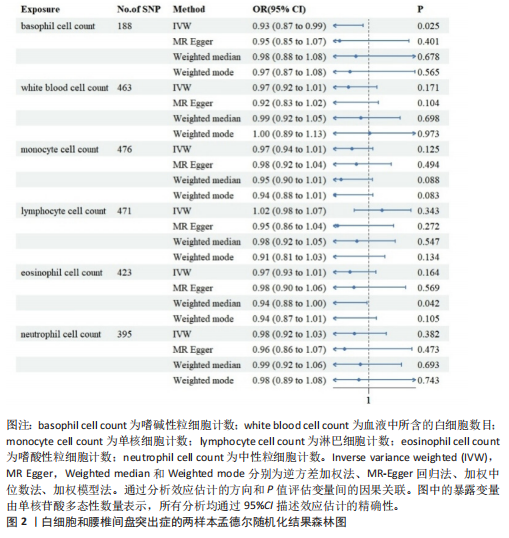
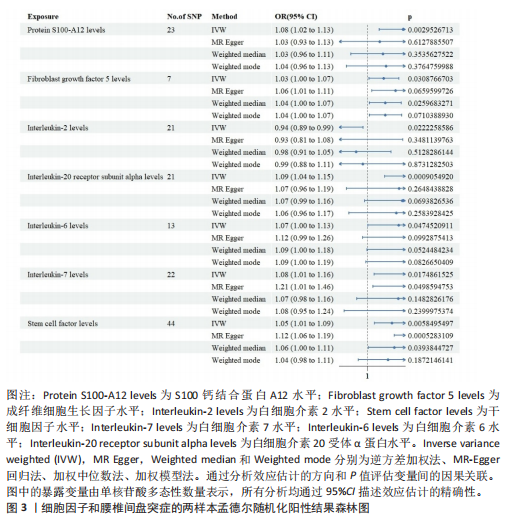
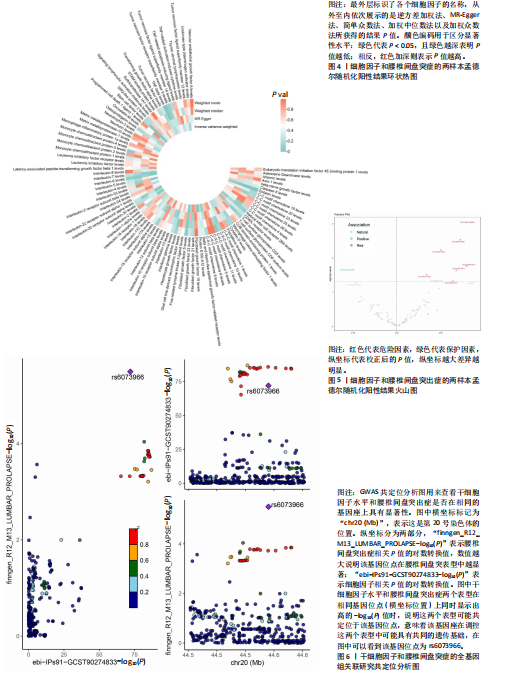
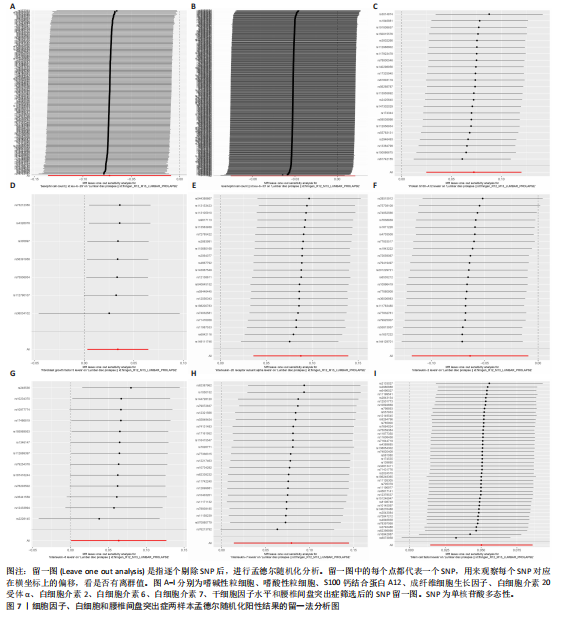
[1] SALO V, MÄÄTTÄ J, SLIZ E, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis conducted in three large biobanks expands the genetic landscape of lumbar disc herniations. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):9424.
[2] POJSKIC M, BISSON E, OERTEL J, et al. Lumbar disc herniation: Epidemiology, clinical and radiologic diagnosis WFNS spine committee recommendations. World Neurosurg X. 2024;22:100279.
[3] WANG Z, LIU X, GAO K, et al. Clinical effects and biological mechanisms of exercise on lumbar disc herniation. Front Physiol. 2024;15:1309663.
[4] JIN L, XIAO L, DING M, et al. Heterogeneous macrophages contribute to the pathology of disc herniation induced radiculopathy. Spine J. 2022;22(4):677-689.
[5] FRANCISCO V, PINO J, GONZÁLEZ-GAY MÁ, et al. A new immunometabolic perspective of intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(1):47-60.
[6] XUE P, WANG Y, LV L, et al. Roles of Chemokines in Intervertebral Disk Degeneration. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2024;28(3):95-108.
[7] RISBUD MV, SHAPIRO IM. Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: pain and disc content. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014; 10(1):44-56.
[8] 高增杰,蒲翔,李来来,等.甾醇酯增加骨质疏松病理性骨折风险:来自IEU-GWAS与芬兰数据库的证据[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(15):2345-2353.
[9] CHEN MH, RAFFIELD LM, MOUSAS A, et al. Trans-ethnic and Ancestry-Specific Blood-Cell Genetics in 746,667 Individuals from 5 Global Populations. Cell. 2020;182(5):1198-1213.e14.
[10] JACOBSEN HE, KHAN AN, LEVINE ME, et al. Severity of intervertebral disc herniation regulates cytokine and chemokine levels in patients with chronic radicular back pain. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(10):1341-1350.
[11] WERNERSSON S, PEJLER G. Mast cell secretory granules: armed for battle. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14(7):478-494.
[12] FOWLKES V, WILSON CG, CARVER W, et al. Mechanical loading promotes mast cell degranulation via RGD-integrin dependent pathways. J Biomech. 2013;46(4):788-795.
[13] KNEILLING M, HÜLTNER L, PICHLER BJ, et al. Targeted mast cell silencing protects against joint destruction and angiogenesis in experimental arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(6):1806-1816.
[14] STEVENS RL, SOMERVILLE LL, SEWELL D, et al. Serosal mast cells maintain their viability and promote the metabolism of cartilage proteoglycans when cocultured with chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 1992; 35(3):325-335.
[15] WIET MG, PISCIONERI A, KHAN SN, et al. Mast Cell-Intervertebral disc cell interactions regulate inflammation, catabolism and angiogenesis in Discogenic Back Pain. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):12492.
[16] LIAO Z, LIU H, MA L, et al. Engineering Extracellular Vesicles Restore the Impaired Cellular Uptake and Attenuate Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. ACS Nano. 2021;15(9):14709-14724.
[17] HE J, ZHANG X, WEI Y, et al. Low-dose interleukin-2 treatment selectively modulates CD4(+) T cell subsets in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Med. 2016;22(9):991-993.
[18] WU PH, KIM HS, JANG IT. Intervertebral Disc Diseases PART 2: A Review of the Current Diagnostic and Treatment Strategies for Intervertebral Disc Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(6):2135.
[19] JORSSEN J, VAN HULST G, MOLLERS K, et al. Single-cell proteomics and transcriptomics capture eosinophil development and identify the role of IL-5 in their lineage transit amplification. Immunity. 2024;57(7): 1549-1566.e8.
[20] YANG BG, SEOH JY, JANG MH. Regulatory Eosinophils in Inflammation and Metabolic Disorders. Immune Netw. 2017;17(1):41-47.
[21] EBO DG, BAHRI R, TONTINI C, et al. Mast cell versus basophil activation test in allergy: Current status. Clin Exp Allergy. 2024;54(6):378-387.
[22] MIYAKE K, KARASUYAMA H. Emerging roles of basophils in allergic inflammation. Allergol Int. 2017;66(3):382-391.
[23] VOGL T, PRÖPPER C, HARTMANN M, et al. S100A12 is expressed exclusively by granulocytes and acts independently from MRP8 and MRP14. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(36):25291-25296.
[24] LIRA-JUNIOR R, HOLMSTRÖM SB, CLARK R, et al. S100A12 Expression Is Modulated During Monocyte Differentiation and Reflects Periodontitis Severity. Front Immunol. 2020;11:86.
[25] FOELL D, KANE D, BRESNIHAN B, et al. Expression of the pro-inflammatory protein S100A12 (EN-RAGE) in rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003;42(11):1383-1389.
[26] FOELL D, WITTKOWSKI H, HAMMERSCHMIDT I, et al. Monitoring neutrophil activation in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis by S100A12 serum concentrations. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(4):1286-1295.
[27] ORCZYK K, SMOLEWSKA E. A Granulocyte-Specific Protein S100A12 as a Potential Prognostic Factor Affecting Aggressiveness of Therapy in Patients with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. J Immunol Res. 2018; 2018:5349837.
[28] FRIEDL A, CHANG Z, TIERNEY A, et al. Differential binding of fibroblast growth factor-2 and -7 to basement membrane heparan sulfate: comparison of normal and abnormal human tissues. Am J Pathol. 1997;150(4):1443-1455.
[29] LI X, AN HS, ELLMAN M, et al. Action of fibroblast growth factor-2 on the intervertebral disc. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008; 10(2):R48.
[30] PRATSINIS H, CONSTANTINOU V, PAVLAKIS K, et al. Exogenous and autocrine growth factors stimulate human intervertebral disc cell proliferation via the ERK and Akt pathways. J Orthop Res. 2012;30(6):958-964.
[31] YANG J, XU W, CHEN D, et al. Evidence from Mendelian randomization analysis combined with meta-analysis for the causal validation of the relationship between 91 inflammatory factors and lumbar disc herniation. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024; 103(47):e40323.
[32] LI J, YANG H, WANG T, et al. IL-20RA is Associated with the Risk of Diabetic Microangiopathy: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Analysis and Clinical Validation. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024;17:4803-4816.
[33] SPOLSKI R, LI P, LEONARD WJ. Biology and regulation of IL-2: from molecular mechanisms to human therapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018;18(10):648-659.
[34] POL JG, CAUDANA P, PAILLET J, et al. Effects of interleukin-2 in immunostimulation and immunosuppression. J Exp Med. 2020; 217(1):e20191247.
[35] ZHANG F, ZHAO X, SHEN H, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death in intervertebral disc degeneration (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2016;37(6):1439-1448.
[36] OROZCO VALENCIA A, CAMARGO KNIRSCH M, et al. Interleukin-2 as immunotherapeutic in the autoimmune diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;81:106296.
[37] HUMRICH JY, VON SPEE-MAYER C, SIEGERT E, et al. Low-dose interleukin-2 therapy in refractory systemic lupus erythematosus: an investigator-initiated, single-centre phase 1 and 2a clinical trial. Lancet Rheumatol. 2019;1(1):e44-e54.
[38] ZHANG R, ZHAO Y, CHEN X, et al. Low-dose IL-2 therapy in autoimmune diseases: An update review. Int Rev Immunol. 2024; 43(3):113-137.
|