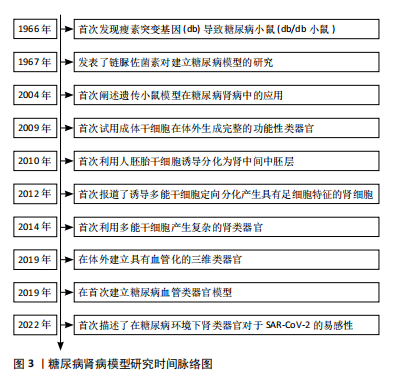
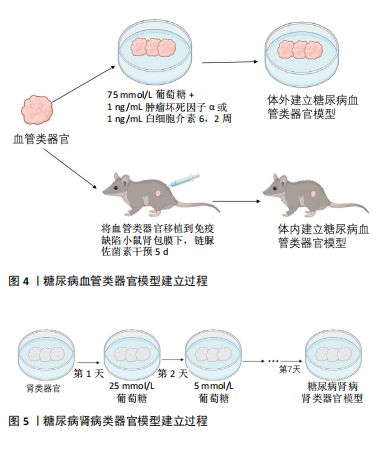
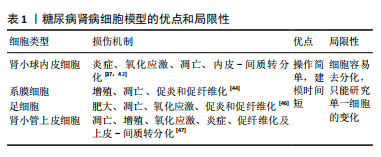
[22]
LONG HY, QIAN ZP, LAN Q, et al. Human pluripotent stem cell-derived kidney organoids: Current progress and challenges. World J Stem Cells. 2024;16(2):114-125.
[23] NISHINAKAMURA R. Human kidney organoids: progress and remaining challenges. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2019;15(10):613-624.
[24] FACIOLI R, LOJUDICE FH, ANAUATE AC, et al. Kidney organoids generated from erythroid progenitors cells of patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. PloS one. 2021;16(8):e0252156.
[25] TRAN T, SONG CJ, NGUYEN T, et al. A scalable organoid model of human autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease for disease mechanism and drug discovery. Cell Stem Cell. 2022;29(7):1083-1101.e7.
[26] DIGBY JLM, VANICHAPOL T, PRZEPIORSKI A, et al. Evaluation of cisplatin-induced injury in human kidney organoids. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020;318(4):F971-F978.
[27] NGUYEN L, WRUCK W, ERICHSEN L, et al. The Nephrotoxin Puromycin Aminonucleoside Induces Injury in Kidney Organoids Differentiated from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cells. 2022;11(4):635.
[28] LI Z, XU H, YU L, et al. Patient-derived renal cell carcinoma organoids for personalized cancer therapy. Clin Transl Med. 2022;12(7):e970.
[29] OISHI H, TABIBZADEH N, MORIZANE R. Advancing preclinical drug evaluation through automated 3D imaging for high-throughput screening with kidney organoids. Biofabrication. 2024;16(3): 10.1088/1758-5090/ad38df.
[30] GAYKEMA LH, VAN NIEUWLAND RY, LIEVERS E, et al. T-Cell Mediated Immune Rejection of Beta-2-Microglobulin Knockout Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Kidney Organoids. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2024;13(1):69-82.
[31] BEYDAG-TASÖZ BS, YENNEK S, GRAPIN-BOTTON A. Towards a better understanding of diabetes mellitus using organoid models. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023;19(4):232-248.
[32] KIM JW, NAM SA, YI J, et al. Kidney Decellularized Extracellular Matrix Enhanced the Vascularization and Maturation of Human Kidney Organoids. Adv Mater. 2022;9(15):e2103526.
[33] NERGER BA, SINHA S, LEE NN, et al. 3D Hydrogel Encapsulation Regulates Nephrogenesis in Kidney Organoids. Adv Mater. 2024;36(14): e2308325.
[34] GARRETA E, MOYA-RULL D, MARCO A, et al. Natural Hydrogels Support Kidney Organoid Generation and Promote In Vitro Angiogenesis. Adv Mater. 2024:e2400306. doi: 10.1002/adma.202400306.
[35] HOMAN KA, GUPTA N, KROLL KT, et al. Flow-enhanced vascularization and maturation of kidney organoids in vitro. Nat Methods. 2019;16(3): 255-262.
[36] KROLL KT, HOMAN KA, UZEL SGM, et al. A perfusable, vascularized kidney organoid-on-chip model. Biofabrication. 2024;16(4). doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/ad5ac0.
[37] HU S, HANG X, WEI Y, et al. Crosstalk among podocytes, glomerular endothelial cells and mesangial cells in diabetic kidney disease: an updated review. Cell Commun Signal. 2024;22(1):136.
[38] TSUJIMOTO H, HOSHINA A, MAE SI, et al. Selective induction of human renal interstitial progenitor-like cell lineages from iPSCs reveals development of mesangial and EPO-producing cells. Cell Rep. 2024;43(2):113602.
[39] SHANKAR AS, TEJEDA-MORA H, DU Z, et al. Interactions of the Immune System with Human Kidney Organoids. Transpl Int. 2024;37:12468.
[40] PECKSEN E, TKACHUK S, SCHRöDER C, et al. Monocytes prevent apoptosis of iPSCs and promote differentiation of kidney organoids. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024;15(1):132.
[41] FANG Q, MA R Y, HE YH, et al. Effects of ferulic acid on inflammation and autophagy levels in glomerular mesangial cells induced by high glucose. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2022;38(5):453-457.
[42] WU M, HAO Y, WU X, et al. SirT7-mediated transcription of fascin in hyperglycemic glomerular endothelial cells contributes to EndMT in diabetic nephropathy. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024; 56(4):586-596.
[43] ZHANG M, JIN Y, GUO X, et al. Resveratrol protects mesangial cells under high glucose by regulating the miR-1231/IGF1/ERK pathway. Environ Toxicol. 2024;39(4):2326-2339.
[44] YU J, LI C, MA L, et al. Transient receptor potential canonical 6 knockdown ameliorated diabetic kidney disease by inhibiting nuclear factor of activated T cells 2 expression in glomerular mesangial cells. Ren Fail. 2022;44(1):1780-1790.
[45] BENZING T, SALANT D. Insights into Glomerular Filtration and Albuminuria. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(15):1437-1446.
[46] YANG C, ZHANG Z, LIU J, et al. Research progress on multiple cell death pathways of podocytes in diabetic kidney disease. Mol Med. 2023;29(1):135.
[47] SLYNE J, SLATTERY C, MCMORROW T, et al. New developments concerning the proximal tubule in diabetic nephropathy: in vitro models and mechanisms. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015:30 Suppl 4: iv60-7.
[48] KUNDU S, GHOSH S, SAHU BD. Scopoletin alleviates high glucose-induced toxicity in human renal proximal tubular cells via inhibition of oxidative damage, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and fibrogenesis. Mol Biol Rep. 2024;51(1):620.
[49] WANG CH, SURBHI, GORAYA S, et al. Fatty acids and inflammatory stimuli induce expression of long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 1 to promote lipid remodeling in diabetic kidney disease. J Biol Chem. 2024;300(1):105502.
[50] CHANG J, YAN J, LI X, et al. Update on the Mechanisms of Tubular Cell Injury in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8: 661076.
[51] LECHNER C, MöNNING U, REICHEL A, et al. Potential and Limits of Kidney Cells for Evaluation of Renal Excretion. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021;14(9):908.
[52] YU P, ZHU H, BOSHOLM CC, et al. Precision nephrotoxicity testing using 3D in vitro models. Cell Biosci. 2023;13(1):231.
[53] JENKINSON SE, CHUNG GW, VAN LOON E, et al. The limitations of renal epithelial cell line HK-2 as a model of drug transporter expression and function in the proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch. 2012;464(6):601-611.
[54] SHRESTHA S, HAQUE ME, IGHOFOSE E, et al. Primary and Immortalized Cultures of Human Proximal Tubule Cells Possess Both Progenitor and Non-Progenitor Cells That Can Impact Experimental Results. J Pers Med. 2023;13(4):613.
[55] JIANG S, SU H. Cellular crosstalk of mesangial cells and tubular epithelial cells in diabetic kidney disease. Cell Commun Signal. 2023; 21(1):288.
[56] CASALENA GA, YU L, GIL R, et al. The diabetic microenvironment causes mitochondrial oxidative stress in glomerular endothelial cells and pathological crosstalk with podocytes. Cell Commun Signal. 2020;18(1):105.
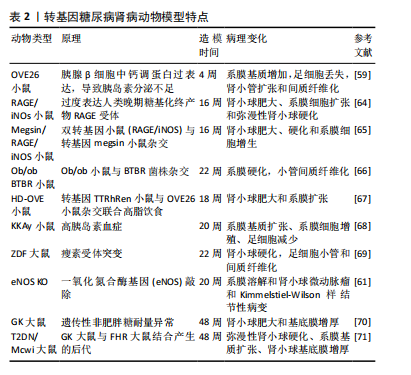
[57] BREYER MD, BöTTINGER E, BROSIUS FC, 3RD, et al. Mouse models of diabetic nephropathy. Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16(1):27-45.
[58] XU J, HUANG Y, LI F, et al. FVB mouse genotype confers susceptibility to OVE26 diabetic albuminuria. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010; 299(3):F487-494.
[59] WANG W, JIANG S, TANG X, et al. Sex differences in progression of diabetic nephropathy in OVE26 type 1 diabetic mice. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866(1):165589.
[60] ZHENG S, HUANG Y, YANG L, et al. Uninephrectomy of diabetic OVE26 mice greatly accelerates albuminuria, fibrosis, inflammatory cell infiltration and changes in gene expression. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2011;119(1):e21-32.
[61] NAKAGAWA T, SATO W, GLUSHAKOVA O, et al. Diabetic endothelial nitric oxide synthase knockout mice develop advanced diabetic nephropathy. JAm Soc Nephrol. 2007;18(2):539-550.
[62] SØGAARD SB, ANDERSEN SB, TAGHAVI I, et al. Super-Resolution Ultrasound Imaging of Renal Vascular Alterations in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats during the Development of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023;13(20):3197.
[63] HUDKINS KL, PICHAIWONG W, WIETECHA T, et al. BTBR Ob/Ob mutant mice model progressive diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;21(9):1533-1542.
[64] YAMAMOTO Y, KATO I, DOI T, et al. Development and prevention of advanced diabetic nephropathy in RAGE-overexpressing mice. J Clin Invest. 2001;108(2):261-268.
[65] INAGI R, YAMAMOTO Y, NANGAKU M, et al. A severe diabetic nephropathy model with early development of nodule-like lesions induced by megsin overexpression in RAGE/iNOS transgenic mice. Diabetes. 2006;55(2):356-366.
[66] OPAZO-RíOS L, SANCHEZ MATUS Y, RODRIGUES-DíEZ RR, et al. Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and renoprotective effects of SOCS1 mimetic peptide in the BTBR ob/ob mouse model of type 2 diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020;8(1):e001242.
[67] THIBODEAU JF, HOLTERMAN CE, BURGER D, et al. A novel mouse model of advanced diabetic kidney disease. PloS one. 2014;9(12):e113459.
[68] DU J, DONG W, LI H, et al. Protective effects of IFN-γ on the kidney of type- 2 diabetic KKAy mice. Pharmacol Rep. 2018;70(3):607-613.
[69] CHANDER PN, GEALEKMAN O, BRODSKY SV, et al. Nephropathy in Zucker diabetic fat rat is associated with oxidative and nitrosative stress: prevention by chronic therapy with a peroxynitrite scavenger ebselen.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15(9):2391-2403.
[70] JOHN A, AMIRI L, SHAFARIN J, et al. Alterations in Energy Metabolism, Mitochondrial Function and Redox Homeostasis in GK Diabetic Rat Tissues Treated with Aspirin. Life (Basel). 2022;12(1):104.
[71] NOBREGA MA, FLEMING S, ROMAN RJ, et al. Initial characterization of a rat model of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 2004;53(3):735-742.
[72] WAUMAN J, ZABEAU L, TAVERNIER J. The Leptin Receptor Complex: Heavier Than Expected?. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017:8:30.
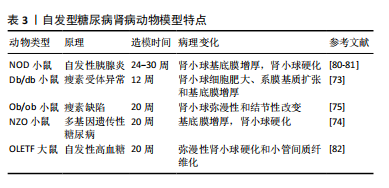
[73] CHOW F, OZOLS E, NIKOLIC-PATERSON DJ, et al. Macrophages in mouse type 2 diabetic nephropathy: correlation with diabetic state and progressive renal injury. Kidney Int. 2004;65(1):116-128.
[74] TALUKDAR A, BASUMATARY M. Rodent models to study type 1 and type 2 diabetes induced human diabetic nephropathy. Mol Biol Rep. 2023;50(9):7759-7782.
[75] SURIANO F, VIEIRA-SILVA S, FALONY G, et al. Novel insights into the genetically obese (ob/ob) and diabetic (db/db) mice: two sides of the same coin. Microbiome. 2021;9(1):147.
[76] WALTER DL, THUMA JR, MALGOR R, et al. Consequences of Both Coxsackievirus B4 and Type 1 Diabetes on Female Non-Obese Diabetic Mouse Kidneys. Microorganisms. 2021;9(11):2357.
[77] AZUSHIMA K, GURLEY SB, COFFMAN TM. Modelling diabetic nephropathy in mice. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018;14(1):48-56.
[78] VELASQUEZ MT, KIMMEL PL, MICHAELIS OET. Animal models of spontaneous diabetic kidney disease. FASEB J. 1990;4(11):2850-2859.
[79] MELEZ KA, HARRISON LC, GILLIAM JN, et al. Diabetes is associated with autoimmunity in the New Zealand obese (NZO) mouse. Diabetes. 1980;29(10):835-840.
[80] DOI T, HATTORI M, AGODOA LY, et al. Glomerular lesions in nonobese diabetic mouse: before and after the onset of hyperglycemia. Lab Invest. 1990;63(2):204-212.
[81] MAEDA M, YABUKI A, SUZUKI S, et al. Renal lesions in spontaneous insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in the nonobese diabetic mouse: acute phase of diabetes. Vet Pathol. 2003;40(2):187-195.
[82] KATSUDA Y, OHTA T, MIYAJIMA K, et al. Diabetic complications in obese type 2 diabetic rat models. Exp Anim. 2014;63(2):121-132.
[83] GIRALT-LÓPEZ A, MOLINA-VAN DEN BOSCH M, VERGARA A, et al. Revisiting Experimental Models of Diabetic Nephropathy. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(10):3587.
[84] 叶桐江,郑博文,赵琳,等. 链脲佐菌素诱导1型糖尿病大鼠模型的最佳禁食时间与最优剂量[J].兰州大学学报(医学版),2019, 45(2):52-55.
[85] 冷昌龙,皮明山,龚晓康.单次大剂量对比多次小剂量STZ诱导C57BL/6J小鼠糖尿病肾病模型的研究[J]. 中国比较医学杂志,2021, 31(9):113-118.
[86] FURMAN BL. Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Models in Mice and Rats. Curr Protoc. 2021;1(4):e78.
[87] 修贤杰,张萍,郑小鹏,等.多因素干预对STZ制备糖尿病肾病模型的影响研究[J].糖尿病新世界,2019,22(14):197-198.
[88] 黎娅,吴穹,马晓雨,等.高脂饮食和链脲佐菌素建立2型糖尿病大鼠模型的影响因素[J].菏泽医学专科学校学报,2020,32(1):91-93.
[89] 李小会,王琦,贾国华,等.STZ诱导联合高脂饮食及右肾切除糖尿病肾病模型大鼠病程早、中、晚期的界定[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志,2019,20(8):667-670+655.
[90] 闫永恒,李渐鹏,刘战伟,等.不同2型糖尿病肾病模型建立方法及成模特点比较[J].中国食物与营养,2016,22(1):65-69.
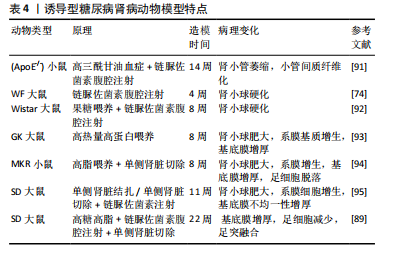
[91] JIMéNEZ-CASTILLA L, MARíN-ROYO G, OREJUDO M, et al. Nephroprotective Effects of Synthetic Flavonoid Hidrosmin in Experimental Diabetic Nephropathy. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(12): 1920.
[92] ORABY MA, EL-YAMANY MF, SAFAR MM, et al. Amelioration of Early Markers of Diabetic Nephropathy by Linagliptin in Fructose-Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Nephron. 2019;141(4):273-286.
[93] 徐孝平,寿旗扬,陈方明,等.高热量高蛋白饮食诱导GK大鼠糖尿病肾病模型的建立[J].中国比较医学杂志,2012,22(4):53-57+92.
[94] 印红爱,吴勇军,喻嵘,等.高脂喂养加单侧肾切除制作小鼠糖尿病肾病模型研究[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2013,33(11):17-18+27.
[95] 祁珊珊,何佳,孙泽,等.糖尿病肾病SD大鼠模型的建立和评价[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2021,37(9):1114-1116+1125.
[96] 文雪,马跃荣.糖尿病肾病病证结合动物模型研究进展[J].亚太传统医药,2018,14(5):117-119.
[97] 黄越燕.病证结合动物模型的研究现状与思考[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2018,13(10):1459-1462.
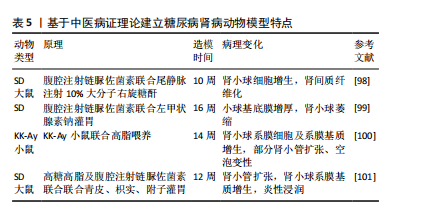
[98] 庞欣欣,彭紫凝,邢玉凤,等.基于病证结合探讨血瘀证糖尿病肾病大鼠肾损害与内质网应激的关系[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2020,26(20):74-81.
[99] 韩佳瑞,邢玉凤,彭紫凝,等.基于病证结合探讨糖尿病肾病阴虚证大鼠肾损害与自噬的关系[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2021,23(3):938-947.
[100] 高云霄,蔺亚东,彭菊琴,等.KK-Ay小鼠糖尿病肾病模型气阴两虚证的演变与评价[J].中华中医药杂志,2023,38(8):3830-3835.
[101] 陈鹏德,姚蓝,郭凤,等.基于肠道菌群探讨气阴两虚证糖尿病肾脏疾病动物模型[J].天然产物研究与开发,2023,35(12):2040-2048.