| [1] 徐静静,蔡景龙,王黔,等.人瘢痕组织脱细胞真皮基质的组织结构和生物力学性能[J].中华医学杂志, 2015,95(10): 770-775.
[2] 吴起,王甲汉,任加良,等.瘢痕微粒皮联合异种脱细胞真皮基质治疗中厚皮供区创面效果观察[J].中华烧伤杂志, 2014,30(4):363-365.
[3] 冯祥生,陈晓东,谭家驹,等.异种(猪)脱细胞真皮基质在瘢痕整形中的应用[J].中华整形外科杂志, 2007,23(5): 391-393.
[4] Kanzaki M,Yamato M,Takagi R,et al.Controlled collagen crosslinking process in tissue-engineered fibroblast sheets for preventing scar contracture on the surface of lungs.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013;7(5): 383-391.
[5] Yang JH,Shim SW,Lee BY,et al.Skin-derived stem cells in human scar tissues: a novel isolation and proliferation technique and their differentiation potential to neurogenic progenitor cells.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010;16(4):619-629.
[6] Klinger M,Caviggioli F,Chiaratti A,et al.Autologous Fat Transplantation in Severe Burn Scar Outcomes: a New Perspective for Cell Therapy and Tissue Engineering//Controlled Release Society Annual Meeting and Exposition; 20070707-11; Long Beach, CA(US).2007:548-549.
[7] 李云青,章宏伟,汤建平,等.复合皮移植于烧创伤和瘢痕修复中的疗效观察[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2006,26(12):1282-1282.
[8] 姜笃银,陈璧,徐明达,等.异种脱细胞真皮基质的制作和临床应用观察[J].中华烧伤杂志,2002,18(1):15-18.
[9] 李守聚.异体脱细胞真皮基质与自体皮片复合移植的临床应用[J].中国美容医学,2012,21(11):1484-1486.
[10] 袁凯平,萧艳珊,谢广中,等.真皮脂肪瓣和脱细胞真皮基质修复面部凹陷性瘢痕的对比研究[J].现代诊断与治疗, 2015,26(12):2811-2812.
[11] 周杰,罗艺,徐刚,等.脱细胞真皮基质加自体瘢痕表皮在瘢痕挛缩畸形整复中的应用[J].中国美容医学, 2012, 21(11): 1498.
[12] Han Y,Tao R,Han Y,et al.Microencapsulated VEGF gene-modified umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells promote the vascularization of tissue engineered dermis and experimental study.Cytotherapy. 2014; 16(2):160-169.
[13] 胡顺鹏.新型胶原真皮支架材料的制备与性能表征[D].济南:山东大学,2010.
[14] 王晓川.烧伤变性真皮基质可再生利用的初步研究[D].济南:山东大学,2012.
[15] 阮树斌,冯祥生,陈晓东,等.脱细胞(猪)基质早期封闭浅度大面积烧伤创面的临床研究[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2008,3(2):177-182.
[16] Lynch MP,Chung MT,Rinker BD,et al.Dermal autografts as a substitute for acellular dermal matrices (ADM) in tissue expander breast reconstruction: A prospective comparative study.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg.2013; 66(11):1534-1542.
[17] Elliott LF,Ghazi BH,Otterburn DM,et al.The scarless latissimus dorsi flap for full muscle coverage in device-based immediate breast reconstruction: an autologous alternative to acellular dermal matrix.Plast Reconstr Surg.2011;128(1):71-79.
[18] Takami Y,Matsuda T,Yoshitake M,et al.Dispase/ detergent treated dermal matrix as a dermal sustitute. Burns.1996;22(3):182-190.
[19] Jiong C,Jiake C,Chunmao H,et al.Clinical application and long-term follow-up study of porcine acellular dermal matrix combined with autoskin grafting.J Burn Care Res.2010;31(2):280-285.
[20] 王晓川,李川,单菲,等.烧伤变性脱细胞真皮基质可再生利用的实验研究[J].中华烧伤杂志,2012,28(3):201-206.
[21] 陈博,彭代智,左海斌,等.新生小牛皮肤的形态学和生物力学特点及脱细胞方法探索[J].重庆医学, 2012,41(11): 1043-1046,封2.
[22] 汲婧,刘子源,张晶,等.脱细胞真皮基质在角膜中植入性的生物力学研究[J].力学学报,2014,46(1):145-154.
[23] Sch?Nmeyr B,Clavin N,Avraham T,et al.Synthesis of a tissue-engineered periosteum with acellular dermal matrix and cultured mesenchymal stem cells.Tissue Eng Part A.2009;15(7):1833-1841.
[24] Wang GQ,Xia ZF.Transplantation of epidermis of scar tissue on acellular dermal matrix.Burns. 2009;35(3): 352-355.
[25] 林煌,李文志,闫秀娟,等.激光微孔脱细胞真皮基质生物力学测试[J].中国美容医学,2010,19(5):694-696.
[26] [26] 刘坡,祁少海,舒斌,等.异体脱细胞真皮基质作为组织工程皮肤真皮支架的可行性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(21):3864-3868..
[27] Feng X,Tan J,Pan Y,et al.Control of hypertrophic scar from inception by using xenogenic (porcine) acellular dermal matrix (ADM) to cover deep second degree burn.Burns.2006;32(3):293-298.
[28] 陈博.新生小牛与成人皮肤组织学及生物力学性能的比较和牛脱细胞真皮基质的制备[D].第三军医大学,2012.
[29] 赵京玉,柴家科,宋慧锋等.异种(猪)脱细胞真皮基质移植对皮肤弹性的影响[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2012, 6(11):2937-2940.
[30] 徐静静.人瘢痕组织脱细胞真皮基质的组织结构 和生物力学性能[D].青海大学,2015. |
.jpg)
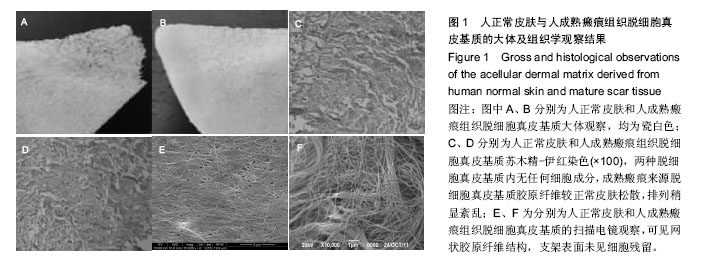
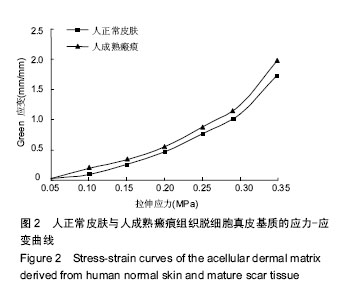
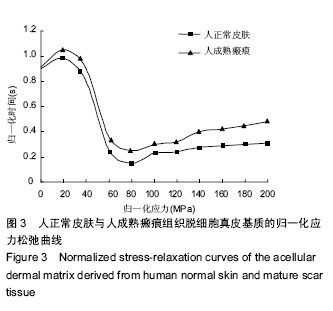
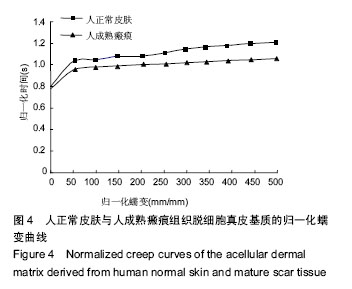
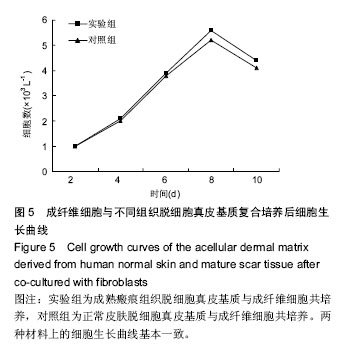
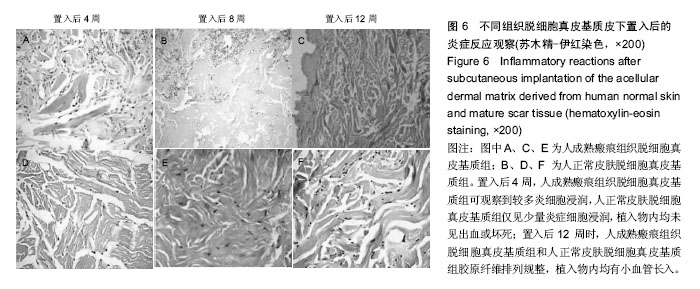
.jpg)
.jpg)