| [1] 吴毅.分化型甲状腺癌诊治中值得关注的一些问题[J].中国实用外科杂志,2011,31(5):374-375.
[2] 滕卫平,刘永锋,高明,等.甲状腺结节和分化型甲状腺癌诊治指南[J].中国肿瘤临床,2012,39(17):1249-1272.
[3] Lee YS,Nam KH,Chung WY,et al.Post-operative complicationsof thyroid cancer in single center experience.Korean Med Sci.2012;25(4):541-545.
[4] 陈曦.甲状腺手术中甲状旁腺的保护[J].中国实用外科杂志,2010,30(10):895-897.
[5] Moon HJ,Sung JM,Kim EK,et al.Diagnostic performance of gray-scale US and elastography in solid thyroid nodules.Radiology. 2012;262(3):1002-1013.
[6] Brito JP,Gionfriddo MR,Al NA,et al.The accuracy of thyroid nodule ultrasound to predict thyroid cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2014;99(4):1253-1263.
[7] Melo M,da Rocha AG,Vinagre J,et al.TERT Promoter Mutations Are a Major Indicator of Poor Outcome in Differentiated Thyroid Carcinomas.J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2014;99(5):e754-e765.
[8] Xing M,Liu R,Liu X,et al. BRAF V600E and TERT Promoter Mutations Cooperatively Identify the Most Aggressive Papillary Thyroid Cancer With Highest Recurrence. J Clin Oncol.2014;32(25):2718-2726.
[9] Liu X,Qu S,Liu R,et al.TERT Promoter Mutations and Their Association with BRAF V600E Mutation and Aggressive Clinicopathological Characteristics of Thyroid Cancer.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(6): e1130-e1136.
[10] 王卓颖,吴毅.分化型甲状腺癌的诊治指南解读[J].外科理论与实践,2014,19(3):185-188.
[11] 中国医师协会外科医师分会甲状腺外科医师委员会.甲状腺及甲状旁腺手术中神经电生理监测临床指南(中国版)[J].中国实用外科杂志,2013,33(6):470-474.
[12] 孙辉,刘晓莉.甲状腺手术中喉返神经和喉上神经的保护[J].中国实用外科杂志,2012,32(5):356-359.
[13] Wu CW,Dionigi G,Sun H,et al.Intraoperative neuromonitoring for the early detection and prevention of RLN traction injury in thyroid surgery: A porcine model.Surgery.2014;155(2):329-339.
[14] 朱精强,汪洵理,魏涛,等.纳米碳甲状旁腺负显影辨认保护技术在甲状腺癌手术中的应用[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2013,20(9):992-994.
[15] 田文,姚京.甲状腺全切除术在甲状腺癌外科治疗中的价值及合理选择[J].中国实用外科杂志,2014,34(1):52-54.
[16] Davidson HC, Park BJ,Johnson JT. Papillary thyroid cancer:controversies in the management of neck metastasis.Laryngoscope. 2008;118(12):2161-2165.
[17] 曾玉剑,钱军,程若川,等.甲状腺癌术中淋巴示踪剂应用对于甲状旁腺保护作用的研究[J].重庆医学, 2012,41(11): 1076,1088.
[18] 邱树升,李良,李新兵,等.美蓝法定位前哨淋巴结活检在cN0分化型甲状腺癌治疗中的应用[J].中国肿瘤外科杂志, 2012,4(4):242-244.
[19] 苏力夫,张生彬,朱永蒙.纳米碳示踪前哨淋巴结在cN0 甲状腺乳头状癌中的应用[J].中国现代医学杂志, 2013, 23(7): 110-112.
[20] 尹源,汪晓东,吕东昊,等.淋巴示踪剂在结直肠癌外科的研究进展[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2010,17(3): 306-308.
[21] Yang F,Jin C,Yang D,et al.Magnetic functionalised carbon nanotubes as drug vehicles for cancer lymph node metastasis treatment.Eur J Cancer. 2011; 47(12): 1873-1882.
[22] 蔡长茂,李威.纳米炭在普外科恶性肿瘤诊治中的应用[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2010,24(9):833-834.
[23] 傅朝春,徐安书,张杰,等.甲状腺手术中预防甲状旁腺损伤的体会[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2013,19(3): 333-334.
[24] 朱精强.分化型甲状腺癌颈淋巴结清扫的相关问题[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2013,19(8):809-813.
[25] 闫利英,李随勤,张少强,等.甲状腺全切及近全切术中甲状旁腺的原位保护[J].临床耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 2006,20(21): 980-982.
[26] 黄韬.甲状腺术中损伤的预防和处理[J].中国实用外科杂志,2008,28(3):179-180.
[27] 赵挺,颜育祥,许践刚,等.975例甲状腺疾病患者手术预防甲状旁腺损伤体会[J].中国肿瘤,2007,16(6):467-468.
[28] 车红缨,曾玉剑,程中.纳米炭淋巴示踪剂在胃癌淋巴结清扫和病理检查中的价值[J].重庆医学, 2009,38(20):2571- 2572.
[29] 杨晓晖,王勇,王平.纳米碳在腔镜甲状腺癌手术中的应用[J].腹腔镜外科杂志, 2013,18(4):262-265.
[30] 杨志芳,岳瑞雪,朱智,等.纳米碳在cN0 期甲状腺乳头状癌中央区淋巴结清扫手术中的应用[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2013,20(9):976-980.
[31] 张筱骅,郝儒田,尤捷,等.甲状腺淋巴管造影在鉴别甲状旁腺中的意义[J].温州医学院学报,2010,40(1):31,35.
[32] 朱精强,汪洵理,魏涛,等.纳米碳甲状旁腺负显影辨认保护技术在甲状腺癌手术中的应用[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2013,20(9):992-994.
[33] 高庆军,王南鹏,周彦,等.甲状腺乳头状癌颈部淋巴结转移规律及影响因素分析[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2013, 20(3):303-309.
[34] 赏金标,王可敬.甲状腺乳头状腺癌的前哨淋巴结研究[J].国际耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2006,30(1):33-34,48.
[35] Besli? N.The role of sentinel lymph node detection in management of patients with breast cancer.Med Arh. 2008;62(4):240-241.
[36] Lee SK,Choi JH,Lim HI,et al.Sentinel lymph node biopsy in papillary thyroid cancer:comparison study of blue dye method and combined radioisotope and blue dye method in papillary thyroid cancer.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2009;35(9):974-979.
[37] 王晓雷,吴跃煌,徐震纲,等.纳米碳在鉴别甲状腺周围淋巴结和甲状旁腺中的作用[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2009,44(2):136-140.
[38] 江国斌,方红燕,蔡建明.纳米碳混悬液示踪前哨淋巴结在甲状腺乳头状癌中的应用[J].中国癌症杂志, 2010,20 (12): 938-940.
[39] Hao RT,Chen J,Zhao LH,et al.Sentinel lymph node biopsy using carbon nanoparticles for Chinese patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2012; 38(8):718-724.
[40] 贾中明,刘艳,黄秋林.纳米炭定位前哨淋巴结在cN0甲状腺乳头状癌中的临床研究[J].临床合理用药杂志, 2013, 4(9C):9-11.
[41] Hou TZ,Chen X,Peng HJ,et al.Design Principles for Heteroatom-Doped Nanocarbon to Achieve Strong Anchoring of Polysulfides for Lithium-Sulfur Batteries.Small.2016.doi:10.1002/smll.201600809.[Epub ahead of print]
[42] Wang Z,Xiao S,An Y,et al. Co(II)<sub>1-x</sub> Co(0)<sub>x/3</sub>Mn(III)<sub>2x/3</sub>S Nanoparticles Supported on B/N-Codoped Mesoporous Nanocarbon as a Bifunctional Electrocatalyst of Oxygen Reduction/Evolution for High-Performance Zinc-Air Batteries.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2016.[Epub ahead of print]
[43] Yang F,He D,Wang M,et al.Ultrastrong Chemiluminescence Activity of Nanocarbon Materials after Ozonation and Their Effects on Different Chemiluminescent Systems.Chemistry.2016.doi: 10.1002/chem.201600520.[Epub ahead of print]
[44] Belosludov RV,Rhoda HM,Zhdanov RK,et al.Conceptual design of tetraazaporphyrin- and subtetraazaporphyrin-based functional nanocarbon materials: electronic structures, topologies, optical properties, and methane storage capacities.Phys Chem Chem Phys.2016;18(19):13503-13518.
[45] Yang Y,Shi F,Chen X,et al.Sentinel lymph node detection of rabbit tongue by indirect CT lymphography combined with nanocarbon tracer.Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi.2015;29(24):2151-2154. |
.jpg)
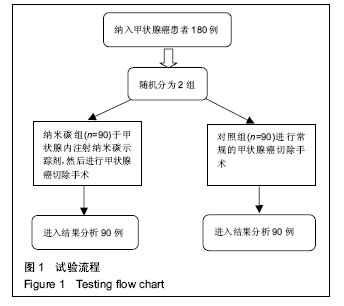
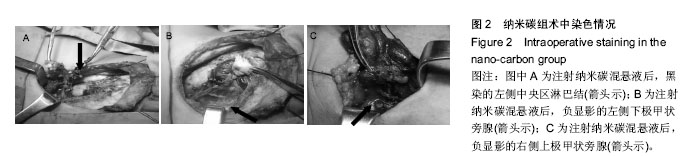
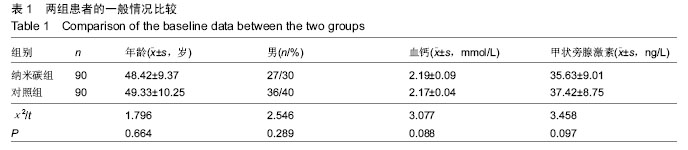
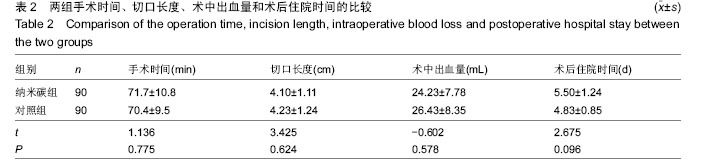

.jpg)