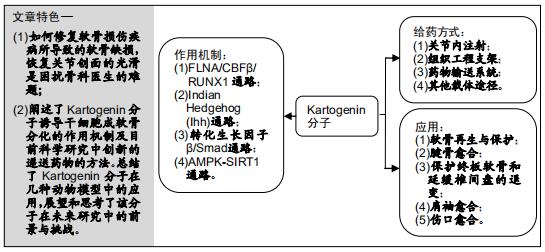
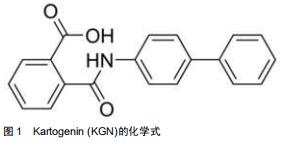
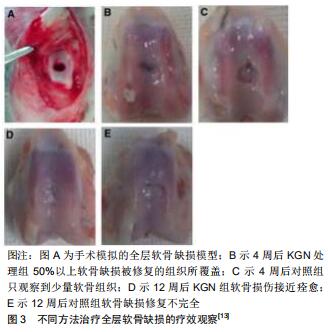
|
[1] 邵加华,陈松,谢金硕,等. Kartogenin与软骨修复的研究进展[J]. 第二军医大学学报, 2016,37(4):471-476.
[2] TRICHE R, MANDELBAUM BR. Overview of cartilage biology and new trends in cartilage stimulation. Foot Ankle Clin. 2013; 18(1): 1-12.
[3] CHOI E, LEE J, LEE S, et al. Potential therapeutic application of small molecule with sulfonamide for chondrogenic differentiation and articular cartilage repair. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.2016;26(20):5098-5102.
[4] JOHNSON K, ZHU S, TREMBLAY MS, et al. A stem cell-based approach to cartilage repair. Science. 2012; 336(6082):717-721.
[5] KOU L, XIAO S, SUN R, et al. Biomaterial-engineered intra-articular drug delivery systems for osteoarthritis therapy.Drug Deliv. 2019; 26(1):870-885.
[6] SHERWOOD JC, BERTRAND J, ELDRIDGE SE, et al. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of cartilage damage and repair. Drug Discov Today. 2014;19(8):1172-1177.
[7] LIU C, MA X, LI T, et al. Kartogenin, transforming growth factor-β1 and bone morphogenetic protein-7 coordinately enhance lubricin accumulation in bone-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cell BiolInt. 2015; 39(9):1026-1035.
[8] VALIANI A,IZADI MA,BAHRAMIAN H,et al.Comparison between the effect of kartogenin and TGFβ3 on chondrogenesis of human adipose- derived stem cells in fibrin scaffold.Bratisl Lek Listy. 2017;118:591-597.
[9] ONO Y, ISHIZUKA S, KNUDSON CB, et al. Chondroprotective effect of kartogenin on cd44-mediatedfunctions in articular cartilage and chondrocytes. Cartilage. 2014; 5(3):172-180.
[10] DECKER RS, KOYAMA E, ENOMOTO-IWAMOTO M, et al. Mouse limb skeletal growth and synovial joint development are coordinately enhanced by Kartogenin. Dev Biol. 2014; 395(2): 255-267.
[11] WANG Y, CHEN G, YAN J, et al. Upregulation of SIRT1 by kartogenin enhances antioxidant functions and promotes osteogenesis in human mesenchymal stem cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:1368142.
[12] WANG D, TAN H, LEBASCHI AH, et al. Kartogenin enhances collagen organization and mechanical strength of the repaired enthesis in a murine model of rotator cuff repair. Arthroscopy. 2018;34:2579-2587.
[13] XU X, SHI D, SHEN Y, et al. Full-thickness cartilage defects are repaired via a microfracture technique and intraarticular injection of the small-molecule compound kartogenin. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17(1) : 20.
[14] RAI V, DILISIO MF, DIETZ NE, et al. Recent strategies in cartilage repair: a systemic review of the scaffold development and tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(8): 2343-2354.
[15] LI X, DING J, ZHANG Z, et al. Kartogenin-incorporated thermogel supports stem cells for significant cartilage regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(8):5148-5159.
[16] YIN H, WANG J, GU Z, et al. Evaluation of the potential of kartogenin encapsulated poly(L-lactic acid-co-caprolactone)/collagen nanofibers for tracheal cartilage regeneration. J Biomater Appl. 2017;32(3): 331-341.
[17] SHI D, XU X, YE Y, et al. Photo-cross-linked scaffold with kartogenin-encapsulated nanoparticles for cartilage regeneration. Acs Nano. 2016;10(1):1292-1299.
[18] KANG ML, JEONG SY, IM GI. Hyaluronic acid hydrogel functionalized with self-assembled micelles of amphiphilic pegylated kartogenin for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(13-14): 630-639.
[19] HU Q, DING B, YAN X, et al. Polyethylene glycol modified PAMAM dendrimer delivery of kartogenin to induce chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Nanomedicine. 2017;13(7):2189-2198.
[20] HUANG H. Editorial commentary: kartogenin promotes wounded enthesis regeneration. Arthroscopy. 2018;34(9):2588-2589.
[21] JING H, ZHANG X, GAO M, et al. Kartogenin preconditioning commits mesenchymal stem cells to a precartilaginous stage with enhanced chondrogenic potential by modulating JNK and β-catenin-related pathways. FASEB J. 2019;33:5641-5653.
[22] ZHOU Y, ZHANG J, YANG J, et al. Kartogenin with PRP promotes the formation of fibrocartilage zone in the tendon-bone interface. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;11(12):3445-3456.
[23] GRANADOS-MONTIEL J, CRUZ-LEMINI M, RANGEL-ESCAREÑO C, et al. SERPINA9 and SERPINB2: Novel Cartilage Lineage Differentiation Markers of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Kartogenin.Cartilage. 2018:1947603518809403.
[24] KWON JY, LEE SH, NA HS, et al. Kartogenin inhibits pain behavior, chondrocyte inflammation, and attenuates osteoarthritis progression in mice through induction of IL-10.Sci Rep. 2018;8:13832.
[25] DORMAN LJ, TUCCI M, BENGHUZZI H. In vitro effects of bmp-2, bmp-7, and bmp-13 on proliferation and differentation of mouse mesenchymal stem cells. Biomed Sci Instrum. 2012;48(9): 81-87.
[26] PANDOLFI L, MINARDI S, TARABALLI F, et al. Composite microsphere-functionalized scaffold for the controlled release of small molecules in tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng. 2016;7: 2041731415624668.
[27] KANG ML, KO JY, KIM JE, et al. Intra-articular delivery of kartogenin-conjugated chitosan nano/microparticles for cartilage regeneration. Biomaterials. 2014;35(37):9984-9994.
[28] MASSARO M, BUSCEMI G, ARISTA L, et al. Multifunctional carrier based on halloysite/laponite hybrid hydrogel for kartogenin delivery. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2019;10:419-424.
[29] CAI JY, ZHANG L, CHEN J. Kartogenin and its application in regenerative medicine. Curr Med Sci. 2019;39:16-20.
[30] CHEN L, DONG SW, TAO X, et al. Autologous platelet-rich clot releasate stimulates proliferation and inhibits differentiation of adult rat tendon stem cells towards nontenocyte lineages. J Int Med Res. 2012; 40(4):1399-1409.
[31] LI J, LEE WY, WU T, et al. Near-infrared light-triggered release of small molecules for controlled differentiation and long-term tracking of stem cells in vivo using upconversion nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2016; 110: 1-10.
[32] MARX RE. Platelet-rich plasma: evidence to support its use. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004;62(4):489-496.
[33] ZHANG J, WANG JH. Kartogenin induces cartilage-like tissue formation in tendon-bone junction. Bone Res. 2014; 2(1):61-70.
[34] HIBINO N, HAMADA Y, SAIRYO K, et al. Callus formation during healing of the repaired tendon-bone junction. A rat experimental model. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89(11):1539-1544.
[35] FAN W, LI J, YUAN L, et al. Intra-articular injection of kartogenin-conjugated polyurethane nanoparticles attenuates the progression of osteoarthritis. Drug Deliv 2018;25:1004-1012.
[36] CANAL F, SANCHIS J, VICENT MJ, et al. Polymer–drug conjugates as nano-sized medicines. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2011;22(6): 894-900.
[37] WANG J, WANG Y, SUN X, et al. Biomimetic cartilage scaffold with orientated porous structure of two factors for cartilage repair of knee osteoarthritis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47:1710-1721.
[38] KANG ML, KIM JE, IM GI, et al. Thermo-responsive nanospheres with independent dual drug release profiles for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Acta Biomater. 2016;39:65-78.
[39] ZHANG J, YUAN T, ZHENG N, et al. The combined use of kartogenin and platelet-rich plasma promotes fibrocartilage formation in the wounded rat achilles tendon enthuses. Bone Joint Res. 2017;6(4): 231-244.
[40] 郑权,徐宏光,汪景,等.小分子药物kartogenin保护终板软骨退变的实验研究[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2014, 19(8): 846-850.
[41] HUANG Y, JIANG T, CHEN J, et al. Effects of kartogenin on the attenuated nucleus pulposus cell degeneration of intervertebral discs induced by interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41:749-756.
[42] ZHU Y, TAN J, ZHU H, et al. Development of kartogenin-conjugated chitosan-hyaluronic acid hydrogel for nucleus pulposus regeneration. Biomater Sci. 2017;5:784-791.
[43] ZHANG J, XIA W, LIU P, et al. Chitosan modification and pharmaceutical/biomedical applications. Mar Drugs. 2010;8(7) : 1962-1987.
[44] KOU L, XIAO S, SUN R, et al. Biomaterial-engineered intra-articular drug delivery systems for osteoarthritis therapy. Drug Deliv. 2019; 26:870-885.
[45] SPAKOVA T, PLSIKOVA J, HARVANOVA D, et al. Influence of Kartogenin on Chondrogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow-Derived MSCs in 2D Culture and in Co-Cultivation with OA Osteochondral Explant. Molecules. 2018; 23(1). pii: E181.
[46] MAUDENS P, SEEMAYER CA, THAUVIN C, et al. Nanocrystal-polymer particles: extended delivery carriers for osteoarthritis treatment. Small. 2018;14. doi: 10.1002/smll.201703108.
[47] LI H, JIANG J, WU Y, et al. Potential mechanisms of a periosteum patch as an effective and favourable approach to enhance tendon-bone healing in the human body. Int Orthop. 2012;3(3): 665-669.
[48] WONG MW, QIN L, TAI JK, et al. Engineered allogeneic chondrocyte pellet for reconstruction of fibrocartilage zone at bone-tendon junction-a preliminary histological observation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2004;70(2):362-367.
[49] ZHOU Q, ZHANG JH, YUAN S, et al. A new insight of kartogenin induced the mesenchymal stem cells (mscs) selectively differentiate into chondrocytes by activating the bone morphogenetic protein 7 (BMP-7)/Smad5 Pathway. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:4960-4967.
[50] 王一帆,何帆. Kartogenin在制备提高骨髓间充质干细胞抗氧化能力药物的应用. 申请/专利号:CN201810071064.9,公开/公告号: CN108451940A.
[51] LIU F, XU H. A novel kartogenin-platelet-rich plasma gel enhances chondrogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and promotes wounded meniscus healing in vivo.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10:201.
[52] BLIDDAL H, HENRIKSEN M. Osteoarthritis: Time to put steroid injections behind us? Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13(9): 519-520.
[53] 丁伟,谭洪波.KGN修复软骨、促进腱-骨愈合作用的研究进展[J].山东医药,2017, 57(16):102-104.
[54] BISHOP J, KLEPPS S, LO IK, et al. Cuff integrity after arthroscopic versus open rotator cuff repair:arospective study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006;3(3):290-299.
[55] MARINI JC, FORLINO A. Replenishing cartilage from endogenous stem cells. New Eng J Med. 2012;26(26):2522-2524.
|