| [1] Marsh JL.Tibial plateau fracture//Bucholz RW, Robert W, Heckman JD.Rockwood and Green’s fractures in adults.7th ed.Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins,2010: 1781-1833.
[2] Cho KY,Oh HS,Yoo JH,et al.Treatment of schatzker type V and VI tibial plateau fractures using a midline longitudinal incision and dual plating. Knee Surg. 2013;2: 77-83.
[3] Prasad GT,Kumar TS,Kumar RK,et al.Functional outcome of schatzker type V and VI tibial plateau fractures treated with dual plates. Ind J Orthop. 2013;2: 188-194.
[4] Solomon LB, Stevenson AW, Lee YC,et al. Posterolateral and anterolateral approaches to unicondylar posterolateral tibial plateau fractures: a comparative study. Injury. 2013;11: 1561-1568.
[5] 储旭东,刘晓晖,陈伟南,等.经腓骨小头上入路治疗胫骨平台后外侧髁骨折的临床研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2013,27(2):155-159.
[6] Johnson EE,Timon S,Osuji C. Surgical technique: Tscherne-Johnson extensile approach for tibial plateau fractures. Clin Orhop. 2013;9: 2760-2767.
[7] Frosch KH,Balcarek P,Walde T,et al.A new posterolateral approach without fibula osteotomy for the treatment of tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;8: 515-520.
[8] He X,Ye P,Hu Y, et al. A posterior inverted L-shaped approach for the treatment of posterior bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;1: 23-28.
[9] Biggi F, Di Fabio S, D’Antimo C, et al. Tibial plateau fractures: internal fixation with locking plates and the MIPO technique. Injury. 2010;11: 1178-1182.
[10] Raza H, Hashmi P, Abbas K, et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for tibial plateau fractures. J Orhop Surg. 2012;1: 42-47.
[11] Lasanianos NG,Garnavos C,Magnisalis E,et al.A comparative biomechanical study for complex tibial plateau fractures: nailing and compression bolts versus modern and traditional plating.Injury. 2013;10: 1333-1339.
[12] Yoo BJ,Beingessner DM,Barei DP.Stabilization of the posteromedial fragment in bicondylar tibial plateau fractures: a mechanical comparison of locking and nonlocking single and dual plating methods. J Trauma. 2010;1: 148-155.
[13] Ehlinger M,Rahme M,Moor BK,et al.Reliability of locked plating in tibial plateau fractures with a medial component. Orthop Trauma Surg Res. 2012;2: 173-179.
[14] Weaver MJ,Harris MB,Strom AC,et al.Fracture pattern and fixation type related to loss of reduction in bicondylar tibial plateau fractures.Injury. 2012;6: 864-869.
[15] 巴雪峰,孙改生,凯瑟尔,等.胫骨平台骨折的治疗新进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,11(6): 1104-1107.
[16] Nikolaou VS,Tan HB,Haidukewych G,et al.Proximal tibial fractures: early experience using polyaxial locking-plate technology. Int Orthop. 2011;8: 1215-1221.
[17] Laible C,Earl-Royal E,Davidovitch R,et al.Infection after spanning external fixation for high-energy tibial plateau fractures: is pin site-plate overlap a problem. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;2: 92-97.
[18] Mankar SH,Golhar AV,Shukla M,et al.Outcome of complex tibial plateau fractures treated with external fixator. Ind J Orthop. 2012;5: 570-574.
[19] 王宏川,舒衡生.外固定架在高能量胫骨平台骨折治疗中的应用进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(10): 1001-1004.
[20] Malakasi A,Lallos SN,Chronopoulos E,et al. Comparative study of internal and hybrid external fixation in tibial condylar fractures.Eur J Orthop Surg. 2013;1: 97-103.
[21] El-Alfy B,Othman A,Mansour E.Indirect reduction and hybrid external fixation in management of comminuted tibial plateau fractures.Acta Orthop Belg. 2011;3: 349-354.
[22] Babis GC, Evangelopoulos DS, Kontovazenitis P, et al. High energy tibial plateau fractures treated with hybrid external fixation. J Orthop Surg. 2011;6: 35.
[23] Ariffin HM, Mahdi NM, Rhani SA, et al. Modified hybrid fixator for High-energy schatzker V and VI tibial plateau fractures. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2011;1: 21-26.
[24] Dall’oca C,Maluta T,Lavini F,et al.Tibial plateau fractures: compared outcomes between ARIF and ORIF. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2012;3: 163-175.
[25] Siegler J,Galissier B,Marcheix PS,et al.Percutaneous fixation of tibial plateau fractures under arthroscopy: a medium term perspective. Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011; 1: 44-50.
[26] Ruiz-Ibán M,Diaz -Heredia J,Elías-Martín E,et al. Repair of meniscal tears associated with tibial plateau fractures: a review of 15 cases. Am J Sports Med. 2012; 10: 2289-2295.
[27] Pizanis A, Garcia P, Pohlemann T, et al. Balloon tibioplasty: a useful tool for reduction of tibial plateau depression fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;7: 88-93.
[28] Vendeuvre T,Babusiaux D,Brèque C,et al. Tuberoplasty: minimally invasive osteosynthesis technique for tibial plateau fractures. Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;99: 267-272.
[29] 张永刚.有限元法发展及其应用[J].科技情报开发与经济, 2007,17(11):178-179.
[30] 彭春政,张胜年,陆爱云.人体躯干骨骼-肌肉-韧带结构三维有限元模型的建立和验证[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2010,29(6):702-705.
[31] 方国芳,林荔军,于博,等.不同状态下股骨的应力分布及临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(17):3045-3047.
[32] 孙卫东,温建民.足部有限元建模方法应用现状[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(13):2457-2461.
[33] 黄诸侯,李俊,陈日齐,等.跟骨三维有限元模型的建立及其骨折发生机制[J].中国骨伤,2012,25(2):97-101.
[34] 李晓淼,沈奕,王伟力.全膝关节假体三维有限元模型的建立[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(13): 2304-2308.
[35] 袁平,王万春.膝关节三维有限元模型的建立及生物力学分析[J].中南大学学报,2010,35(1):85-89.
[36] 徐灵军,朱海波,张银网,等.人工髋关节活体有限元建模及力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(26): 4770-4775.
[37] 王友良,杨杰山.三维有限元分析在颈椎生物力学中的研究现状[J].临床骨科杂志,2011,14(1):89-92.
[38] 李正东,邹冬华,刘宁国,等.人体骨盆有限元模型的建立及其在法医学鉴定中的应用价值[J].法医学杂志,2010, 26(6): 406-412.
[39] 程永耿,王新伟,袁文.颈椎前路分节段减压融合术三维有限元分析[J].脊柱外科杂志,2008,6(6):356-359.
[40] 陈家麟,茅祖斌,吴小涛.四种经椎间孔腰椎间融合固定方式的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008,12(39):7605-7610.
[41] 郑良孝,聂林.骶骨螺钉四种固定方式生物力学特性的有限元分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008,23(4): 302-305.
[42] 刘立峰,蔡锦方,梁进.跟骨骨折内固定方法的有限元模拟比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2003,11(8):557-558.
[43] 李文锋,侯树勋,陈金栋.微型外固定器治疗Bennett骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2006,9(5):427-428.
[44] 孟立民,苏啸天,张银光,等.微型外固定支架和克氏针治疗Bennett骨折的三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(9):1626-1630.
[45] Watson MA, Mathias KJ, Maffulli N, et al. The effect of clamping a tensioned wire: implications for the Ilizarov external fixation system. Proc Ins Mech Eng. 2003; 21(7): 91-98.
[46] 王志杰.有限元法在骨应力分析及骨科内外固定系统研究中的应用[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2006,24(1): 107-110. |
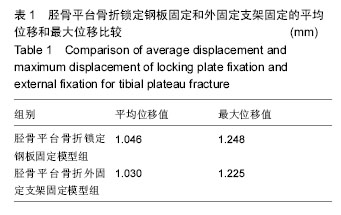
.jpg)
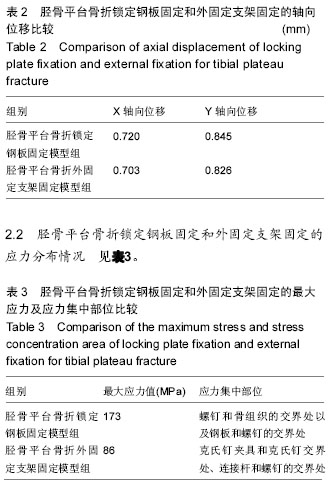

.jpg)
.jpg)