中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (13): 3379-3391.doi: 10.12307/2026.340
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
骨骼肌源性外泌体调控骨形成及运动干预的作用
陆碧琼1,韦忠建2
- 1广西民族师范学院体育学院,广西壮族自治区崇左市 532200;2贺州学院教师教育学院,广西壮族自治区贺州市 542899
-
接受日期:2025-09-05出版日期:2026-05-08发布日期:2025-12-26 -
通讯作者:韦忠建,讲师,贺州学院教师教育学院,广西壮族自治区贺州市 542899 -
作者简介:陆碧琼,女,1984年生,壮族,2024年菲律宾黎刹大学毕业,博士,副教授,主要从事运动生理学研究。
Skeletal muscle-derived exosome-mediated regulation of bone formation and role of exercise intervention
Lu Biqiong1, Wei Zhongjian2
- 1College of Physical Education, Guangxi Minzu Normal University, Chongzuo 532200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2School of Teacher Education, Hezhou University, Hezhou 542899, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Accepted:2025-09-05Online:2026-05-08Published:2025-12-26 -
Contact:Wei Zhongjian, Lecturer, School of Teacher Education, Hezhou University, Hezhou 542899, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Lu Biqiong, PhD, Associate professor, College of Physical Education, Guangxi Minzu Normal University, Chongzuo 532200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
外泌体:是直径为30-150 nm的纳米级囊泡,广泛存在于生物体液中。外泌体能够携带多种生物分子,如蛋白质、脂质、RNA(包括miRNA和mRNA)等,由细胞通过内吞作用释放到外部环境中。外泌体不仅在细胞通讯中起着重要作用,还参与调控成骨细胞的分化、矿化。骨形成:是骨骼系统发育和修复的基础过程,主要通过成骨细胞完成。骨形成的过程分为初期的骨基质合成阶段、矿化阶段以及成熟骨的形成阶段。成骨细胞通过合成骨基质(主要是胶原蛋白)并促进矿物质沉积来形成新骨。骨形成的调控因素包括生长因子、转录因子、细胞信号通路等,其中Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号通路、骨形态发生蛋白2、Runt相关转录因子2等分子在骨形成过程中扮演着至关重要的角色。
摘要
背景:骨形成异常是导致骨折风险增加和生活质量下降的主要原因之一。骨骼肌作为重要的分泌器官,其产生的骨骼肌源性外泌体与骨形成密切相关。最新研究显示运动可能通过调节骨骼肌源性外泌体的分泌进而调控骨形成。因此,深入探讨骨骼肌源性外泌体调控骨形成的作用及机制,对于提高生活质量和减少骨折风险具有重要意义。
目的:旨在综述骨骼肌源性外泌体在骨形成中的作用及其潜在机制,特别是运动干预对骨骼肌源性外泌体的调节作用,为骨形成异常的治疗提供新的思路。
方法:检索中国知网(CNKI)和PubMed数据库,使用“Exosome,Skeletal Muscle-Derived Exosomes, Bone Formation,Osteoblast,Exercise”作为英文检索词,“外泌体,骨骼肌源性外泌体,骨形成,成骨细胞,运动”作为中文检索词,筛选数据库建库至2024年11月期间发表的相关文献。根据文献的相关性、质量以及研究内容的适宜性,最终纳入了81篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①当前通过多组学、组织学和分子生物学手段发现骨骼肌源性外泌体中的miR-1、miR-133a、miR-133b、miR-206和miR-27,以及热休克蛋白、胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5、肌连蛋白和中胚层配对同源蛋白2,通过Wnt/β-连环蛋白、骨形态发生蛋白2、Runt相关转录因子2等信号通路调控成骨分化,改善骨质疏松;②不同类型、强度和持续时间的运动干预在调节骨骼肌源性外泌体释放及骨代谢方面具有不同的影响,但由于体内外泌体追踪和鉴定的复杂性,目前仍然难以精确识别运动后循环外泌体的来源,未来的研究需要进一步探索具体机制。综上,骨骼肌源性外泌体在骨代谢中的作用日益受到关注,运动干预通过调节外泌体的释放为骨代谢疾病的治疗提供了新的可能性。
中图分类号:
引用本文
陆碧琼, 韦忠建. 骨骼肌源性外泌体调控骨形成及运动干预的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(13): 3379-3391.
Lu Biqiong, Wei Zhongjian. Skeletal muscle-derived exosome-mediated regulation of bone formation and role of exercise intervention[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3379-3391.
2.1.1 外泌体的发现及生物发生途径 近年来,外泌体干预被认为是调控骨代谢及相关疾病的有效策略[1]。外泌体是一种直径为30-150 nm的细胞外膜囊泡,广泛存在于血液、尿液、唾液等体液中[2]。外泌体最早由STAHL等在1983年发现,后来由JOHNSTONE在同年命名为“外泌体”(图3)[3]。最初未认识到外泌体的生物学功能,直到1996年,研究者才发现外泌体能够携带细胞内的蛋白质、脂质和RNA,并在细胞间传递信息。近年来,外泌体在细胞间的作用机制,特别是其携带miRNA、mRNA、DNA及其他蛋白质的方式,成为研究重点。外泌体提取与纯化技术的进步为其在诊断和治疗中的广泛应用提供了新机遇。
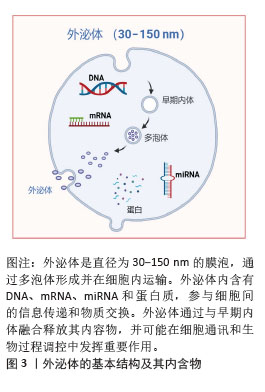
外泌体的形成起始于多泡体或晚期内体的内陷过程,产生腔内囊泡[4]。这一过程通过内体分选转运复合体途径和非内体分选转运复合体依赖性(非经典)途径完成,前者是研究最深入且广泛接受的机制之一[5-6]。外泌体携带的生物活性分子,包括蛋白质、脂质和核酸,经过严格的分选与包装,具有细胞特异性,且随细胞状态变化而动态改变[4]。以miRNA为例,被包装的miRNA含有一段保守的GGAG特异性序列,这一序列在胞质miRNA中并不存在。该序列可与胞质异质核糖核蛋白A2B1结合,从而介导miRNA特异性地包装入外泌体[7]。而蛋白质的包装则主要通过内体分选转运复合体、四跨膜蛋白和脂质依赖性机制实现[8]。
2.1.2 骨骼肌源性外泌体的特性 2010年,GUESCINI等[9]首次证实骨骼肌细胞能够分泌骨骼肌源性外泌体,这一开创性发现为理解细胞间通讯机制提供新的研究视角。骨骼肌源性外泌体作为重要的细胞间信使,携带多种生物活性分子,包括肌因子和外泌体RNA等,这些分子通过多样化的递送机制作用于靶细胞,从而诱导特定的细胞反应[10-11]。值得注意的是,骨骼肌源性外泌体不仅可以影响邻近细胞,还能够通过循环系统作用于远程靶细胞[12-13]。
蛋白质组学分析揭示,骨骼肌源性外泌体不仅含有典型的外泌体标志蛋白,还富集大量参与信号转导的功能性蛋白。同时,骨骼肌源性外泌体中还包含特异性的脂质、DNA和生物活性肽等分子,通过释放入血液循环系统,骨骼肌源性外泌体得以与全身各个组织进行广泛的信息交流,在维持机体整体稳态中发挥重要作用。值得注意的是,在骨骼肌组织中高度富集的miRNAs也被发现存在于骨骼肌源性外泌体中[9]。尽管目前与骨代谢相关的骨骼肌源性外泌体携带的miRNAs数量有限,但其生物学效应已得到初步证实。研究表明,经荧光标记的C2C12成肌细胞来源外泌体能够被MC3T3-E1成骨细胞前体细胞有效摄取,并显著促进其向成骨细胞方向分化,这种促分化效应主要表现为:碱性磷酸酶活性增强、细胞外基质矿化程度提高,以及成骨标志基因碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素和Runt相关转录因子2 mRNA表达水平显著上调[14-16]。
2.2 骨骼肌源性外泌体miRNAs在骨形成中的作用 目前虽有研究报道骨骼肌源性外泌体中不同miRNAs的含量,但受实验设计的影响,骨骼肌源性外泌体中不同miRNAs的丰度尚不明确[17]。以往研究将肌肉特异性的miRNA称为“myomiR”,包括miR-1、miR-133a、miR-133b和miR-206,共同占人和小鼠骨骼肌中miRNA表达的近25%[18]。该综述通过总结myomiR,发现报道最多的是与骨形成有关的骨骼肌源性外泌体miR-27a,以及骨骼肌源性外泌体中其他关键miRNAs与骨形成的关系。通过研究这些miRNA的机制,可以更好地理解它们如何在骨骼肌与骨骼之间传递信号,调控骨形成,并为相关骨代谢疾病的治疗提供潜在的靶向治疗策略(图4)。
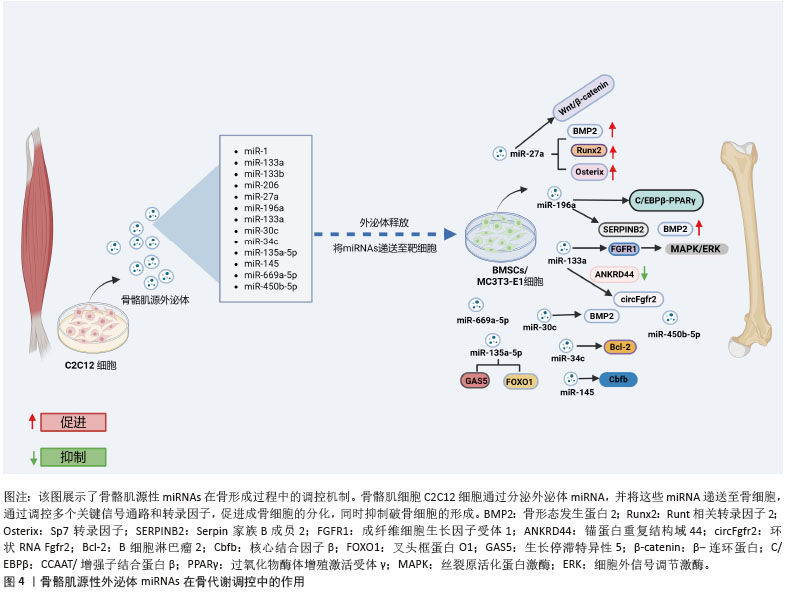
2.2.1 miR-1的调控机制 目前对于miR-1的具体机制研究较少[19-20],研究显示骨质疏松症患者miR-1-3p水平显著降低[21]。通过TargetScan和PicTar软件预测miR-1-3p的直接靶基因是分泌卷曲相关蛋白1 (secreted frizzled-related protein 1,SFRP1)。miR-1-3p过表达刺激小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化并抑制脂肪生成,而抗酒石酸盐酸性磷酸酶染色表明,体内抑制miR-1-3p表达提高了破骨细胞活性,提示miR-1-3p可能通过调节骨吸收来影响骨量。此外,miR-1-3p通过增强成骨细胞分化重要通路Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号传导促进骨形成[21]。综上,miR-1-3p通过分泌卷曲相关蛋白1抑制Wnt通路的激活,促进成骨细胞分化。miR-1-3p还能够将骨髓间充质干细胞的命运从脂肪定向为骨细胞,从而减少骨髓脂肪生成,具有预防骨髓脂肪肥胖的潜力。
2.2.2 miR-133调控机制 近期研究揭示了miR-133家族尤其是miR-133a-3p在骨代谢调控中的关键作用。过表达miR-133a-3p不仅显著抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖能力和存活率,同时也抑制其成骨分化能力,促进脂肪细胞分化[22],这表明miR-133a-3p在骨-脂代谢平衡中发挥着重要的调控作用。此外,体内实验表明,骨髓间充质干细胞特异性敲除miR-133a-3p可有效缓解去卵巢小鼠的骨质流失,进一步验证miR-133a-3p在骨质疏松发病机制中的关键作用,为骨质疏松症的治疗提供新的潜在靶点[22]。
在分子机制层面,miR-133a-3p与锚蛋白重复结构域44(ankyrin repeat domain 44,ANKRD44)之间存在直接的效应子-靶点关系。研究发现,去势小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞中miR-133a-3p表达显著上调,进一步功能验证表明,miR-133a-3p过表达显著抑制骨髓间充质干细胞中成骨相关基因的表达,导致碱性磷酸酶活性降低和矿化能力下降。值得注意的是,锚蛋白重复结构域44过表达能够逆转miR-133a-3p对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的抑制作用,这一发现进一步证实锚蛋白重复结构域44在miR-133a-3p介导的成骨调控网络中的核心地位[23]。在信号通路调控方面,成纤维细胞生长因子受体1作为丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)/细胞外信号调节激酶信号通路的关键上游调控因子,被确认为是 miR-133a-3p的重要靶点[22]。还有研究显示转录因子特异性蛋白1通过调控miR-133a-3p/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶3信号轴,加速骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[24]。此外,环状RNA Fgfr2作为miR-133a-3p的分子海绵,通过竞争性结合miR-133a-3p来调控其活性,从而影响成骨过程[25]。进一步研究还发现,miR-133a-3p 可通过靶向远端无翅型同源框蛋白3(distal-less homeobox 3,DLX3)和成骨因子Runt相关转录因子2抑制成骨分化[25],这些发现进一步揭示miR-133a-3p介导的成骨调控网络的复杂性。
综上,miR-133a-3p通过调控多个靶基因和信号通路,影响骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨与成脂分化,并在骨质疏松病理过程中发挥重要作用。miR-133a-3p在成纤维细胞生长因子受体1/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶轴、特异性蛋白1/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶3 轴及环状RNA介导的内源竞争RNA调控网络中均为关键角色,为骨质疏松的潜在治疗策略提供了新的理论依据。
2.2.3 miR-206的调控机制 miR-206在调节骨形成和成骨细胞分化中起关键作用。研究表明,miR-206过表达抑制成骨细胞分化[26]。miR-206通过靶向成骨细胞中的连接蛋白43(connexin 43,Cx43)抑制成骨细胞分化,导致小鼠骨量减少。研究通过两个不同数据库的计算方法,从众多潜在靶标基因中确定连接蛋白43,并通过miR-206 的异位表达显著下调荧光素酶活性,确定连接蛋白43是miR-206在体内的真正靶标。此外,在过表达miR-206转基因小鼠模型中发现,微型计算机断层扫描(micro-computed tomography,μCT)分析显示骨小梁和骨微结构受损,呈现低骨量表型;在蛋白水平,碱性磷酸酶2及连接蛋白43蛋白表达显著降低,而其他成骨基因Runt相关转录因子2和Osterix的表达不受影响,进一步表明miR-206通过连接蛋白43独立于Runt相关转录因子2和Osterix调节成骨细胞分化[26]。CHEN等[27]研究发现,成骨诱导第7天和第14天,miR-206 在人骨髓间充质干细胞中表达显著下调。此外,在骨髓间充质干细胞中过表达 miR-206会下调碱性磷酸酶活性和骨钙素的分泌以及降低成骨标志物Runt相关转录因子2和骨桥蛋白 mRNA水平。值得注意的是,miR-206通过靶向和抑制成骨分化关键指标谷氨酰胺酶的表达来抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。miR-206可以直接与谷氨酰胺酶mRNA的3’非翻译区结合。过表达miR-206的骨髓间充质干细胞中谷氨酰胺酶升高促进谷氨酰胺代谢和成骨分化能力恢复[27]。这提出了miR-206通过调节谷氨酰胺代谢介导的成骨机制的新见解,可能有助于开发针对骨骼疾病的治疗剂。
2.2.4 miR-27a
(1)miR-27a的调控机制:高通量测序分析结果显示,miR-27a-3p是C2C12细胞分泌的外泌体中丰度较高的miRNA之一[28]。通过基因本体(gene ontology,GO)和京都基因与基因组百科全书(Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes,KEGG)通路分析,进一步发现miR-27a的靶基因涉及多个生物学过程,包括间充质细胞分化、骨形成和骨骼发育,且在多个关键的成骨信号通路中发挥着重要作用,尤其是转化生长因子β/骨形态发生蛋白、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶和Wnt信号通路[29]。miR-23a簇(包括miR-27a、miR-23a和miR-24-2)基因敲除后,微型计算机断层扫描分析显示,基因敲除小鼠的股骨密度显著低于对照小鼠,这表明miR-23a簇的缺失显著干扰骨重塑并加剧了骨质疏松症的进展。尽管这一发现提示miRNA可能在骨代谢调控中发挥重要作用,但miR-27a是否导致骨代谢失调仍需要进一步研究。miR-27a在肌成纤维细胞中的表达能够促进成骨细胞分化[29]。当miR-27a-3p沉默时,骨骼肌源性外泌体的成骨分化促进作用被抑制[28],同时骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化标志物的表达降低[30-32],这进一步证明miR-27a-3p在成骨分化中的关键作用。
在分子机制方面,miR-27a通过抑制半胱天冬酶3/9和Bcl-2家族蛋白Bax的表达,显著提升碱性磷酸酶活性,并通过上调骨形态发生蛋白2、Runt相关转录因子2及Osterix等成骨标志基因的表达来驱动成骨分化和细胞增殖[33]。前列腺癌患者的转录组学分析进一步揭示,miR-27a-3p的表达量与成骨因子骨形态发生蛋白2的水平呈正相关[34]。然而,过表达miR-27a的研究表明,通过抑制转化生长因子β/骨形态发生蛋白超家族成员(如骨形态发生蛋白2、骨形态发生蛋白受体1A和Smad9)的表达,能够抑制成骨分化,反映出miR-27a在成骨过程中扮演着复杂的调节角色[35]。荧光素酶报告基因分析显示,miR-27a-3p通过其3’非翻译区靶向并调控骨形成早期反应基因Osterix表达,进一步抑制前成骨细胞分化,并促进骨形成[36]。生物信息学分析结合实验验证结果表明,miR-27a的靶基因磷酸肌醇3-激酶激活可以逆转miR-27a对人骨髓间充质干细胞分化的抑制作用[37]。此外,双荧光素酶报告基因检测还发现,miR-27a-3p能够靶向并调控过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ的表达[38]。在外泌体的作用下,miR-27a-3p的增加会导致其靶标腺瘤性结肠息肉病蛋白的表达下调,进而激活β-连环蛋白信号通路,促进成骨分化[39]。生物信息学分析和实验验证也显示,分泌卷曲相关蛋白1是miR-27a-3p的下游靶标。分泌卷曲相关蛋白1过表达可显著抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,并消除miR-27a-3p对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的促进作用,这一过程通过调节Wnt3a/β-连环蛋白信号通路实现[40]。转录组测序技术还表明,miR-27a-3p在原代小鼠成骨细胞和骨髓细胞中具有较高的表达水平[41]。尽管miR-27a-3p在骨骼肌源性外泌体中可能发挥一定的作用,但它在成骨过程中可能是次要调节因子。
综上,miR-27a在C2C12细胞分泌的骨骼肌源性外泌体中表现出较高的丰度,显著促进骨形成,并参与多个成骨相关的信号通路,如转化生长因子β/骨形态发生蛋白、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶和Wnt等。
(2)miR-27a参与肌-骨交叉对话相关疾病:已有研究表明,血清miR-27a-3p与肌肉质量密切相关。TASCA等[42-43]研究发现,肌萎缩性侧索硬化症患者和慢性肾病引起的肌肉萎缩患者血清miR-27a水平均显著下降,这提示因疾病引起的肌肉萎缩可能会下调miR-27a的分泌。来自骨质疏松患者的骨髓间充质干细胞分析表明,miR-27a表达显著降低骨形成相关基因表达,而脂肪生成相关基因表达增加。通过双荧光素酶报告基因检测发现miR-27a直接靶向肌细胞增强因子2c(myocyte enhancer factor 2c,Mef2c),在骨质疏松患者中,miR-27a表达水平与肌细胞增强因子2c表达呈负相关[44]。这表明,miR-27a不仅对骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化至关重要,还可能通过调控成骨相关因子,影响骨质疏松症的病理过程;进一步研究发现,miR-27a-5p通过靶向自噬相关基因4B(autophagy related 4B,Atg4B)的3’非翻译区直接抑制自噬相关基因4B的表达,进而促进成骨[45]。在股骨头坏死大鼠模型中,组学结果显示miR-27a下调与过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ(peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma,PPARγ)和骨形态发生蛋白拮抗因子1(gremlin 1,GREM1)的表达呈负相关。双荧光素酶报告基因检测进一步证实,过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ和骨形态发生蛋白拮抗因子1是miR-27a的直接靶点[46]。
综上,血清miR-27a-3p与肌肉质量密切相关,疾病如肌萎缩性侧索硬化症和慢性肾病可导致miR-27a-3p显著下降。miR-27a在骨质疏松症中表达减少,调控骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,并通过靶向肌细胞增强因子2c、自噬相关基因4B、过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ和骨形态发生蛋白拮抗因子1影响骨代谢,揭示其在骨质疏松等疾病中的关键作用。
(3)miR-27a与炎症:骨骼肌源性外泌体不仅在骨代谢中发挥重要作用,还具有显著抗氧化和抗炎功能。研究表明,过表达miR-27a能够促进体内新骨形成和骨整合,并通过改善体外条件下肿瘤坏死因子α对骨形成的抑制作用,正向调节成骨与血管生成的偶联[47]。
在炎症环境下,miR-27a的作用尤为突出。在卵巢切除小鼠模型中,血清肿瘤坏死因子α水平显著升高,同时骨骼组织中的miR-27a-3p表达显著降低。进一步研究发现,体外肿瘤坏死因子α的干预抑制了骨髓间充质干细胞中miR-27a-3p的表达,提示炎症因子对miR-27a的调节作用可能参与骨质疏松症的发展过程,这表明miR-27a不仅在骨形成中发挥作用,还可能通过调节炎症反应对骨代谢产生深远影响。此外,牙周炎患者的牙龈样本中miR-27a-5p水平较低,这进一步强调miR-27a在炎症反应中的重要角色。靶点验证分析揭示,磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物(phosphatase and tensin homolog,PTEN)是miR-27a的直接靶点,通过阻断磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物的表达,可以有效减少体内外的炎症反应[48],这为miR-27a作为抗炎治疗靶点提供新的线索,尤其在与骨代谢相关的炎症性疾病中,miR-27a的调节作用可能为治疗策略的优化提供新的思路。
2.2.5 其他关键miRNAs的调控作用 越来越多的证据表明miRNAs在成骨细胞分化中的重要作用,尤其是通过成肌细胞外泌体传递这些miRNAs调控成骨细胞的增殖、分化和矿化过程,揭示了它们在骨质疏松等骨代谢疾病中的潜在应用。
WANG等[49]研究表明,miR-23a、miR-30c、miR-34c等miRNAs通过调控Runt相关转录因子2等成骨因子的表达,促进成骨细胞的增殖和分化,加速新骨的形成。例如,miR-30c通过调节骨形态发生蛋白信号通路,抑制骨发育过程中的缺陷[49]。Linc01133上调可促进人牙周韧带干细胞成骨分化,抑制miR-30c后这一作用消失[50]。这表明,miR-30c在骨细胞分化过程中的调控作用不仅涉及直接靶向基因,还与非编码RNA的互作密切相关。
通过Target 数据库预测miR-34c-5p和Bcl-2之间的靶向结合位点,揭示miR-34c-5p在骨代谢中的潜在作用。miR-34c-5p上调显著抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖,同时促进碱性磷酸酶、Runt相关转录因子2和骨钙素的表达,显示miR-34c-5p对成骨分化的促进作用;相反,miR-34c-5p抑制剂则逆转这些效应。Bcl-2上调逆转了miR-34c-5p的影响[51]。脂多糖刺激后miR-34c显著上调,miR-34c过表达显著抑制碱性磷酸酶、Runt相关转录因子2、骨钙素和骨形态发生蛋白2等成骨基因表达。碱性磷酸酶活性分析和茜素红S染色显示,成骨分化和矿化结节形成均因miR-34c的过表达而显著逆转[52],这表明miR-34c在骨代谢中的复杂作用,提示其可能在骨质疏松等疾病的调控中扮演重要角色。
miR-145被确定为核心结合因子β亚基(core binding factor beta subunit,Cbfb)基因的关键调节因子。miR-145与miR-34c合作降低了内源性核心结合因子β亚基表达并抑制成骨细胞生成,表明miR-145可能在体内骨再生中起抑制作用[53]。
miR-196a-5p在骨修复过程中可能通过增强骨生成信号传导发挥重要作用。通过微型计算机断层扫描和组织病理学分析结果显示,miR-196a-5p过表达能够显著促进大鼠颅骨缺损后的新骨再生,并在12周后显著促进骨缺损的闭合[54]。通过对骨髓间充质干细胞进行mRNA微阵列分析,发现miR-196a-5p过表达引起959个差异表达基因出现,其中34个上调和925个下调。Serpin家族B成员2(serpin family b member 2,SERPINB2)是miR-196a-5p的潜在靶基因之一,Serpin家族B成员2缺失显著增强了间充质干细胞的碱性磷酸酶活性和体外矿化能力[54]。实验结果表明,骨骼肌源性外泌体中富含miR-196a-5p,转染miR-196a-5p到MC3T3-E1细胞中,不仅显著增加Osterix、碱性磷酸酶和骨钙素的mRNA水平,而且能够显著提高骨形态发生蛋白2刺激下MC3T3-E1成骨前体细胞中Osterix和碱性磷酸酶的mRNA表达水平,这提示miR-196a-5p可能是这一过程的关键调控因子。在绝经期骨质疏松患者的研究中,发现赖氨酸氧化酶样1反义RNA1(lysyl oxidase like 1 antisense RNA1,LOXL1-AS1)的表达显著升高,并且在骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中赖氨酸氧化酶样1反义RNA1表达下降,说明过表达赖氨酸氧化酶样1反义RNA1抑制了成骨分化,同时促进了成脂分化。通过荧光素酶报告基因分析,进一步验证赖氨酸氧化酶样1反义RNA1是miR-196a-5p的竞争性内源RNA,揭示miR-196a-5p在miRNA调控网络中的关键作用。miR-196a-5p通过靶向调控高迁移率族蛋白A2基因的表达,反向调节了骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨与成脂分化[55]。
在骨质疏松小鼠模型中,miR-135a-5p表达上调,而生长抑制转录因子5(growth arrest-specific 5,GAS5)和叉头框蛋白O1(forkhead box O1,FOXO1)表达水平显著下降[56]。进一步研究发现,生长抑制转录因子5过表达可促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,这揭示非编码RNA之间复杂的相互调控关系在骨代谢中的重要性[56]。
综上,成肌细胞外泌体中miRNAs通过与多种信号通路的相互作用,调控成骨细胞的增殖、分化及矿化过程。尤其是miR-30c、miR-34c等,通过靶向多种骨生成相关因子,如Runt相关转录因子2、Bcl-2、碱性磷酸酶等,促进或抑制骨代谢过程。miR-196a-5p通过调节多条信号通路,尤其是骨形态发生蛋白、Serpin家族B成员2以及CCAAT/增强子结合蛋白β/过氧化物酶体增殖激活受体γ途径,在骨形成和修复过程中起着至关重要的作用。此外,miR-196a-5p不仅通过直接影响成骨标志基因的表达促进骨生成,还可能通过间接调控脂肪细胞分化和骨脂肪平衡。这些发现为开发基于miRNA的骨质疏松治疗策略提供了理论依据,通过进一步探索miRNA与外泌体在骨代谢中的协同作用,可能会为临床骨病的治疗提供新的靶点和策略。
2.3 骨骼肌源性外泌体中蛋白质在骨代谢调控中的作用 随着骨代谢研究的深入,骨骼肌源性外泌体中多种蛋白质的作用逐渐受到关注。遗憾的是,目前没有研究聚焦于骨骼肌源性外泌体中具体有哪些蛋白质,因此按照被发现与骨形成相关的时间先后顺序综述。胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5(insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5,IGFBP-5)最早被发现可以通过与胰岛素样生长因子1(insulin-like growth factor 1,IGF-1)的协同作用促进骨形成,调控成骨分化。随后,研究揭示热休克蛋白(heat shock proteins,HSPs)通过调控多个信号通路(如骨形态发生蛋白、转化生长因子β、Hippo/Yes相关蛋白)参与骨重塑。最后,补体C1q肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白15 (C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein 15,CTRP15)和配对相关同源框蛋白2(Paired Related Homeobox 2,PRRX2)能够调节骨代谢,补体C1q肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白15负向调节成骨细胞分化,配对相关同源框蛋白2则促进成骨分化并增强骨形成。近期研究表明,这些蛋白通过骨骼肌与骨骼的信号传递影响骨形成、修复和重塑,进一步强调了骨骼肌源性外泌体在骨代谢中的关键作用(表1)。
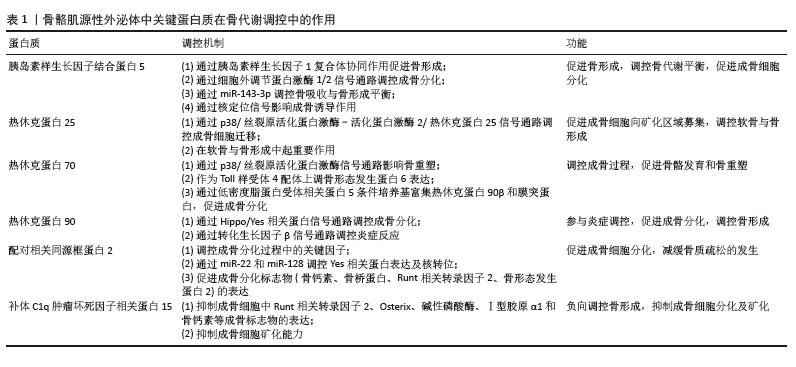
2.3.1 胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5 骨骼肌源性外泌体含有多种生物活性因子,在肌肉与骨的相互作用中发挥重要作用。其中,胰岛素样生长因子1及其结合蛋白家族成员在骨代谢调控过程中尤为关键。研究发现,C2C12成肌细胞衍生的骨骼肌源性外泌体中含有信号转导蛋白——胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5,这一蛋白在骨骼中的含量随年龄增加而下降[57]。在肢端肥大症患者中,骨小梁骨的微型计算机断层扫描结果和生物力学能力均表现出下降趋势,而这一变化与血清中胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5水平呈正相关[58]。在动物实验中,胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5已被证明能够诱导局部骨形成,特别是在小鼠和大鼠模型中,胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5在骨消耗期显著增加,且呈剂量依赖性[59]。单独使用胰岛素样生长因子1或胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5并未显著改善骨量,而胰岛素样生长因子1与胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5联合使用则明显增强股骨和胫骨的皮质厚度、面积以及矿物质密度,提示胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5可能通过骨膜作用促进骨形成,这进一步强调胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5在胰岛素样生长因子1信号调控中的协同作用。此外,胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5在人骨髓间充质干细胞早期成骨分化过程中显著增加,表明其在成骨分化过程中发挥重要作用。实验表明,过表达胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5促进细胞外调节蛋白激酶1/2信号通路激活,进而促进成骨分化过程,而沉默胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5表达则抑制这一现象,表明胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5可能通过细胞外调节蛋白激酶1/2信号通路调控成骨细胞的分化和功能[60]。值得注意的是,富含miR-143-3p的外泌体能够沉默胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5的表达,从而扰乱成骨-破骨细胞平衡,导致牙周骨的破坏[61],这一发现揭示胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5 在骨吸收与骨形成动态平衡过程中的重要性。胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5 还可通过核定位信号影响生物学功能。研究发现,胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5的核定位信号缺失会阻止其进入细胞核,消除其对牙髓间充质干细胞的促进作用[62]。这种核定位的丧失显著削弱胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5通过c-Jun氨基末端激酶和细胞外调节蛋白激酶信号通路对牙髓间充质干细胞的成骨诱导作用,表明胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5的核定位可能是其调控成骨分化的关键因素。
综上,胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5作为骨骼肌源性外泌体中的关键因子,在成骨调控和骨代谢平衡中发挥重要作用,其通过胰岛素样生长因子1复合体协同作用、细胞外调节蛋白激酶1/2介导的信号通路、miR-143-3p调控及核定位机制等多个分子机制影响骨形成和修复过程。尤其是在骨代谢紊乱状态下,胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5可能通过调节骨膜作用、成骨细胞分化及骨-破骨细胞动态平衡,展现出作为治疗骨质疏松症及骨损伤的潜在靶点的应用前景。
2.3.2 热休克蛋白
(1)热休克蛋白的调控机制:热休克蛋白在细胞的应激反应和蛋白质稳态中发挥着重要作用,特别是在骨代谢和成骨过程中。热休克蛋白作为分子伴侣,不仅调控蛋白质折叠、稳定性和降解,还能通过调控多个信号通路影响骨骼的发育、重塑和修复。研究表明,热休克蛋白25、热休克蛋白70和热休克蛋白90在C2C12成肌细胞衍生的骨骼肌源性外泌体中富集,并在成骨细胞分化过程中发挥关键作用。热休克蛋白不仅是细胞应激反应的重要调节因子,还在骨形态发生蛋白信号通路、Hippo/Yes相关蛋白信号通路及转化生长因子β介导的成骨调控机制中发挥重要功能。
热休克蛋白25在骨代谢过程中通过p38/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶-活化蛋白激酶2/热休克蛋白25信号通路调控成骨细胞迁移。研究发现,在骨形态发生蛋白2处理的骨髓间充质干细胞中,热休克蛋白25可促进成骨细胞向矿化区域募集,而不依赖于细胞分裂控制蛋白42或p21激活激酶活性,提示热休克蛋白25可能与骨形态发生蛋白信号通路的调节密切相关[63]。此外,研究发现成人长骨生长板以及喉和气管软骨中的肥厚软骨细胞中有热休克蛋白25免疫反应性。静息期或增殖期的软骨细胞均未表现出热休克蛋白25免疫反应性。在胚胎下颌骨中,Meckel软骨前部和中间部的静止和增殖软骨细胞从妊娠第12天到第15天显示出热休克蛋白25免疫反应性,而后部的软骨细胞没有免疫反应性;在妊娠第16天后,Meckel软骨中的整体热休克蛋白25免疫反应性强度显著降低,并且在位于Meckel软骨退化部分的肥大软骨细胞中没有检测到免疫反应性。将热休克蛋白25 mRNA的反义寡核苷酸应用于第10天胚胎下颌外植体的培养基上,抑制了Meckel 软骨前部和中部的发育[64],进一步验证热休克蛋白25在软骨与骨形成中的重要作用,但这一过程与生长发育的具体时间有关。
热休克蛋白70作为一种分子伴侣,协调蛋白质的折叠与稳态,对于骨骼发育具有重要作用。研究发现,热休克蛋白70抑制剂通过成骨细胞中的p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路,促使前列腺素E1刺激下的白细胞介素6合成,进一步影响骨重塑[65]。此外,热休克蛋白70还作为内源性天然Toll样受体4的配体,能够上调骨形态发生蛋白6的表达,从而促进成骨过程。溶酶体关联膜蛋白3过表达则通过释放热休克蛋白70,激活Toll样受体4信号通路,进一步影响骨细胞功能和骨骼代谢[66]。
热休克蛋白90在成骨细胞分化过程中也起到了关键调节作用。研究发现,低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白5 (low density lipoprotein receptor related protein 5,LRP5)过表达可在条件培养基中富集热休克蛋白90β和重组膜突蛋白(recombinant moesin,MSN),从而增强分泌型磷蛋白1/骨桥蛋白表达,并促进成骨分化。热休克蛋白90ab1和重组膜突蛋白是非典型的肿瘤抑制蛋白。在机制上,热休克蛋白90ab1免疫沉淀潜伏的转化生长因子β和灭活的转化生长因子β[67]。敲低热休克蛋白90β,但不敲低热休克蛋白90α,抵消Hippo信号传导的大肿瘤抑制激酶1 (large tumor suppressor homolog 1,LATS1)蛋白水平,导致大肿瘤抑制因子失活和Yes相关蛋白中PDZ结合基序的转录共激活因子的激活,抵消成骨细胞分化。间充质干细胞中大肿瘤抑制基因消融足以消除热休克蛋白90抑制诱导的成骨细胞分化,这表明是热休克蛋白90β而不是热休克蛋白90α伴侣阻止Smad蛋白E3泛素连接酶1介导和泛素化依赖性大肿瘤抑制激酶蛋白酶体降解[68],从而维持Hippo/Yes相关蛋白轴的活性,促进成骨过程。
(2)热休克蛋白与疾病和炎症:在成骨不全症中,突变导致前胶原在内质网腔中错误折叠,并逃脱内质网质量控制机制,从而激活整合应激反应[69]。研究发现,在G610C突变型成骨细胞中,整合应激反应受线粒体热休克蛋白70和激活转录因子5调控[69],提示热休克蛋白在成骨不全症的病理进程中可能发挥重要作用。
研究发现,热休克蛋白90抑制剂17-二甲基胺乙基衍生物(17-DMAG)和奥那司匹(AT13387)增强转化生长因子β诱导的热休克蛋白27表达,转化生长因子β抑制剂改善这一现象。热休克蛋白90抑制剂格尔德霉素(Geldanamycin)、奥那司匹和17-二甲基胺乙基衍生物不影响转化生长因子β刺激的Smad2磷酸化。格尔德霉素不影响转化生长因子β刺激的p44/p42丝裂原活化蛋白激酶或p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶磷酸化,但显著增强转化生长因子β刺激的应激激活蛋白激酶/c-Jun氨基末端激酶磷酸化。奥那司匹还增加应激激活蛋白激酶/c-Jun氨基末端激酶磷酸化。此外,SP600125是应激激活蛋白激酶/c-Jun氨基末端激酶的特异性抑制剂,显著抑制奥那司匹或格尔德霉素对转化生长因子β诱导的热休克蛋白27表达水平的增强作用[70],这提示热休克蛋白90可能在转化生长因子β介导的炎症调控过程中发挥作用。
综上,热休克蛋白通过参与多条信号通路和分子机制在骨代谢和成骨分化中发挥关键作用,特别是在骨质疏松症、成骨不全症及骨炎症相关疾病的调控过程中,热休克蛋白可能作为潜在的靶点,有望为开发新的治疗策略提供重要依据。未来的研究可进一步探索热休克蛋白介导的分子机制,以推动热休克蛋白靶向疗法在骨代谢性疾病中的临床应用。
2.3.3 配对相关同源框蛋白2的调控机制 配对相关同源框蛋白2是配对相关同源框蛋白家族中的一类关键转录因子,广泛参与胚胎发育过程中颅面和肢体的形成[71]。近年来的研究表明,配对相关同源框蛋白2不仅在肌肉发育过程中发挥重要作用,还在骨代谢调控尤其是成骨分化过程中具有关键的调节作用。研究发现,C2C12来源的骨骼肌源性外泌体能显著提高成骨细胞的分化能力,特别是在茜素红染色实验中表现出明显的矿化沉积。沉默配对相关同源框蛋白2后,这一效果被完全抑制,说明配对相关同源框蛋白2的表达对外泌体在骨形成中的作用至关重要。小鼠配对相关同源框蛋白2突变模型出现明显的骨骼发育缺陷,这进一步验证配对相关同源框蛋白2在骨骼形成中的关键作用。此外,在骨髓间充质干细胞中,配对相关同源框蛋白2过表达促进了多个成骨分化标志物如骨钙素、骨桥蛋白、Runt相关转录因子2和骨形态发生蛋白2的mRNA及蛋白表达,而沉默配对相关同源框蛋白2则逆转了这一效果[72]。
从机制层面看,配对相关同源框蛋白2调控成骨分化过程中的关键因子,沉默配对相关同源框蛋白2消除肿瘤坏死因子对Osterix的抑制作用,增强Osterix的表达[73]。此外,配对相关同源框蛋白2还能直接与miR-22启动子结合,促进其转录和表达,从而通过miR-128海绵效应增强成骨调节因子Yes相关蛋白的表达及核转位,最终促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[72]。敲除配对相关同源框蛋白2能够显著抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[72]。
综上所述,配对相关同源框蛋白2作为骨骼肌源性外泌体的重要组成部分,调控骨代谢过程中的多种信号通路,其作用不仅限于促进或抑制骨形成,还涉及复杂的转录调控和miRNA机制。通过miR-22和miR-128的调控,配对相关同源框蛋白2促进成骨分化,减缓骨质疏松的发生。
2.3.4 补体C1q肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白15 补体C1q肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白15作为一种主要在骨骼肌组织中表达的肌因子,具有与脂肪细胞因子脂联素类似的结构域结构。这一蛋白质家族成员在调节肌肉和骨骼相互作用中可能发挥重要作用,尤其在骨骼肌与骨代谢之间的跨系统信号传递中。一项研究发现,补体C1q肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白15处理成骨细胞24 h,显著抑制多个关键成骨因子表达,包括Runt相关转录因子2、Osterix、碱性磷酸酶、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白和骨钙素等成骨标志物mRNA水平[74]。进一步的研究发现,补体C1q肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白15对碱性磷酸酶基因的抑制作用呈剂量依赖性,提示补体C1q肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白15在短时间内即可显著改变成骨细胞的转录活性。除了对基因表达的影响外,补体C1q肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白15还通过抑制成骨细胞矿化能力进一步影响骨形成[74],这一现象进一步验证补体C1q肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白15在骨形成过程中的负向调控作用,并提示其可能通过Runt相关转录因子2/ Osterix/碱性磷酸酶轴或Ⅰ型胶原蛋白/骨钙素途径影响成骨细胞的终末分化及矿化功能。
综上,补体C1q肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白15作为骨骼肌源性分泌蛋白,在成骨细胞骨形成中发挥负向调控作用。通过抑制Runt相关转录因子2、Osterix、碱性磷酸酶、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白和骨钙素等成骨关键基因的表达,显著降低成骨细胞的矿化能力,补体C1q肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白15在肌肉-骨骼系统的信号传递中扮演了重要的抑制性作用。这些发现不仅深化了对补体C1q肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白15在骨代谢调控中功能的认识,也提示其可能作为肌肉-骨骼交互作用中的潜在调控靶点,为肌肉萎缩相关的骨代谢异常及骨质疏松的干预提供新的研究方向。
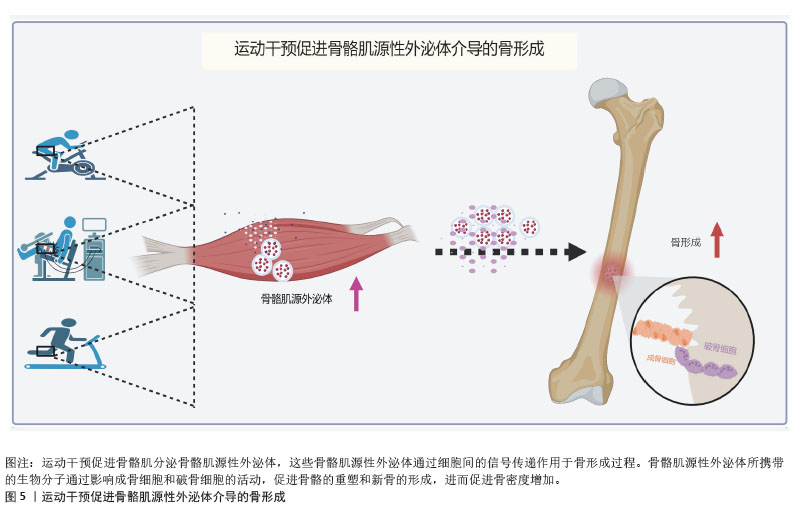
2.4 运动干预对骨骼肌源性外泌体介导骨形成的影响 过往研究显示,运动可促进骨骼肌源性外泌体及其产物的分泌,单次运动会加速骨骼肌源性外泌体的分泌,调节身体对运动训练的代谢反应[75];长期运动也能促进骨骼肌源性外泌体生成[76]。蛋白质组学分析证实,耐力运动可诱导热休克蛋白60快速释放至循环中,并增加线粒体拷贝数[77]。然而,这一发现并不意味着所有的联合运动方案都可以诱导外泌体释放的增加。例如,在0-24 h内,在站立跳跃和下坡跑步活动组合后,未检测到血浆外泌体数量的变化[78]。在抗阻训练过程中,骨骼肌中骨骼肌源性外泌体中的miR-133a表达增加,调节机体能量代谢和肌肉相关蛋白,这提示运动可能会诱导骨骼肌中外泌体的生物发生和释放。而运动对身体两大器官骨-骨骼肌的作用尤为显著,骨骼肌与骨组织之间存在密切的相互作用,运动是否促进骨骼肌分泌骨骼肌源性外泌体及其携带的生物活性因子在骨代谢调节中发挥重要作用目前暂不明确。近年来,新型的模拟运动干预的治疗方式神经肌肉电刺激(neuromuscular electrical stimulation,NMES)逐渐受到关注。神经肌肉电刺激被视为肌肉收缩的被动模式,通常用于治疗肌肉减少症或骨质疏松症。虽然神经肌肉电刺激本质上是一种被动干预方法,与传统的主动运动干预有所不同,但两者在生理反应上具有一定的重叠性。神经肌肉电刺激能够模拟肌肉收缩,并有效改善肌肉力量、骨密度等生理参数,因此在临床上常作为传统运动干预的补充手段,尤其适用于运动能力受限的患者。
最新研究发现,去神经支配的骨骼肌在神经肌肉电刺激干预下能够有效改善骨质疏松症[79],其机制之一是通过外泌体作为信号载体促进骨形成。神经肌肉电刺激诱导的肌肉收缩显著抑制肌肉萎缩,并且随着肌肉肥大的发生,骨质疏松症的病理表型得到显著改善,通过NanoSight分析测量外泌体中的颗粒浓度,观察到骨质疏松大鼠体内颗粒浓度明显低于假手术组,且神经肌肉电刺激干预8周后血浆中颗粒浓度明显升高。更有趣的是,单腿神经肌肉电刺激干预能够显著改善大鼠两侧腿的骨质疏松症,这一现象可能与外泌体介导的长期内分泌效应有关。为验证这一假设,研究者向失神经支配的大鼠体内注射外源性骨骼肌源性外泌体,结果发现骨质疏松症得到了显著改善。此外,研究还发现,来自萎缩骨骼肌的外泌体会抑制MC3T3-E1成骨细胞的分化,而来自神经肌肉电刺激处理骨骼肌的外泌体则能够加速体外成骨分化[79]。将骨骼肌来源外泌体与分化的MC3T3-E1成骨细胞共同培养后,成骨相关基因的表达上调,碱性磷酸酶活性和矿化沉积也显著增强[79-80]。神经肌肉电刺激诱导的骨骼肌收缩能够在一定程度上逆转骨质疏松症的发生,表明骨骼肌源性外泌体作为传递成骨信号的载体,在肌肉与骨骼之间的跨组织信号传递中发挥着重要作用。
遗憾的是,尽管越来越多的证据支持运动/肌肉收缩可诱导骨骼肌源性外泌体的生物发生和释放,但由于体内外泌体追踪和鉴定的复杂性,目前仍然难以精确识别运动后循环外泌体的来源。例如,运动后血液中外泌体浓度的急剧升高,是否全部来自骨骼肌仍未完全确定。此外,外泌体内miRNA、蛋白质和脂质在骨形成中的具体作用仍需进一步探索。因此,未来研究需要进一步优化外泌体分离和溯源技术,并结合动物模型和临床研究,揭示不同运动模式(有氧运动、抗阻训练、神经肌肉电刺激)对骨骼肌源性外泌体调控骨代谢的影响,从而为骨质疏松症及其他骨代谢相关疾病的干预提供更加精准的策略[81](图5)。
| [1] RONG S, WANG L, PENG Z, et al. The mechanisms and treatments for sarcopenia: could exosomes be a perspective research strategy in the future? J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2020;11(2):348-365. [2] HARDING C, STAHL P. Transferrin recycling in reticulocytes: pH and iron are important determinants of ligand binding and processing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983;113(2):650-658. [3] PAN BT, JOHNSTONE RM. Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: selective externalization of the receptor. Cell. 1983; 33(3):967-978. [4] HESSVIK NP, LLORENTE A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(2): 193-208. [5] WOLLERT T, HURLEY JH. Molecular mechanism of multivesicular body biogenesis by ESCRT complexes. Nature. 2010;464(7290):864-869. [6] BAIETTI MF, ZHANG Z, MORTIER E, et al. Syndecan-syntenin-ALIX regulates the biogenesis of exosomes. Nat Cell Biol. 2012; 14(7):677-685. [7] VILLARROYA-BELTRI C, GUTIÉRREZ-VÁZQUEZ C, SÁNCHEZ-CABO F, et al. Sumoylated hnRNPA2B1 controls the sorting of miRNAs into exosomes through binding to specific motifs. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2980. [8] VILLARROYA-BELTRI C, BAIXAULI F, GUTIÉRREZ-VÁZQUEZ C, et al. Sorting it out: regulation of exosome loading. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014;28:3-13. [9] GUESCINI M, GUIDOLIN D, VALLORANI L, et al. C2C12 myoblasts release micro-vesicles containing mtDNA and proteins involved in signal transduction. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316(12):1977-1984. [10] MIAO C, ZHANG W, FENG L, et al. Cancer-derived exosome miRNAs induce skeletal muscle wasting by Bcl-2-mediated apoptosis in colon cancer cachexia. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;24:923-938. [11] GUO L, QUAN M, PANG W, et al. Cytokines and exosomal miRNAs in skeletal muscle-adipose crosstalk. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2023;34(10):666-681. [12] NI P, YANG L, LI F. Exercise-derived skeletal myogenic exosomes as mediators of intercellular crosstalk: a major player in health, disease, and exercise. J Physiol Biochem. 2023;79(3):501-510. [13] FORTERRE A, JALABERT A, CHIKH K, et al. Myotube-derived exosomal miRNAs downregulate Sirtuin1 in myoblasts during muscle cell differentiation. Cell Cycle. 2014; 13(1):78-89. [14] 李然,王中奇,牛芮涵,等.衰老小鼠骨骼肌组织外泌体对骨代谢调控作用的研究[J].解放军医学院学报,2024,45(5): 509-515+534. [15] XU Q, CUI Y, LUAN J, et al. Exosomes from C2C12 myoblasts enhance osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 pre-osteoblasts by delivering miR-27a-3p. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018; 498(1):32-37. [16] ARAB F, AGHAEE BAKHTIARI SH, PASDAR A, et al. Evaluation of osteogenic induction potency of miR-27a-3p in adipose tissue-derived human mesenchymal stem cells (AD-hMSCs). Mol Biol Rep. 2023;50(2):1281-1291. [17] XU JF, YANG GH, PAN XH, et al. Altered microRNA expression profile in exosomes during osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2014; 9(12):e114627. [18] MYTIDOU C, KOUTSOULIDOU A, KATSIOLOUDI A, et al. Muscle-derived exosomes encapsulate myomiRs and are involved in local skeletal muscle tissue communication. FASEB J. 2021;35(2): e21279. [19] HENSLEY AP, MCALINDEN A. The role of microRNAs in bone development. Bone. 2021;143:115760. [20] BEMBEN DA, CHEN Z, BUCHANAN SR. Bone-Regulating MicroRNAs and Resistance Exercise: A Mini-Review. Osteology. 2022; 2(1):11-20. [21] GU H, SHI S, XIAO F, et al. MiR-1-3p regulates the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells to prevent osteoporosis by targeting secreted frizzled-related protein 1. Bone. 2020;137:115444. [22] WANG G, WAN L, ZHANG L, et al. MicroRNA-133a Regulates the Viability and Differentiation Fate of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells via MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway by Targeting FGFR1. DNA Cell Biol. 2021;40(8):1112-1123. [23] LI M, SHEN YJ, CHAI S, et al. miR-133a-3p inhibits the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by regulating ankyrin repeat domain 44. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2021;40(4): 329-339. [24] ZHONG L, SUN Y, WANG C, et al. SP1 regulates BMSC osteogenic differentiation through the miR-133a-3p/MAPK3 axis : SP1 regulates osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024; 19(1):396. [25] XU C, XU Z, LI G, et al. CircFgfr2 promotes osteogenic differentiation of rat dental follicle cells by targeting the miR-133a-3p/DLX3 signaling pathway. Heliyon. 2024; 10(11):e32498. [26] INOSE H, OCHI H, KIMURA A, et al. A microRNA regulatory mechanism of osteoblast differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(49):20794-20799. [27] CHEN Y, YANG YR, FAN XL, et al. miR-206 inhibits osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by targetting glutaminase. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(3):BSR20181108. [28] KYEI B, ODAME E, LI L, et al. Knockdown of CDR1as Decreases Differentiation of Goat Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cells via Upregulating miR-27a-3p to Inhibit ANGPT1. Genes (Basel). 2022;13(4):663. [29] ZHANG H, LUAN J, CUI Y, et al. Loss of miR-23a cluster in skeletal muscle can suppress bone remodeling. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2021;10(2):109-113. [30] LAI G, ZHAO R, ZHUANG W, et al. BMSC-derived exosomal miR-27a-3p and miR-196b-5p regulate bone remodeling in ovariectomized rats. PeerJ. 2022;10:e13744. [31] OU-YANG Y, DAI MM. Screening for genes, miRNAs and transcription factors of adipogenic differentiation and dedifferentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):46. [32] DU G, CHENG X, ZHANG Z, et al. TGF-Beta Induced Key Genes of Osteogenic and Adipogenic Differentiation in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells and MiRNA-mRNA Regulatory Networks. Front Genet. 2021;12:759596. [33] BAI Y, LIU Y, JIN S, et al. Expression of microRNA‑27a in a rat model of osteonecrosis of the femoral head and its association with TGF‑β/Smad7 signalling in osteoblasts. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(2): 850-860. [34] FURESI G, DE JESUS DOMINGUES AM, ALEXOPOULOU D, et al. Exosomal miRNAs from Prostate Cancer Impair Osteoblast Function in Mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1285. [35] GONG Y, XU F, ZHANG L, et al. MicroRNA expression signature for Satb2-induced osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow stromal cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014; 387(1-2):227-239. [36] XU Y, LI D, ZHU Z, et al. miR‑27a‑3p negatively regulates osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3‑E1 preosteoblasts by targeting osterix. Mol Med Rep. 2020; 22(3):1717-1726. [37] TANG J, YU H, WANG Y, et al. miR-27a promotes osteogenic differentiation in glucocorticoid-treated human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by targeting PI3K. J Mol Histol. 2021;52(2):279-288. [38] CUI Y, HUANG T, ZHANG Z, et al. The potential effect of BMSCs with miR-27a in improving steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):21051. [39] KITASE Y, BARRAGAN L, QING H, et al. Mechanical induction of PGE2 in osteocytes blocks glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis through both the β-catenin and PKA pathways. J Bone Miner Res. 2010; 25(12):2657-2668. [40] ZHANG DF, JIN XN, MA X, et al. Tumour necrosis factor α regulates the miR-27a-3p-Sfrp1 axis in a mouse model of osteoporosis. Exp Physiol. 2024;109(7): 1109-1123. [41] TAKADA Y, TAKAFUJI Y, MIZUKAMI Y, et al. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Blunts the Osteogenic Effects of Muscle Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles by Affecting Muscle Cells. Calcif Tissue Int. 2023;112(3): 377-388. [42] TASCA E, PEGORARO V, MERICO A, et al. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers of muscle differentiation and atrophy in ALS. Clin Neuropathol. 2016;35(1):22-30. [43] WANG B, ZHANG C, ZHANG A, et al. MicroRNA-23a and MicroRNA-27a Mimic Exercise by Ameliorating CKD-Induced Muscle Atrophy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017; 28(9):2631-2640. [44] YOU L, PAN L, CHEN L, et al. MiR-27a is Essential for the Shift from Osteogenic Differentiation to Adipogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(1):253-265. [45] LI X, CHEN R, LI Y, et al. miR-27a-5p-Abundant Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived From Epimedium-Preconditioned Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells Stimulate Osteogenesis by Targeting Atg4B-Mediated Autophagy. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:642646. [46] GU C, XU Y, ZHANG S, et al. miR-27a attenuates adipogenesis and promotes osteogenesis in steroid-induced rat BMSCs by targeting PPARγ and GREM1. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38491. [47] WU X, GU Q, CHEN X, et al. MiR-27a targets DKK2 and SFRP1 to promote reosseointegration in the regenerative treatment of peri-implantitis. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(1):123-134. [48] DENG L, HUO PC, FENG MT, et al. miR-27a-5p alleviates periodontal inflammation by targeting phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2023;38(4):309-320. [49] WANG W, WANG D, LI X, et al. Toxicity mechanisms regulating bone differentiation and development defects following abnormal expressions of miR-30c targeted by triclosan in zebrafish. Sci Total Environ. 2022;850:158040. [50] LI Q, ZHOU H, WANG C, et al. Long non-coding RNA Linc01133 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells via microRNA-30c / bone gamma-carboxyglutamate protein axis. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):9602-9612. [51] LIU B, GAN W, JIN Z, et al. The Role of miR-34c-5p in Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int J Stem Cells. 2021;14(3):286-297. [52] LIU J, LI D, SUN X, et al. Icariine Restores LPS-Induced Bone Loss by Downregulating miR-34c Level. Inflammation. 2016;39(5): 1764-1770. [53] FUKUDA T, OCHI H, SUNAMURA S, et al. MicroRNA-145 regulates osteoblastic differentiation by targeting the transcription factor Cbfb. FEBS Lett. 2015;589(21): 3302-3308. [54] WANG Y, ZHANG S, YANG H, et al. MicroRNA-196a-5p overexpression in Wharton’s jelly umbilical cord stem cells promotes their osteogenic differentiation and new bone formation in bone defects in the rat calvarium. Cell Tissue Res. 2022;390(2):245-260. [55] ZHANG L, XIE H, LI S. LncRNA LOXL1-AS1 controls osteogenic and adipocytic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in postmenopausal osteoporosis through regulating the miR-196a-5p/Hmga2 axis. J Bone Miner Metab. 2020;38(6):794-805. [56] WANG X, ZHAO D, ZHU Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA GAS5 promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by regulating the miR-135a-5p/FOXO1 pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2019;496:110534. [57] MOHAN S, BAYLINK DJ. Serum insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-4 and IGFBP-5 levels in aging and age-associated diseases. Endocrine. 1997;7(1):87-91. [58] UELAND T, EBBESEN EN, THOMSEN JS, et al. Decreased trabecular bone biomechanical competence, apparent density, IGF-II and IGFBP-5 content in acromegaly. Eur J Clin Invest. 2002;32(2):122-128. [59] BAUSS F, LANG K, DONY C, et al. The complex of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-I (rhIGF-I) and its binding protein-5 (IGFBP-5) induces local bone formation in murine calvariae and in rat cortical bone after local or systemic administration. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2001;11(1):1-9. [60] ZHANG ZM, MIN L, JIANG DL, et al. Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 5: an Important Regulator of Early Osteogenic Differentiation of hMSCs. Folia Biol (Praha). 2021;67(3):118-125. [61] XIAO J, DENG Y, XIE J, et al. Apoptotic vesicles from macrophages exacerbate periodontal bone resorption in periodontitis via delivering miR-143-3p targeting Igfbp5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):658. [62] SUN Z, LI J, LIU H, et al. Insulin-Like Growth Factor-Binding Protein 5 Promotes the Cell Proliferation and Osteogenic Potential of Dental Pulp Stem Cells Dependent on Its Nuclear Localisation Sequence. J Oral Rehabil. 2024;51(12):2664-2674. [63] GAMELL C, SUSPERREGUI AG, BERNARD O, et al. The p38/MK2/Hsp25 pathway is required for BMP-2-induced cell migration. PLoS One. 2011;6(1):e16477. [64] SHIMADA M, YAMAMOTO M, WAKAYAMA T, et al. Different expression of 25-kDa heat-shock protein (Hsp25) in Meckel’s cartilage compared with other cartilages in the mouse. Anat Embryol (Berl). 2003;206(3):163-173. [65] KUROYANAGI G, TACHI J, FUJITA K, et al. HSP70 inhibitors upregulate prostaglandin E1-induced synthesis of interleukin-6 in osteoblasts. PLoS One. 2022;17(12):e0279134. [66] MO YQ, NAKAMURA H, TANAKA T, et al. Lysosomal exocytosis of HSP70 stimulates monocytic BMP6 expression in Sjögren’s syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2022; 132(6):e152780. [67] SUN X, LI K, HASE M, et al. Suppression of breast cancer-associated bone loss with osteoblast proteomes via Hsp90ab1/moesin-mediated inhibition of TGFβ/FN1/CD44 signaling. Theranostics. 2022; 12(2):929-943. [68] QU M, GONG Y, JIN Y, et al. HSP90β chaperoning SMURF1-mediated LATS proteasomal degradation in the regulation of bone formation. Cell Signal. 2023;102:110523. [69] GORRELL L, MAKAREEVA E, OMARI S, et al. ER, Mitochondria, and ISR Regulation by mt-HSP70 and ATF5 upon Procollagen Misfolding in Osteoblasts. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(29):e2201273. [70] KUROYANAGI G, TOKUDA H, FUJITA K, et al. Upregulation of TGF-β-induced HSP27 by HSP90 inhibitors in osteoblasts. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):495. [71] PFAHLER S, DISTL O. Effective population size, extended linkage disequilibrium and signatures of selection in the rare dog breed lundehund. PLoS One. 2015;10(4): e0122680. [72] LI Y, WANG X, PAN C, et al. Myoblast-derived exosomal Prrx2 attenuates osteoporosis via transcriptional regulation of lncRNA-MIR22HG to activate Hippo pathway. Mol Med. 2023;29(1):54. [73] LU X, BECK GR JR, GILBERT LC, et al. Identification of the homeobox protein Prx1 (MHox, Prrx-1) as a regulator of osterix expression and mediator of tumor necrosis factor α action in osteoblast differentiation. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(1):209-219. [74] KAWAGUCHI M, KAWAO N, TAKAFUJI Y, et al. Myonectin inhibits the differentiation of osteoblasts and osteoclasts in mouse cells. Heliyon. 2020;6(5):e03967. [75] GARNER RT, SOLFEST JS, NIE Y, et al. Multivesicular body and exosome pathway responses to acute exercise. Exp Physiol. 2020;105(3):511-521. [76] WHITHAM M, PARKER BL, FRIEDRICHSEN M, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Provide a Means for Tissue Crosstalk during Exercise. Cell Metab. 2018;27(1):237-251.e4. [77] BARONE R, MACALUSO F, SANGIORGI C, et al. Skeletal muscle Heat shock protein 60 increases after endurance training and induces peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 α1 expression. Sci Rep. 2016;6:19781. [78] LOVETT JAC, DURCAN PJ, MYBURGH KH. Investigation of Circulating Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNA Following Two Consecutive Bouts of Muscle-Damaging Exercise. Front Physiol. 2018;9:1149. [79] XING Z, GUO L, LI S, et al. Skeletal muscle-derived exosomes prevent osteoporosis by promoting osteogenesis. Life Sci. 2024; 357:123079. [80] FERNANDES CJC, SILVA RA, FERREIRA MR, et al. Vascular smooth muscle cell-derived exosomes promote osteoblast-to-osteocyte transition via β-catenin signaling. Exp Cell Res. 2024;442(1):114211. [81] 庄曙昭,肖卫华.骨骼肌源性外泌体功能及其运动调控[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2020,42(9):1676-1683. |
| [1] | 张庆彤, 陈乐琴, 刘昶, 陈昱廷, 郭睿武. 内源性大麻素系统调控运动动机的神经机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [2] | 刘金龙, 阿卜杜吾普尔•海比尔, 白 臻, 苏丹阳, 苗 鑫, 李 菲, 杨晓鹏. 不同非手术方法治疗青少年特发性脊柱侧凸效果的系统综述与网状Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2370-2379. |
| [3] | 程旗圣, 居来提·买提肉孜, 肖 扬, 张陈伟, 帕尔哈提·热西提. 新型变径螺钉在腰椎改良皮质骨轨迹中的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2162-2171. |
| [4] | 陈惠挺, 曾伟权, 周剑鸿, 王 杰, 庄聪颖, 陈培友, 梁泽乾, 邓伟明. 椎体成形中拖尾锚定治疗伴裂隙征骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2145-2152. |
| [5] | 曾 轩, 翁 汭, 叶仕成, 唐佳栋, 莫 凌, 李文超. 两种腰椎旋扳手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症:生物力学差异的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2153-2161. |
| [6] | 刘文龙, 董 磊, 肖争争, 聂 宇. 骨质疏松患者行固定平台单髁置换后胫骨假体松动的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2191-2198. |
| [7] | 陈 龙, 王小阵, 席金涛, 鲁齐林. 短节段置钉联合可扩张聚醚醚酮置换体在骨质疏松椎体中的生物力学性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2226-2235. |
| [8] | 李智斐, 韩 斌, 柳秋丽, 张展鸣, 韦浩凯, 左匡时, 张翼升. 基于动作捕捉技术分析神经根型颈椎病患者的颈椎运动特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2286-2293. |
| [9] | 曹 涌, 滕虹良, 邰鹏飞, 李骏达, 朱腾旗, 李兆进. 细胞因子和卫星细胞在肌肉再生中的相互作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1808-1817. |
| [10] | 胡雄科, 刘少华, 谭 谦, 刘 昆, 朱光辉. 紫草素干预骨髓间充质干细胞改善老年小鼠股骨的微结构[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1609-1615. |
| [11] | 潘 冬, 杨加玲, 田 卫, 王东济, 朱 政, 马文超, 刘 娜, 付常喜. 抗阻运动激活衰老大鼠骨骼肌卫星细胞:脂联素受体1途径的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(7): 1736-1746. |
| [12] | 温广伟, 甄颖豪, 郑泰铿, 周淑怡, 莫国业, 周腾鹏, 李海山, 赖以毅. 异银杏素对破骨细胞分化的影响和机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1348-1358. |
| [13] | 钟彩红, 肖晓歌, 李 明, 林剑虹, 洪 靖. 运动相关髌腱炎发病的生物力学机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1417-1423. |
| [14] | 侯超文, 李兆进, 孔健达, 张树立. 骨骼肌衰老主要生理变化及运动的多机制调控作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1464-1475. |
| [15] | 孙尧天, 徐 凯, 王沛云. 运动影响铁代谢对免疫性炎症疾病调控的潜在机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1486-1498. |
随着全球人口老龄化进程的加剧,骨形成异常已成为影响老年人群体的重要公共卫生问题。尽管当前治疗策略主要集中于抗骨吸收的药物和促进骨形成的药物,但往往存在疗效不稳定、长期依赖及不良反应等问题。因此,开发新型治疗策略,尤其是靶向骨形成的分子机制,成为重要课题。此外,尽管运动已被证明对骨形成具有积极影响,但其对骨骼肌源性外泌体的调节作用尚未得到充分研究。因此,探索骨骼肌源性外泌体及其miRNA在骨质疏松症中的作用机制以及与运动的关系,具有重要的研究价值和临床应用潜力。
该综述重点研究骨骼肌源性外泌体在正常和病理状态下如何通过影响Wnt/β-连环蛋白、骨形态发生蛋白/Runt相关转录因子2等关键信号通路调节骨细胞的增殖、分化和矿化。此外,探讨了运动对骨骼肌源性外泌体分泌的调节作用及其对骨形成的影响。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2024年11月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 数据库建库至2024年11月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网、PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词:“外泌体,骨骼肌源性外泌体,骨形成,成骨细胞,运动”;英文检索词:“Exosome,Skeletal Muscle-Derived Exosomes,Bone Formation,Osteoblast,Exercise”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著和综述。
1.1.6 检索策略 以PubMed数据库为例,检索策略见图1。
1.1.7 检索文献量 初步检索纳入文献共计476篇。
1.2 纳入标准 ①骨骼肌源性外泌体对骨代谢、骨形成的作用机制;②运动对骨形成、成骨细胞的影响,以及骨骼肌源性外泌体在其中的作用;③研究中提供充分数据或证据,能够支持外泌体对骨代谢调节的潜在影响。
1.3 排除标准 ①与文章主题相关性低的文献;②研究质量较差及证据等级较低的文献;③无法获取全文的文献以及重复性文献。
1.4 资料整合 共检索到476篇相关文献,其中排除395篇文献,实际纳入81篇文献,中文2篇,英文79篇,见图2。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
然而,尽管已有许多研究揭示了骨骼肌源性外泌体在骨代谢中的潜力,但仍存在亟待解决的问题。例如,外泌体的具体作用机制尚不明了,不同来源的外泌体在骨代谢中的功能可能存在差异。此外,外泌体的靶向递送及其生物学效应的可控性仍需优化,以确保其在临床应用中的安全性与有效性。
3.2 此综述的特点 该综述通过综合分析已有文献,系统阐述了骨骼肌源性外泌体在骨代谢中的作用及其潜在机制,重点讨论了外泌体中的miRNA、蛋白质和其他分子如何调节骨形成相关基因与信号通路。不同于以往将肌肉与骨骼作为独立研究领域的做法,该综述进一步深入探讨了肌肉与骨骼之间的相互作用,尤其是外泌体介导的相互通讯。通过细致分析骨骼肌源性外泌体如何通过调控miRNA表达促进或抑制成骨细胞的分化,该综述为骨质疏松症的治疗提供了新的分子靶点和潜在的生物治疗策略。
3.3 此综述的局限性 尽管该综述在梳理骨骼肌源性外泌体调节骨代谢的机制方面做出较为全面的总结,但仍然存在一定局限性。首先,外泌体研究多集中于细胞与动物模型,缺乏大规模的临床研究数据支持;其次,骨骼肌源性外泌体的来源、制备及生物学特性仍存在较大的异质性,不同实验条件下获得的外泌体可能在功能上存在差异,如何标准化外泌体的提取和功能验证仍是未来研究中的挑战;此外,外泌体的长期效应、体内代谢途径以及对不同组织的影响等问题仍需通过进一步的研究来解答。
3.4 此综述的重要意义 该综述为研究肌肉-骨骼相互作用提供新的视角,阐明骨骼肌源性外泌体在骨代谢中的关键作用。随着对外泌体生物学特性的深入了解,以及外泌体技术的不断进步,骨骼肌源性外泌体有望成为未来骨质疏松症治疗的重要策略。通过探讨外泌体介导的成骨分化机制,以及开发高效的外泌体递送系统,将有助于推动这一领域的研究进展。总之,该综述为骨质疏松症等骨代谢疾病的治疗开辟新的思路和研究方向,具有重要的理论价值和临床应用潜力。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
文题释义:
外泌体:是直径为30-150 nm的纳米级囊泡,广泛存在于生物体液中。外泌体能够携带多种生物分子,如蛋白质、脂质、RNA(包括miRNA和mRNA)等,由细胞通过内吞作用释放到外部环境中。外泌体不仅在细胞通讯中起着重要作用,还参与调控成骨细胞的分化、矿化。
骨形成:是骨骼系统发育和修复的基础过程,主要通过成骨细胞完成。骨形成的过程分为初期的骨基质合成阶段、矿化阶段以及成熟骨的形成阶段。成骨细胞通过合成骨基质(主要是胶原蛋白)并促进矿物质沉积来形成新骨。骨形成的调控因素包括生长因子、转录因子、细胞信号通路等,其中Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号通路、骨形态发生蛋白2、Runt相关转录因子2等分子在骨形成过程中扮演着至关重要的角色。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
近年来,骨骼肌源性外泌体在骨代谢中的作用逐渐受到研究者的关注。外泌体作为细胞间信息传递的载体,能够携带miRNA、蛋白质等生物活性分子,调控多种生物过程。这一发现为治疗骨质疏松等骨代谢异常疾病提供了新的思路。当前,骨骼肌源性外泌体中的miRNAs和蛋白质被认为是骨形成的重要调控因子。然而,目前对骨骼肌源性外泌体的具体机制尚不完全清楚,尤其是如何通过不同的miRNA和蛋白质调控骨形成过程,目前未见报道。这篇综述在这一研究热点前沿的基础上,结合骨骼肌源性外泌体的最新研究成果,探讨主动和被动运动干预对骨形成的影响,为未来的临床治疗提供理论依据。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||