| [1] 周君琳,凌亦凌,苏庆军,等.外源性一氧化碳抗大鼠肢体缺血再灌注所致肺损伤的实验研究[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2006,22(2):303-306.
[2] Atabai K,Matthay MA.The pulmonary physician in critical care-5: acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome:definitions and epidemiology. Thorax. 2002;57:452-458.
[3] Li L,Moore PK.An overview of the biological significance of endogenous gases: new roles for old molecules.Biochem Soc Trans.2007;35:1138-1141.
[4] Moody BF,Calvert JW.Emergent role of gasotransmitters in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Medical Gas Res.2011;1:3.
[5] Zhao YR,Wang D,Liu Y,et al.The PI3K/Akt, p38MAPK, and JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathways Mediate the Protection of SO2 Against Acute Lung Injury Induced by Limb Ischemia/Reperfusion in Rats.J Physiol Sci. 2016;66(3):229-239..
[6] 赵彦瑞,刘洋,王东,等.PI3K/Akt和JAK2/STAT3信号转导通路在SO2抗大鼠肢体缺血再灌注致急性肺损伤中的作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2015,31(11):2076-2082.
[7] Huang XL,Liu Y,Zhou JL,et al.Role of Sulfur Dioxide in Acute Lung Injury Following Limb Ischemia /Rep erfusion in Rats.J Biochem Mol Toxicol.2013;27(8):389-397.
[8] 周君琳,黄新莉,黎宁,等.二氧化硫对大鼠肢体缺血再灌注所致肺损伤的影响及其作用机制[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2013,29(10):1747-1752.
[9] 杨运彩,周君琳,黄新莉,等.一氧化碳释放分子对肢体缺血-再灌注所致肺损伤的作用[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2012, 21(1):43-47.
[10] 周君琳,黄新莉,仲维佳,等.硫化氢对肢体缺血再灌注所致大鼠急性肺损伤的作用及机制[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2011,27(1):9-13.
[11] 刘洋,单磊,周君琳,等.MAPKs在硫化氢抗大鼠肢体缺血再灌注所致肺损伤中的作用[J].昆明医学院学报,2011, 32(9):16-20.
[12] Zhou JL,Li G,Hai Y,et al.Protection of CO-rel easing molecule against lung injury induced by limb ischemia- reperfusion.Chin J Traumatol.2009;12(2):71-76.
[13] 周君琳,凌亦凌,李陈利,等.一氧化氮和过氧亚硝基阴离子在肢体缺血再灌注致肺损伤中的作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2003,24(6):158-160.
[14] 周君琳,凌亦凌,鲁士宝,等.丝裂原活化蛋白激酶在一氧化碳抗大鼠肢体缺血再灌注所致肺损伤中的作用[J].中华实验外科杂志,2005,22(2):163-165.
[15] Bloch KD,Ichinose F,Roberts JJ,et al.Inhaled NO as a therapeutic agent. Cardiovasc Res.2007;75:339-348.
[16] Afshari A,Brok J,Moller AM,et al.Inhaled nitric oxide for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and acute lung injury in children and adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.2010;(7):CD002787.
[17] Ryter SW,Choi AM.Heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide: novel therapeutic strategies in critical care medicine.Curr Drug Targets.2010;11:1485-1494.
[18] Ren Y.Natural occurrence of carbonyl sulfide and ethyl formate in grains.In Proceedings of the International Conference on Controlled Atmosphere and Fumigation in Stored Products,2002.
[19] Balazy M,Abu-Yousef IA,Harpp DN,et al.Identification of carbonyl sulfide and sulfur dioxide in porcine coronary artery by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry, possible relevance to EDHF.Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2003;311(3):728-734.
[20] Cohen SM,Siddiqi FA,Darakchiev B,et al.Attenuation of acute lung injury caused by hind-limb ischemia- reperfusion injury by butyrolactone anti-inflammatory agent FLl003.J Trauma. 1997;43(2):247-252.
[21] Lardinois1 Q,Kirby PJ,Morgan DL,et al.Mass spectrometric analysis of rat cerebrospinal fluid proteins following exposure to the neurotoxicant carbonyl sulfide.Rapid Commun.Mass Spectrom. 2014; 28:2531-2538.
[22] 刘俊锋,耿春梅,牟玉静,等.羰基硫(COS)在土壤中的吸收与转化[J].环境化学,2004, 23(6):615-620.
[23] 牟玉静,周丽,张晓山,等.羰基硫(COS)在麦田土壤中的地气交换[J].中国科学(B辑 化学),2001,1(3):261-264.
[24] 聂亚峰,席淑琪,张晋华,等.环境因素对土壤含硫气体释放的影响[J].环境化学,2001, 20(1):38-42.
[25] 刘俊锋,耿春梅,张逸,等.羰基硫(COS)在五种富氧型土壤中的吸收与转化[J].环境化学, 2011,30(3):579-584.
[26] 王冠,孙同华,张宏波,等.催化水解法低温脱除煤气中羰基硫的研究[J].现代化工,2014, 34(1):60-63.
[27] 沈芳,上官炬,樊惠玲.工艺条件对中温羰基硫水解催化转化率的影响[J].太原理工大学学报,2009,40(1):32-34.
[28] 范健,雷军.COS脱除技术进展[J].安徽化工,2007,33(4): 3-5.
[29] 柯明,许赛威,刘成翠,等.常温羰基硫水解催化剂的研究进展[J].石油与天然气化工,2007,36(4):271-274.
[30] 李新学,刘迎新,魏雄辉.羰基硫脱除技术[J].现代化工 ,2004,24(8):19-22.
[31] Katayama Y,Narahara Y,Inoue Y,et al.A thiocyanate hydrolase of Thiobacillus thioparus. A novel enzyme catalyzing the formation of carbonyl sulfide from thiocyanate, J Biol Chem.1992;267:9170-9175.
[32] Vlasceanu L,Popa R,Kinkle BK.Characterization of Thiobacillus thioparus LV43 and its distribution in a chemoautotrophically based groundwater ecosystem.Appl Environ Microbiol. 1997;63: 3123-3127.
[33] Schultz CP,Ahmed MK,Dawes C,et al.Thiocyanate levels in human saliva: quantitation by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy.Anal Biochem. 1996;240:7-12.
[34] Spagnolo A,Torsello S,Morisi G,et al.Serum thiocyanate levels as an objective measure of smoking habits in epidemiological studies.Eur J Epidemiol. 1988;4(2):206-211.
[35] Zheng T,Altura BT,et al.Magnesium modulates contractile responses of rat aorta to thiocyanate: a possible relationship to smoking-induced atherosclerosis.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.1999; 157:77-84.
[36] Kelly DP, Wood AP, Iordan SL, et al.Biological production and consumption of gaseous organic sulphur compounds.Biochem Soc Trans.1994; 22: 1011-1015.
[37] Chengelis CP,Neal RA.Studies of Carbonyl Sulfide Toxicity: Metabolism by Carbonic Anhydrasel.Toxicol Appl Pharm.1980;55:198-202.
[38] Morgan DL,Little PB,Herr DW,et al.Neurotoxicity of carbonyl sulfide in F344 rats following inhalation exposure for up to 12 weeks.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2004;200:131.
[39] Morrison JP,Ton TV,Collins JB, et al.Gene expression studies reveal that DNA damage, vascular perturbation, and inflammation contribute to the pathogenesis of carbonyl sulfide neurotoxicity.Toxicol Pathol.2009; 37: 502.
[40] Sills RC,Morgan DL,Herr DW,et al.Contribution of magnetic resonance microscopy in the 12-week neurotoxicity evaluation of carbonyl sulfide in Fischer 344 rats.Toxicol Pathol.2004;32:501.
[41] Lardinois O,Kirby PJ,Morgan DL,et al.Mass spectrometric analysis of rat cerebrospinal fluid proteins following exposure to the neurotoxicant carbonyl sulfide. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2014;28(23):2531-2538. |
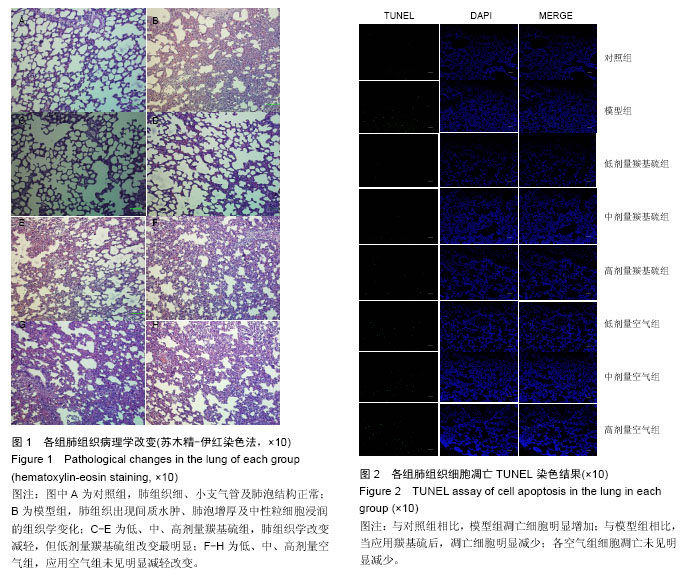
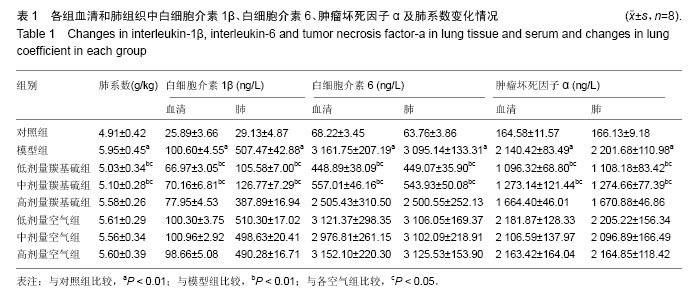
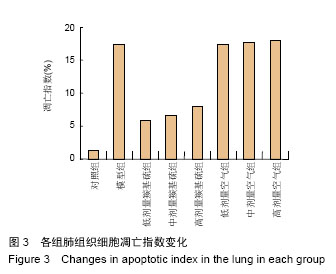
.jpg)
.jpg)