应用股骨防旋髓内钉治疗;对照组30例应用锁定接骨板治疗,观察患者手术情况、功能恢复情况、并发症等。
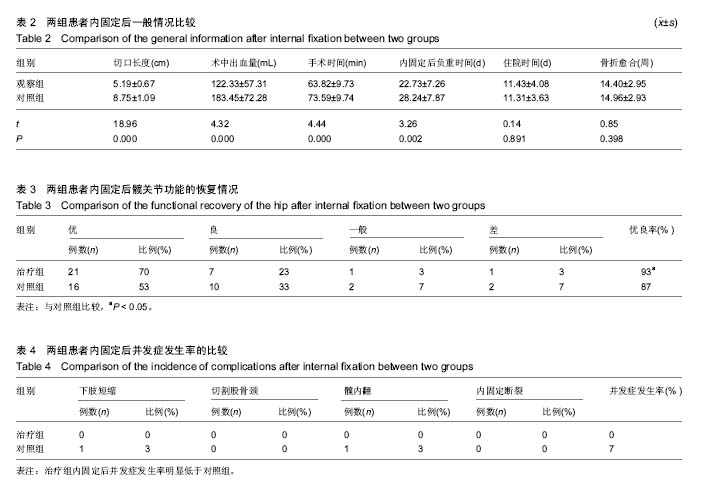
结果与结论:①治疗组患者切口长度、手术时间、术中出血量、负重时间均显著短于对照组(P < 0.01);②治疗组Harris功能评分及髋关节功能优良率均显著高于对照组(P < 0.05);③治疗组内固定后并发症发生率明显低于对照组;④结果说明,应用股骨防旋髓内钉可显著提高骨折复位固定的治疗效果。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-6541-8702(王江静)
中图分类号:
.jpg)