[21]
HEISE T. The future of insulin therapy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2021; 175:108820.
[22] KAKLEAS K, SOLDATOU A, KARACHALIOU F, et al. Associated autoimmune diseases in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). Autoimmun Rev. 2015;14(9):781-797.
[23] XU L, LI Y, DAI Y, et al. Natural products for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: Pharmacology and mechanisms. Pharmacol Res. 2018;130:451-465.
[24] ZHENG Y, LEY SH, HU FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018; 14(2):88-98.
[25] SINGH R, BARDEN A, MORI T, et al. Advanced glycation end-products: a review. Diabetologia. 2001;44(2):129-146.
[26] MAURI-OBRADORS E, ESTRUGO-DEVESA A, JANÉ-SALAS E, et al. Oral manifestations of Diabetes Mellitus. A systematic review. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2017;22(5):e586-e594.
[27] SWEENEY SC. Alterations in tissue and serum ceruloplasmin concentration associated with inflammation. J Dent Res. 1967;46(6): 1171-1176.
[28] ZHANG C, LI Q, LAI S, et al. Attenuation of diabetic nephropathy by Sanziguben Granule inhibiting EMT through Nrf2-mediated anti-oxidative effects in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017;205:207-216.
[29] HUANG H, JIANG Y, MAO G, et al. Protective effects of allicin on streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats. J Sci Food Agric. 2017;97(4):1359-1366.
[30] RAMALINGAM L, MENIKDIWELA K, LEMIEUX M, et al. The renin angiotensin system, oxidative stress and mitochondrial function in obesity and insulin resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017;1863(5):1106-1114.
[31] YARIBEYGI H, ATKIN SL, SAHEBKAR A. Mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetes and the regulatory roles of antidiabetic agents on the mitochondrial function. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(6):8402-8410.
[32] ACKERMAN CM, CHANG CJ. Copper signaling in the brain and beyond. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(13):4628-4635.
[33] TSVETKOV P, COY S, PETROVA B, et al. Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science. 2022;375(6586): 1254-1261.
[34] 林锦贤,王攀,吴欣谋,等.铜稳态失调诱导调节性细胞死亡及其调控的研究进展[J].江苏大学学报(医学版),2022,32(4):306-317.
[35] LIN CC, HUANG HH, HU CW, et al. Trace elements, oxidative stress and glycemic control in young people with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2014;28(1):18-22.
[36] OZDEMIR G, OZDEN M, MARAL H, et al. Malondialdehyde, glutathione, glutathione peroxidase and homocysteine levels in type 2 diabetic patients with and without microalbuminuria. Ann Clin Biochem. 2005; 42(Pt 2):99-104.
[37] SEBIO RM, FERRAROTTI N, LAIRION F, et al. Brain oxidative stress in rat with chronic iron or copper overload. J Inorg Biochem. 2019; 199:110799.
[38] LIEW G, LEI Z, TAN G, et al. Metabolomics of Diabetic Retinopathy.Curr Diab Rep. 2017;17(11):102.
[39] LIU Y, MIAO J. An Emerging Role of Defective Copper Metabolism in Heart Disease. Nutrients. 2022;14(3):700.
[40] CUI X, WANG Y, LIU H, et al. The Molecular Mechanisms of Defective Copper Metabolism in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:5418376.
[41] BOUDINA S, ABEL ED. Diabetic cardiomyopathy revisited. Circulation. 2007;115(25):3213-3223.
[42] ZHANG L, WARD ML, PHILLIPS AR, et al. Protection of the heart by treatment with a divalent-copper-selective chelator reveals a novel mechanism underlying cardiomyopathy in diabetic rats. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2013;12:123.
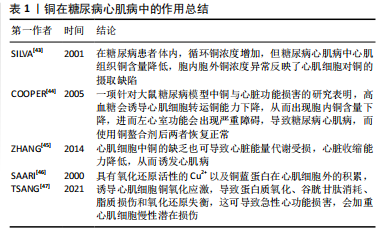
[43] SILVA J, WILLIAMS R. The Biological Chemistry of the Elements: The Inorganic Chemistry of Life, 2nd ed; Clarendon: Oxford, UK, 2001:418-435.
[44] COOPER GJ, CHAN YK. Demonstration of a Hyperglycemia-Driven Pathogenic Abnormality of Copper Homeostasis in Diabetes and Its Reversibility by Selective Chelation: Quantitative Comparisons Between the Biology of Copper and Eight Other Nutritionally Essential Elements in Normal and Diabetic Individuals. Diabetes. 2005;54: 1468-1476.
[45] ZHANG S, LIU H, AMARSINGH GV, et al. Diabetic cardiomyopathy is associated with defective myocellular copper regulation and both defects are rectified by divalent copper chelation. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2014;13:100.
[46] SAARI JT. Copper deficiency and cardiovascular disease: role of peroxidation, glycation, and nitration. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2000; 78(10):848-855.
[47] TSANG T, DAVIS CI, BRADY DC. Copper biology. Curr Biol. 2021;31(9): R421-R427.
[48] FERNÁNDEZ-RODARTE BA, SOTO-DOMÍNGUEZ A, GONZÁLEZNAVARRO A, et al. Copper induces damage, oxidative stress and cell death in endothelium of chronic intoxicated Wistar rats. Int J Morphol. 2022; 40(1): 10-17.
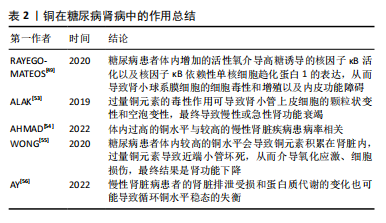
[49] RAYEGO-MATEOS S, MORGADO-PASCUAL JL, OPAZO-RÍOS L, et al. Pathogenic Pathways and Therapeutic Approaches Targeting Inflammation in Diabetic Nephropathy. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(11):3798.
[50] 党佳蓉,党琳慧,郭煦妍,等.糖尿病肾病的发病机制研究[J].医学信息,2022,35(17):161-165.
[51] YANG C, GAO B, ZHAO X, et al. Executive summary for China Kidney Disease Network (CK-NET) 2016 Annual Data Report. Kidney Int. 2020;98(6):1419-1423.
[52] PERSSON F, ROSSING P. Diagnosis of diabetic kidney disease: state of the art and future perspective. Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 2018;8(1):2-7.
[53] ALAK G, YELTEKIN AÇ, UÇAR A, et al. Borax Alleviates Copper-Induced Renal Injury via Inhibiting the DNA Damage and Apoptosis in Rainbow Trout. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2019;191(2):495-501.
[54] AHMAD S, ÄRNLÖV J, LARSSON SC. Genetically Predicted Circulating Copper and Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients. 2022;14(3):509.
[55] WONG A, WILSON-FRANK CR, HOOSER SB, et al. Chronic copper toxicosis in a crossbred heifer calf. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2020;32(3):458-462.
[56] AY A, ALKANLI N, USTUNDAG S. Investigation of the Relationship Between IL-18 (- 607 C/A), IL-18 (- 137 G/C), and MMP-2 (- 1306 C/T) Gene Variations and Serum Copper and Zinc Levels in Patients Diagnosed with Chronic Renal Failure. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022; 200(5):2040-2052.
[57] NIU YY, ZHANG YY, ZHU Z, et al. Elevated intracellular copper contributes a unique role to kidney fibrosis by lysyl oxidase mediated matrix crosslinking. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(3):211.
[58] ANTONETTI DA, KLEIN R, GARDNER TW. Diabetic retinopathy. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(13):1227-1239.
[59] STITT AW, CURTIS TM, CHEN M, et al. The progress in understanding and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016;51: 156-186.
[60] AUGUSTINE J, TROENDLE EP, BARABAS P, et al. The Role of Lipoxidation in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Retinopathy. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;11:621938.
[61] 万文萃,龙洋.糖尿病视网膜病变的流行病学、病因学与发病机制研究现状[J].眼科新进展,2022,42(9):673-679.
[62] BROWNLEE M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature. 2001;414(6865):813-820.
[63] GUZIK TJ, MUSSA S, GASTALDI D, et al. Mechanisms of increased vascular superoxide production in human diabetes mellitus: role of NAD(P)H oxidase and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circulation. 2002;105(14):1656-1662.
[64] YILDIRIM Z, UÇGUN NI, KILIÇ N, et al. Antioxidant enzymes and diabetic retinopathy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1100:199-206.
[65] 陶玉滨,许勇臣.糖尿病视网膜病变中血清铜蓝蛋白水平变化的意义[J]. 实用预防医学,2009,16(5):1591-1592.
[66] WALTER RM JR, URIU-HARE JY, OLIN KL, et al. Copper, zinc, manganese, and magnesium status and complications of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1991;14(11):1050-1056.
[67] DOŞA MD, HANGAN LT, CRAUCIUC E, et al. Influence of therapy with metformin on the concentration of certain divalent cations in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2011;142(1):36-46.
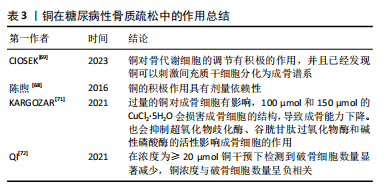
[68] 陈煦,王新力,邹远康,等.微小RNA在骨质疏松症治疗中的作用及机制的研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(6):786-790.
[69] CIOSEK Ż, KOT K, ROTTER I. Iron, Zinc, Copper, Cadmium, Mercury, and Bone Tissue. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(3):2197.
[70] DING H, GAO YS, WANG Y, et al. Dimethyloxaloylglycine increases the bone healing capacity of adipose-derived stem cells by promoting osteogenic differentiation and angiogenic potential. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23(9):990-1000.
[71] KARGOZAR S, MOZAFARI M, GHODRAT S, et al. Copper-containing bioactive glasses and glass-ceramics: From tissue regeneration to cancer therapeutic strategies. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021; 121:111741.
[72] QI Y, WANG H, CHEN X, et al. The role of TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling pathway and oxidative stress in the inhibition of osteoblast mineralization by copper chloride. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2021; 84:103613.
[73] BERNHARDT A, BACOVA J, GBURECK U, et al. Influence of Cu2+ on Osteoclast Formation and Activity In Vitro. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:2451.
[74] ALBERT DA, WARD A, ALLWEISS P, et al. Diabetes and oral disease: implications for health professionals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012;1255:1-15.
[75] American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2013;36 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S67-S74.
[76] AHMAD R, HAQUE M. Oral Health Messiers: Diabetes Mellitus Relevance. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021;14:3001-3015.
[77] NIBALI L, GKRANIAS N, MAINAS G, et al. Periodontitis and implant complications in diabetes. Periodontol 2000. 2022;90(1):88-105.
[78] DEMMER RT, JACOBS DR JR, DESVARIEUX M. Periodontal disease and incident type 2 diabetes: results from the First National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey and its epidemiologic follow-up study. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(7):1373-1379.
[79] KOCHER T, KÖNIG J, BORGNAKKE WS, et al. Periodontal complications of hyperglycemia/diabetes mellitus: Epidemiologic complexity and clinical challenge. Periodontol 2000. 2018;78(1):59-97.
[80] MAURI-OBRADORS E, ESTRUGO-DEVESA A, JANÉ-SALAS E, et al. Oral manifestations of Diabetes Mellitus. A systematic review. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2017;22(5):e586-e594.
[81] KUDIYIRICKAL MG, PAPPACHAN JM. Diabetes mellitus and oral health. Endocrine. 2015;49(1):27-34.
[82] MOORE PA, WEYANT RJ, MONGELLUZZO MB, et al. Type 1 diabetes mellitus and oral health: assessment of periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 1999;70(4):409-417.
[83] TEEUW WJ, GERDES VE, LOOS BG. Effect of periodontal treatment on glycemic control of diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(2):421-427.
[84] JANKET SJ, WIGHTMAN A, BAIRD AE, et al. Does periodontal treatment improve glycemic control in diabetic patients? A meta-analysis of intervention studies. J Dent Res. 2005;84(12):1154-1159.
[85] DARRÉ L, VERGNES JN, GOURDY P, et al. Efficacy of periodontal treatment on glycaemic control in diabetic patients: A meta-analysis of interventional studies. Diabetes Metab. 2008;34(5):497-506.
[86] DOMMISCH H, KUZMANOVA D, JÖNSSON D, et al. Effect of micronutrient malnutrition on periodontal disease and periodontal therapy. Periodontol 2000. 2018;78(1):129-153.
[87] VASILYEV VB. Looking for a partner: ceruloplasmin in protein-protein interactions. Biometals. 2019;32(2):195-210.
[88] WU H, GUO H, LIU H, et al. Copper sulfate-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress promotes hepatic apoptosis by activating CHOP, JNK and caspase-12 signaling pathways. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020; 191:110236.
[89] LIU H, GUO H, JIAN Z, et al. Copper Induces Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in the Mouse Liver. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020: 1359164.
[90] LUO Q, SONG Y, KANG J, et al. mtROS-mediated Akt/AMPK/mTOR pathway was involved in Copper-induced autophagy and it attenuates Copper-induced apoptosis in RAW264.7 mouse monocytes. Redox Biol. 2021;41:101912.
[91] KRUMSCHNABEL G, EBNER HL, HESS MW, et al. Apoptosis and necroptosis are induced in rainbow trout cell lines exposed to cadmium. Aquat Toxicol. 2010;99(1):73-85.
[92] DEIGENDESCH N, ZYCHLINSKY A, MEISSNER F. Copper Regulates the Canonical NLRP3 Inflammasome. J Immunol. 2018;200(5):1607-1617.
[93] LIAO J, YANG F, TANG Z, et al. Inhibition of Caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis attenuates copper-induced apoptosis in chicken hepatocytes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019;174:110-119.
[94] RAKSHIT A, KHATUA K, SHANBHAG V, et al. Cu2+ selective chelators relieve copper-induced oxidative stress in vivo. Chem Sci. 2018;9(41): 7916-7930.
[95] MAHER P. Potentiation of glutathione loss and nerve cell death by the transition metals iron and copper: Implications for age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018;115:92-104.