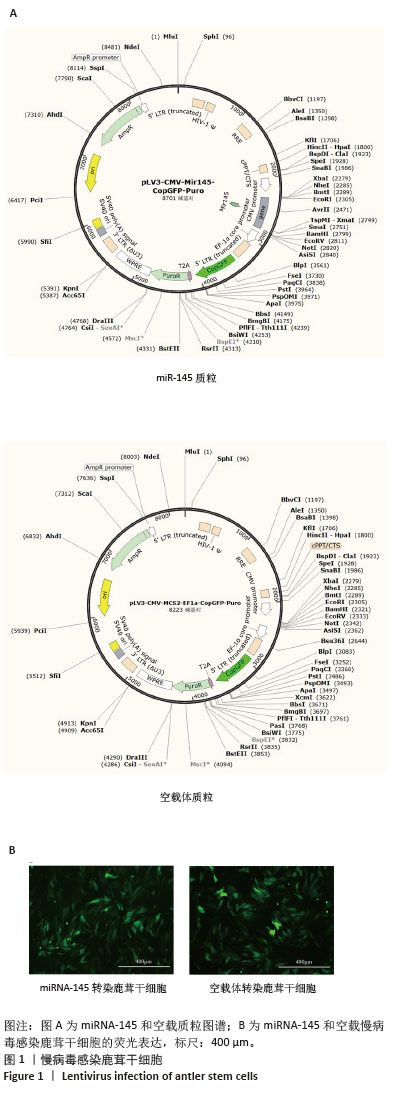
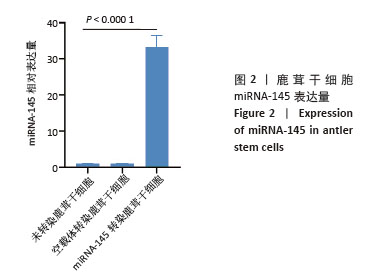
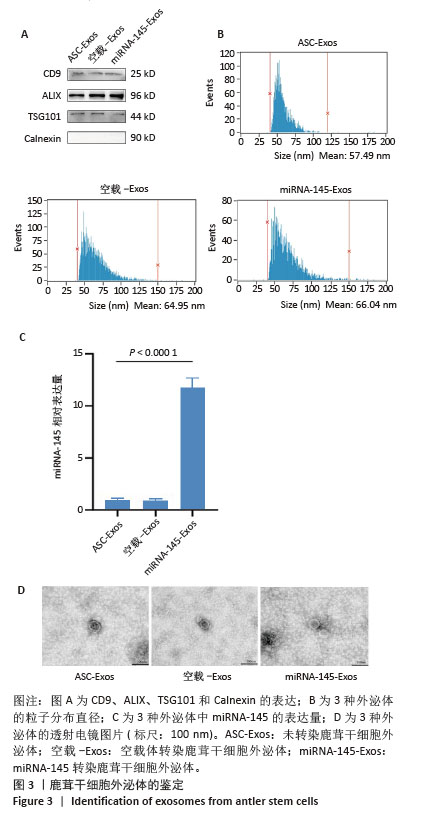
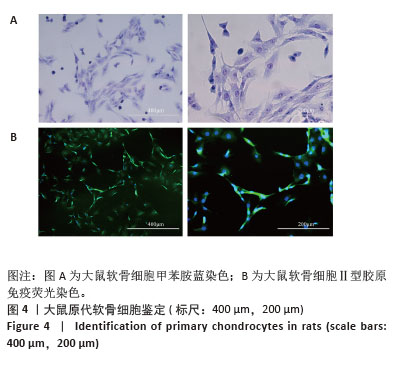
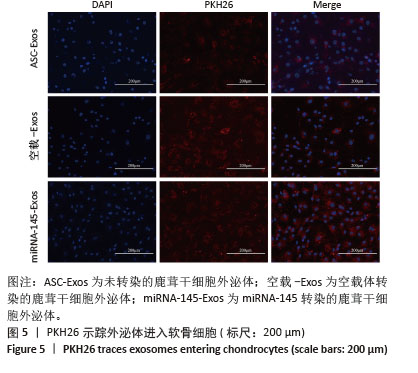
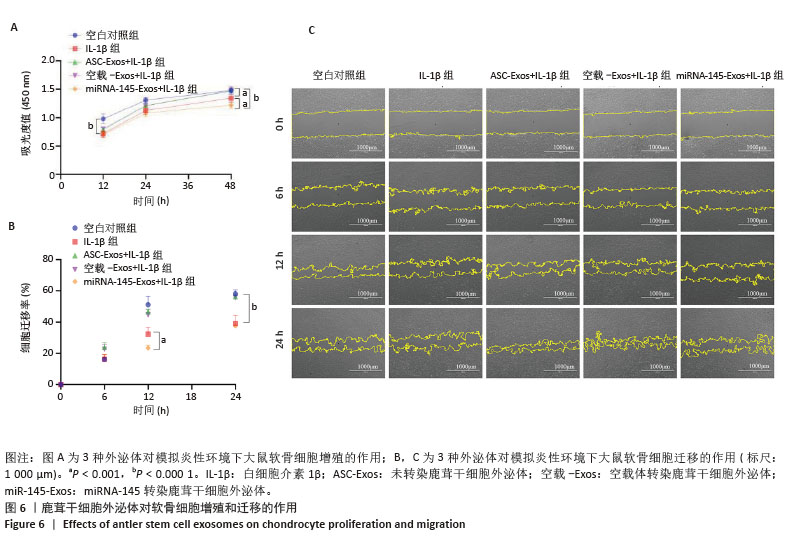
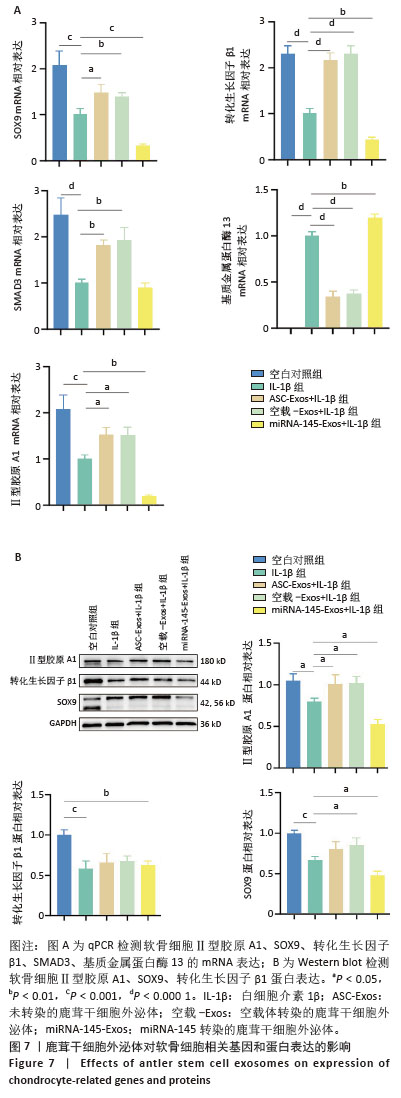
[1] 中华医学会物理医学与康复学分会,四川大学华西医院.中国膝骨关节炎康复治疗指南(2023版)[J].中国循证医学杂志,2024,24(1): 1-14.
[2] ZHANG L, YANG H, LIU J, et al. Metabolomics-based Approach to Analyze the Therapeutic Targets and Metabolites of a Synovitis Ointment for Knee Osteoarthritis. Current Pharmaceutical Analysis. 2023;19(3):222-234.
[3] XIA Z, MA P, WU N, et al. Altered function in cartilage derived mesenchymal stem cell leads to OA-related cartilage erosion. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8(2):433-446.
[4] IM GI, HENROTIN Y. Regenerative medicine for early osteoarthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2023;15:1759720X231194813.
[5] RAPOSO G, STOORVOGEL W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200(4):373-383.
[6] LOBB RJ, BECKER M, WEN SW, et al. Optimized exosome isolation protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:27031.
[7] TIAN X, HE X, QIAN S, et al. Immunoregulatory effects of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. BIOCELL.2023;47(5):1085-1093.
[8] PEKÁČOVÁ A, BALOUN J, ŠVEC X, et al. Non-coding RNAs in diseases with a focus on osteoarthritis. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023;14(3): e1756.
[9] YAMAZAKI A, TOMO Y, ETO H, et al. A pilot study of microRNA assessment as a means to identify novel biomarkers of spontaneous osteoarthritis in dogs. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):18152.
[10] 周珏.鹿茸干细胞分泌蛋白促进大鼠软骨缺损修复[D].北京:中国农业科学院,2023.
[11] 秦涛.鹿茸四区段mRNA-microRNA表达谱测定、分析及蜡片区调控网络构建[D].北京:中国农业科学院,2020.
[12] LI C, LITTLEJOHN RP, SUTTIE JM. Effects of insulin-like growth factor 1 and testosterone on the proliferation of antlerogenic cells in vitro. J Exp Zool. 1999;284(1):82-90.
[13] FAN B, LI C, SZALAD A, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes ameliorate peripheral neuropathy in a mouse model of diabetes. Diabetologia. 2020;63(2):431-443.
[14] KIM J, TRAN AN, LEE JY, et al. Human Fetal Cartilage-Derived Progenitor Cells Exhibit Anti-Inflammatory Effect on IL-1β-Mediated Osteoarthritis Phenotypes In Vitro. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2022;19(6):1237-1250.
[15] 刘冬阳,黄昕彤,赖晋锋,等.中国中老年人慢性病共病流行趋势研究[J].中国慢性病预防与控制,2024,32(4):244-249.
[16] 王伟康,刘晓冬,周长林,等.MiRNAs在骨关节炎发生发展中的调控作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(35):5709-5715.
[17] JIANG S, LIU Y, XU B, et al. Noncoding RNAs: New regulatory code in chondrocyte apoptosis and autophagy. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2020;11(4):e1584.
[18] PALAMÀ MEF, COCO S, SHAW GM, et al. Xeno-free cultured mesenchymal stromal cells release extracellular vesicles with a “therapeutic” miRNA cargo ameliorating cartilage inflammation in vitro. Theranostics. 2023;13(5):1470-1489.
[19] YIN B, NI J, WITHEREL CE, et al. Harnessing Tissue-derived Extracellular Vesicles for Osteoarthritis Theranostics. Theranostics. 2022;12(1): 207-231.
[20] ZHOU J, ZHAO J, WANG Y, et al. Repair of Mechanical Cartilage Damage Using Exosomes Derived from Deer Antler Stem Cells. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024;29(8):309.
[21] KIM M, SHIN DI, CHOI BH, et al. Exosomes from IL-1β-Primed Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibited IL-1β- and TNF-α-Mediated Inflammatory Responses in Osteoarthritic SW982 Cells. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;18(4):525-536.
[22] LI S, STÖCKL S, LUKAS C, et al. Curcumin-primed human BMSC-derived extracellular vesicles reverse IL-1β-induced catabolic responses of OA chondrocytes by upregulating miR-126-3p. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):252.
[23] GAO JY, WANG XJ, YU JP, et al. Loss of autophagy in condylar chondrocytes causes increased apoptosis rate in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis of rats. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020; 55(5):343-347.
[24] ABO-ZALAM HB, ABDELSALAM RM, ABDEL-RAHMAN RF, et al. In Vivo Investigation of the Ameliorating Effect of Tempol against MIA-Induced Knee Osteoarthritis in Rats: Involvement of TGF-β1/SMAD3/NOX4 Cue. Molecules. 2021;26(22):6993.
[25] PU P, QINGYUAN M, WEISHAN W, et al. Protein-Degrading Enzymes in Osteoarthritis. Z Orthop Unfall. 2021;159(1):54-66.
[26] 杨均,李澎.转化生长因子β诱导骨髓间充质干细胞分化为半月板纤维软骨细胞[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(15):2412-2419.
[27] FONGSODSRI K, TIYASATKULKOVIT W, CHAISRI U, et al. Sericin promotes chondrogenic proliferation and differentiation via glycolysis and Smad2/3 TGF-β signaling inductions and alleviates inflammation in three-dimensional models. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):11553.
[28] KISHTA MS, KHAMIS A, AM H, et al. Exploring the tumor-suppressive role of miRNA-200c in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Potential and mechanisms of exosome-mediated delivery for therapeutic applications. Transl Oncol. 2025;51:102216.
[29] WANG Z, WANG W, ZUO B, et al. Identification of potential pathogenic genes related to osteoporosis and osteoarthritis. Technol Health Care. 2024;32(6):4431-4444.
[30] MUÑOZ EL, FUENTES FB, FELMER RN, et al. Extracellular vesicles in mammalian reproduction: a review. Zygote. 2022;30(4):440-463.
[31] YANG F, XIONG WQ, LI CZ, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells mediate extracellular matrix remodeling in osteoarthritis through the transport of microRNA-29a. World J Stem Cells. 2024;16(2):191-206.
[32] LIN T, WU N, WANG L, et al. Inhibition of chondrocyte apoptosis in a rat model of osteoarthritis by exosomes derived from miR‑140‑5p‑overexpressing human dental pulp stem cells. Int J Mol Med. 2021;47(3):7.
[33] JOUNG S, YOON DS, CHO S, et al. Downregulation of MicroRNA-495 Alleviates IL-1β Responses among Chondrocytes by Preventing SOX9 Reduction. Yonsei Med J. 2021;62(7):650-659.
[34] LIU H, LIU P. Kartogenin Promotes the BMSCs Chondrogenic Differentiation in Osteoarthritis by Down-Regulation of miR-145-5p Targeting Smad4 Pathway. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;18(6): 989-1000.
[35] MARTINEZ-SANCHEZ A, LAZZARANO S, SHARMA E, et al. High-Throughput Identification of MiR-145 Targets in Human Articular Chondrocytes. Life (Basel). 2020;10(5):58.
[36] WU M, LIU F, YAN L, et al. MiR-145-5p restrains chondrogenic differentiation of synovium-derived mesenchymal stem cells by suppressing TLR4. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2022;41(7): 625-642. |