中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (1): 248-259.doi: 10.12307/2025.565
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
不同嵌合抗原受体T细胞相关靶点治疗B细胞血液恶性肿瘤:长期随访数据综述
许凡萍,李勤椿,唐冬芳
- 湖南科技学院,湖南省永州市 425199
-
收稿日期:2024-09-07接受日期:2024-11-22出版日期:2026-01-08发布日期:2025-07-02 -
通讯作者:唐冬芳,博士,讲师,湖南科技学院,湖南省永州市 425199 -
作者简介:许凡萍,女,1992年生,福建省漳州市人,汉族,2018年昆明理工大学毕业,硕士,助理实验师,主要从事细胞生物学和医学检验工作。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(32101022),项目负责人:唐冬芳;湖南省自然科学基金项目(2022JJ40158),项目负责人:唐冬芳;湖南省教育厅科学研究项目(22A0572),项目负责人:唐冬芳;湖南省应用特色学科建设项目
Targeting diverse chimeric antigen receptor T cell-related targets in treatment of B-cell hematological malignancies: a review of long-term follow-up data
Xu Fanping, Li Qinchun, Tang Dongfang
- Hunan University of Science and Engineering, Yongzhou 425199, Hunan Province, China
-
Received:2024-09-07Accepted:2024-11-22Online:2026-01-08Published:2025-07-02 -
Contact:Tang Dongfang, PhD, Lecturer, Hunan University of Science and Engineering, Yongzhou 425199, Hunan Province, China -
About author:Xu Fanping, MS, Assistant experimentalist, Hunan University of Science and Engineering, Yongzhou 425199, Hunan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 32101022 (to TDF); Hunan Natural Science Foundation, No. 2022JJ40158 (to TDF); Scientific Research Project of Hunan Provincial Education Department, No. 22A0572 (to TDF); Hunan Province Applied Characteristic Discipline Construction Project
摘要:
文题释义:
嵌合抗原受体T细胞疗法:是一种免疫治疗技术,通过基因工程手段改造患者的T细胞,使其表面表达能识别肿瘤抗原的嵌合抗原受体,从而激活并引导T细胞精准杀死癌细胞。这种疗法在血液肿瘤中显示出显著疗效,已有多款嵌合抗原受体T细胞产品获批上市。B细胞血液恶性肿瘤:起源于血液或骨髓中的B细胞,包括各种类型的B细胞淋巴瘤和B细胞白血病。例如,B细胞急性淋巴细胞性白血病、慢性淋巴细胞性白血病、非霍奇金淋巴瘤中的B细胞类型(如弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤)等。
摘要
背景:嵌合抗原受体T (chimeric antigen receptor T,CAR-T)细胞疗法是治疗B细胞血液恶性肿瘤的前沿方法,其能高效且特异性地识别并杀伤肿瘤细胞,不受主要组织相容性复合体限制。
目的:旨在梳理CAR-T细胞的结构、发展历程及上市产品进展,总结CAR-T细胞治疗B细胞血液恶性肿瘤的长期疗效,并探讨治疗后的毒副作用、复发性及解决策略,同时综述潜在靶点治疗B细胞血液恶性肿瘤的进展。
方法:以“嵌合抗原受体T细胞,B细胞恶性肿瘤,毒副作用,免疫疗法”为中文检索词,以“CAR-T、B cell hematological malignancies,Toxic side effects,Immunotherapy”为英文检索词在中国知网、万方数据库、PubMed数据库检索CAR-T细胞相关靶点治疗B细胞恶性肿瘤的文献。
结果与结论:①美国食品药品监督管理局和中国国家药品监督管理局共批准11款CAR-T细胞产品,主要针对B细胞血液恶性肿瘤的CD19和B细胞成熟抗原靶点;②长期随访数据显示,CAR-T细胞治疗为B细胞血液恶性肿瘤患者带来高缓解率和持久反应,但存在抗原丢失或下调导致的复发问题;③CAR-T细胞治疗存在高毒副作用、高复发率和耐药性等问题,限制了其广泛应用;④未来研究的方向包括开发新的靶点、联合治疗等策略,以提高CAR-T细胞的持久性和抗肿瘤活性。
中图分类号:
引用本文
许凡萍, 李勤椿, 唐冬芳. 不同嵌合抗原受体T细胞相关靶点治疗B细胞血液恶性肿瘤:长期随访数据综述[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(1): 248-259.
Xu Fanping, Li Qinchun, Tang Dongfang. Targeting diverse chimeric antigen receptor T cell-related targets in treatment of B-cell hematological malignancies: a review of long-term follow-up data[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 248-259.
2.1.1 CAR-T细胞的组成结构及作用机制 CAR是一种跨膜嵌合蛋白,它结合T细胞形成可特异性识别和消除特定肿瘤细胞的CAR-T细胞,是CAR-T细胞的核心部件,通过反转录病毒或慢病毒转导,含胞外区、铰链区、跨膜区及胞内区4个结构域[2-3]。
各结构域具有特定的功能:①胞外区可由轻链和重链连接而成的单链可变片段(single chain fragment variable,scFv),能够特异性识别肿瘤相关抗原(tumor-associated antigens,TAAs)的单克隆抗体[4]。②铰链区是针对不同肿瘤相关抗原设计铰链区长度,以便结合靶抗原。③跨膜区选取CD3、CD8或CD28等跨膜受体蛋白作为细胞膜的锚点连接细胞内外,影响胞内区的激活信号传递,因此在活化T细胞中起重要作用。④胞内区是受体的功能端,由CD3ζ活化信号(包含免疫受体酪氨酸活化基序ITAM)和1个或1个以上的共刺激结构域[如CD28、CD134(OX40)、CD137(4-1BB)、ICOS]组成细胞内信号转导区域[2]。其中,CD28跨膜结构域作为最稳定的受体在临床中广泛应用。正常T细胞依赖T细胞受体识别抗原,T细胞受体与主要组织相容性复合体(major histocompatibility complex,MHC)分子提呈的肿瘤抗原短肽结合,通过信号通路产生级联反应活化为细胞毒性T淋巴细胞,特异性结合有相同MHC抗原肽的肿瘤细胞进而发挥细胞毒性作用[5]。而CAR-T细胞可以针对肿瘤细胞抗原构建特定的单克隆抗体,通过scFv特异性识别肿瘤特异性抗原直接将信号传到T细胞内,使T细胞活化并释放穿孔素/颗粒酶等细胞因子从而破坏肿瘤细胞[6],同时形成免疫记忆T细胞,发挥长效抗肿瘤作用。CAR-T细胞不受肿瘤MHC表达下调的限制性和抗原呈递细胞的局限,能用于治疗下调MHC Ⅰ类分子导致的免疫逃逸引起的肿瘤疾病,且CAR靶点范围较广,能识别包括蛋白质、脂类和糖类等多种物质[7-8]。
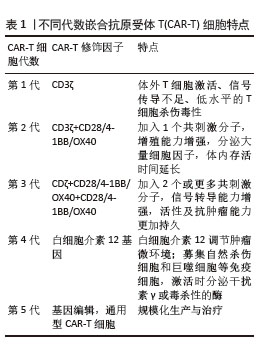
2.1.2 CAR-T发展历程及分类 按照使用的细胞种类,细胞治疗分为免疫细胞治疗和干细胞治疗。其中,过继性细胞免疫疗法是免疫细胞治疗的主要方向。目前经历3种形式发展,包括肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞(tumor infiltrating lymphocyte,TIL)疗法、T细胞受体基因工程改造的T(TCR-T)细胞疗法、CAR-T细胞疗法。TIL疗法需要从切除肿瘤中分离肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞,经体外进行扩增和培养后,再回输到体内[9]。TCR-T细胞疗法需要从外周血中分离出T细胞进行分子生物学改造,将能识别肿瘤特异性抗原的T细胞受体转导到T细胞中[10]。2022年1月美国食品药品监督管理局(Food and Drug Administration,FDA)批准全球首款治疗实体瘤(无法切除或转移性葡萄膜黑色素瘤)的TCR-T疗法产品Kimmtrak[11]。通过改造T细胞受体结构可以获得CAR-T细胞,CAR-T细胞具有靶向抗原精准识别的特点,表现出高特异性和强抗肿瘤疗效。CAR结构差异会影响T细胞活性、增殖和抗肿瘤持久性[12]。不同的CAR-T细胞共刺激结构域或胞内信号区域,代表着不同的CAR-T代数[13],目前已经发展到第5代,见表1。
5代CAR-T细胞基本结构示意图,见图3[14]。
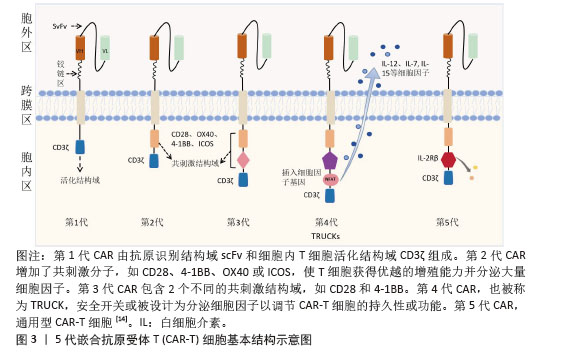
①第1代:CAR-T仅有1个激活结构域CD3ζ组成。由于缺少共刺激信号,CAR-T细胞在患者体内无法持续存在,对肿瘤无效。随着研究深入发现共刺激信号对于T细胞的活化至关重要,因而在胞内区增加1个或1个以上共刺激信号形成了第2代CAR-T细胞[15]。②第2代:CAR-T细胞具有1个激活结构域和1个共刺激结构域[16]。CAR-T细胞增强信号传递并产生大量的细胞因子,提高了效应T细胞增殖能力和抗肿瘤作用[17]。目前,临床普遍使用第2代CAR-T细胞,并取得了较好的临床疗效。为进一步提高T细胞的细胞活性和毒性,对T细胞的抗肿瘤信号通路深入研究,开发了第3代和第4代CAR-T细胞。③第3代:CAR-T细胞包含1个激活结构域和2个或更多的共刺激结构域的分子,进一步提升活化T细胞产生更多的细胞因子,发挥更持久的活性和抗肿瘤效力[18]。但研究发现,第3代CAR-T细胞的临床表现并未优于甚至劣于第2代CAR-T细胞。④第4代:第4代CAR-T细胞也称为TRUCK细胞,是在第2代CAR-T的基础上插入特定细胞因子的基因,如白细胞介素基因或表达自杀的基因:白细胞介素7、白细胞介素12、白细胞介素15、白细胞介素21和iCaspase-9等[19-21]。第4代CAR-T细胞可活化T细胞核因子的转录相应元件[22]。通过对致癌靶点的特异性识别来刺激活化T细胞的最小启动子,在肿瘤区域分泌相应的细胞因子白细胞介素12,进而调节肿瘤微环境,募集并活化巨噬细胞和自然杀伤细胞(NK细胞)等免疫细胞到肿瘤部位,通过激活内源性免疫反应更有效地消除肿瘤细胞,同时减少化疗等预处理[23]。到目前为止,第3代和第4代CAR-T细胞尚未有产品获批。⑤第5代CAR-T细胞目前处于早期阶段[24]。在第2代基础上构建通用型CAR-T细胞,通常采用BBIR CAR或SUPRA CAR设计以提高CAR靶向识别的灵活性[25]。也有通过敲除内源性T细胞受体和人类白细胞抗原Ⅰ类分子的设计思路,以降低异体移植的免疫排斥反应,避免异体T细胞对宿主器官的免疫攻击,从而增加CAR-T细胞的可控性。显然,CAR-T的改进是当下一个备受关注的领域,研究人员希望开发出更有效、更安全的免疫疗法。
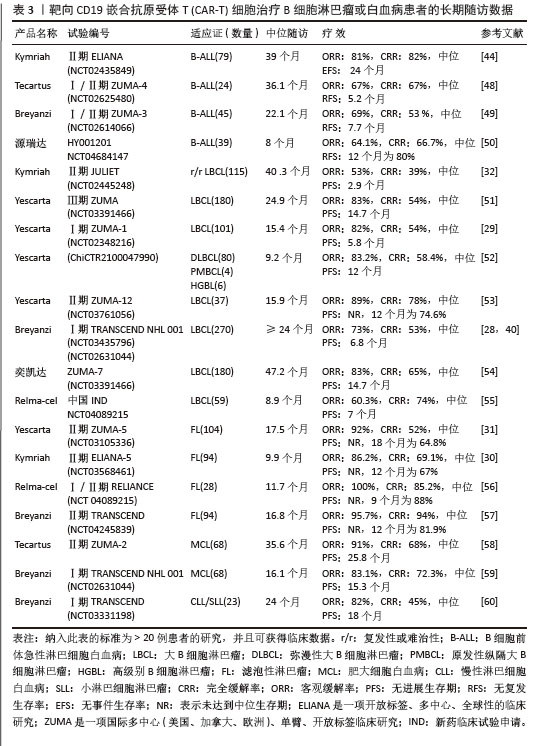
2.1.3 CAR-T细胞上市产品 随着第2代CD19靶向CAR-T细胞国际临床试验的成功进行,免疫细胞治疗已成为癌症治疗的前沿领域。2017年,FDA批准了全球首款CAR-T细胞疗法产品——诺华的Kymriah上市[26-27]。截至目前,全球已经上市11款CAR-T细胞疗法产品(表2),其中经美国FDA共批准的有6款,经中国国家药品监督管理局(National Medical Products Administration,NMPA)批准上市的有5款。这些获批的产品均为2代自体CAR-T细胞,结构成熟、临床效果较突出。根据嵌合抗原受体的胞外区结构分为2类:①以CD19靶点的分别为Kymriah、Yescarta、Tecartus、Breyanzi、奕凯达、Relma-cel和源瑞达,其中5种用于治疗复发性或难治性大B细胞淋巴瘤(large B cell lymphoma,LBCL),4款用于治疗复发或难治性滤泡性淋巴瘤(follicular lymphoma,FL),2款用于治疗复发/难治性套细胞淋巴瘤(mantle cell lymphoma,MCL),2款用于治疗B细胞急性淋巴细胞白血病(B cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia,B-ALL),1款用于治疗复发/难治性慢性淋巴细胞白血病/小淋巴细胞淋巴瘤(chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic leukemia,CLL/SLL),1款用于治疗B细胞前体急性淋巴细胞白血病的青少或儿童[28-32];②以BCMA靶点的分别为Abecma、Carvykti、福可苏和赛恺泽,用于治疗多发性骨髓瘤(multiple myeloma,MM)患者。
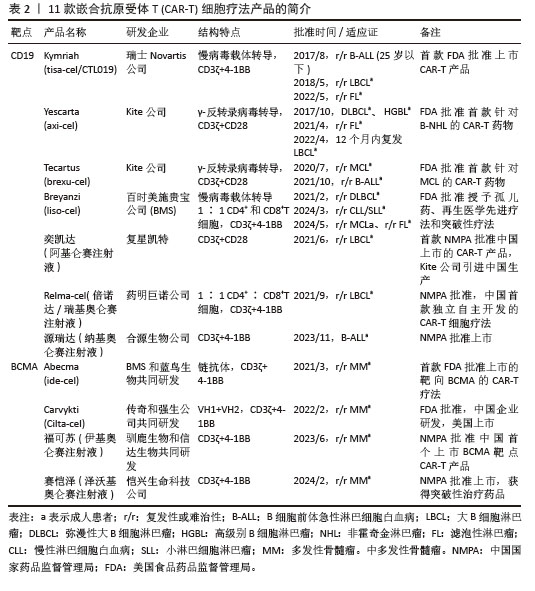
值得一提的是,除源瑞达CD19的CAR使用的是自主研发的scFv(HI19a)单链抗体外,其他产品CD19的CAR结构胞外域均使用鼠源FMC63单链抗体。
Kymriah用4-1BB作为共刺激结构域而不是CD28,其相关临床试验数据最多,可治疗疾病范围也最广。Kymriah和Yescarta使用慢病毒载体转导自体T细胞;而Yescarta和Tecartus的CAR基因使用γ-反转录病毒传递,因此针对的适应证有所不同。此外,Tecartus采用了XLP制造工艺进行T细胞筛选和淋巴细胞富集,去除了恶性细胞,其结构和Yescarta非常相像。与其他产品不同的是,Breyanzi和Relma-cel以1∶1 CD4+∶CD8+ T细胞组成递送。Abecma的CAR胞外结构域为鼠源11D5-3组成抗BCMA单链抗体。而Carvykti的CAR包含两种来源的单域抗体,这两种靶向BCMA产品的嵌合抗原受体基因都是通过慢病毒传递的。CAR-T细胞产品治疗血液恶性肿瘤具有得天独厚优势、发展迅速,临床上取得了显著的效果。国内众多企业都在积极参与,推动技术的创新和应用,为免疫细胞治疗的发展提供了强大的动力,也为患者带来了更多的治疗选择。
2.2 CAR-T细胞治疗血液系统恶性肿瘤的相关靶点
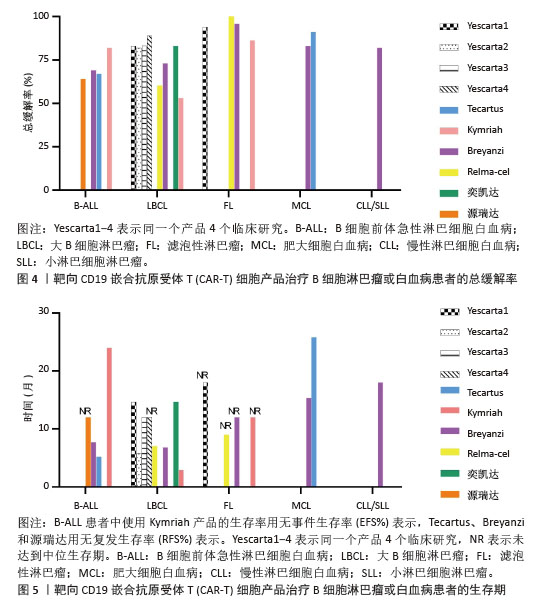
2.2.1 靶向CD19的CAR-T细胞疗法 CD19是Ⅰ型跨膜糖蛋白,属于Ig超家族,在B细胞表面发挥特异性信号转导的受体。CD19在多种B细胞恶性肿瘤表面表达,而不在其他正常组织上表达。由于CD19的表达程度高于CD20、CD22,因此CD19被认为是CAR-T治疗B细胞恶性肿瘤的首选靶点,也是血液系统恶性肿瘤相关抗原中研究最彻底的靶点[33]。目前,抗CD19 CAR-T的获批适应证已覆盖B-ALL(儿童、成人)和NHL当中的LBCL、FL、MCL,并正在积极探索其他亚型的适应证。靶向CD19的CAR-T细胞治疗的r/r B-ALL患者中可诱导83%-93%的应答率[34]。国际骨髓移植研究中心(Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research,CIBMTR)分析了255例接受CAR-T治疗的B-ALL儿童患者,完全缓解率为85.5%,12个月无事件生存期(event-free survival,EFS)为52.4%[35]。BRUDNO等[36]在Ⅰ期临床试验中,20例B细胞淋巴瘤患者首次使用抗CD19-CAR(Hu19-CD828Z)T细胞,完全缓解率为55%,出现严重的神经毒性的患者仅有5%。WANG等[37]对23例r/r B-ALL患者在CAR-T治疗14 d后进行评估,缓解率为82%。MYERS等[38]在一项临床试验中,72例1-29岁r/r B-ALL患者接受人源化的抗CD19 CAR-T(huCART19)细胞治疗,73%的患者治疗后6个月仍检测到CAR-T细胞,12个月和24个月的无复发生存率分别为84%和74%,表现出了长期的疗效。目前的研究显示抗CD19 CAR-T细胞治疗r/r NHL患者效果良好,在一项涉及43例r/r B细胞淋巴瘤或CLL患者的研究中,58%的治疗患者获得了完全缓解,这部分完全缓解患者中有76%保持长期缓解,持续时间为43-113个月[39]。ABRAMSON等[40]评估了Breyanzi在269例r/r LBCL患者中的疗效,客观缓解率为73%,细胞因子释放综合征(cytokine release syndrome,CRS)≥3级为2%,患者得到长期的缓解率。而在ZUMA-1研究中,患者获得客观缓解率和完全缓解分别82%,54%[29]。2022年的一项研究中,抗CD19 CAR-T细胞治疗r/r FL的94例患者进行中位随访16.59个月,客观缓解率为86.2%,完全缓解率为69.1%,CRS为48.5%(等级≥3,0%),免疫效应细胞相关神经毒性综合征(immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome,ICANS)为4.1%(等级≥3,1%),无治疗相关死亡事件[30],CAR-T细胞表现出高反应性和可控毒性,但CD19的下调或突变容易导致复发,仍然是该疗法面临的重大挑战[41-42]。2021年国际血液和骨髓移植研究中心数据显示,接受CAR-T治疗的451例患有r/r B-ALL的儿童/年轻人,中位随访21.5个月,客观缓解率为86.8%,12个月无复发生存率为62.5%,CRS≥3级为17.8%和发生ICANS为10%[43]。然而,在临床治疗中,需要更长时间的随访以充分了解药物的持续性。
目前,已知的接受靶向CD19的CAR-T细胞产品治疗的B细胞淋巴瘤或白血病患者长期预后的数据,包括17项研究提供已上市靶向CD19的CAR-T细胞产品的随访数据。在ELIANA、ZUMA、JULIET等国际研究中[39,44-46],均显示CD19 CAR-T细胞治疗B-ALL患者保持长期缓解,最长有5年之久。结合图4和图5可以看到,整体数据显示客观缓解率为53%-100%,并保持长期缓解。Yescarta及奕凯达治疗LBCL患者总缓解率较高,客观缓解率最高达到89%。治疗B-ALL的4款产品中Kymriah的缓解率最好,中位无事件生存期长达2年之久。治疗FL的4款产品均有较高缓解率,均达到86%以上,其中Relma-cel在3个月时的客观缓解率达到了100%,但随着时间推移会有所降低。治疗MCL以及CLL/SLL的产品缓解率均达到80%以上。半数以上的MCL患者在接受Tecartus产品治疗后2年仍处于缓解期,这表明了抗CD19 CAR-T细胞在B细胞恶性肿瘤治疗中具有长期有效的活性[47]。总的来说,这些结果表明大部分接受抗CD19 CAR-T细胞治疗的患者获得了较好缓解率,不需要进一步干预就能治愈疾病,见表3[28-32,40,44,48-60]。然而,抗原丢失或下调是肿瘤耐药性的常见原因,复发仍不可避免。因此,迫切需要开发更多的靶点和治疗模式以提高临床疗效。
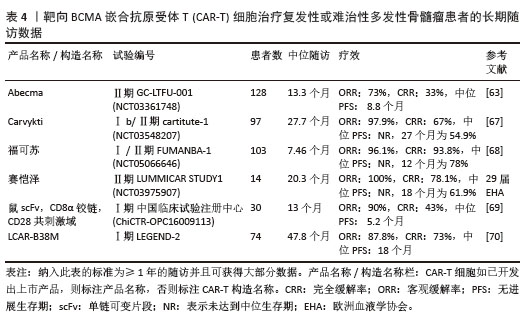
2.2.2 靶向BCMA CAR-T细胞疗法 BCMA也称为CD269,是一种跨膜糖蛋白,是肿瘤坏死因子受体超家族的成员,表达于成熟的B淋巴细胞,较少表达于造血干细胞和正常组织中。BCMA的过度表达和激活与MM的进展相关[61],这使得BCMA成为MM重要治疗靶点。近5年来,抗BCMA CAR-T细胞的临床试验数量稳步增长。RAJE等[62]对33例r/r MM患者输注bb2121细胞,完全缓解率和客观缓解率为85%,45%,23例患者出现CRS(≥3级,6%)。16例有副反应的患者的微小残留病变评估均为阴性,证实了抗BCMA的CAR-T细胞治疗MM的抗肿瘤活性。另一项研究中128例接受Abecma治疗,客观缓解率为97%,完全缓解率为67%,仅有5%的患者发生≥3级的CRS[63],因此Abecma治疗MM得到较高的缓解率。针对成熟浆细胞上缺乏BCMA可能会限制疗效和复发的问题,KANG等[64]设计了新型tan-CAR,胞外区由scFv-BCMA和scFv-CD19串联,可同时表达靶向BCMA和CD19。双靶CAR-T细胞在体内外对CD19和 BCMA抗原阳性肿瘤细胞均有显著的抗肿瘤作用。不同靶向抗原的联合应用有助于降低复发率,为CAR-T细胞治疗提供新的策略。
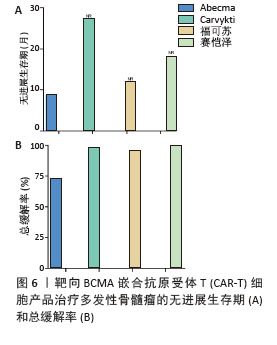
2023年,根据美国临床肿瘤学术年会(American Society of Clinical Oncology,ASCO)报告,伊基奥仑赛注射液治疗r/r MM患者增加至103例的Ⅰ/Ⅱ期临床试验研究,客观缓解率为96.1%,完全缓解率为74.3%。12个月的无进展生存率为78.8%,仅出现1例≥3级CRS,无≥3级ICANS[65]。这些患者发生的毒副作用得到了较好的处理,获得良好的长期疗效。与CD19靶向CAR-T细胞相比,由于这些结构的发展较晚,接受BCMA靶向CAR-T细胞治疗r/r MM患者的长期效果相关数据较少。目前共有6项研究,见表4[63,67-70],患者的客观缓解率从73%-100%不等。结合图6,可以看到上市产品中Abecma、Carvykti、福可苏的总缓解较高。Carvykti的中位无进展生存期达到27个月,半数以上的患者得到了长期的疗效。大部分患者达到完全缓解或更好,随着时间的推移无进展生存期有下降的趋势。这些数据表明抗BCMA CAR-T细胞治疗对r/r MM表现出持久的反应[66],但治疗后BCMA表达下调、复发以及耐药的机制仍然不明确,需进一步研究。
2.2.3 其他潜在靶点及双靶向CAR-T细胞疗法 目前,全球的研发管线正迅速扩张,已达到一千多项,其中CD19和BCMA是CAR-T细胞产品开发中最常见的靶点,在治疗血液肿瘤方面取得突破性的进展,但临床资料显示大多数患者仍会复发[71],主要是因为单靶点免疫治疗存在原发性耐药和复发等问题。因而,双特异性CAR-T细胞疗法可能是解决这些问题的新策略。
(1)靶向CD20、CD22、CD123联合CD19 CAR-T细胞疗法:CD20、CD22、CD123均在B细胞淋巴瘤等血液系统恶性肿瘤中表达[72],是治疗血液恶性肿瘤的潜在靶点。多项研究证实双靶点方法有更高的缓解率,可以优化反应率、降低复发率[73-74]。抗CD20 CAR-T细胞治疗17例r/r NHL患者的Ⅰ/Ⅱ期试验中,完全缓解率为54.5%[75]。为了防止抗原逃逸,SANG等[76]设计双靶点CD19/CD20 CAR-T细胞联合治疗r/r DLBCL,证明联合治疗是安全可行的。PAN等[77]对34例B-ALL患者在抗CD19 CAR-T细胞治疗失败后接受了抗CD22 CAR-T细胞治疗,CR/CRi达到70.5%,大部分患者轻度CRS和ICANS。因此,抗CD22 CAR-T细胞治疗可作为补充治疗以降低复发率。另一项双靶向CD19/CD22 CAR-T细胞治疗51例r/r B-ALL患者Ⅰ/ Ⅱ期试验中,客观缓解率为72.2%,中位无进展生存期为13.6个月,CRS和ICANS分别为22.4%和1.12%[78],患者获得较好的缓解率。YAN等[79]设计了同时具有白血病抗原CD19和CD123双信号传导的CAR-T细胞。在体内外实验中,双靶向CD19/CD123 CAR-T细胞均能够独立地清除肿瘤细胞。复合CAR比单一的CD19-CAR具有更高的缓解率和更低的复发率,防止由于抗原丢失或单一靶抗原表达不清而复发,有望成为癌症治疗的有力手段。
(2)靶向CD38、CD138、CD229与MM治疗:CD38在MM细胞上高表达,促进MM细胞的存活和增殖。临床试验显示,使用第2代抗CD138 CAR-T细胞治疗5例r/r MM患者,经过7个月的随访治疗,其中至少4例患者病情稳定,抗CD138 CAR-T细胞能有效消除MM细胞[80]。然而,CD38在造血细胞和活化淋巴细胞上也有表达[81]。尽管抗CD38 CAR-T细胞在小鼠模型中表现出显著的抗肿瘤作用,但它们也损害了正常的造血细胞和淋巴细胞。临床上,CD38经常与其他靶点(如BCMA和CD138)结合产生双特异性CAR-T细胞,从而降低抗原逃逸的风险[82-83]。CD229在MM细胞表面上高度表达,临床前研究发现靶向CD229 CAR-T细胞有效地消除了MM细胞[84]。研究者除了开发出针对血液系统恶性肿瘤有效治疗靶点外,双特异性CAR-T细胞治疗代表一种研究新途径,不断有临床数据证实其活性和有效性,为细胞治疗带来新希望。此文章讨论的所有潜在的CAR-T细胞治疗靶点均具有其独特性,仍需要广泛的未来临床研究来证明其安全性和适用性。
2.3 CAR-T细胞疗法面临的挑战和解决途径 随着医学技术的进步,CAR-T细胞疗法显示出良好的疗效,为癌症患者带来了新的希望,但出现的不良事件和风险仍然是主要的挑战。CAR-T细胞免疫治疗复杂性对技术要求高、存储与运输要求严格,并且缺乏行业通用的质量标准。2016年的魏则西事件和2017年的Juno和Kite公司的临床试验失败案例,以及CAR-T细胞疗法的复发性和存在的毒副作用,如CRS、ICANS、脱靶效应和全身性过敏反应等都引起广泛关注;CD19细胞也在正常B淋巴细胞表面,抗肿瘤的同时也会损伤 B细胞造成再生障碍[85],导致低丙种球蛋白血症和频繁感染等[86];CAR-T细胞的增殖及持久性也是限制其疗效稳定与持久的重要因素,治疗后的耐药性也不容忽视。目前,虽然已有一些应对措施,如药物治疗和基因修饰,但这些并发症可能会随时危及生命。因此,需要进一步优化CAR结构并联合其他手段进行有效干预以提高疗效,同时探索潜在机制并在疾病发展早期阶段进行识别。
2.3.1 CAR-T细胞疗法的毒副作用与解决策略 CRS和ICANS是与CAR-T细胞治疗相关的两种最突出的毒性,通常发生在治疗的1个月之内,CRS大多为低级别,但ICANS更常见的是高级别,30%-45%的患者发生ICANS 3级或4级[87]。虽然发生大于3级CRS和ICANS在大多数情况下能降级,但与CAR-T细胞治疗相关的严重毒性可能会损害其疗效,甚至发展成危及生命的疾病,如多器官功能障碍、败血症和弥散性血管内凝血[88]。
(1) CRS:是最常见的并发症,约半数以上治疗者会发生,肿瘤细胞与CAR-T细胞之间的CD40/CD40L相互作用促进Fas介导的细胞凋亡,裂解的肿瘤细胞释放出大量的损伤相关分子模式,这些损伤相关分子模式(可以激活内源性免疫细胞(如巨噬细胞和树突状细胞)引起全身性免疫炎症反应,释放炎症细胞因子和趋化因子,如干扰素、肿瘤坏死因子、粒细胞巨噬细胞集落刺激因子、白细胞介素(白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素12等)[89],其临床表现多样,涉及多个系统,临床常见感染相似症状,若治疗不及时可能会迅速发展成危及生命的疾病[90]。此外,严重的CRS与CAR-T细胞相关脑病综合征和凝血功能障碍的风险增加相关[91],CAR-T细胞治疗期间凝血功能障碍的发生率约为50%[91-92],89%的患者通常在治疗后两三天发生CRS(3级/4级,24%),一两周达到高峰。CRS的病理学已经得到了广泛的研究,并且已经制定了适当的管理策略。针对1级一般采用解热药;2级通过鼻导管补充低流量氧气或使用托珠单抗和皮质类固醇药物;3级则一般考虑重症监护病房( ICU)管理[88]。临床CRS危重症首选激素及类固醇类药物以消除过多的CAR-T细胞。近期研究显示,在接受CAR-T细胞治疗后发生CRS≥2级的患者经激素治疗后,反而比CRS < 2级患者获得更高的缓解率和更长的无进展生存期,这表明适当的CRS可能有助于CAR-T细胞治疗的疗效[93]。
据报道,1例通过全身血液滤过成功改善了严重CRS危机[94],但降低了CAR-T细胞的疗效。因此,阐明发生CRS的潜在机制有助于预防和管理这些不良事件。
(2) ICANS:是CAR-T细胞治疗的第二常见并发症,表现为多种症状,严重者出现脑水肿、血脑屏障功能障碍以及少数死亡病例[95-96]。有研究表明,由于血脑屏障的破坏,T细胞、巨噬细胞以及CAR-T细胞可以渗透到中枢神经系统[97],这些浸润的免疫细胞和细胞因子可诱导脑内巨噬细胞的小胶质细胞活化,进一步扩大局部炎症反应,最终导致神经毒性[98]。ICANS在治疗后四五天出现,可同时或独立于CRS发生[99]。目前,针对1级ICANS通常使用类固醇治疗;对于2级和3级ICANS,常使用皮质类固醇治疗,但由于神经系统本身的复杂性,缓解神经系统毒性疗效有限[100]。
(3) OTOT:在CAR-T细胞疗法的临床治疗中,已有报道不同程度非脱靶的肿瘤外毒性(On-Target,Off-Tumor toxicity,OTOT)反应,OTOT源于CAR-T细胞对表达相同抗原的正常组织识别和裂解而产生细胞毒性,包括CAR和靶细胞形成的免疫突触、释放穿孔素和颗粒酶以及分泌细胞因子均可能对正常组织造成损伤,严重时会导致死亡[101]。有报道在接受抗CD19 CAR-T细胞治疗的B细胞恶性肿瘤患者中观察到致命性脑水肿的罕见病例,发现大脑的周细胞高表达CD19相关基因,是CAR-T Off-Tumor的靶细胞[102]。除此之外,CAR-T细胞疗法还有许多新发现的毒性和不良反应,如血液毒性、神经认知和运动功能减退障碍,甚至心肌病增加风险等[103-105]。
(4)解决策略:虽然CAR-T细胞治疗的毒副作用明显,但是其相关研究已成为肿瘤细胞治疗领域的热点。CAR-T细胞输注后长期和早期使用激素及体内较高的累积剂量可显著缩短总生存期,使用高剂量的激素会显著缩短无进展生存期,激素使用的持续时间和时机会影响CAR-T细胞治疗疗效?[106]。因此,在使用激素时,应尽量少用、晚用,以减少对CAR-T疗法疗效的负面影响。同时,研究人员正积极地探寻问题解决策略。主要的解决策略有:①针对细胞毒性的问题可通过改进CAR-T细胞结构,降低细胞毒性。CAR-T细胞产品由特定患者的T细胞定制,所以产品无法达到严格的统一标准。CAR-T细胞仅是调整细胞内信号域以活化更多的T细胞产生免疫效应,但却伴随不断增大的细胞毒性。BRUDNO等[36]实验表明CAR-T细胞释放的细胞因子水平取决于CAR的铰链和跨膜结构域。一种由AUTO1构建有快速关闭率的低亲和力CD19 CAR-T细胞疗法,接受AUTO1治疗的20例成年患者中缓解率为85%,12个月无事件生存率为48.3%,无CRS(≥3级);3例患者出现3级ICANS,但降至1级或在72 h内消退[107]。②通过调整给药策略降低剂量以降低细胞毒副作用。目前常规的给药方式是对患者进行特定剂量单次输注。FREY等[108]试验发现,通过调整优化给药方式,高剂量分次输注的患者2年总生存率为73%。在AUTO1试验中使用分次治疗后,患者显示无CRS(≥3级)[106]。因此,细胞分次输注和剂量调整在保留其疗效的同时,可以优化CAR-T细胞的安全性,降低毒副作用发生率。③通过常规药物治疗减小毒副作用。采取药物或其他辅助手段对CRS和ICANS进行治疗。2017年,FDA批准托珠单抗治疗重度CRS[109],早期使用托珠单抗、类固醇和阿那白滞素(IL-1Ra)可以降低严重CRS和ICANS的发生率并且不影响CAR-T细胞的短期疗效[110-112]。④针对OTOT的问题,研究者通过加入“自杀基因”或“分子开关”等片段的CAR来修饰T细胞实现可控凋亡。选择某些药物或毒素敏感的基因导入CAR-T细胞中表达一个可通过外源物质(如药物)诱导的细胞死亡信号[113],或外部信号(如特定小分子或抗体结合)来激活或抑制的CAR-T细胞,通过设计可调节活性的CAR-T细胞,增强靶效应,降低OTOT。然而,如何确保自杀基因或分子开关的高效表达、避免对正常细胞的影响以及确保在需要时快速有效地激活等问题都需要进一步的研究和优化。另一种策略设计双特异性CAR分子,需要同时存在2种肿瘤抗原或存在1种不在正常细胞表面的肿瘤抗原才能活化CAR-T细胞,以此来减少脱靶效应。LI等[114]通过泛癌分析,识别了多个肿瘤细胞表面显著表达的靶点,利用双抗原对来筛选肿瘤特异性高表达抗原,以及运用合成生物学和逻辑电路设计来增强治疗的靶向性。精确的选择靶点和创新的治疗设计,可以有效降低毒副作用,为CAR-T细胞疗法的特异性和安全性提供了新的研究方向。
随着CAR-T细胞治疗恶性血液肿瘤越来越受到关注,CAR-T细胞疗法使用范围也在逐渐扩大,已有一些研究团队开发了预测这些不良反应的模型,预测模型的开发有助于识别相关毒性的危险因素,以期提高疗法的安全性和有效性,但仍需进一步验证和优化[115-116]。目前的策略强调持续监测、快速检测和通过支持性治疗、抗细胞因子或皮质类固醇治疗进行早期干预,但是这些干预措施是否会影响CAR-T细胞的治疗效果也是研究的重点。
2.3.2 CAR-T细胞疗法的复发率问题与解决策略 尽管抗CD19 CAR-T细胞疗法取得较好的疗效,但大部分患者治疗后会复发,复发率的高低也是CAR-T细胞疗效的关键评价标准。国际临床试验结果均表明CAR-T细胞疗法无进展生存期或无事件生存率较低,而中位无复发生存期和总生存期也都低于24个月,这种情况常见于靶向CD19治疗B-ALL的病例中,归咎原因可能与肿瘤自身的特性以及抗原逃逸有关。抗CD19 CAR-T细胞治疗后出现了2种主要的复发模式:第一种是抗原阳性复发,即CD19存在却不被抗CD19 CAR-T细胞识别,可能由于突变和选择性剪接导致含有同源表位的细胞表面片段不存在[117]。复发也与受者体内CAR-T细胞持久性差有关[118],共刺激结构域的同一性是细胞输注后持续性的决定因素。有证据表明,与CD28结构域相比,4-1BB结构域的持久性更长、峰值更高,产生更显著的抗肿瘤活性[48,119]。因此,优化CAR-T细胞的构建,如设计CD4与CD8比例为1∶1的CAR-T细胞已被证明具有优异的抗肿瘤作用[120]。第二种是抗原阴性复发,已被证明通过多种机制发展,包括免疫逃逸、谱系转换和双等位基因突变,这些细胞失去CD19表达以避免CAR-T细胞识别,无法发挥免疫效应,肿瘤细胞趁机逃亡,迅速增殖。高达30%的患者出现CD19阴性复发[71],同时,经靶向BCMA的CAR-T细胞治疗中也发现抗原阳性或阴性细胞导致复发[121],这凸显了单抗原定向治疗的缺陷。
为解决复发问题,已有许多策略被提出,包括寻找新的抗肿瘤靶点、设计多靶向抗原,二次输注CAR-T细胞以及与异基因造血干细胞移植等。①开发识别多种抗原的多靶向CAR-T细胞是一种有效降低CAR-T细胞治疗复发的方法,其中双靶向CAR-T细胞已被证明可以降低抗原阴性复发的风险[122-124],除CD19外,可以选择CD20、CD22和CD123作为B细胞恶性肿瘤中双靶向CAR的靶标。靶向3种抗原(CD19、CD20和CD22)的Tri CAR或Side CAR策略也已经开发出来,Tri CAR在小鼠模型中减轻了CD19阴性复发[125]。另一项临床前研究中,靶向CD19/CD20/CD22 CAR-T细胞构建并成功地消除了小鼠B淋巴瘤[126]。针对多靶向抗原是否存在潜在脱靶、产生的免疫效应是否会互相影响等问题,仍有待进一步研究。②CAR-T细胞在大多数患者中无法诱导持久反应,临床研究证实二次输注CAR-T细胞让患者得到更好的巩固治疗效果[127]。③2021年,美国血液学年会(ASH)公布一种异体CAR-T细胞PBCAR0191,治疗15例r/r B-ALL患者,未发生移植物抗宿主反应初步证实同种异体细胞的安全性和有效性[128]。有一项分析52例儿童和年轻人在CD19或CD22 CAR-T细胞治疗达到完全缓解后,接受了低强度的同种异体细胞移植,1年后总生存率、无事件生存率和移植相关死亡率分别为87.7%,73%和2.2%[129]。同种异体移植是进一步巩固CAR-T细胞治疗后防止复发的选择之一,但存在移植物抗宿主反应的潜在风险。④异基因造血干细胞移植进行巩固治疗。近期一项研究中,利用供者来源CD7 CAR-T细胞与异基因造血干细胞移植序贯治疗的一体化策略,无需清髓性预处理化疗和移植物抗宿主反应预防药物,避免化疗药物的毒副反应,CAR-T细胞在患者体内长期存续,降低复发率[130]。目前,相关报道随访时间比较短,长期疗效有待于进一步的医学研究证实。除此之外,增加靶细胞的免疫原性可能也是一种可行的策略,小分子分泌酶抑制剂可以减少BCMA的脱落,促进CAR-T细胞对MM细胞的识别[131]。
| [1] PORTER DL, LEVINE BL, KALOS M, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells in chronic lymphoid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(8):725-733. [2] LIU J, ZHONG JF, ZHANG X, et al. Allogeneic CD19-CAR-T cell infusion after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in B cell malignancies. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10(1):35. [3] TIMMERS M, ROEX G, WANG Y, et al. Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cell Therapy in Multiple Myeloma: Beyond B Cell Maturation Antigen. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1613. [4] YOON S, EOM GH. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy: A Novel Modality for Immune Modulation. Chonnam Med J. 2020;56(1):6-11. [5] TI D, NIU Y, WU Z, et al. Genetic engineering of T cells with chimeric antigen receptors for hematological malignancy immunotherapy. Sci China Life Sci. 2018;61(11):1320-1332. [6] ZHANG C, LIU J, ZHONG JF, et al. Engineering CAR-T cells. Biomark Res. 2017;5:22. [7] GELDRES C, SAVOLDO B, DOTTI G. Chimeric antigen receptor-redirected T cells return to the bench. Semin Immunol. 2016;28(1):3-9. [8] HOLZINGER A, ABKEN H. CAR T Cells: A Snapshot on the Growing Options to Design a CAR. Hemasphere. 2019;3(1):e172. [9] MATSUEDA S, CHEN L, LI H, et al. Recent clinical researches and technological development in TIL therapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024;73(11):232. [10] MORGAN RA, DUDLEY ME, WUNDERLICH JR, et al. Cancer regression in patients after transfer of genetically engineered lymphocytes. Science. 2006;314(5796):126-129. [11] NATHAN P, HASSEL JC, RUTKOWSKI P, et al. Overall Survival Benefit with Tebentafusp in Metastatic Uveal Melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2021; 385(13):1196-1206. [12] SALVARIS R, FEDELE PL. Targeted Therapy in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. J Pers Med. 2021;11(8):715. [13] ZHAO Z, CHEN Y, FRANCISCO NM, et al. The application of CAR-T cell therapy in hematological malignancies: advantages and challenges. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018;8(4): 539-551. [14] ZHANG X, ZHU L, ZHANG H, et al. CAR-T Cell Therapy in Hematological Malignancies: Current Opportunities and Challenges. Front Immunol. 2022;13:927153. [15] BAKER DJ, ARANY Z, BAUR JA, et al. CAR T therapy beyond cancer: the evolution of a living drug. Nature. 2023;619(7971):707-715. [16] QU C, ZHANG H, CAO H, et al. Tumor buster - where will the CAR-T cell therapy ‘missile’ go? Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):201. [17] HU Y, SUN J, WU Z, et al. Predominant cerebral cytokine release syndrome in CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cell therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 2016;9(1):70. [18] ROSELLI E, BOUCHER JC, LI G, et al. 4-1BB and optimized CD28 co-stimulation enhances function of human mono-specific and bi-specific third-generation CAR T cells. J Immunother Cancer. 2021;9(10):e003354. [19] LANITIS E, ROTA G, KOSTI P, et al. Optimized gene engineering of murine CAR-T cells reveals the beneficial effects of IL-15 coexpression. J Exp Med. 2021;218(2):e20192203. [20] DUAN D, WANG K, WEI C, et al. The BCMA-Targeted Fourth-Generation CAR-T Cells Secreting IL-7 and CCL19 for Therapy of Refractory/Recurrent Multiple Myeloma. Front Immunol. 2021;12:609421. [21] HUANG R, LI X, HE Y, et al. Recent advances in CAR-T cell engineering. J Hematol Oncol. 2020; 13(1):86. [22] ROSELLI E, FRIELING JS, THORNER K, et al. CAR-T Engineering: Optimizing Signal Transduction and Effector Mechanisms. BioDrugs. 2019;33(6):647-659. [23] LIU E, MARIN D, BANERJEE P, et al. Use of CAR-Transduced Natural Killer Cells in CD19-Positive Lymphoid Tumors. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(6): 545-553. [24] TOKAREW N, OGONEK J, ENDRES S, et al. Teaching an old dog new tricks: next-generation CAR T cells. Br J Cancer. 2019;120(1):26-37. [25] CHO JH, COLLINS JJ, WONG WW. Universal Chimeric Antigen Receptors for Multiplexed and Logical Control of T Cell Responses. Cell. 2018;173(6):1426-1438.e11. [26] BRENTJENS RJ, DAVILA ML, RIVIERE I, et al. CD19-targeted T cells rapidly induce molecular remissions in adults with chemotherapy-refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5(177):177ra38. [27] MULLARD A. FDA approves first CAR T therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16(10):669. [28] ABRAMSON JS, PALOMBA ML, GORDON LI, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): a multicentre seamless design study. Lancet. 2020;396(10254):839-852. [29] NEELAPU SS, LOCKE FL, BARTLETT NL, et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(26):2531-2544. [30] FOWLER NH, DICKINSON M, DREYLING M, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma: the phase 2 ELARA trial. Nat Med. 2022;28(2):325-332. [31] JACOBSON CA, CHAVEZ JC, SEHGAL AR, et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel in relapsed or refractory indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (ZUMA-5): a single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022;23(1):91-103. [32] SCHUSTER SJ, TAM CS, BORCHMANN P, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes of tisagenlecleucel in patients with relapsed or refractory aggressive B-cell lymphomas (JULIET): a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22(10): 1403-1415. [33] YAMADA S, KANEKO MK, SAYAMA Y, et al. Development of Novel Mouse Monoclonal Antibodies Against Human CD19. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 2020;39(2): 45-50. [34] TU S, HUANG R, GUO Z, et al. Shortening the ex vivo culture of CD19-specific CAR T-cells retains potent efficacy against acute lymphoblastic leukemia without CAR T-cell-related encephalopathy syndrome or severe cytokine release syndrome. Am J Hematol. 2019;94(12): E322-E325. [35] PASQUINI MC, HU ZH, CURRAN K, et al. Real-world evidence of tisagenlecleucel for pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2020;4(21):5414-5424. [36] BRUDNO JN, LAM N, VANASSE D, et al. Safety and feasibility of anti-CD19 CAR T cells with fully human binding domains in patients with B-cell lymphoma. Nat Med. 2020;26(2): 270-280. [37] WANG J, MOU N, YANG Z, et al. Efficacy and safety of humanized anti-CD19-CAR-T therapy following intensive lymphodepleting chemotherapy for refractory/relapsed B acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2020;191(2):212-222. [38] MYERS RM, LI Y, BARZ LEAHY A, et al. Humanized CD19-Targeted Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T Cells in CAR-Naive and CAR-Exposed Children and Young Adults With Relapsed or Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(27): 3044-3055. [39] CAPPELL KM, SHERRY RM, YANG JC, et al. Long-Term Follow-Up of Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(32): 3805-3815. [40] ABRAMSON JS, PALOMBA ML, GORDON LI, et al. Two-Year Follow-up of Transcend NHL 001, a Multicenter Phase 1 Study of Lisocabtagene Maraleucel (liso-cel) in Relapsed or Refractory (R/R) Large B-Cell Lymphomas (LBCL). Blood. 2021; 138(Supplement 1):2840-2843. [41] MAJZNER RG, MACKALL CL. Tumor Antigen Escape from CAR T-cell Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2018;8(10):1219-1226. [42] PARK JH, RIVIÈRE I, GONEN M, et al. Long-Term Follow-up of CD19 CAR Therapy in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2018; 378(5):449-459. [43] JOHN S, PULSIPHER MA, MOSKOP A, et al. Real-World Outcomes for Pediatric and Young Adult Patients with Relapsed or Refractory (R/R) B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) Treated with Tisagenlecleucel: Update from the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) Registry. Blood. 2021;138(Supplement 1):428. [44] LAETSCH TW, MAUDE SL, RIVES S, et al. Three-Year Update of Tisagenlecleucel in Pediatric and Young Adult Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in the ELIANA Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41(9):1664-1669. [45] SHAH SD, GHOBADI A, OLUWOLE OO, et al. Two-year follow-up of KTE-X19, an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, in adult patients (Pts) with relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (R/R B-ALL) in ZUMA-3. J Hematol Oncol. 2022; 40(16):256-257. [46] CHONG EA, RUELLA M, SCHUSTER SJ, et al. Five-Year Outcomes for Refractory B-Cell Lymphomas with CAR T-Cell Therapy. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384(7):673-674. [47] LOCKE FL, GHOBADI A, JACOBSON CA, et al. Long-term safety and activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma (ZUMA-1): a single-arm, multicentre, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(1):31-42. [48] WAYNE AS, HUYNH V, HIJIYA N, et al. Three-year results from phase I of ZUMA-4: KTE-X19 in pediatric relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 2023;108(3):747-760. [49] SHAH BD, GHOBADI A, OLUWOLE OO, et al. KTE-X19 for relapsed or refractory adult B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: phase 2 results of the single-arm, open-label, multicentre ZUMA-3 study. Lancet. 2021; 398(10299):491-502. [50] 中国临床肿瘤学会(CSCO)白血病专家委员会,中国医师协会血液科医师分会,中华医学会血液学分会. 纳基奥仑赛注射液临床应用指导原则(2023年版)[J].白血病·淋巴瘤,2024,33(1):1-11. [51] LOCKE FL, MIKLOS DB, JACOBSON CA, et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel as Second-Line Therapy for Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2022; 386(7):640-654. [52] ZHAO WL, LI YH, ZOU DH, et al. Efficacy and safety of Axicabtagene ciloleucel (Axi‐cel) for the treatment of relapse/refractory non‐Hodgkin lymphoma: First real‐world data in Chinese population. Hematol Oncol. 2023;41(S2):457-458. [53] NEELAPU SS, DICKINSON M, MUNOZ J, et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel as first-line therapy in high-risk large B-cell lymphoma: the phase 2 ZUMA-12 trial. Nat Med. 2022;28(4):735-742. [54] WESTIN JR, OLUWOLE OO, KERSTEN MJ, et al. Survival with Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(2):148-157. [55] YING Z, YANG H, GUO Y, et al. Relmacabtagene autoleucel (relma-cel) CD19 CAR-T therapy for adults with heavily pretreated relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma in China. Cancer Med. 2021;10(3):999-1011. [56] YING Z, ZOU D, YANG H, et al. Preliminary efficacy and safety of Relmacabtagene autoleucel (Carteyva) in adults with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma in China: A phase I/II clinical trial. Am J Hematol. 2022;97(12):E436-E438. [57] UNITED STATES FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION. FDA approves lisocabtagene maraleucel for relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma.(2024-05-15) https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-lisocabtagene-maraleucel-relapsed-or-refractory-mantle-cell-lymphoma. [58] WANG M, MUNOZ J, GOY A, et al. Three-Year Follow-Up of KTE-X19 in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma, Including High-Risk Subgroups, in the ZUMA-2 Study. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41(3):555-567. [59] PHILLIPS TJ, MARTIN A, LEE AD, et al. Estimating the health care costs associated with receipt of lisocabtagene maraleucel: Insights from adults with mantle cell lymphoma (TRANSCEND NHL 001). J Clin Oncol. 2024; 42(16_suppl):7028-7028. [60] SIDDIQI T, SOUMERAI JD, DORRITIE KA, et al. Phase 1 TRANSCEND CLL 004 study of lisocabtagene maraleucel in patients with relapsed/refractory CLL or SLL. Blood. 2022;139(12):1794-1806. [61] SHAH N, CHARI A, SCOTT E, et al. B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) in multiple myeloma: rationale for targeting and current therapeutic approaches. Leukemia. 2020;34(4):985-1005. [62] RAJE N, BERDEJA J, LIN Y, et al. Anti-BCMA CAR T-Cell Therapy bb2121 in Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(18):1726-1737. [63] MUNSHI NC, ANDERSON LD JR, SHAH N, et al. Idecabtagene Vicleucel in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(8):705-716. [64] KANG L, ZHANG J, LI M, et al. Characterization of novel dual tandem CD19/BCMA chimeric antigen receptor T cells to potentially treat multiple myeloma. Biomark Res. 2020;8:14. [65] LI C, WANG D, SONG Y, et al. A Phase 1/2 Study of a Novel Fully Human B-Cell Maturation Antigen-Specific CAR T Cells (CT103A) in Patients with Relapsed and/or Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Blood. 2021; 138(Supplement 1):547. [66] SAMUR MK, FULCINITI M, AKTAS SAMUR A, et al. Biallelic loss of BCMA as a resistance mechanism to CAR T cell therapy in a patient with multiple myeloma. Nat Commun. 2021; 12(1):868. [67] MARTIN T, USMANI SZ, BERDEJA JG, et al. Ciltacabtagene Autoleucel, an Anti-B-cell Maturation Antigen Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy, for Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma: CARTITUDE-1 2-Year Follow-Up. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41(6): 1265-1274. [68] 中国国家药品监督管理局.国家药监局附条件批准伊基奥仑赛注射液上市[EB/OL]. (2023-06-30) https://www.nmpa.gov.cn/directory/web/nmpa/zhuanti/ypqxgg/gggzjzh/20230630195006116.html. [69] LI C, CAO W, QUE Y, et al. A phase I study of anti-BCMA CAR T cell therapy in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma and plasma cell leukemia. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(3):e346. [70] ZHAO WH, WANG BY, CHEN LJ, et al. Four-year follow-up of LCAR-B38M in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma: a phase 1, single-arm, open-label, multicenter study in China (LEGEND-2). J Hematol Oncol. 2022; 15(1):86. [71] RUELLA M, MAUS MV. Catch me if you can: Leukemia Escape after CD19-Directed T Cell Immunotherapies. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2016;14:357-362. [72] PIERCE JM, MEHTA A. Diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic role of CD30 in lymphoma. Expert Rev Hematol. 2017;10(1):29-37. [73] CUI W, ZHANG X, DAI H, et al. Tandem CD19/CD22 Dual Targets CAR T-Cells Bridging Hematopoietic Stem Cells Transplantation Acquires Robust Remission for Relapsed and Refractory B Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Patients. Blood. 2021;138(Supplement 1): 1753. [74] CUI W, ZHANG X, DAI H, et al. Tandem CD19/CD22 Dual Targets CAR-T Cells Therapy Acquires Superior CR Rate Than CD19 CAR-T Cells: A Case Controlled Study. Blood. 2020;136(Supplement 1):44. [75] ZHANG WY, LIU Y, WANG Y, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of CART-20 cells in patients with refractory or relapsed B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: 5-years follow-up results of the phase I and IIa trials. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2017;2:17054. [76] SANG W, SHI M, YANG J, et al. Phase II trial of co-administration of CD19- and CD20-targeted chimeric antigen receptor T cells for relapsed and refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Med. 2020;9(16):5827-5838. [77] PAN J, NIU Q, DENG B, et al. CD22 CAR T-cell therapy in refractory or relapsed B acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2019;33(12): 2854-2866. [78] WANG N, HU X, CAO W, et al. Efficacy and safety of CAR19/22 T-cell cocktail therapy in patients with refractory/relapsed B-cell malignancies. Blood. 2020;135(1):17-27. [79] YAN LE, ZHANG H, WADA M, et al. Targeting Two Antigens Associated with B-ALL with CD19-CD123 Compound Car T Cell Therapy. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020;16(2):385-396. [80] SUN C, MAHENDRAVADA A, BALLARD B, et al. Safety and efficacy of targeting CD138 with a chimeric antigen receptor for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Oncotarget. 2019;10(24):2369-2383. [81] VAN DE DONK NW, JANMAAT ML, MUTIS T, et al. Monoclonal antibodies targeting CD38 in hematological malignancies and beyond. Immunol Rev. 2016;270(1):95-112. [82] MEI H, LI C, JIANG H, et al. A bispecific CAR-T cell therapy targeting BCMA and CD38 in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14(1):161. [83] TANG Y, YIN H, ZHAO X, et al. High efficacy and safety of CD38 and BCMA bispecific CAR-T in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022;41(1):2. [84] RADHAKRISHNAN SV, LUETKENS T, SCHERER SD, et al. CD229 CAR T cells eliminate multiple myeloma and tumor propagating cells without fratricide. Nat Commun. 2020; 11(1):798. [85] BRUDNO JN, KOCHENDERFER JN. Current understanding and management of CAR T cell-associated toxicities. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2024; 21(7):501-521. [86] PORTER DL, HWANG WT, FREY NV, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T cells persist and induce sustained remissions in relapsed refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Sci Transl Med. 2015;7(303):303ra139. [87] NEELAPU SS, TUMMALA S, KEBRIAEI P, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy - assessment and management of toxicities. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018;15(1):47-62. [88] LEE DW, SANTOMASSO BD, LOCKE FL, et al. ASTCT Consensus Grading for Cytokine Release Syndrome and Neurologic Toxicity Associated with Immune Effector Cells. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25(4): 625-638. [89] BULLOCK TNJ. CD40 stimulation as a molecular adjuvant for cancer vaccines and other immunotherapies. Cell Mol Immunol. 2022;19(1):14-22. [90] RIEGLER LL, JONES GP, LEE DW. Current approaches in the grading and management of cytokine release syndrome after chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2019;15:323-335. [91] JIANG H, LIU L, GUO T, et al. Improving the safety of CAR-T cell therapy by controlling CRS-related coagulopathy. Ann Hematol. 2019;98(7):1721-1732. [92] WANG Y, QI K, CHENG H, et al. Coagulation Disorders after Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy: Analysis of 100 Patients with Relapsed and Refractory Hematologic Malignancies. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020;26(5):865-875. [93] DONG R, JIANG S, CHEN Y, et al. Prognostic Significance of Cytokine Release Syndrome in B Cell Hematological Malignancies Patients After Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2021;41(12):469-476. [94] LIU Y, CHEN X, WANG D, et al. Hemofiltration Successfully Eliminates Severe Cytokine Release Syndrome Following CD19 CAR-T-Cell Therapy. J Immunother. 2018;41(9):406-410. [95] TORRE M, SOLOMON IH, SUTHERLAND CL, et al. Neuropathology of a Case With Fatal CAR T-Cell-Associated Cerebral Edema. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2018;77(10): 877-882. [96] WANG Z, HAN W. Biomarkers of cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity related to CAR-T cell therapy. Biomark Res. 2018;6:4. [97] DENG Q, HAN G, PUEBLA-OSORIO N, et al. Characteristics of anti-CD19 CAR T cell infusion products associated with efficacy and toxicity in patients with large B cell lymphomas. Nat Med. 2020;26(12):1878-1887. [98] MORRIS EC, NEELAPU SS, GIAVRIDIS T, et al. Cytokine release syndrome and associated neurotoxicity in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2022;22(2):85-96. [99] HUNTER BD, JACOBSON CA. CAR T-Cell Associated Neurotoxicity: Mechanisms, Clinicopathologic Correlates, and Future Directions. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2019;111(7): 646-654. [100] SCHUBERT ML, SCHMITT M, WANG L, et al. Side-effect management of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy. Ann Oncol. 2021;32(1):34-48. [101] FLUGEL CL, MAJZNER RG, KRENCIUTE G, et al. Overcoming on-target, off-tumour toxicity of CAR T cell therapy for solid tumours. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2023;20(1):49-62. [102] PARKER KR, MIGLIORINI D, PERKEY E, et al. Single-Cell Analyses Identify Brain Mural Cells Expressing CD19 as Potential Off-Tumor Targets for CAR-T Immunotherapies. Cell. 2020;183(1): 126-142.e17. [103] GANATRA S, REDD R, HAYEK SS, et al. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy-Associated Cardiomyopathy in Patients With Refractory or Relapsed Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Circulation. 2020;142(17):1687-1690. [104] WUDHIKARN K, PENNISI M, GARCIA-RECIO M, et al. DLBCL patients treated with CD19 CAR T cells experience a high burden of organ toxicities but low nonrelapse mortality. Blood Adv. 2020;4(13):3024-3033. [105] VAN OEKELEN O, ALEMAN A, UPADHYAYA B, et al. Neurocognitive and hypokinetic movement disorder with features of parkinsonism after BCMA-targeting CAR-T cell therapy. Nat Med. 2021;27(12):2099-2103. [106] STRATI P, AHMED S, FURQAN F, et al. Prognostic impact of corticosteroids on efficacy of chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy in large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2021;137(23): 3272-3276. [107] RODDIE C, DIAS J, O’REILLY MA, et al. Durable Responses and Low Toxicity After Fast Off-Rate CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor-T Therapy in Adults With Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(30):3352-3363. [108] FREY NV, SHAW PA, HEXNER EO, et al. Optimizing Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy for Adults With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(5):415-422. [109] LE RQ, LI L, YUAN W, et al. FDA Approval Summary: Tocilizumab for Treatment of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell-Induced Severe or Life-Threatening Cytokine Release Syndrome. Oncologist. 2018;23(8):943-947. [110] LIU S, DENG B, YIN Z, et al. Corticosteroids do not influence the efficacy and kinetics of CAR-T cells for B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 2020;10(2):15. [111] GARDNER RA, CEPPI F, RIVERS J, et al. Preemptive mitigation of CD19 CAR T-cell cytokine release syndrome without attenuation of antileukemic efficacy. Blood. 2019;134(24):2149-2158. [112] PARK JH, SAUTER CS, PALOMBA ML, et al. A Phase II Study of Prophylactic Anakinra to Prevent CRS and Neurotoxicity in Patients Receiving CD19 CAR T Cell Therapy for Relapsed or Refractory Lymphoma. Blood. 2021;138(Supplement 1):96. [113] AUTIO KA, BONI V, HUMPHREY RW, et al. Probody Therapeutics: An Emerging Class of Therapies Designed to Enhance On-Target Effects with Reduced Off-Tumor Toxicity for Use in Immuno-Oncology. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26(5):984-989. [114] LI X, ZHOU J, ZHANG W, et al. Pan-Cancer Analysis Identifies Tumor Cell Surface Targets for CAR-T Cell Therapies and Antibody Drug Conjugates. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(22):5674. [115] SESQUES P, KIRKWOOD AA, KWON M, et al. Novel prognostic scoring systems for severe CRS and ICANS after anti-CD19 CAR T cells in large B-cell lymphoma. J Hematol Oncol. 2024;17(1):61. [116] GRITTI G, BELOUSOV A, RELF J, et al. Predictive model for the risk of cytokine release syndrome with glofitamab treatment for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2024;8(14):3615-3618. [117] WANG Z, WU Z, LIU Y, et al. New development in CAR-T cell therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 2017; 10(1):53. [118] HAY KA, GAUTHIER J, HIRAYAMA AV, et al. Factors associated with durable EFS in adult B-cell ALL patients achieving MRD-negative CR after CD19 CAR T-cell therapy. Blood. 2019; 133(15):1652-1663. [119] MAUDE SL, LAETSCH TW, BUECHNER J, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Children and Young Adults with B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(5):439-448. [120] TURTLE CJ, HANAFI LA, BERGER C, et al. CD19 CAR-T cells of defined CD4+:CD8+ composition in adult B cell ALL patients. J Clin Invest. 2016; 126(6):2123-2138. [121] ALI SA, SHI V, MARIC I, et al. T cells expressing an anti-B-cell maturation antigen chimeric antigen receptor cause remissions of multiple myeloma. Blood. 2016;128(13):1688-1700. [122] TONG C, ZHANG Y, LIU Y, et al. Optimized tandem CD19/CD20 CAR-engineered T cells in refractory/relapsed B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2020;136(14):1632-1644. [123] ZANETTI SR, VELASCO-HERNANDEZ T, GUTIERREZ-AGÜERA F, et al. A novel and efficient tandem CD19- and CD22-directed CAR for B cell ALL. Mol Ther. 2022; 30(2):550-563. [124] DAI H, WU Z, JIA H, et al. Bispecific CAR-T cells targeting both CD19 and CD22 for therapy of adults with relapsed or refractory B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13(1):30. [125] FOUSEK K, WATANABE J, JOSEPH SK, et al. CAR T-cells that target acute B-lineage leukemia irrespective of CD19 expression. Leukemia. 2021;35(1):75-89. [126] SCHNEIDER D, XIONG Y, WU D, et al. Trispecific CD19-CD20-CD22-targeting duoCAR-T cells eliminate antigen-heterogeneous B cell tumors in preclinical models. Sci Transl Med. 2021; 13(586):eabc6401. [127] GAUTHIER J, BEZERRA ED, HIRAYAMA AV, et al. Factors associated with outcomes after a second CD19-targeted CAR T-cell infusion for refractory B-cell malignancies. Blood. 2021; 137(3):323-335. [128] JAIN N, KANTARJIAN H, SOLOMON SR, et al. Preliminary Safety and Efficacy of PBCAR0191, an Allogeneic ‘Off-the-Shelf’ CD19-Directed CAR-T for Patients with Relapsed/Refractory (R/R) CD19+ B-ALL. Blood. 2021; 138(Supplement 1):650. [129] ZHANG Y, CHEN H, SONG Y, et al. Chimeric antigens receptor T cell therapy as a bridge to haematopoietic stem cell transplantation for refractory/ relapsed B-cell acute lymphomalastic leukemia. Br J Haematol. 2020;189(1):146-152. [130] HU Y, ZHANG M, YANG T, et al. Sequential CD7 CAR T-Cell Therapy and Allogeneic HSCT without GVHD Prophylaxis. N Engl J Med. 2024; 390(16):1467-1480. [131] PONT MJ, HILL T, COLE GO, et al. γ-Secretase inhibition increases efficacy of BCMA-specific chimeric antigen receptor T cells in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2019;134(19): 1585-1597. |
| [1] | 吕国庆, 艾孜麦提江·肉孜, 熊道海. 鸢尾素抑制人关节软骨细胞中铁死亡的作用及其机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1359-1367. |
| [2] | 王正业, 刘万林, 赵振群. miRNA在激素诱导股骨头坏死机制中的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1207-1214. |
| [3] | 余伟杰, 曹东东, 郭天赐, 牛朴钰, 杨家麟, 王思敏, 刘爱峰. 经皮内镜腰椎间盘切除后复发风险预测模型的系统评价和Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(3): 749-759. |
| [4] | 薛 慧, 李东楠, 赵雅迪, 陈 超, 谢宗源. Ph染色体阳性急性淋巴细胞白血病移植前后BCR/ABL基因表达与复发的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(1): 139-144. |
| [5] | 静如意, 陈颖欣, 曹 蕾. 深板层角膜移植与穿透性角膜移植治疗基质角膜营养不良预后的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1626-1633. |
| [6] | 杨溢珂, 任亚锋, 李 冰, 尚文雅, 黄 靖, 郭 佳, 刘慧瑶. 脊髓损伤后细胞自噬的调控治疗机制及策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(18): 3885-3896. |
| [7] | 董政沁, 郑 琦, 吴关贸, 王文娜, 陈乐琴. 鸢尾素、运动、疾病与健康的新关联[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(18): 3897-3905. |
| [8] | 周丽君, 张克远, 王 茜, 俞 丽, 徐飞虎, 丁 红, 马海蓉. 环状RNA通过细胞内机制参与骨关节炎的发病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(35): 5716-5722. |
| [9] | 彭英楠, 边志磊, 张素平, 李 丽, 曹伟杰, 万鼎铭. CD34+细胞数对单倍体造血干细胞移植治疗恶性血液病的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 1-6. |
| [10] | 王慧达, 孙小桐, 毕 蓝, 王子轩, 张荣和. 黄芪多糖在正畸骨改建中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(32): 5214-5218. |
| [11] | 刘修齐, 陈 方, 仲鹤鹤, 熊华章, 吕国庆, 吴术红, 刘 毅. 改良弹性固定Latarjet术治疗伴明显关节盂骨缺损复发性肩关节前脱位的短期随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(29): 4684-4689. |
| [12] | 付东阁, 何静子. 运动损伤滑膜组织转录组数据分析及骨关节炎关键通路和特征基因[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(28): 4554-4558. |
| [13] | 李 鑫, 罗鸣然, 李 根, 程 琳, 潘 彬, 袁 峰. 建立与验证经皮内窥镜腰椎间盘切除后复发风险的预测模型[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(13): 2087-2092. |
| [14] | 慈文韬, 章鑫隆, 闫 石, 王 钊. 降低诱导膜技术治疗骨髓炎后感染复发的问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(28): 4546-4552. |
| [15] | 蔡胜胜, 梅 衡, 张学全, 邓 劲, 曹 俊, 何 斌. 制备HPe6DF复合纳米粒子增强光动力治疗效果[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(10): 1566-1573. |
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2024年7月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2010年1月至2024年7月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中文数据库:中国知网、万方数据库;英文数据库:PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“嵌合抗原受体T细胞,B细胞恶性肿瘤,毒副作用,免疫疗法”。英文检索词为“CAR-T,B cell hematological malignancies,Toxic side effects,Immunotherapy”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著,综述,述评,病例报告。
1.1.6 检索策略 以PubMed数据库为例,检索策略见图1。
1.1.7 检索文献量 中文文献522篇,英文文献2 904篇。
1.2 纳入标准 ①CAR-T细胞相关治疗靶点治疗B细胞恶性肿瘤;②CAR-T细胞上市产品;③原创性高且结论明确的研究;④近10 年发表在权威杂志上的文献。
1.3 排除标准 ①与此次研究内容相关性差的文献;②内容重复性研究。
1.4 资料整合 共检索到3 426篇相关文献,其中排除3 295篇文献,实际纳入131篇文献,包括中文1篇文献,英文130篇文献。检索流程见图2。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
文题释义:
嵌合抗原受体T细胞疗法:是一种免疫治疗技术,通过基因工程手段改造患者的T细胞,使其表面表达能识别肿瘤抗原的嵌合抗原受体,从而激活并引导T细胞精准杀死癌细胞。这种疗法在血液肿瘤中显示出显著疗效,已有多款嵌合抗原受体T细胞产品获批上市。
B细胞血液恶性肿瘤:起源于血液或骨髓中的B细胞,包括各种类型的B细胞淋巴瘤和B细胞白血病。例如,B细胞急性淋巴细胞性白血病、慢性淋巴细胞性白血病、非霍奇金淋巴瘤中的B细胞类型(如弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤)等。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
本文对已上市产品CAR-T细胞治疗B细胞恶性肿瘤的长期疗效数据进行全面总结,这为临床决策提供了宝贵的参考。与同类研究相比,本文不仅关注了治疗效果,还深入探讨了治疗后的毒副作用和复发问题,并提出了针对性的解决策略。当前,CAR-T治疗的研究热点集中在提高治疗的特异性、降低毒性、以及如何克服肿瘤微环境中的免疫抑制。此外,开发新的靶点和联合治疗策略也是研究的前沿方向。随着更多适应证的开发和临床试验的进行,CAR-T治疗的潜力将进一步得到发挥,有望实现更精准的靶向和更低的毒副作用,从而提高治愈率并改善患者的生活质量。
#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||