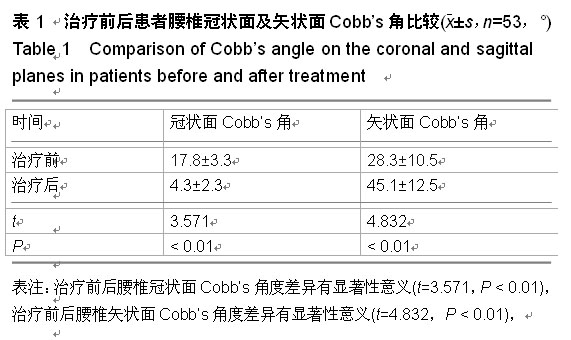
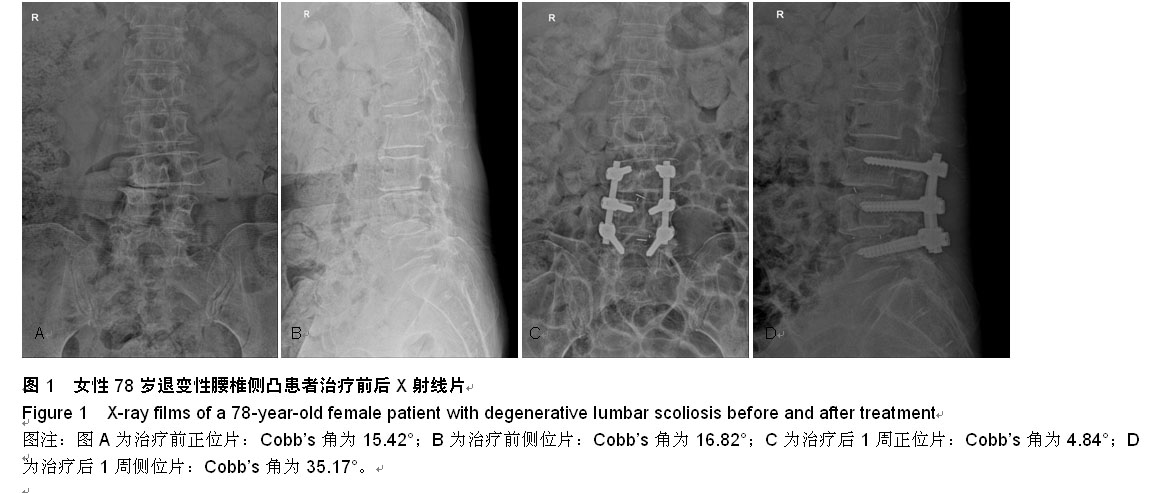
| [1] Dangelmajer S, Zadnik PL, Rodriguez ST, et al. Minimally invasive spine surgery for adult degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Neurosurg Focus.2014;36(5):E7.
[2] Avraam P, Ensor E, Francis D,et al. Degenerative lumbar scoliosis associated with spinal stenosis. Spine J. 2007; 7(4):428-436.
[3] Gupta MC. Degenerative scoliosis. Options for surgical management. Orthop Clin North Am. 2003;34(2):269-279.
[4] Ploumis A, Transfledt EE, Denis F. Degenerative lumbar scoliosis associated with spinal stenosis. Spine J.2007; 7(4): 428-436.
[5] Vaccaro AR, Ball ST. Indications for instrumentation in degenerative lumbar spinal disorders. Orthopedics 2000; 23:260-271.
[6] Glassman SD, Bridwell K, Dimar JR, et al. The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinaldeformity. Spine. 2005; 30(18):2024-2029.
[7] 叶庭均,梁裕.退变性脊柱侧凸的诊断和治疗进展[J].脊柱外科杂志,2010,8(3):182-185.
[8] Aebi M. The adult scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2005;14:925-948.
[9] Daffner SD, Vaccaro AR. Adult degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2003;32:77-82.
[10] Gupta MC. Degenerative scoliosis. Options for surgical management. Orthop Clin North Am 2003;34:269-279.
[11] Cho KJ, Kim YT, Shin SH, et al. Surgical Treatment of Adult Degenerative Scoliosis. Asian Spine J. 2014;8(3):371-381.
[12] Iida T, Ohyama Y, Katayanagi J, et al. Differences between pre-existing type and de novo type left convex thoracolumbar / lumbar scoliosis. Scoliosis. 2015;10(Suppl 2):S6.
[13] Iida T. Differences between pre-existing type and de novo type left convex thoracolumbar / lumbar scoliosis. Scoliosis. 2015;10(Suppl 1):O33.
[14] Bradford DS, Tay BK, Hu SS. Adult scoliosis: surgical indications, operative management, complications, and outcomes. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1999;24:2617- 2629.
[15] Marchesi DG, Aebi M. Pedicle fixation devices in the treatment of adult lumbar scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1992;17(8 Suppl):S304-309.
[16] Oskouian RJ Jr, Shaffrey CI. Degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2006;17(3):299-315.
[17] Sharma AK, Kepler CK, Girardi FP, et al. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion:Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes at 1 Year: A Preliminary Report. Spinal Disord Tech.2011;24(4): 242-250.
[18] Transfeldt EE, Topp R,Mehbod AA,Winter RB. Surgical outcomes of decompression, decompression with limited fusion, and decompression with full curve fusion for degenerative scoliosis with radiculopathy. Spine. 2010;35(20): 1872-1875.
[19] Berven SH, Lowe T. The Scoliosis Research Society classification for adult spinal deformity. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2007; 18(2):207-213.
[20] Birknes JK, Whie AP, Albert TJ, et al. Adult degenerative scoliosis: a review. Neurosurgery. 2008; 63(3):94-103.
[21] Tribus CB. Degenerative lumbar scoiosis: evaluation and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2003;11(3): 174-183.
[22] Waddell B, Briski D, Qadir R, et al.Lateral lumbar interbody fusion for the correction of spondylolisthesis and adult degenerative scoliosis in high-risk patients: early radiographic results and complications. Ochsner J. 2014;14(1):23-31.
[23] Pateder DB, Kebaish KM, Cascio BM, et al. Posterior only versus combined anterior and posterior approaches to lumbar scoliosis in adults: a radiographic analysis. Spine. 2007; 32(14):1551-1554.
[24] 李方财,陈其昕,陈维善,等.选择性经椎间孔椎间融合结合后路融合术治疗退行性腰椎侧凸[J].中华骨科杂志, 2009,29(9): 806-810.
[25] Gupta MC. Degenerative scoliosis. Options for surgical management. Orthop Clin North Am. 2003;34:269-279
[26] Edwards CC 2nd, Bridwell KH, Patel A, et al. Thoracolumbar deformity arthrodesis to L5 in adults: the fate of the L5-S1 disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:2122-2131.
[27] Cho KJ, Suk SI, Park SR, et al. Arthrodesis to L5 versus S1 in long instrumentation and fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2009;18:531-537.
[28] Bransford R, Goergens E, Briody J, et al. Effect of zoledronic acid in an L6-L7 rabbit spine fusion model. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(4):557-562.
[29] Kodera R, Miyazaki M, Yoshiiwa T, et al. Manipulation of anabolic and catabolic responses with bone morphogenetic protein and zoledronic acid in a rat spinal fusion model. Bone. 2013;58C:26-32.
[30] Ohtori S, Inoue G, Orita S, et al. Comparision of teriparatide and bisphosphonate treatment to reduce pedicle screw loosening after lumbar spinal fusion surgery in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis from a bone quality perspective. Spine. 2013;38(8):487-492.
[31] Hirsch BP, Unnanuntana A, Cunningham ME, et al. The effect of the therapies for osteoporosis on spine fusion: a systematic review. Spine. 2013; 13(2): 190-199.
[32] Kobayashi T, Atsuta Y, Takemitsu M, et al. A prospective study of de novo scoliosis in a community based cohor. Spine. 2006; 31:178-182.
[33] Schwab F, Dubey A, Gamez L, et al. Adult scoliosis: prevalence,SF-36,and nutritional parameters in an elderly volunteer populationt. Spine. 2005;30:1082-1085.
[34] 杨诚,高春华,彭宝淦.腰椎退变性侧凸的外科治疗策略[J].脊柱外科杂志, 2012,10(6):330-333. |