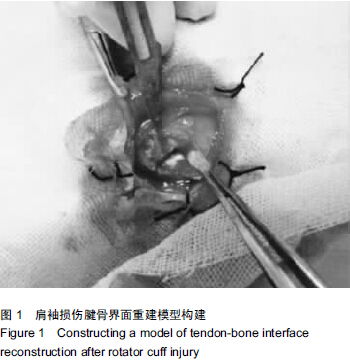
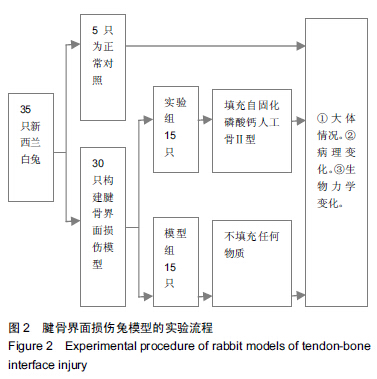
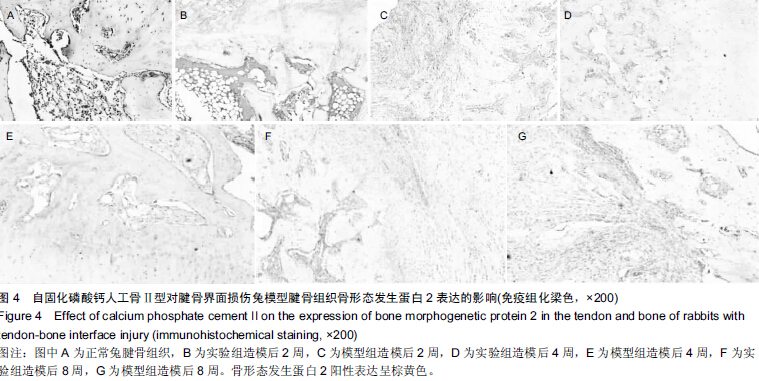
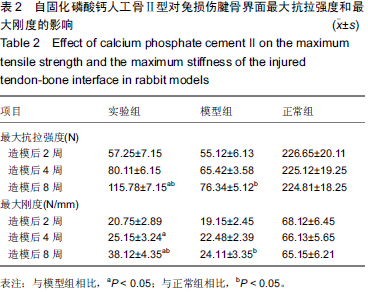
| [1] 毕建超,刘焕彩,吴晓林,等.关节镜探查清理术联合小切口肩袖修补术治疗肩袖损伤[J].山东医药,2014,54(11):76-77.
[2] 张燕,文巍,罗进勇,等.骨形态发生蛋白9定向诱导多潜能干细胞成骨分化[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2009,36(10): 1291- 1298.
[3] 庄泽,卢华定,陈郁鲜,等.肩袖损伤后单排与双排缝合方法比较的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(29):4742-4751.
[4] 刘树学,任明达,肖铮,等.磁共振平扫与磁共振关节造影在肩袖撕裂诊断中的应用价值[J].实用放射学杂志,2013,29(4): 615-618.
[5] 黄欣,韦海明,梁敏华,等.增生性瘢痕中时序变化的骨形态发生蛋白及其受体[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(50): 8691- 8696.
[6] 张喜海,黄树华,李森,等.自固化磷酸钙人工骨Ⅱ修复兔腱-骨损伤的生物力学变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(25): 3937- 3941.
[7] 倪锋,皇甫小桥,赵金忠,等.人工骨材料磷酸钙及硫酸钙在腱-骨愈合中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(21): 3815-3821.
[8] 皇甫小桥.人工骨生物材料促进肌腱-骨隧道愈合的实验研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2007.
[9] 倪锋,刘益飞.磷酸钙促进前交叉韧带重建后腱-骨愈合的实验研究[J].交通医学,2011,25(1):9-13,16.
[10] 孔祥喆,赵金忠,皇甫小桥,等.纽扣钢板悬吊固定自体腘绳肌肌腱前交叉韧带重建术后远端骨隧道填充磷酸三钙人工骨的临床分析[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2014,(3):337-345.
[11] Wang X, Ma J, Wang Y, et al. Bone repair in radii and tibias of rabbits with phosphorylated chitosan reinforced calcium phosphate cements. Biomaterials. 2002;23(21):4167-4176.
[12] 薛元锁,时述山,李亚非,等.激素性股骨头坏死病程中骨形态发生蛋白-2的改变及其意义[J].中华实验外科杂志,2000,17(5): 455-456,插2.
[13] 沈奕,李晓淼,王伟力.骨形态发生蛋白7在骨科的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(26):4864-4867.
[14] 黄树华.自固化磷酸钙人工骨-Ⅱ型对兔肩袖腱——骨界面损伤后修复的影响[D].泸州:泸州医学院,2014.
[15] 张勇,闫景龙,张志鹏,等.自固化磷酸钙人工骨黏附颗粒骨复合物的生物学效能[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(9):90-92.
[16] 曾忠友,金才益,陆金荣,等.椎弓根螺钉系统加自固化磷酸钙人工骨灌注治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2001,17(5): 284-286.
[17] 朱从亚,周海斌.体外冲击波对大鼠冈上肌腱止点损伤重建后腱-骨愈合进程的影响[J].中国当代医药,2013,20(34):10-12.
[18] Smartt JM Jr, Karmacharya J, Gannon FH, et al. Repair of the immature and mature craniofacial skeleton with a carbonated calcium phosphate cement: assessment of biocompatibility, osteoconductivity, and remodeling capacity. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;115(6):1642-1650.
[19] 王鹏程.肩袖损伤修复后不同强度应力刺激效果的实验研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2010.
[20] 高庆峰.应用去细胞真皮基质联合富血小板血浆重建兔巨大肩袖损伤的实验研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2014.
[21] 蒋胜波,董跃福,刘旭东,等.应力负荷对关节镜下骨铆钉治疗兔急性肩袖损伤后骨-肌腱修复过程的影响[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2013,(2):93-98.
[22] 王文波,陈统一,陈中伟,等.自固化磷酸钙人工骨体内植入长期实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2002,9(5):460-463.
[23] 李鹏,郝微.自固化磷酸钙人工骨与磷酸锌水门汀修复髓室底穿孔的临床对比[J].中国伤残医学,2013,21(6):202-202.
[24] 李鹏,勘武生,程煜芳,等.自固化磷酸钙人工骨(CPC)修复骨肿瘤骨缺损的初步临床应用[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2008, 5(2): 18-19,24.
[25] 陈红卫,赵钢生,鲍丰,等.载药自固化磷酸钙人工骨治疗慢性骨髓炎[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2005,20(10):673-675.
[26] 李森,靳安民,付国建,等.应力刺激下兔冈上肌腱急性断裂术后腱-骨修复Ⅰ、Ⅲ型胶原的表达变化[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2010, 28(3):308-311.
[27] 王文波,陈中伟,陈统一,等.自固化磷酸钙人工骨的生物学安全性试验研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2001,20(3):193-199.
[28] 陶旭.不同界面处理方式对肩袖止点腱-骨愈合影响的研究[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2011.
[29] 韩振学,李志仙.自固化磷酸钙人工骨植骨联合可塑形钛板内固定治疗 Sanders Ⅲ, Ⅳ型跟骨骨折[J].潍坊医学院学报,2014, (6):414-416.
[30] 刘宏建,杜靖远,梁惠民,等.经皮椎体成形术充填自固化磷酸钙人工骨治疗疼痛性骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折(附23例报告)[J].山东医药,2004,44(15):3-5.
[31] 陈奇.肩袖冈上肌骨-肌腱结合部损伤愈合模型的实验研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2013.
[32] 翁益民,应晓洲,水小龙,等.关节损伤修复后影响腱-骨愈合因素的研究进展[J].浙江实用医学,2013,(3):218-221.
[33] 曲伟,李霞,周致勇.自固化磷酸钙人工骨在跟骨骨折治疗中的应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2006,20(6):680-681.
[34] 赵东升,殷军,张强,等.经皮椎体成形术自固化磷酸钙人工骨充填治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩性骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2006, 8(1):20-23.
[35] 张德辉,黄昌林,黄涛,等.自固化磷酸钙人工骨在腰椎结核病灶清除术中的初步应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2005,19(8): 682-683.
[36] 于晓雯,杨星光,陆男吉,等.自固化磷酸钙人工骨载药治疗创伤性骨髓炎的初步观察[J].中华创伤杂志,2005,21(z1):58-61.
[37] 李森,靳安民,付国建,等.被动训练对兔冈上肌腱急性断裂术后腱-骨修复中BMP-2表达的影响[J].重庆医学,2010,39(15): 1985-1987.
[38] 陈男.低剂量X线照射对大鼠肩袖损伤重建术后腱-骨愈合的实验研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2013.
[39] 车凌宾,周琦,叶庭均,等.应力丧失对急性肩袖损伤腱骨愈合影响的实验研究[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2015,(2):224-228.
[40] Burkus JK. Surgical treatment of the painful motion segment: matching technology with indications. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(16 Suppl):S7-15.
[41] 王卓,郭华艳,黄远亮.自固化磷酸钙人工骨修补髓室底穿孔的临床研究[J].现代预防医学,2012,39(21):5794-5795.
[42] 邢叔星.促进腱-骨界面修复重建愈合的研究进展[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,18(4):327-330.
[43] 罗涛,王蕾,邓廉夫.应力刺激在肩袖损伤修复中的作用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2005,7(9):862-864.
[44] 李志超.自体BMSC与rhVEGF165促进肩袖损伤腱骨愈合的研究[D].北京:军医进修学院,2011.
[45] Yoshii T, Ueki H, Kato T, et al. Severe kyphotic deformity resulting from collapses of cemented and adjacent vertebrae following percutaneous vertebroplasty using calcium phosphate cement. A case report. Skeletal Radiol. 2014; 43(10):1477-1480.
[46] 曹红彬.骨诱导生物材料和rhBMP-2对肌腱在骨隧道愈合作用的实验研究[D].上海:上海第二医科大学,2005.
[47] Xu Z, Xu W, Wang C, et al. Effectiveness of long segment fixation combined with vertebroplasty for severe osteoporotic thoracolumbar compressive fractures. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013;27(11):1331-1337.
[48] Heo HD, Cho YJ, Sheen SH, et al. Morphological changes of injected calcium phosphate cement in osteoporotic compressed vertebral bodies. Osteoporos Int. 2009;20(12): 2063-2070.
[49] Frankel BM, Monroe T, Wang C. Percutaneous vertebral augmentation: an elevation in adjacent-level fracture risk in kyphoplasty as compared with vertebroplasty. Spine J. 2007; 7(5):575-582.
[50] Qin DA, Song JF, Wei J, et al. Analysis of the reason of secondary fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2014;27(9):730-733.
[51] [Vougioukas V, Hubbe U, Kogias E, et al. Vertebroplasty combined with image-guided percutaneous cement augmented transpedicular fixation for the treatment of complex vertebral fractures in osteoporotic patients. J Neurosurg Sci. 2010;54(4):135-141.
[52] Kim KH, Kuh SU, Chin DK, et al. Kyphoplasty versus vertebroplasty: restoration of vertebral body height and correction of kyphotic deformity with special attention to the shape of the fractured vertebrae. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012; 25(6):338-344.
[53] Zhang C, Zhu K, Zhou J, et al. Influence on adjacent lumbar bone density after strengthening of T12, L1 segment vertebral osteoporotic compression fracture by percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous kyphoplasty. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013;27(7):819-823.
[54] Ishiguro S, Kasai Y, Sudo A, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fractures using calcium phosphate cement. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2010;18(3):346-351.
[55] Korovessis P, Hadjipavlou A, Repantis T. Minimal invasive short posterior instrumentation plus balloon kyphoplasty with calcium phosphate for burst and severe compression lumbar fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(6):658-667.
[56] Heo DH, Choi JH, Kim MK, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of vertebroplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with avascular osteonecrosis: a minimum 2-year follow-up study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(7):E423-429.
[57] 付国建,靳安民,李森,等.肩袖损伤模型兔持续被动活动对骨-肌腱界面早期修复的影响:MRI不同时点影像证实[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(7):1187-1190.
[58] 付国建.rhBMP-2对肩袖腱-骨界面损伤后愈合影响的组织学及生物力学研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2010.
[59] 付国建,靳安民,张力,等.rhBMP-2对兔肩袖损伤重建术后腱-骨愈合的组织学及生物力学研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010, 18(10):828-831.
[60] 王文波,陈中伟,陈统一.自固化磷酸钙人工骨的最新研究进展[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2000,17(1):80-83.
[61] 朱志海,曹鹏,梁裕,等.腹腔镜下多孔自固化磷酸钙人工骨复合重组人骨形态发生蛋白2在山羊腰椎体间融合中的作用[J].中华医学杂志,2010,90(21):1503-1506.
[62] Jindong Z, Hai T, Junchao G, et al. Evaluation of a novel osteoporotic drug delivery system in vitro: alendronate-loaded calcium phosphate cement. Orthopedics. 2010;33(8).
[63] Chou J, Hao J, Ben-Nissan B, et al. Coral exoskeletons as a precursor material for the development of a calcium phosphate drug delivery system for bone tissue engineering. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(11):1662-1665.
[64] 李森,靳安民,付国建,等.被动应力刺激兔冈上肌腱急性断裂修复后腱-骨界面的组织学变化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(15):2667-2670.
[65] 王鹏程,靳安民,付国建,等.急性肩袖损伤早期修复过程中不同强度应力刺激的生物力学反应[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(11):1971-1974. |