[1] CAO M, SHENG R, SUN Y, et al. Delivering Microrobots in the Musculoskeletal System. Nanomicro Lett. 2024;16(1):251.
[2] GBD 2021 Other Musculoskeletal Disorders Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of other musculoskeletal disorders, 1990-2020, and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023;5(11):e670-e682.
[3] 张印恩,马铮,倪国骅,等.mFI-5预测老年全膝关节置换术后早期并发症的应用[J].医学研究与战创伤救治,2024, 37(6):593-597.
[4] PARK S, RAHAMAN KA, KIM YC, et al. Fostering tissue engineering and regenerative medicine to treat musculoskeletal disorders in bone and muscle. Bioact Mater. 2024;40:345-365.
[5] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977.
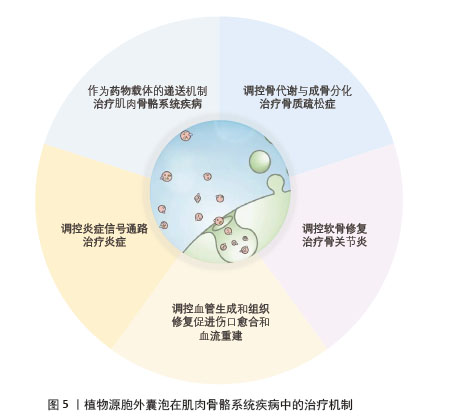
[6] MAO X, LI T, QI W, et al. Advances in the study of plant-derived extracellular vesicles in the skeletal muscle system. Pharmacol Res. 2024;204:107202.
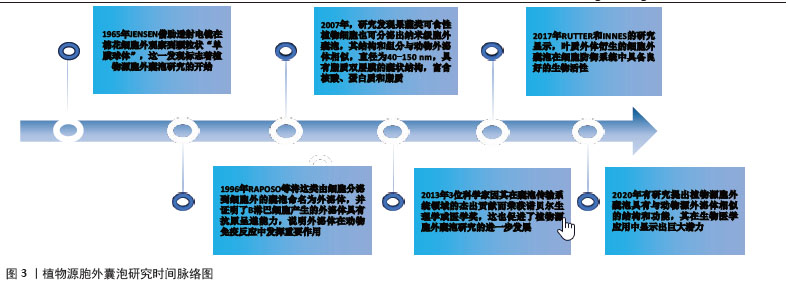
[7] JENSEN WA. The ultrastructure and histochemistry of the synergids of cotton. Am J Bot. 1965;52:238-256.
[8] 赵淑举,黄佳欣,李师鹏,等.植物细胞外囊泡研究进展[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2024,46(6):1295-1302.
[9] 朱珍珠,江睿,廖柳月,等.植物胞外囊泡的结构、生物活性及其在食药递送方面的应用[J].食品工业科技,2022, 43(21):422-432.
[10] 赵梦,李思敏,张蕾,等.植物来源囊泡及其生物医学应用研究进展[J].药学学报,2021,56(8):2039-2047+2036.
[11] WANG Q, ZHUANG X, MU J, et al. Delivery of therapeutic agents by nanoparticles made of grapefruit-derived lipids. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1867.
[12] XU Z, XU Y, ZHANG K, et al. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles (PDEVs) in nanomedicine for human disease and therapeutic modalities. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):114.
[13] LIAN MQ, CHNG WH, LIANG J, et al. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles: Recent advancements and current challenges on their use for biomedical applications. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022;11(12): 12283.
[14] 李俊言,王文苹,张祎,等.植物类中药来源囊泡的研究进展[J].浙江大学学报(医学版),2023,52(3):349-360.
[15] 蔡鹏,张明真,高博雯.植物源细胞外囊泡在炎症性肠病治疗中的应用[J].现代生物技术研究,2023,1(1):6-11.
[16] CALZONI E, BERTOLDI A, CUSUMANO G, et al. Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Natural Nanocarriers for Biotechnological Drugs. Processes. 2024;12(12):2938.
[17] LANGELLOTTO MD, RASSU G, SERRI C, et al. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles: a synergetic combination of a drug delivery system and a source of natural bioactive compounds. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025; 15(3):831-845.
[18] KIM J, LI S, ZHANG S, et al. Plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles and their therapeutic activities. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022;17(1):53-69.
[19] ZENG YB, DENG X, SHEN LS, et al. Advances in plant-derived extracellular vesicles: isolation, composition, and biological functions. Food Funct. 2024;15(23): 11319-11341.
[20] KIM SQ, KIM KH. Emergence of Edible Plant-Derived Nanovesicles as Functional Food Components and Nanocarriers for Therapeutics Delivery: Potentials in Human Health and Disease. Cells. 2022; 11(14):2232.
[21] DING L, CHANG C, LIANG M, et al. Plant‐Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Emerging Tools for Cancer Therapeutics. Advanced Therapeutics. 2024;7(11):2400256.
[22] WANG Y, WANG J, MA J, et al. Focusing on Future Applications and Current Challenges of Plant Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022; 15(6):708.
[23] SHAO M, JIN X, CHEN S, et al. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles -a novel clinical anti-inflammatory drug carrier worthy of investigation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;169:115904.
[24] 郭丰硕,李美艺,张子腾,等.老年骨质疏松风险预测新标杆—TyG-BMI的诊断潜力[J].中国实验诊断学,2025,29(1): 51-55.
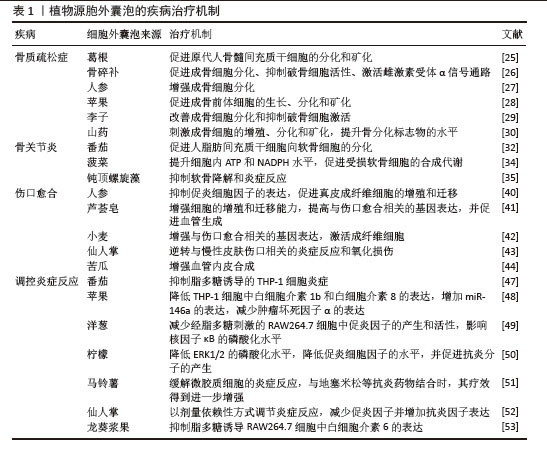
[25] ZHAN W, DENG M, HUANG X, et al. Pueraria lobata-derived exosome-like nanovesicles alleviate osteoporosis by enhacning autophagy. J Control Release. 2023;364: 644-653.
[26] ZHAO Q, FENG J, LIU F, et al. Rhizoma Drynariae-derived nanovesicles reverse osteoporosis by potentiating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via targeting ERα signaling. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024;14(5): 2210-2227.
[27] YANG N, ZHANG X, LI L, et al. Ginsenoside Rc Promotes Bone Formation in Ovariectomy-Induced Osteoporosis In Vivo and Osteogenic Differentiation In Vitro. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11):6187.
[28] SIM Y, SEO HJ, KIM DH, et al. The Effect of Apple-Derived Nanovesicles on the Osteoblastogenesis of Osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 Cells. J Med Food. 2023;26(1): 49-58.
[29] PARK YS, KIM HW, HWANG JH, et al. Plum-Derived Exosome-like Nanovesicles Induce Differentiation of Osteoblasts and Reduction of Osteoclast Activation. Nutrients. 2023; 15(9):2107.
[30] HWANG JH, PARK YS, KIM HS, et al. Yam-derived exosome-like nanovesicles stimulate osteoblast formation and prevent osteoporosis in mice. J Control Release. 2023;355:184-198.
[31] 李宜金,黎嘉澔,张海涛,等.关节康片干预软骨稳态保护膝骨关节炎小鼠关节软骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2026,30(12): 2994-3004.
[32] YILDIRIM M, ÜNSAL N, KABATAŞ B, et al. Effect of Solanum lycopersicum and Citrus limon-Derived Exosome-Like Vesicles on Chondrogenic Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024;196(1):203-219.
[33] LIANG Y, XU X, LI X, et al. Chondrocyte-Targeted MicroRNA Delivery by Engineered Exosomes toward a Cell-Free Osteoarthritis Therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020; 12(33):36938-36947.
[34] CHEN P, LIU X, GU C, et al. A plant-derived natural photosynthetic system for improving cell anabolism. Nature. 2022; 612(7940):546-554.
[35] LIANG F, ZHENG Y, ZHAO C,et al. Microalgae-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Synergize with Herbal Hydrogel for Energy Homeostasis in Osteoarthritis Treatment. ACS Nano. 2025;19(8):8040-8057.
[36] 曾斌,梁宇杰,邓志钦,等.细胞外囊泡在治疗膝骨关节炎中的作用与前景[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2023,50(7): 1573-1583.
[37] 陈玲玲,程海霞,顾清昕,等.氧疗在伤口愈合中的研究进展[J].护理学,2023, 12(6):1000-1005.
[38] CHENG B, FU X. The Role of Stem Cell on Wound Healing After Revascularization-Healing Following Revascularization-Unlocking Skin Potential. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2024;23(1):63-69.
[39] LI A, LI D, GU Y, et al. Plant-derived nanovesicles: Further exploration of biomedical function and application potential. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023;13(8): 3300-3320.
[40] YANG S, LU S, REN L, et al. Ginseng-derived nanoparticles induce skin cell proliferation and promote wound healing. J Ginseng Res. 2023;47(1):133-143.
[41] KIM M, PARK JH. Isolation of Aloe saponaria-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Investigation of Their Potential for Chronic Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(9):1905.
[42] ŞAHIN F, KOÇAK P, GÜNEŞ MY, et al. In Vitro Wound Healing Activity of Wheat-Derived Nanovesicles. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2019;188(2):381-394.
[43] VALENTINO A, CONTE R, BOUSTA D, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Opuntia ficus-indica Fruit (OFI-EVs) Speed Up the Normal Wound Healing Processes by Modulating Cellular Responses. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(13):7103.
[44] 王玮琪,羊月婷,苏志宏,等.植物来源细胞外囊泡在创面修复中作用的研究进展[J].中华烧伤与创面修复杂志,2024, 40(12):1199-1204.
[45] 丁恺志,龚妍春,李晓诺,等.NLRP3 炎性小体在肌肉骨骼系统疾病中的作用[J].生物工程学报,2024,40(2):337-349.
[46] LOU K, LUO H, JIANG X, et al. Applications of emerging extracellular vesicles technologies in the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1364401.
[47] MAMMADOVA R, MAGGIO S, FIUME I, et al. Protein Biocargo and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Tomato Fruit-Derived Nanovesicles Separated by Density Gradient Ultracentrifugation and Loaded with Curcumin. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(2):333.
[48] TRENTINI M, ZANOTTI F, TIENGO E, et al. An Apple a Day Keeps the Doctor Away: Potential Role of miRNA 146 on Macrophages Treated with Exosomes Derived from Apples. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(2):415.
[49] KANG SJ, KIM SE, SEO MJ, et al. Suppression of inflammatory responses in macrophages by onion-derived extracellular vesicles. J Ind Eng Chem. 2022;115:287-297.
[50] RAIMONDO S, URZÌ O, MERAVIGLIA S, et al. Anti-inflammatory properties of lemon-derived extracellular vesicles are achieved through the inhibition of ERK/NF-κB signalling pathways. J Cell Mol Med. 2022;26(15):4195-4209.
[51] ISHIDA T, KAWADA K, JOBU K, et al. Exosome-like nanoparticles derived from Allium tuberosum prevent neuroinflammation in microglia-like cells. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2023;75(10):1322-1331.
[52] NASELLI F, VOLPES S, CARDINALE PS, et al. New Nanovesicles from Prickly Pear Fruit Juice: A Resource with Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Nutrigenomic Properties. Cells. 2024;13(21):1756.
[53] EMMANUELA N, MUHAMMAD DR, IRIAWATI, et al. Isolation of plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles (PDENs) from Solanum nigrum L. berries and Their Effect on interleukin-6 expression as a potential anti-inflammatory agent. PLoS One. 2024; 19(1):e0296259.
[54] FENG J, XIU Q, HUANG Y, et al. Plant-Derived Vesicle-Like Nanoparticles as Promising Biotherapeutic Tools: Present and Future. Adv Mater. 2023;35(24):e2207826.
[55] LU J, ZHANG Y, YANG X, et al. Harnessing exosomes as cutting-edge drug delivery systems for revolutionary osteoarthritis therapy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;165: 115135.
[56] WANG Q, REN Y, MU J, et al. Grapefruit-Derived Nanovectors Use an Activated Leukocyte Trafficking Pathway to Deliver Therapeutic Agents to Inflammatory Tumor Sites. Cancer Res. 2015;75(12):2520-2529.
[57] FANG Z, LIU K. Plant-derived extracellular vesicles as oral drug delivery carriers. J Control Release. 2022;350:389-400.
[58] WU P, WU W, ZHANG S, et al. Therapeutic potential and pharmacological significance of extracellular vesicles derived from traditional medicinal plants. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1272241.
[59] HAN R, ZHOU D, JI N, et al. Folic acid-modified ginger-derived extracellular vesicles for targeted treatment of rheumatoid arthritis by remodeling immune microenvironment via the PI3K-AKT pathway. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025; 23(1):41.
[60] WANG X, XIN C, ZHOU Y, et al. Plant-Derived Vesicle-like Nanoparticles: The Next-Generation Drug Delivery Nanoplatforms. Pharmaceutics. 2024;16(5):588.
[61] DEL POZO-ACEBO L, LÓPEZ DE LAS HAZAS MC, TOMÉ-CARNEIRO J, et al. Therapeutic potential of broccoli-derived extracellular vesicles as nanocarriers of exogenous miRNAs. Pharmacol Res. 2022;185:106472. |