Design
Randomized, controlled experiments with repeated measurements.
Time and setting
The experiment was completed at the Department of Orthopedics, Zhujiang Hospital of Southern Medical University, and School of Bioengineering and Materials, South China University of Technology, China from October 2004 to April 2005.
Materials
Thirty-eight adult New Zealand rabbits which were littermates and homologues, clean grade, 18-22 months of age, half male and female, 1.8-2.3 kg of body mass were enrolled. Forty Kunming mice with half male and female, clean grade, aged 4 weeks, weighing 18-22 g, were selected. All animals were provided by the Experimental Animal Center of Southern Medical University (license No. 2004A047), and were housed at 22-24 ℃ in a humidity of 55%-60%, with 12-hour dark/like circle and with free access to food and water. All protocols were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Southern Medical University, China.
Methods
Preparation of nano-HA/PHBV-PEG-GM microspheres
Preparation of nano-HA-GM: gentamicin sulfate and nano-HA at the mass ratio of 2:1 were dissolved in water, and mixed with nano-HA (short rod-like nano-HA at a length of tens of nanometers, provided by South China University of Technology, China; Figure 1A), followed by 20 minutes ultrasonic dispersion, and then the mixture was magnetically stirred for 70 hours. After that, the mixture was lyophilized to obtain white lyophilized powder, nano-HA-GM. Preparation of nano-HA PHBV-PEG-GM microspheres: nano-HA-GM lyophilized power was dispersed in dichloromethane solution containing PHBV at the mass ratio of 1: 4; wherein, a certain amount of PEG20000 (the mass ratio of PEG20000 and PHBV was 2:1). Then, the mixture solution was quickly poured into the outer aqueous phase, containing 4 g/L methylcellulose, with an oil-water phase volume ratio of 1:10, and stirred vigorously until dichloromethane was completely volatilized, centrifuged, filtered, washed with water. After collection and freeze-drying, the drug loading amount was 86 g/L as previously reported[7],followed by sterilized by ethylene oxide for standby (Figure 1B).
Preparation of plastic nano-HA/PHB-PEG-GM- DDS
Nano-HA/PHBV-PEG-GM microspheres were mixed with 20 g/L human fibrin solution and complex liquid of calcium chloride (40 mol/L), thrombin (833.5 nkat/L), aprotinin (133.36 kat/L) and tranexamic acid (20 g/L) at a ratio of 1 mg:1 μL:1 μL followed by vigorous stirring, to obtain plastic nano-HA/ PHBV-PEG-GM-DDS (Figure 1C), in which the gentamicin content was 23.2 g/L. Plastic nano-HA/ PHBV-PEG-GM-DDS was prepared by the Center of Orthopedics, Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University, China in cooperation with the School of Materials Science and Bioengineering, South China University of Technology, China.
.jpg)
Acute systemic toxicity test
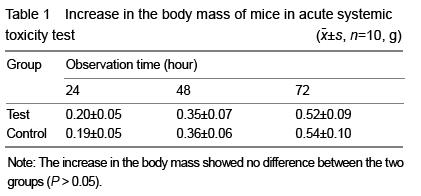
Twenty Kunming mice were randomly divided into test group and control group. Plastic nano-HA/ PHBV-PEG-GM-DDS (3.0 g) was added into 30 mL of sterile saline and extracted at 121 ℃ for 1 hour. After filtration with 0.22 μm millipore filter, 100 g/L extract liquid was made. Under aseptic conditions, 0.05 mL/g extract liquid was intraperitoneally injected into the mice in the test group, and the same volume of normal saline was given in the control group. Mice in both two groups were observed for general condition and death, and the body mass changes were recorded at 24, 48, 72 hours.
Implantation test and subacute/chronic systemic toxicity test
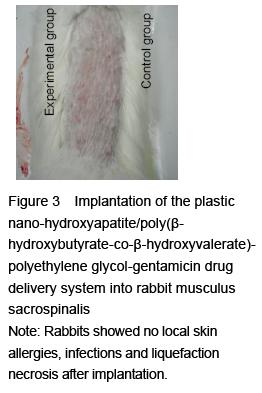
Intramuscular embedment: 18 New Zealand white rabbits were randomly divided into experimental and control groups (n=9 per group). Rabbits in the experimental group were given intravenous anesthesia of 1 mg/kg chloral hydrate, to expose the bilateral back muscles. 0.3 mL plastic nano-HA/PHBV-PEG-GM-DDS was implanted into the musculus sacrospinalis on both sides (Figure 2). Rats in the control group were given no treatment.
.jpg)
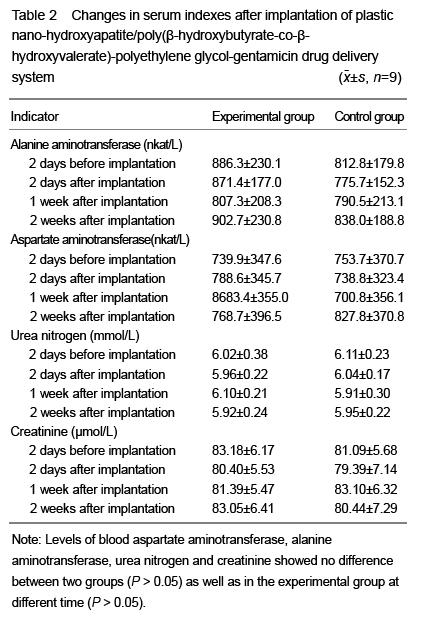
Intraosseous embedment: In the experimental group, the lateral epicondyles of bilateral femurs were exposed and drilled, and then 0.3 mL plastic nano-HA/PHBV-PEG-GM-DDS was implanted; in the control group, there was no implantation. Blood aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, urea nitrogen and creatinine were detected before and 2 days, 1 and 2 weeks after implantation.
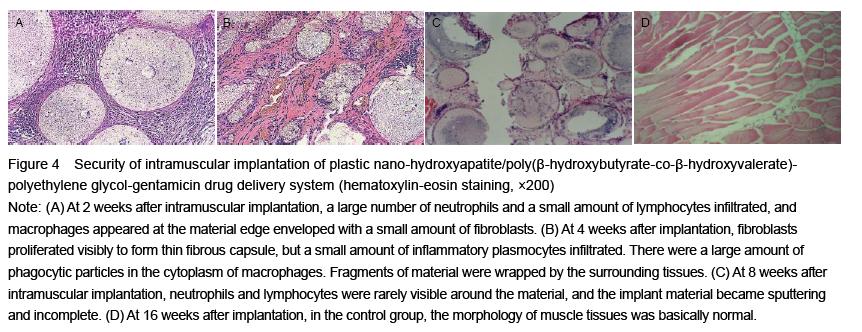
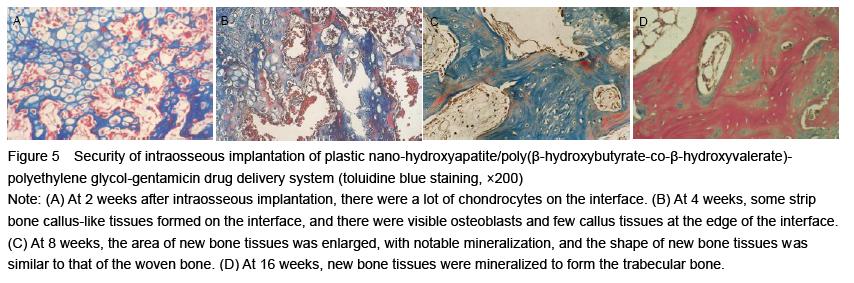
In the intramuscular implantation test, blood samples were extracted from the rabbit ear vein to detect levels of aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, urea nitrogen and creatinine before and at 2 days, 1 and 2 weeks after implantation. The implant materials and surrounding tissues were removed at 2, 4, 8 and 16 weeks after implantation to observe whether they are integrated. Then, the implanted compound materials and surrounding tissues were taken to make paraffin sections that were subjected to hematoxylin-eosin staining and toluidine blue staining for histological observation of inflammatory cell changes, fibrous capsule formation and the presence or absence of necrosis and calcification. At 16 weeks after implantation, the liver and spleen tissues were observed generally and pathologically.
Hemolytic test
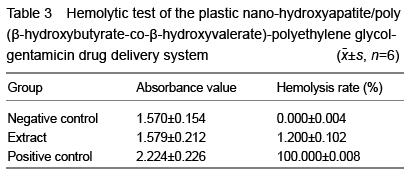
Under aseptic conditions, rabbit blood sample 2 mL was extracted via cardiac puncture and immediately mixed with 20 g/L potassium oxalate (0.5 mL) for anticoagulation. Then, 17.5 mL of normal saline was added to make 10% anticoagulant rabbit blood. 0.5 g plastic nano-HA/PHBV-PEG-GM-DDS was added into 4 mL of normal saline, incubated at a 37 ℃ water bath for 1 hour, followed by addition of 1 mL anticoagulant rabbit blood, joggled, incubated at the 37 ℃ water bath for 3 hours, and centrifuged at 1 000 r/min centrifugal for 5 minutes. The supernatant was taken to detect absorbance value at 540 nm using an ELx808 absorbance microplate reader. In the negative control group, there was no plastic nano-HA/PHBV-PEG-GM- DDS. In the positive control group, 1 g/L sodium bicarbonate solution (4 mL) was added. The hemolysis rate was calculated as the following formula: hemolysis ratio=(absorbance of experimental group-absorbance of negative control group)/ (absorbance of positive control group-absorbance of negative control group)×100%.
Cytotoxicity test
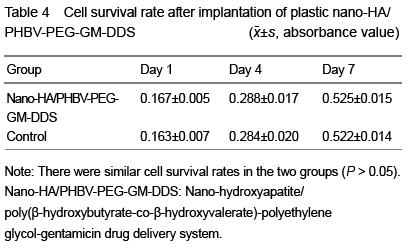
The cytotoxicity was detected by MTT assay. Plastic nano-HA/PHBV-PEG-GM-DDS was made into 3 mm× 3 mm×1 mm rectangular sheets, and rinsed with triple-distilled water. Rabbit bone marrow (7 mL) was extracted, added into 2 mL lymphocyte separation medium, centrifuged at 2 500 r/min for 15 minutes. Separating medium containing cell layer were sucked up and added into PBS followed by pipetting. Bone marrow cell culture medium was seeded in 24-well plates, and 1 mL medium solution and 3 mm×3 mm× 1 mm compound material sheet were placed per well. In the control group, only cells were seeded onto the 24-well plates. At 1, 4, 7 days after seeding, MTT assay used to detect cytotoxicity, and ELx808 absorbance microplate reader to detect absorbance value at 490 nm. Cell morphology and adhesion were also observed.
Intracutaneous stimulation test
2 g plastic nano-HA/PHBV-PEG-GM-DDS was taken, dissolved in 10 mL saline for sterile extraction at 37 ℃ for 72 hours. At 24 hours before the experiment, a 5 cm×15 cm rabbit fur area was shaved at both sides of the spine in four rabbits, with no skin damage, to prepare injection extracts. 0.2 mL extract solution was respectively injected intradermally into five points located at one side of the spine with an interval of 2 cm in each rabbit; on the contralateral side, 0.2 mL normal saline was injected as blank control. Erythema and edema at injection sites were detected and recorded immediately and at 24, 48, 72 hours after injection. The degree of skin reactions are classified into five grades as per the GB/T14233-2-93.
.jpg)
Main outcome measures
Acute systemic toxicity test, implantation test, subacute/chronic systemic toxicity test, hemolytic test, cytotoxicity test and intracutaneous stimulation test.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed by the first author using SPSS 10.0. Statistical analysis was performed by independent-sample
t-test and one-way analysis of variance followed by the Student-Newman- Keuls
post hoc test. A value of
P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)