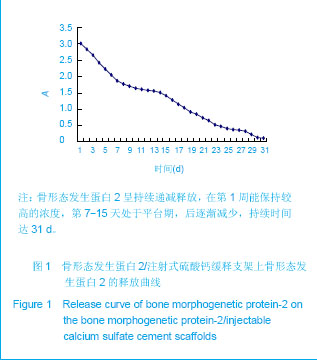
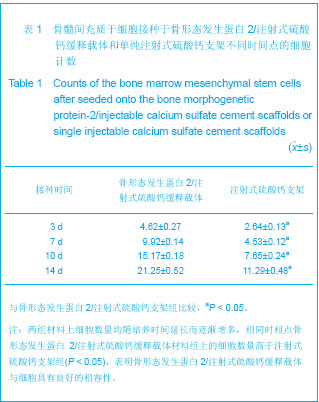
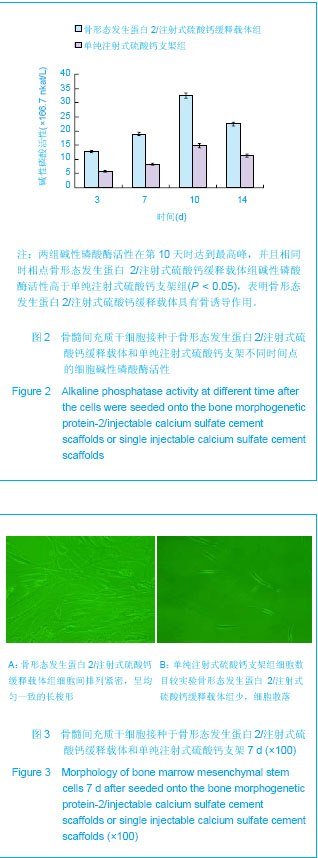
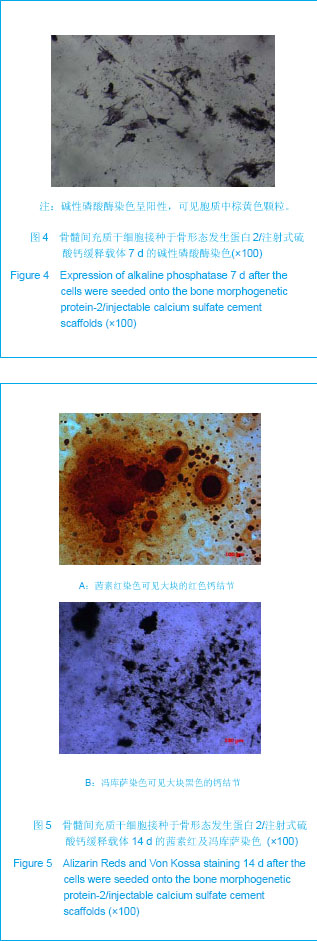
| [1] Liu H,Zhang YG.Shengwu Guke Cailiao yu Linchuang Yanjiu. 2012;9(2):32-34.刘昊,张永刚.骨组织工程的研究应用与进展[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2012,9(2):32-34.[2] Huang Y,Ren J,Ren T,et al. Bone marrow stromal cells cultured on poly (lactide-co-glycolide)/nano-hydroxyapatite composites with chemical immobilization of Arg-Gly-Asp peptide and preliminary bone regeneration of mandibular defect thereof.J Biomed Mater Res A.2010;95(4):993-1003.[3] Wang C,Wang Z,Li A,et al.Repair of segmental bone-defect of goat’s tibia using a dynamic perfusion culture tissue engineering bone. J Biomed Mater Res A.2010; 92(3): 1145-1153.[4] Pirraco RP,Obokata H,Iwata T,et al.Development of osteogenic cell sheets for bone tissue engineering applications.Tissue Eng Part A.2011;17(11-12):1507-1515.[5] Liu SZ,Hou YD. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(42):7911-7914.刘顺振,侯玉东.骨组织工程支架材料的研究进展及临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(42):7911-7914.[6] Li DY,Zheng X,Chen YX.Chuangshang Waike Zazhi. 2013; 15(1):87-90.李东亚,郑欣,陈一心.骨组织工程支架材料应用于大段骨缺损的实验研究进展[J].创伤外科杂志,2013,15(1):87-90.[7] Guo Y,Zhang XZ,Wu JM,et al.Zhongguo Kangfu Yixue Zazhi. 2006;21(7):579-581.郭勇,张西正,武继民,等. 人骨形成蛋白-2基因成骨诱导作用研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2006,21(7):579-581.[8] Mousset B,Benoit MA,Delloye C,et al. Biodegradable implants for potential use in bone infection. An in vitro study of antibiotic loaded calcium sulfate.Int Orthop.1995;19:157-161.[9] Qian D,Ma P,Li Y,et al.Jiangsu Daxue Xuebao. 2009; 19(2): 118-120.钱栋,马鹏,李阳,等. 骨形成蛋白-2结合纤维连接蛋白体外诱导骨髓间充质干细胞分化为成骨细胞的观察[J].江苏大学学报, 2009,19(2):118-120.[10] Urist MR. Bone :formation by autoinduction. 1965. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(395):4-10.[11] Sciadini MF,Johnson KD.Evaluation of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 as a bone-graft substitute in a caninesegmental defect model.Orthop Res.2000; 18(2): 289-302.[12] Bouxsein ML,Turek TJ,Blake CA,et al. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 accelerates healing in a rabbit ulnar osteotomy model.Bone Joint Surg Am.2001; 83-A(8): 1219-1230.[13] Li RH,Bouxsein ML,Blake CA,et al. rhBMP-2 injected in a calciumphosphate paste(alpha-BSM) accelerates healing in the rabbit ulnar osteotomy model. Orthop Res.2003; 21(6): 997-1004.[14] Lieberman JR,Daluishi A,Einhorn TA.The role of growth factors in the repair of bone, Biology and clinical applications.Bone Joint Surg AM.2002;84-A(6):1032-1044.[15] Winn SR,Uludag H,Hollinger JO.Carrier system for bone morphogenetics proteins.Clin Orthop.1999;367(6):95-106.[16] Tian XZ,Liu Y,Chen H,et al.Shandong Yiyao. 2008;48(9): 143-144.田学忠,刘越,陈华,等.硫酸钙人工骨研究进展[J].山东医药, 2008,48(9): 143-144.[17] Yu M.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu.2010;14(47):8869-8871.俞猛.骨组织工程支架材料修复骨缺损的特性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(47):8869-8871.[18] Turner TM,Urban RM,Hall DJ,et al.Local and systemic levels of tobramycin delivered from calcium sulfate bone graft substitute pellets. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2005;437(2):97-104.[19] Beardmore AA,Brooks DE,Wenke JC,et al. Effectiveness of local antibiotic delivery with an osteoinductive and osteoconductive bone-graft substitute. Bone Joint Surg AM. 2005;87(1):107-112.[20] Xu XF,Liu XP,Wang MW,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(25):4636-4640.徐晓峰,刘小平,王明伟,等.血管内皮生长因子-纳米晶胶原基骨缓释系统与人骨髓间充质干细胞的体外生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(25):4636-4640.[21] Xu XF,Xu CZ,Ma P,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2009;13(16):3052-3057.徐晓峰,徐成振,马鹏,等.细胞支架与骨形态发生蛋白及血管内皮生长因子复合修复大鼠股骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2009, 13(16):3052-3057.[22] Xu XF,Liu XP,Wang MW,et al.Zhongguo Shengwu Yixue Gongcheng Xuebao. 2010;29(5):741-746.徐晓峰,刘小平,王明伟,等. 纳米晶胶原基骨/血管内皮生长因子缓释支架对人骨髓间充质干细胞体外粘附增殖的影响[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2010,29(5):741-746.[23] Yang LJ, Jin Y, Hu YY. Xi'an: Shanxi Science & Technology Press.1993: 232-237.杨连甲,金岩,胡蕴玉.口腔和骨科的生物活性材料[M].西安:陕西科学技术出版社, 1993: 232-237.[24] Walsh WR,M orb erg P,Yu Y,et al. Response of a calcium sulfate bone graft substitute in a confined cancellous defect. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(406):228-236. |
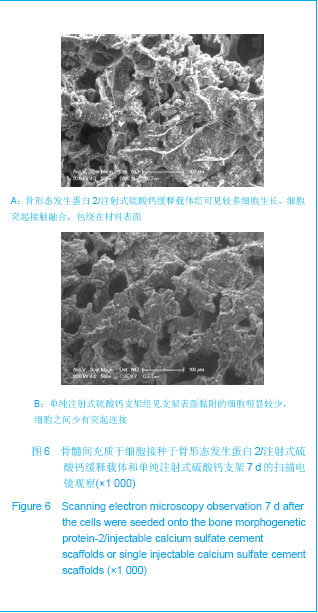
.jpg)