中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (4): 926-935.doi: 10.12307/2026.532
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨退变:机制及再生的挑战
杨 肖,白月辉,赵甜甜,王东昊,赵 琛,袁 硕
- 河北医科大学口腔医院·口腔医院修复科·河北省口腔医学重点实验室·河北省口腔健康技术创新中心,河北省石家庄市 050017
-
收稿日期:2024-11-27接受日期:2025-01-25出版日期:2026-02-08发布日期:2025-05-20 -
通讯作者:赵琛,博士,主任医师,河北医科大学口腔医院·口腔医院修复科·河北省口腔医学重点实验室·河北省口腔健康技术创新中心,河北省石家庄市 050017 并列通讯作者:袁硕,硕士,副主任医师,河北医科大学口腔医院·口腔医院修复科·河北省口腔医学重点实验室·河北省口腔健康技术创新中心,河北省石家庄市 050017 -
作者简介:杨肖,女,1997年生,河北省石家庄市人,汉族,河北医科大学在读硕士,医师,主要从事口腔修复学方面的研究。 -
基金资助:2022年河北省政府资助临床医学优秀人才培养和基础课题研究项目(361029),项目负责人:赵琛;2023年河北省医学科学研究指令性课题(20230184),项目负责人:赵琛;河北省财政厅河北省卫生健康委2024年政府资助临床优秀人才项目(ZF2024154),项目负责人:袁硕
Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges
Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo
- Department of Prosthodontics, Stomatological Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Hebei Provincial Oral Health Technology Innovation Center, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2024-11-27Accepted:2025-01-25Online:2026-02-08Published:2025-05-20 -
Contact:Zhao Chen, PhD, Chief physician, Department of Prosthodontics, Stomatological Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Hebei Provincial Oral Health Technology Innovation Center, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China Co-corresponding author: Yuan Shuo, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Prosthodontics, Stomatological Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Hebei Provincial Oral Health Technology Innovation Center, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Yang Xiao, Master candidate, Physician, Department of Prosthodontics, Stomatological Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Hebei Provincial Oral Health Technology Innovation Center, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:2022 Hebei Provincial Government Subsidized Clinical Medicine Outstanding Talent Training and Basic Topics Research Project, No. 361029 (to ZC); Directive Subjects for Medical Science Research in Hebei Province in 2023, No. 20230184 (to ZC); 2024 Government-funded Clinical Excellence Program of Hebei Provincial Department of Finance/Hebei Provincial Health and Health Commission, No. ZF2024154 (to YS)
摘要:
文题释义:
颞下颌关节骨关节炎:是一种常见的影响患者生活质量的关节退行性疾病,其病理表现为髁突软骨退变、进行性滑膜炎、软骨下骨重建和骨赘形成;炎症、氧化应激、异常机械应力等是发病的主要原因,临床表现为关节疼痛、弹响和功能障碍。
软骨退变:是颞下颌关节骨关节炎早期典型的病理特征;其发病机制复杂,目前认为软骨基质的降解、滑膜炎、氧化应激、软骨血管生成、细胞外囊泡、软骨细胞凋亡、肥大、铁死亡等都会导致软骨退变。
背景:目前颞下颌关节骨关节炎的发病机制不明确,传统临床治疗策略是缓解疼痛和减少炎症等对症治疗,可在一定程度上阻止疾病的进展,但无法逆转软骨的破坏。软骨退变作为颞下颌关节骨关节炎发生最主要的病理特征之一,越来越多的研究集中在其发生机制,旨在为颞下颌关节的再生提供理想的治疗方案。
目的:对颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨退变机制的研究进展进行综述。
方法:以“颞下颌关节骨关节炎,软骨基质降解,滑膜炎,氧化应激,软骨细胞肥大,软骨细胞凋亡,铁死亡,自噬,软骨血管生成,细胞外囊泡”为中文检索词,以“temporomandibuar joint osteoarthritis,degradation of cartilage matrix,synovitis,oxidative stress,chondrocyte hypertrophy,chondrocyte apoptosis,ferroptosis,autophagy,angiogenesis,extracellular vesicles”为英文检索词,分别在PubMed数据库和中国知网进行文献检索,检索时限为2004年1月至2024年10月。通过分析和阅读文献进行筛选,按照纳入排除标准最终纳入81篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①软骨基质降解酶分泌增加,引起软骨基质的降解,导致软骨退变;②滑膜炎通过巨噬细胞M1型极化及炎性递质的产生促进软骨退变;③氧化应激通过活性氧的过度产生加重炎症反应促进软骨退变;④软骨细胞表型变化及死亡,导致软骨基质合成的减少,导致软骨退变;⑤软骨下骨的血管穿透钙化软骨层到达软骨浅层,破坏软骨的结构,致软骨退变;⑥炎症状态下血清来源的细胞外囊泡携带的生物活性物质也会促进颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨退变。
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-6122-0309(杨肖)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
杨 肖, 白月辉, 赵甜甜, 王东昊, 赵 琛, 袁 硕. 颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨退变:机制及再生的挑战[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(4): 926-935.
Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935.
2.1.1 软骨及软骨基质的组成 关节软骨由细胞外基质和软骨细胞组成,见图3。细胞外基质主要由胶原和蛋白多糖等成分组成。胶原纤维是软骨基质中最主要的组成部分,呈三维网状结构包绕软骨细胞,为关节软骨提供了重要的抗拉伸特性[5]。髁突软骨基质胶原纤维的主要成分是Ⅱ型胶原,完整的胶原纤维对软骨细胞的存活至关重要[6]。蛋白聚糖是细胞外基质中另一重要组成部分,由一个透明质酸细丝和附着于其上的多个聚集蛋白聚糖分子
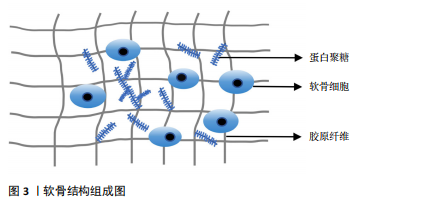
组成,聚集蛋白聚糖通过核心蛋白非共价地附着于透明质酸细丝上[7]。蛋白聚糖占据软骨细胞外基质的纤维间空间,并为软骨提供渗透特性,使其具有抵抗压缩负荷的能力。在颞下颌关节骨关节炎时蛋白聚糖会被多种蛋白水解酶降解,组织会承受更大的应变,最终影响软骨基质的稳态[8]。软骨细胞是软骨内唯一的细胞类型,可以合成和分泌软骨基质及相关细胞因子,软骨细胞的功能受损会直接导致软骨的破坏,软骨细胞周围包裹着大量细胞外基质,基质可以保护细胞免受损伤,还可以充当细胞的信号传感器,并有助于维持软骨细胞表型,软骨细胞与软骨基质相互作用,共同维持软骨的稳态[9]。
2.1.2 参与软骨基质代谢的主要介质 胶原蛋白和聚集蛋白聚糖的降解是软骨基质降解的核心,基质金属蛋白酶和血小板结合蛋白基序的解聚蛋白样金属蛋白酶(a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with a thrombospondin motifs,ADAMTS)是分解聚集蛋白聚糖的最重要介质,基质金属蛋白酶13是降解Ⅱ型胶原蛋白的主要蛋白酶[10]。性别决定区Y框蛋白9(SRY-box transcription factor 9,SOX9)在软骨细胞分化和软骨形成中起着关键作用,可增强软骨特异性基因编码Ⅱ型胶原蛋白α1链基因(collagen Type II alpha-1,COL2A1)及聚集蛋白聚糖基因的表达,抑制软骨细胞肥大,可以诱导胰岛素样生长因子1、转化生长因子β和骨形态发生蛋白2等合成代谢生长因子产生,对软骨基质合成十分重要[11]。在正常软骨中,细胞外基质的合成及分解处于动态平衡,平衡一旦打破,关节软骨将发生不可逆的降解,最终加剧软骨的退变。
2.1.3 表观遗传参与调控软骨基质降解 表观遗传是指在基因的DNA序列不发生改变的情况下,对基因表达进行各类修饰,引起基因的功能发生可遗传的改变,主要机制包括DNA甲基化、组蛋白修饰及非编码RNA调控。研究表明表观遗传在颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨基质降解中扮演着重要角色,通过多种机制调控软骨退变,为颞下颌关节骨关节炎的发病机制提供了新的视角,并有望成为未来治疗颞下颌关节骨关节炎的潜在靶点。
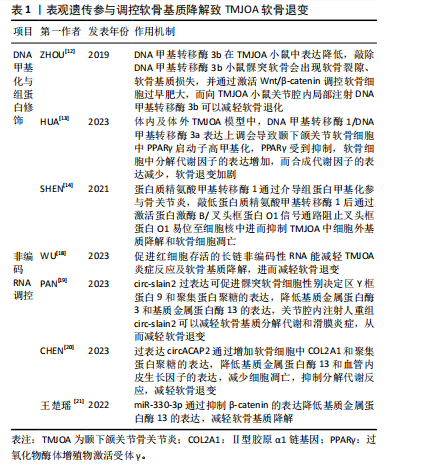
DNA甲基化与组蛋白修饰:DNA甲基化由DNA甲基转移酶家族控制,包括DNA甲基转移酶1、DNA甲基转移酶3a和DNA甲基转移酶3b,DNA甲基转移酶3b在颞下颌关节骨关节炎小鼠中表达降低,敲除DNA甲基转移酶3b小鼠髁突软骨会出现软骨裂隙、软骨基质损失,并通过激活Wnt/β-catenin调控软骨细胞过早肥大,而向颞下颌关节骨关节炎小鼠关节腔内局部注射DNA甲基转移酶3b可以减轻软骨退化[12]。研究发现,在颞下颌关节骨关节炎中存在过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ(peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ,PPARγ)的表观遗传抑制,体内颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨和体外炎症条件下的髁突软骨细胞中,DNA甲基转移酶1/DNA甲基转移酶3a表达上调,导致颞下颌关节软骨细胞中PPARγ启动子高甲基化,PPARγ受到抑制,软骨细胞中分解代谢因子的表达增加,而合成代谢因子的表达减少,导致软骨退变,而DNA去甲基化剂地西他滨干预可逆转PPARγ启动子的高甲基化,恢复PPARγ的表达,从而减轻软骨退化并促进软骨稳态[13]。蛋白质精氨酸甲基转移酶1是组蛋白转移酶的一种,通过介导组蛋白甲基化参与骨关节炎,研究表明敲低蛋白质精氨酸甲基转移酶1后能激活蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B,AKT)/叉头框蛋白O1信号通路阻止叉头框蛋白O1易位至细胞核中进而抑制颞下颌关节骨关节炎中细胞外基质降解和软骨细胞凋亡,应用蛋白质精氨酸甲基转移酶1的选择性抑制剂 AMI-1可抑制蛋白质精氨酸甲基转移酶1的表达并改善颞下颌关节骨关节炎的病理表现[14]。沉默信息调节因子2相关酶类3(Sirtuin 3,SIRT3)也是表观遗传中重要的因子,其介导的组蛋白乙酰化修饰可影响软骨、滑膜、骨及血管等颞下颌关节结构的生长发育。SIRT缺乏使基质降解相关的基因表达增强,与软骨基质合成相关基因表达减少,且可早期发生软骨细胞肥大分化,导致软骨退变[15]。有研究证明组蛋白去乙酰化酶抑制剂可以抑制组蛋白乙酰化,抑制基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶13等基因表达,从而达到软骨保护的作用[16]。
非编码RNA调控软骨基质降解:随着基因组学技术和生物信息学方法的进步,越来越多的学者阐明非编码RNA的功能,尤其是长链非编码RNA、微小RNA和环状RNA在参与软骨细胞代谢、软骨基质损伤等骨关节炎发生发展中的功能[17]。
长链非编码RNA是长度超过200个碱基的RNA分子,缺乏蛋白质编码能力,研究表明敲除促进红细胞存活的长链非编码性RNA加重了颞下颌关节骨关节炎的炎症和软骨基质降解,导致软骨退变[18]。环状RNA是通过RNA反向剪接、外显子或内含子环化形成的一类具有闭环结构的RNA。研究发现circ-slain2 可以减轻软骨基质的分解代谢反应和滑膜炎症,减轻颞下颌关节软骨退变[19];此外circACAP2在颞下颌关节骨关节炎的发病和进展中起到保护作用,过表达circACAP2可以减轻软骨细胞及细胞外基质的分解代谢反应,调节软骨细胞增殖和凋亡,减轻软骨退变[20]。MiRNA具有调控关节软骨稳态的作用,研究发现miR-330-3p通过抑制β-catenin(cadherin-associated protein beta 1,CTNNB1)的表达,降低了基质金属蛋白酶13的表达,减轻颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨基质降解[21]。 上述非编码RNA在软骨退变中通过多种机制发挥作用,这些研究为骨关节炎的诊断和治疗提供了新的思路和潜在靶点。见表1。
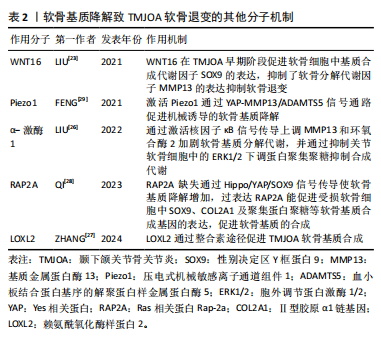
2.1.4 软骨基质降解的其他分子机制 WNT16属于富含半胱氨酸的糖蛋白家族中的一种,通过经典WNT途径及非经典WNT途径进行信号转导,在维持软骨稳态中发挥重
要作用,在小鼠膝关节炎模型中,过表达WNT16 显著抑制了骨骼发育过程中的软骨细胞肥大,并通过级联反应导致软骨基质的主要成分Ⅱ型胶原减少[22]。在颞下颌关节骨关节炎模型的研究表明WNT16不仅促进软骨基质的合成因子SOX9的表达,而且抑制分解代谢因子基质金属蛋白酶13、ADAMTS5的表达,在颞下颌关节骨关节炎早期阶段通过抑制软骨基质的降解发挥重要保护作用[23]。在兔膝关节骨缺损模型中发现局部 WNT16 治疗可以缓解骨关节炎、抑制骨吸收并促进新骨形成,可能成为治疗颞下颌关节骨关节炎的有效药物[24]。α-激酶1是一种新发现的固有免疫的胞质模式识别受体,能介导炎症反应,在膝关节炎中表达上调,并通过增强 NOD 样受体蛋白 3 (NOD-like receptor protein 3,NLRP3)的产生加重软骨细胞代谢紊乱[25]。α-激酶1在颞下颌关节骨关节炎中可以通过激活核因子κB信号传导上调基质金属蛋白酶13和环氧合酶2加剧软骨基质分解代谢,并通过抑制关节软骨细胞中的细胞外信号调节激酶1/2 (extracellular signal- regulated kinase 1/2,ERK1/2)下调蛋白聚集聚糖抑制合成代谢[26],因此,α-激酶1可能是骨关节炎发病机制的新型分解代谢调节因子,有望成为骨关节炎的诊断标志物与治疗靶点。另外,多种机械传导信号分子参与调控软骨退变,整合素是一种跨膜蛋白,在外部细胞外基质和细胞内部之间传递化学和机械刺激,赖氨酰氧化酶样蛋白2是一种细胞外酶,可催化肽基赖氨酸残基的氧化脱氨作用,促进软骨细胞外基质中赖氨酰衍生的胶原蛋白和弹性蛋白交联的形成,研究表明颞下颌关节骨关节炎时,赖氨酰氧化酶样蛋白2通过整合素途径调节软骨细胞中胶原蛋白的表达促进软骨基质合成,应用重组赖氨酰氧化酶样蛋白2可促进Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和蛋白多糖的表达,改善机械应力诱导的软骨基质退行性变化,因此可以通过调节赖氨酰氧化酶样蛋白2的表达和活性来减轻骨关节炎的病理变化[27]。Ras 相关蛋白Rap-2a是细胞内机械信号传导分子,可以将物理应力转化为软骨细胞中的生物信号,以响应过度的机械应力。QI等[28]研究发现Ras 相关蛋白Rap-2a 感应颞下颌关节骨关节炎基质硬度变化调节 Hippo/YAP 通路进而调控软骨基质合成功能,Ras 相关蛋白Rap-2a 缺失通过 Hippo/YAP/SOX9信号传导使软骨基质降解增加,损害软骨稳态,而过表达Ras 相关蛋白Rap-2a能促进受损软骨细胞中SOX9、COL2A1及聚集蛋白聚糖等软骨基质合成基因的表达,促进软骨基质的合成。压电式机械敏感离子通道组件1(Piezo type mechanosensitive ion channel component1,Piezo1)是一种机械敏感离子通道蛋白,在外界机械力的刺激下,可以引起Ca2+内流,将机械信号转化为生物信号传递至细胞内,参与多种生理和病理过程,FENG等[29]研究发现在颞下颌关节骨关节炎中表达上调,Piezo1可以通过 YAP-MMP13/ADAMTS5信号通路促进机械诱导的软骨退变。青蒿素被发现是一种有效的 Piezo1 激活抑制剂,体外实验结果证实,可以降低 ADAMTS5、基质金属蛋白酶13的表达,并减轻骨关节炎小鼠软骨损伤[30]。上述分子通过不同机制在软骨退变中发挥作用,为颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨退变的机制提供了新的见解。见表2。
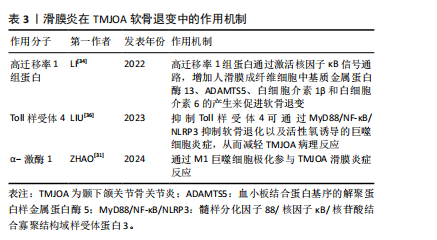
2.2 滑膜炎在软骨退变中的作用机制研究 颞下颌关节骨关节炎中的滑膜细胞释放的炎症因子会募集巨噬细胞,可使其极化为促炎的M1型或抗炎M2型,α-激酶1可以使M1巨噬细胞极化促进颞下颌关节滑膜炎[31],促炎M1型巨噬细胞又会增加炎性因子及软骨基质降解酶表达[32],导致疼痛和软骨退变。同时,受损的细胞及软骨基质的降解产物会进一步激活巨噬细胞,形成恶性循环,使滑膜炎及软骨退变加剧[33]。滑膜炎通过复杂分子机制导致颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨退变,高迁移率 1 组蛋白是一种高度保守的核蛋白,可与多种细胞表面受体结合,研究发现炎症状态下高迁移率 1 组蛋白高表达,并通过激活核因子κB信号通路,增加人滑膜成纤维细胞中基质金属蛋白酶13、ADAMTS5、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6的产生,因此可通过抑制高迁移率 1 组蛋白减轻颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨退变[34]。研究表明,中药制剂新痹痛灵能降低滑膜组织中高迁移率 1 组蛋白 mRNA 的表达及抑制高迁移率 1组蛋白,减少相关炎症通路的激活,减轻膝关节炎大鼠关节肿胀[35]。Toll样受体4是一种模式识别受体,在颞下颌关节骨关节炎患者滑膜中高表达,研究发现抑制Toll样受体4通过 MyD88/NF-κB/NLRP3 抑制软骨退化以及巨噬细胞炎症,从而减轻颞下颌关节骨关节炎病理进程[36]。有研究表明白藜芦醇通过抑制Toll样受体4/髓样分化因子88/核因子κB信号通路,下调人关节软骨细胞炎症因子的表达,从而减轻膝关节骨关节炎的炎症反应[37]。上述靶点药物仅在膝关节中有研究,对治疗颞下颌关节骨关节炎有一定的参考作用。见表3。
2.3 氧化应激在软骨退变中的作用机制研究 活性氧通常在细胞中以低水平产生,当活性氧产生增加,抵抗氧化应激的细胞防御机制被激活,进而清除细胞中活性氧分子。氧化应激是活性氧的产生与清除之间不平衡的结果,软骨细胞中活性氧的积累导致的氧化应激是慢性炎症的驱动原因[38]。此外炎症反应也可以激活软骨细胞的氧化应激系统并产生大量炎症因子,通过加速细胞外基质降解、促进线粒体功能障碍及诱导细胞凋亡等方式,共同介导软骨退变[39]。葡萄糖-6-磷酸脱氢酶是戊糖磷酸途径的限速酶,还原型烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸(nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate,NAPDH)是戊糖磷酸途径的主要产物,葡萄糖-6-磷酸脱氢酶通过提供NAPDH帮助清除活性氧,研究证实敲低髁突软骨细胞中的葡萄糖-6-磷酸脱氢酶可以降低分解代谢酶基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶13和炎性细胞因子白细胞介素6的表达,并通过降低NAPDH减少活性氧产生,减轻髁状软骨细胞的炎症状态,进而减轻软骨退变[40]。目前关于活性氧诱导颞下颌关节骨关节炎发生时软骨退变机制的研究相对较少,这一领域仍需进一步的深入探索。针对活性氧这一致病因素,MA等[41]研究出了一种可注射的活性氧多功能水凝胶,用来装载牙髓干细胞,有效促进了颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨基质的合成,协同改善颞下颌关节骨关节炎氧化应激微环境及促进巨噬细胞M2极化,靶向修复髁突软骨缺损。氧化铈纳米粒子因强大的抗氧化特性和对慢性疾病的潜在预防和治疗作用而受到广泛研究,它可以降低软骨细胞和软骨外植体中的活性氧水平,抑制软骨基质代谢紊乱和细胞凋亡,从而达到治疗颞下颌关节骨关节炎的效果[42]。维生素C是一种重要的抗氧化剂,在颞下颌关节骨关节炎的治疗中具有潜在的作用,能够中和自由基、减轻氧化应激,从而保护软骨细胞免受氧化损伤;而且可以抑制炎症递质的产生,减轻炎症反应;还可以促进胶原蛋白的合成,促进关节软骨的修复[43]。
2.4 软骨细胞肥大及死亡在软骨退变中的作用机制研究
2.4.1 软骨细胞肥大分化 当颞下颌关节骨关节炎发生时,滑液中的炎性递质影响软骨细胞的功能和形态,发生肥大性分化。这种分化直接影响基质的分泌和合成,破坏细胞外基质的稳态,细胞外基质的变化进一步促进软骨细胞的分解代谢活动,最终导致软骨破坏[44]。肥大性软骨细胞的特征是细胞表达X型胶原、基质金属蛋白酶13、Runt相关转录因子2以及转谷氨酰胺酶2 [45]。肥大性软骨细胞高度表达的基质金属蛋白酶13促进其周围基质降解;当软骨基质中存在X型胶原时,会加速羟基磷灰石沉积过程和软骨矿化[46],软骨矿化后软骨的弹性开始改变,并通过钙化变硬,软骨细胞更难获得营养,因此大多数细胞会发生凋亡,此外,肥大软骨细胞分泌蛋白聚集聚糖、Ⅱ型胶原、SOX9减少,软骨基质合成也随之减少[47]。Runt相关转录因子2是软骨内骨化过程中肥大性软骨细胞介导的软骨基质降解所必需的转录因子[48],当在 Runt相关转录因子2敲除小鼠中诱导骨关节炎模型时,基质降解酶基质金属蛋白酶9、基质金属蛋白酶13、ADAMTS4、ADAMTS5、ADAMTS7和ADAMTS12的基因表达显著降低,抑制软骨基质降解[49]。LI等[50]的研究发现转谷氨酰胺酶 2抑制剂可以减少软骨细胞中环氧合酶2、诱导型一氧化氮合酶、基质金属蛋白酶13和基质金属蛋白酶3的表达水平,并通过抑制核因子κB活化减少软骨细胞蛋白多糖丢失。目前,关于骨关节炎诱导的软骨细胞肥大分化的研究主要集中在膝关节,而对颞下颌关节的相关研究相对较少。
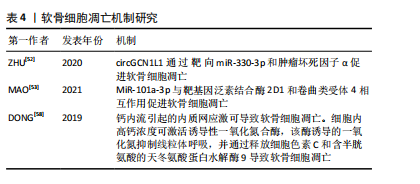
2.4.2 细胞凋亡 细胞凋亡是由基因控制的细胞自主的有序的死亡方式,以维持内环境稳定,具有复杂的分子生物机制[51]。研究发现颞下颌关节骨关节炎患者的circGCN1L1上调,circGCN1L1 通过靶向miR-330-3p和肿瘤坏死因子α促进软骨细胞凋亡[52]。MiR-101a-3p可以与靶基因泛素结合酶 2D1和卷曲类受体 4相互作用促进软骨细胞凋亡[53]。受体相互作用的丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶可促进颞下颌关节骨关节炎滑膜细胞中炎症因子、核因子κB蛋白以及细胞凋亡标志物的升高[54]。近期有报道称,人骨关节炎软骨细胞在受到各种病理因素刺激后发生内质网应激也会导致软骨细胞凋亡。机械应力、氧化应激、炎症反应时会干扰内质网的稳态,细胞内未折叠或错误折叠蛋白质发生积累,从而发生内质网应激[46]。内质网应激通过激活PI3K/AKT信号通路参与软骨细胞凋亡[55]。凋亡后的软骨细胞通过释放细胞内容物和局部炎症递质促进软骨细胞外基质的降解[56]。钙在内质网应激诱导的软骨细胞凋亡中起着至关重要的作用,在机械超负荷的情况下,软骨细胞中的钙浓度会升高[57]。钙内流引起的内质网应激可导致软骨细胞凋亡。细胞内高钙浓度可激活诱导性一氧化氮合酶,该酶诱导的一氧化氮抑制线粒体呼吸,并通过释放细胞色素 C和含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶9导致软骨细胞凋亡[58]。软骨细胞是软骨基质合成和更新的关键细胞,其凋亡会导致基质合成减少。凋亡的软骨细胞无法正常合成和分泌Ⅱ型胶原蛋白、蛋白多糖等基质成分,使得软骨基质的合成速度赶不上降解速度,造成基质成分的丢失和减少,最终导致软骨基质的稳态被破坏,软骨的弹性和抗压性降低,加速软骨的退变和损伤。软骨细胞凋亡机制,见表4。
2.4.3 自噬 自噬是细胞应对外界有害刺激时做出的一种自我调节过程,主要通过产生自噬溶酶体与胞内代谢产物或多余细胞器结合并降解,维持细胞内稳态。当软骨细胞自噬水平下降,自噬囊泡减少,无法吞噬和降解糖原,细胞无法得到必须的葡萄糖作为能量来源,细胞供能不足而发生凋亡。研究发现颞下颌关节骨关节炎组髁突软骨细胞内Ⅱ型胶原和自噬标志物微管相关蛋白1-轻链3表达减少,基质金属蛋白酶13表达增多,软骨细胞的凋亡增加,表明颞下颌关节骨关节炎髁突软骨细胞自噬水平下降致软骨细胞凋亡增加,最终髁突软骨组织出现退变[59],自噬水平受DNA损伤诱导转录物3的调控,YANG等[60]体外研究表明,DNA损伤诱导转录物3通过抑制自噬加剧软骨退变。此外,有研究表明线粒体自噬与颞下颌关节骨关节炎密切相关,线粒体自噬障碍导致缺陷线粒体逐渐积累,从而导致软骨退化[61]。因此,调节自噬可能是治疗颞下颌关节骨关节炎的有效机制。
2.4.4 铁死亡 铁死亡是一种新发现的软骨细胞死亡模式,主要特征是铁代谢失衡、抗氧化失衡和脂质过氧化物积聚。软骨细胞铁死亡的诱导会增加基质金属蛋白酶13 的表达,同时降低Ⅱ型胶原的表达,导致软骨退变[62]。转铁蛋白受体是铁死亡的重要调节器,它可以影响细胞内的铁离子水平。低氧诱导因子1α是一种参与软骨基质分泌和软骨细胞代谢重要的转录因子,同时也是转铁蛋白受体的主要调节因子。缺氧信号可以通过激活低氧诱导因子增加活性氧的产生来促进铁死亡[63]。CHEN等[64]研究发现抑制低氧诱导因子1α或转铁蛋白受体后,颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨细胞 基质金属蛋白酶13表达减少,COL2A1表达增加,表明铁死亡参与了颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨退变,抑制低氧诱导因子1α 或转铁蛋白受体可能是抑制软骨细胞铁死亡的有效靶点。酰基辅酶A合成酶长链家族成员4是促进脂质过氧化的关键酶,可以加速铁死亡的发生[65]。谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶 4是调节细胞铁死亡的主要因子,谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4失活可导致铁依赖性脂质过氧化物在细胞内积累致软骨细胞死亡[66]。CHENG等[67]研究发现颞下颌关节骨关节炎中铁死亡相关蛋白谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4水平降低,酰基辅酶 A 合成酶长链家族成员4水平升高,注射铁死亡抑制剂ferrostatin-1可有效降低酰基辅酶 A 合成酶长链家族成员4的表达;体外实验表明铁死亡抑制剂维持了线粒体的形态和功能,并减轻了活性氧的产生及软骨细胞外基质的降解。这些结果表明,软骨细胞铁死亡在颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨退变的发展和进展中起着重要作用,抑制软骨细胞铁死亡可能是一种有前景的治疗策略。
2.5 血管生成在软骨退变中的作用机制研究 关节软骨的血管化可以反映软骨退化的程度。与其他关节不同的是,颞下颌关节软骨组织能够维持一种持续的、适度的血管生成状态,促血管生成因素与抑制血管生成因素在其软骨内保持平衡状态,维持健康颞下颌关节生理改建[68]。血管生成失衡是颞下颌关节软骨血管化的关键因素。随着骨关节炎的进展,软骨下骨的血管突破钙化软骨层向软骨浅层生长。血管侵袭可破坏关节软骨与软骨下骨边界的完整性,也是对软骨细胞和胶原纤维正常排列的物理破坏,血管内皮细胞可同时分泌多种因子,调节软骨细胞的功能,促进软骨细胞肥大以及软骨内骨化,导致软骨的退变[69]。
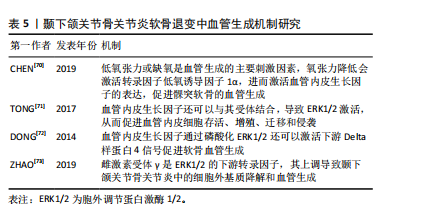
血管内皮生长因子是一种参与血管生成的主要调节因子。骨关节炎病变部位的软骨细胞可分泌血管内皮生长因子,促进邻近正常软骨细胞分泌基质金属蛋白酶、白细胞介素1β等炎性细胞因子,导致软骨退变。低氧张力或缺氧是血管生成的主要刺激因素,氧张力降低会激活转录因子低氧诱导因子1α ,进而激活血管内皮生长因子的表达,促进髁突软骨的血管生成[70]。血管内皮生长因子还可以与其受体2结合,导致 ERK1/2激活,从而促进血管内皮细胞存活、增殖、迁移和侵袭[71]。血管内皮生长因子通过磷酸化 ERK1/2还可以激活下游Delta样蛋白 4信号促进软骨血管生成[72]。雌激素受体γ是ERK1/2 的下游转录因子,其上调导致颞下颌关节骨关节炎中的细胞外基质降解和血管生成[73]。在兔膝关节骨关节炎模型中,贝伐单抗通过抑制血管内皮生长因子和基质金属蛋白酶1的表达,减少血管生成,减轻关节局部炎症,促进软骨修复。尽管血管生成在颞下颌关节骨关节炎中的作用机制已逐渐明确,但目前血管生成抑制剂的研究多局限于膝骨关节炎体外实验和动物模型,临床应用较少且效果尚不明确,仍需进一步研究[74]。髁突软骨的血管化在颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨退变中扮演着关键角色,引起了越来越多学者的关注,但这一过程的发病机制较复杂,需要更深层次的研究来完全理解其内在机制。见表5。
2.6 细胞外囊泡在软骨退变中的作用机制研究 细胞外囊泡是由几乎所有类型细胞在生理或病理状态下分泌的纳米级球状磷脂双层颗粒,可以携带蛋白质、脂质、DNA、微小RNA和mRNA等生物活性物质,通过特定的配体-受体结合模式或内吞作用将其内容物递送至靶细胞。根据直径及产生来源的不同,分为外泌体、微囊泡和凋亡囊泡3种类型[75]。研究表明,细胞外囊泡在整个骨关节炎进展过程中起着至关重要的作用:①一方面,血清来源的细胞外囊泡携带白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α等大量炎性因子,激活滑膜成纤维细胞及滑膜巨噬细胞分泌白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8及金属蛋白酶,导致软骨基质的破坏[76]。这些细胞外囊泡还可以被软骨细胞内吞,从而诱发软骨细胞产生更多的炎性细胞因子和趋化因子,进一步加剧软骨基质的破坏[77]。②此外,异常机械应力下,软骨细胞会分泌含有机械敏感物质的细胞外囊泡,内包含大量炎性细胞因子和组织蛋白酶,通过激活下游Wnt和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路,最后导致软骨退变[78]。近年来,间充质干细胞来源的外泌体对骨关节炎软骨的再生有显著的效果,向大鼠关节腔内注射水凝胶包裹的牙髓间充质干细胞外泌体,可减轻髁突软骨的损伤[79]。WANG等[80]研究发现骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体衍生的小细胞外囊泡可以携带自分泌运动因子,调控河马信号通路,增强软骨细胞的增殖、迁移能力,同时下调炎症因子,促进髁突软骨修复。脂肪干细胞来源的外泌体同样具有软骨修复的效果,将其与丝素蛋白支架结合后植入兔髁突软骨缺损处,结果显示缺损修复良好[81]。外泌体在间充质干细胞治疗颞下颌关节骨关节炎机制中发挥重要作用,且外泌体免疫原性低安全性高,其作为一种无细胞疗法具有巨大的前景。

| [1] 傅开元,雷杰.颞下颌关节紊乱病的分类、诊断及治疗进展[J].口腔医学,2024,44(1):6-10. [2] WANG D, QI Y, WANG Z, et al. Recent Advances in Animal Models, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2023;29(1):62-77. [3] 胡敏.颞下颌关节骨关节炎:认识与挑战[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 2022,57(7):665-673. [4] YUAN W, WU Y, HUANG M, et al. A new frontier in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis treatment: Exosome-based therapeutic strategy. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:1074536. [5] DE BONT LG, BOERING G, HAVINGA P, et al. Spatial arrangement of collagen fibrils in the articular cartilage of the mandibular condyle: a light microscopic and scanning electron microscopic study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1984;42(5):306-313. [6] VOS LM, KUIJER R, HUDDLESTON SLATER JJ, et al. Inflammation is more distinct in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis compared to the knee joint. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;72(1):35-40. [7] HUANG K, WU LD. Aggrecanase and aggrecan degradation in osteoarthritis: a review. J Int Med Res. 2008;36(6):1149-1160. [8] MALDONADO M, NAM J. The role of changes in extracellular matrix of cartilage in the presence of inflammation on the pathology of osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:284873. [9] LIU C, WANG B, XIAO L, et al. Protective effects of the pericellular matrix of chondrocyte on articular cartilage against the development of osteoarthritis. Histol Histopathol. 2018;33(8):757-764. [10] ROUGHLEY PJ, MORT JS. The role of aggrecan in normal and osteoarthritic cartilage. J Exp Orthop. 2014;1(1):8. [11] JIANG S, LIU Y, XU B,et al. Noncoding RNAs: New regulatory code in chondrocyte apoptosis and autophagy. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2020;11(4):e1584. [12] ZHOU Y, CHEN M, O′KEEFE RJ, et al. Epigenetic and therapeutic implications of dnmt3b in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(3):1736-1747. [13] HUA B, QIU J, YE X, et al. Epigenetic PPARγpreservation attenuates temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;124(Pt B):111014. [14] SHEN Q, XIAO Y, CHENG B, et al. PRMT1 promotes extracellular matrix degradation and apoptosis of chondrocytes in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis via the AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2021;141:106112. [15] 杨毓芝,俞燕芳,吴梦婕. 沉默信息调节因子3对颞下颌关节骨关节炎的影响[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志,2022,57(7):756-761. [16] KHAN NM, HAQQI TM. Epigenetics in osteoarthritis: Potential of HDAC inhibitors as therapeutics. Pharmacol Res. 2018;128:73-79. [17] FUJII Y, LIU L, YAGASAKI L, et al. Cartilage Homeostasis and Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11):6316. [18] WU W, HU A, XU H, et al. LincRNA-EPS Alleviates Inflammation in TMJ Osteoarthritis by Binding to SRSF3. J Dent Res. 2023;102(10): 1141-1151. [19] PAN X, ZHAO Z, HUANG X,et al.Circ-Slain2 Alleviates Cartilage Degradation and Inflammation of TMJOA. J Dent Res. 2023;102(13): 1498-1506. [20] CHEN H, QU Z, SHI T,et al.Circular RNA CircACAP2 regulates temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis via miR-21-5p/PLAG1 axis. Oral Dis. 2024;30(7):4440-4453. [21] 王楚瑶,邹璐芗,陆川,等.miR-330-3p在颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨退变中的作用机制研究[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2022,20(4): 320-327. [22] TONG W, ZENG Y, CHOW DHK, et al. Wnt16 attenuates osteoarthritis progression through a PCP/JNK-mTORC1-PTHrP cascade. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78:551-561. [23] LIU X, LI X, HUA B, et al. WNT16 is upregulated early in mouse TMJ osteoarthritis and protects fibrochondrocytes against IL-1β induced inflammatory response by regulation of RUNX2/MMP13 cascade. Bone. 2021;143:115793. [24] YE X, LIU X. Wnt16 signaling in bone homeostasis and osteoarthristis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:1095711. [25] LIU X, ZHAO J, JIANG H, et al. ALPK1 Accelerates the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis by Activating NLRP3 Signaling. J Bone Miner Res. 2022;37(10):1973-1985. [26] LIU X, ZHAO J, JIANG H, et al. ALPK1 Aggravates TMJOA Cartilage Degradation via NF-κB and ERK1/2 Signaling. J Dent Res. 2022;101(12): 1499-1509. [27] ZHANG C, ZHU M, WANG H, et al. LOXL2 attenuates osteoarthritis through inactivating Integrin/FAK signaling. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):17020. [28] QI H, ZHANG Y, XU L, et al. Loss of RAP2A Aggravates Cartilage Degradation in TMJOA via YAP Signaling. J Dent Res. 2023;102(3): 302-312. [29] FENG X, LI S, WANG S, et al. Piezo1 mediates the degradation of cartilage extracellular matrix in malocclusion-induced TMJOA. Oral Dis. 2024;30(4):2425-2438. [30] GAN D, TAO C, JIN X, et al. Piezo1 activation accelerates osteoarthritis progression and the targeted therapy effect of artemisinin. J Adv Res. 2024:62:105-117. [31] ZHAO J, FENG Y, LIU X, et al. The relationship of ALPK1, hyaluronic acid and M1 macrophage polarization in the temporomandibular joint synovitis. J Cell Mol Med. 2024;28(7):e18172. [32] WU Z, WANG Y, ZHU M, et al. Synovial microenvironment in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: crosstalk with chondrocytes and potential therapeutic targets. Life Sci. 2024;354:122947. [33] HU S, LI H, JIANG H, et al. Macrophage Activation in Synovitis and Osteoarthritis of Temporomandibular Joint and Its Relationship with the Progression of Synovitis and Bone Remodeling. Am J Pathol. 2024; 194(2):296-306. [34] Li YY, Feng YP, Liu L, et al. Inhibition of HMGB1 suppresses inflammation and catabolism in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis via NF-κB signaling pathway. Eur J Histochem. 2022;66(3):3357. [35] 谢兴文,陈欣,刘建军,等.HMGB1介导TLR4/NF-κB信号通路干预骨关节炎研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(10):1519-1522+1527. [36] LIU X, LI H, FENG Y, et al. Resatorvid alleviates experimental inflammatory TMJOA by restraining chondrocyte pyroptosis and synovial inflammation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023;25(1):230. [37] 杨萍.白藜芦醇通过调控信号通路治疗膝骨关节炎的研究进展[J].中草药,2023,54(4):1311-1320. [38] ANSARI MY, AHMAD N, HAQQI TM. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of polyphenols. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;129:110452. [39] 牛烁,易军,朱凡茂,等.内质网应激信号通路在骨关节炎中的研究进展[J].赣南医学院学报,2024,44(8):840-844. [40] LIN H, HE K, ZHANG S, et al. Targeting G6PD to mitigate cartilage inflammation in TMJOA: The NOX4-ROS-MAPK axis as a therapeutic avenue. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;139:112688. [41] MA J, LI J, WEI S, et al. Delivery of dental pulp stem cells by an injectable ROS-responsive hydrogel promotes temporomandibular joint cartilage repair via enhancing anti-apoptosis and regulating microenvironment.J Tissue Eng. 2024;15:20417314241260436. [42] XIONG L, BAO H, LI S, et al. Cerium oxide nanoparticles protect against chondrocytes and cartilage explants from oxidative stress via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1076240. [43] 熊山,张程,吴健梅,等.抗氧化剂在骨相关疾病中的应用研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(1):139-144+150. [44] MALDONADO M, NAM J. The role of changes in extracellular matrix of cartilage in the presence of inflammation on the pathology of osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:284873. [45] CHAWLA S, MAINARDI A, MAJUMDER N, et al.Chondrocyte Hypertrophy in Osteoarthritis: Mechanistic Studies and Models for the Identification of New Therapeutic Strategies. Cells. 2022;11(24):4034. [46] GU J, LU Y, LI F, et al. Identification and characterization of the novel Col10a1 regulatory mechanism during chondrocyte hypertrophic differentiation. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5(10):e1469. [47] MACKIE EJ, AHMED YA, TATARCZUCH L, et al. Endochondral ossification: how cartilage is converted into bone in the developing skeleton. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008;40(1):46-62. [48] RASHID H, CHEN H, JAVED A. Runx2 is required for hypertrophic chondrocyte mediated degradation of cartilage matrix during endochondral ossification. Matrix Biol Plus. 2021;12:100088. [49] KILBEY A, BLYTH K, WOTTON S, et al. Runx2 disruption promotes immortalization and confers resistance to oncogene-induced senescence in primary murine fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 2007;67:11263-11271. [50] LI Y, SUN H, LIU X, et al. Transglutaminase 2 inhibitors attenuate osteoarthritic degeneration of TMJ-osteoarthritis by suppressing NF-κB activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;114:109486. [51] JUAN Z, XING-TONG M, XU Z, et al. Potential pathological and molecular mechanisms of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. J Dent Sci. 2023;18(3):959-971. [52] ZHU H, HU Y, WANG C, et al. CircGCN1L1 promotes synoviocyte proliferation and chondrocyte apoptosis by targeting miR-330-3p and TNF-α in TMJ osteoarthritis. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(4):284. [53] MAO D, WU M, WEI J, et al. MicroRNA-101a-3p could be involved in the pathogenesis of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis by mediating UBE2D1 and FZD4. J Oral Pathol Med. 2021;50(2):236-243. [54] CAO X, PENG S, YAN Y, et al. Alleviation of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis by targeting RIPK1-mediated inflammatory signalling. J Cell Mol Med. 2024;28(5):e17929. [55] ZHOU L, WU F, WANG J, et al. Effects of endoplasmic reticulum stress on chondrocyte apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Tissue Cell. 2024;87:102340. [56] HALLETT SA, ONO W, ONO N. The hypertrophic chondrocyte: To be or not to be. Histol Histopathol. 2021;36(10):1021-1036. [57] LI B, GUAN G, MEI L, et al. Pathological mechanism of chondrocytes and the surrounding environment during osteoarthritis of temporomandibular joint. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(11):4902-4911. [58] REN H, YANG H, XIE M, et al. Chondrocyte apoptosis in rat mandibular condyles induced by dental occlusion due to mitochondrial damage caused by nitric oxide. Arch Oral Biol. 2019;101:108-121. [59] 高久瑜,王小健,余建平,等. 大鼠颞下颌关节骨关节炎髁突软骨细胞自噬功能下降对细胞凋亡的影响[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 2020,55(5):343-347. [60] YANG C, DONG W, WANG Y, et al. DDIT3 aggravates TMJOA cartilage degradation via Nrf2/HO-1/NLRP3-mediated autophagy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2024;32(8):921-937. [61] SUN K, JING X, GUO J, et al. Mitophagy in degenerative joint diseases. Autophagy. 2021;17:2082-2092. [62] YAO X, SUN K, YU S, et al. Chondrocyte ferroptosis contribute to the progression of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 2021:27:33-43. [63] ZHANG J, HU Y, WANG Z, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor expression is related to apoptosis and cartilage degradation in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):583. [64] CHEN BY, PATHAK JL, LIN HY, et al. Inflammation Triggers Chondrocyte Ferroptosis in TMJOA via HIF-1α/TFRC. J Dent Res. 2024;103(7): 712-722. [65] HE F, HUANG X, WEI G, et al. Regulation of ACSL4-Catalyzed Lipid Peroxidation Process Resists Cisplatin Ototoxicity. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022:2022:3080263. [66] BERSUKER K, HENDRICKS JM, LI Z, et al. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature. 2019;575(7784): 688-692. [67] CHENG B, ZHANG J, SHEN Q, et al. Liproxstatin-1 alleviates cartilage degradation by inhibiting chondrocyte ferroptosis in the temporomandibular joint. Biol Cell. 2024;116(1):e202300042. [68] RUSCITTO A, MOREL MM, SHAWBER CJ, et al. Evidence of vasculature and chondrocyte to osteoblast transdifferentiation in craniofacial synovial joints: implications for osteoarthritis diagnosis and therapy. FASEB J. 2020;34(3):4445-4461. [69] LIU J, DAI J, WANG Y, et al. Significance of new blood vessels in the pathogenesis of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13(5):2325-2331. [70] CHEN Y, ZHAO B, ZHU Y, et al. HIF-1-VEGF-Notch mediates angiogenesis in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(5): 2969-2982. [71] TONG Q, QING Y, WU Y, et al. Dioscin inhibits colon tumor growth and tumor angiogenesis through regulating VEGFR2 and AKT/MAPK signaling pathways. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014;281:166-173. [72] DONG Y, WU G, ZHU T, et al. VEGF promotes cartilage angiogenesis by phospho-ERK1/2 activation of Dll4 signaling in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis caused by chronic sleep disturbance in Wistar rats. Oncotarget. 2017;8(11):17849-17861. [73] ZHAO H, LIU S, MA C, et al. Estrogen-Related Receptor γ Induces Angiogenesis and Extracellular Matrix Degradation of Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis in Rats. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:1290. [74] 刘映鸿,伊亚婷.血管生成在骨关节炎中的作用机制及治疗启示[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(2):307-313. [75] SHANG XB, BOKER KO, TAHERI S, et at. Extracellular vesicles allow epigenetic mechanotransduction between chondrocytes and osteoblasts. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(24):13282. [76] ZENG G, DENG G, XIAO S, et al. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes-derived exosomal PCGEM1 accelerates IL-1beta-induced apoptosis and cartilage matrix degradation by miR-142-5p/RUNX2 in chondrocytes. Immunol Invest. 2022;51(5):1284-1301. [77] YANG B, LI X, FU C, et al. Extracellular vesicles in osteoarthritis of peripheral joint and temporomandibular joint. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1158744. [78] HODGKINSON T, KELLY DC, CURTIN CM, et al. Mechanosignalling in cartilage: an emerging target for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(2):67-84. [79] DIEZ-GUARDIA V, TIAN Y, GUO Y, et al. Controlled Release of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes from Hydrogels Attenuates Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;23: e2402923. [80] WANG Y, ZHAO M, LI W, et al. BMSC‑derived small extracellular vesicles induce cartilage reconstruction of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis via autotaxin-YAP signaling axis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:656153. [81] LIU Y, ZHANG Z, WANG B, et al. Inflammation-stimulated MSC-derived small extracellular vesicle miR-27b-3p regulates macrophages by targeting CSF-1 to promote temporomandibular joint condylar regeneration. Small. 2022;18(16):e2107354. |
| [1] | 董春阳, 周天恩, 莫孟学, 吕文权, 高 明, 朱瑞凯, 高志伟. 二甲双胍联合血水草敷料治疗深Ⅱ度烧伤创面的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2001-2013. |
| [2] | 吴妍廷, 李 宇, 廖金凤. 氧化镁纳米粒调控成骨与血管生成相关基因表达促进骨缺损愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895. |
| [3] | 吕国庆, 艾孜麦提江·肉孜, 熊道海. 鸢尾素抑制人关节软骨细胞中铁死亡的作用及其机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1359-1367. |
| [4] | 李林臻, 焦泓焯, 陈伟南, 张铭哲, 王建龙, 张君涛. 淫羊藿苷含药血清对脂多糖诱导人软骨细胞炎症损伤的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1368-1374. |
| [5] | 陈 驹, 郑锦畅, 梁 振, 黄成硕, 林 颢, 曾 莉. β-石竹烯对小鼠膝骨关节炎的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1341-1347. |
| [6] | 温广伟, 甄颖豪, 郑泰铿, 周淑怡, 莫国业, 周腾鹏, 李海山, 赖以毅. 异银杏素对破骨细胞分化的影响和机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1348-1358. |
| [7] | 吕晓凡, 黄 懿, 丁留成. 糖尿病膀胱病的线粒体机制与干预治疗[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1508-1515. |
| [8] | 潘鸿飞, 庄圳冰, 徐白云, 杨章阳, 林恺瑞, 詹冰晴, 蓝靖涵, 高 恒, 张南波, 林家煜. 不同浓度金诺芬抑制M1型巨噬细胞功能及修复糖尿病小鼠伤口的价值[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1390-1397. |
| [9] | 彭志伟, 陈 雷, 佟 磊. 木犀草素促进糖尿病小鼠创面愈合的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [10] | 李郝静, 王 新, 宋成林, 张胜男, 陈云昕. 上斜方肌处体外冲击波与运动控制训练治疗慢性非特异性颈痛[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1162-1170. |
| [11] | 刘 煜, 雷森林, 周锦涛, 刘 辉, 李先辉. 有氧和抗阻运动改善肥胖相关认知障碍的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [12] | 王正业, 刘万林, 赵振群. miRNA在激素诱导股骨头坏死机制中的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1207-1214. |
| [13] | 部洋洋, 宁新丽, 赵 琛. 关节腔注射治疗颞下颌关节骨关节炎:不同药物与多种联合治疗方案[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1215-1224. |
| [14] | 文 凡, 向 阳, 朱 欢, 庹艳芳, 李 锋. 运动干预改善2型糖尿病患者的微血管功能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1225-1235. |
| [15] | 刘新月, 李春年, 李一卓, 徐世芳. 口腔牙槽骨缺损的再生修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1247-1259. |
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2024年10月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2004年1月至 2024 年10月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed数据库和中国知网。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“颞下颌关节骨关节炎,软骨基质降解,滑膜炎,氧化应激,软骨细胞肥大,软骨细胞凋亡,铁死亡,自噬,软骨血管生成,细胞外囊泡” ;英文检索词为“temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis,degradation of cartilage matrix,synovitis,oxidative stress,chondrocyte hypertrophy,chondrocyte apoptosis,ferroptosis,angiogenesis,autophagy,extracellular vesicles”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述、述评和荟萃分析等。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 PubMed数据库和中国知网检索策略见图 1。
1.1.8 检索文献量 初次检索出文献340篇,其中英文文献299篇,中文文献41篇。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①有关颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨基质降解的文献;②有关颞下颌关节骨关节炎氧化应激、滑膜炎的文献;③有关颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡、肥大、自噬、铁死亡的文献;④有关颞下颌关节骨关节炎血管生成的文献;⑤有关颞下颌关节骨关节炎细胞外囊泡的文献;⑥优先纳入近5年发表的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①与文章相关性较低或无关的文献;②
重复文献;③无法获取全文的文献。
1.3 质量评估及筛选流程 通过剔除不符合纳入标准的文献,排除与研究目的相关性较低及内容重复、资料陈旧的文献,最终纳入81篇文献进行综述,其中10篇中文文献来源于中国知网数据库,71篇英文文献来源于PubMed数据库。文献筛选流程见图2。
3.2 综述区别于他人他篇的特点 此文与现有文献相比呈现明显的差异:①目前检索到的关于颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨退变的研究均是论著,尚未对其机制进行系统综述;②在时效性方面,该文报道了颞下颌关节软骨退变机制的最新研究进展,分别对软骨基质降解、滑膜炎、氧化应激、软骨血管新生、细胞外囊泡软骨细胞肥大、凋亡、自噬、铁死亡的作用等在软骨退变中的作用机制进行了文献检索及总结归纳;③颞下颌关节骨关节炎发病机制错综复杂,此文主要对颞下颌关节骨关节炎主要的病理表现之一软骨退化的机制研究进行综述;④总结了目前一些针对作用于软骨退变靶点的干预措施,希望为颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨修复再生提供一定的参考价值。
3.3 综述的局限性 颞下颌关节骨关节炎涉及复杂的发病机制,且尚未完全明确,此文仅对软骨退变这一病理表现的发生机制进行了综述;从分子机制及基因层面分析归纳了软骨基质降解,软骨细胞肥大、凋亡、铁死亡,软骨血管新生,炎症反应致软骨退变的机制,尚未总结异常机械应力、创伤、年龄等因素在颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨退变中的作用,但是仍能为颞下颌关节骨关节炎的治疗提供一定的思路。
3.4 综述的重要意义 颞下颌关节骨关节炎的传统临床治疗策略是缓解疼痛和减少炎症的对症治疗,虽然可以在一定程度上阻止疾病的进展,但无法逆转软骨的破坏,该文总结了近些年来颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨退变的机制,希望为颞下颌关节软骨的再生提供理论依据。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 髁突软骨组织缺乏血供及淋巴回流,自愈性极差,因此软骨一旦损伤无法完全恢复,且目前颞下颌关节骨关节炎的确切发病机制并不完全明确。软骨退化是骨关节炎发展中的关键病理特征,尽管在膝关节炎的研究中已有较多探讨,但由于颞下颌关节主要是纤维软骨,而膝关节则以透明软骨为主,两者在结构和性质上存在差异,且具体分子调控机制也不完全相同,因此对于颞下颌关节骨关节炎软骨退变仍需进一步研究。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||