Design
A cytology in vitro and in vivo experimental study.
Setting and time
The study was conducted at Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine from January 2015 to December 2015.
Materials
Cell lines: Human hepatoma HepG2 cell lines were purchased from the Shanghai Cell Bank of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Experimental animals: SPF level BALB/c ASlac-nu mice, female, aged 5-6 weeks, were provided by Slack Limited of Experimental Animal (license No. SCXK (Hu) 2007-2005). They were used for tumor cloning tumorigenicity verification.
Reagents: DMEM medium and trypsin were purchased from Hyclone (Utah, USA); fetal bovine serum (FBS) was purchased from Shanghai Sheng Gong Limited of Biological Engineering (Shanghai, China); penicillin and streptomycin were purchased from Sigma (USA).
Methods
Recovery of HepG2 cells
Cell cryopreservation tubes were quickly removed from the liquid nitrogen, and were put into a 37 ℃ constant temperature water bath immediately, and shaken to dissolve completely. The cell suspension was then moved to a 10 mL glass centrifuge tube, and cultured in high glucose DMEM culture medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum. After centrifugation at room temperature, the supernatant was removed, an appropriate amount of cell culture medium was added and the cells were resuspended by gentle pipetting and placed into the 37 ℃, 5% CO2 incubator. The medium was changed the next day.
Subculture of HepG2 cells
The HepG2 cells in logarithmic growth phase (cells accounted for 80% of the effective area of the bottle bottom) were separated. The cell culture medium was removed and 1 mL of 0.25% trypsin was added at room temperature to digest cells. Cells turned round under microscope, accompanied by loss of cytoplasm and increase of cell gap. High-glucose DMEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum was added before it fell off completely to terminate digestion. The supernatant was removed after centrifugation at room temperature. Finally, high-glucose DMEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum was added and the cells were resuspended by gentle pipetting and placed in the 37 ℃, 5% CO2 incubator.
Preparation of single-cell suspension
When the cells were passaged to the third generation, a bottle of HepG2 cells in the logarithmic growth phase were taken and digested using trypsin for 2 minutes, and the cells were observed under inverted phase contrast microscope, followed by stopping the digestion and collecting the cells by pipetting. When the cell periphery began to retract digestion, the cells were suspended. Following centrifugation at 1 000 r/min, the supernatant was discarded, and the medium was added to resuspend cells. After counting, the pipette was used to draw cell suspension (1-2 drops) to a culture dish, and these cells were mixed and incubated at 37 ℃ for 10-15 minutes.
Single cell isolation and culture
After pre-preparing 200 μL/hole medium was added into 96-well plates, the culture dishes were taken from the 37 ℃ incubator and were placed under inverted microscope. Single cells were drawn by pasteurized smallest-size syringe needle which were connected with a 100 μL pipette and was set one by one into the 96-well plates. Bubbles appeared when the cells were introduced into the 96-well plates.
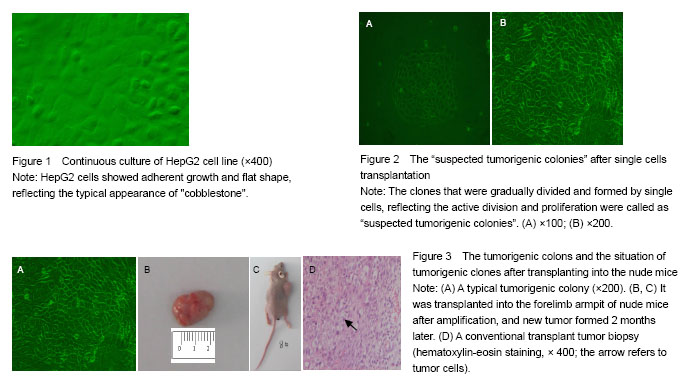
Tumorigenicity verification
According to the separation method, single cells were cultivated into four 96-well plates. Cell quantity, morphology and growth state were recorded at 1 and 2 weeks after culture. At the end, single cell clones were screening preliminarily depended on the number and growth characteristics of cell clones.
Confirmation of tumorigenic clones
The cell clones in the 96-well plate were 1:1 digested, transferred to a new 96-well plate for continuous amplification, and then spread to 24-well plates. The ones that could continue to be amplified in the 6-well plate were judged to be successful tumorigenic clones.
Confirmation of single cell tumorigenic clones
Tumorigenic clones were transplanted into the forelimb armpit of BALB/c ASlac-nu mice when they were expanded to 1×106/well. Tumorigenicity was observed after 2 months.
Hematoxylin-eosin staining
The transplanted tumor was dehydrated after 10% formalin fixation for 18 hours, then the tissue was transparent by xylene, and the transparent tissue was embedded in paraffin. Finally, the slice thickness was 4-6 μm. Slices were stained by hematoxylin for 1-5 minutes, then was rinsed using 1% hydrochloric acid water for 5 seconds, and finally was disseminated for 2 minutes by eosin.
Main outcome measures
Identification results of liver cancer stem cells.
Statistical analysis
SPSS 13.0 statistical software was applied. Chi-square test was used for data comparison, and a value of P ≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程