中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (32): 5130-5135.doi: 10.12307/2024.502
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
骨碎补总黄酮调控H型血管影响大鼠股骨Masquelet诱导膜模型的骨重建
曾志奎1,2,熊 伟3,梁卫东1,钱国文4,梁超轶3,潘 斌3,郭 灵3,魏文强3,邱勋祥3,邓文芳3,袁灵梅1
- 1江西中医药大学附属医院,江西省南昌市 330006;2江西中医药大学中药固体制剂制造技术国家工程研究中心,江西省南昌市 330004;3江西中医药大学,江西省南昌市 330004;4江西理工大学,江西省南昌市 330013
Bone remodeling in the Masquelet-induced membrane model of rat femur by modulation of H-type vessels by total flavonoids of rhizome drynariae
Zeng Zhikui1, 2, Xiong Wei3, Liang Weidong1, Qian Guowen4, Liang Chaoyi3, Pan Bin3, Guo Ling3, Wei Wenqiang3, Qiu Xunxiang3, Deng Wenfang3, Yuan Lingmei1
- 1Affiliated Hospital of Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; 2National Engineering Research Center for Manufacturing Technology of Traditional Chinese Medicine Solid Preparations, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, Jiangxi Province, China; 3Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, Jiangxi Province, China; 4Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, Nanchang 330013, Jiangxi Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
H型血管偶联成骨:H型血管与骨祖细胞、成骨细胞和破骨细胞存在多个水平上相互调控作用,这种成骨和成血管之间在空间和时间上的密切联系称之为 “H型血管偶联成骨”。诱导膜技术:又称Masquelet技术,其对骨缺损的修复分为2个阶段:①诱导膜形成期:首先彻底清除病灶区内所有坏死组织,在骨缺损处放置聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥旷置,因局部异物炎症刺激反应,4-6周后在骨水泥周围形成一层类似滑膜的组织,称之为诱导膜。②骨重建修复期:第一阶段手术后4-6 周,切开诱导膜移除骨水泥,然后在诱导膜内植骨。因诱导膜不仅拥有良好的血供还能分泌相关成骨因子,可促进移植骨和宿主骨的融合,最终完成骨修复。
背景:多项研究发现,骨碎补总黄酮可促进诱导膜中血管新生、改善诱导膜生物性能、加速诱导膜技术骨重建,但相关分子机制仍需进一步探究。
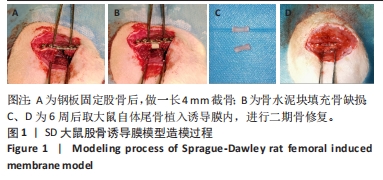
目的:观察骨碎补总黄酮通过调控H型血管对大鼠股骨Masquelet诱导膜模型骨重建的影响。方法:将36只雄性SD大鼠按体质量分层后随机分为空白组、模型组、中药组,每组12只,3组均建立4 mm右后肢股骨骨缺损模型,模型组与中药组骨缺损处充填聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥;造模后6周,空白组骨缺损处填充大鼠自体尾骨,模型组与中药组取出诱导膜内的骨水泥后植入大鼠自体尾骨。植骨第3天开始,中药组灌胃给予骨碎补总黄酮157.5 mg/(kg·d),其余两组灌胃给予生理盐水,连续给药至植骨后8周。植骨后8周取材进行相关检测。
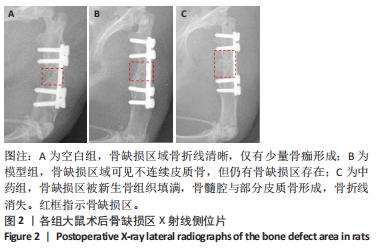
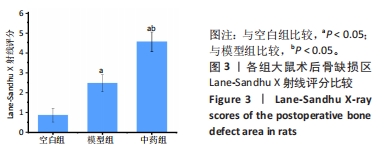
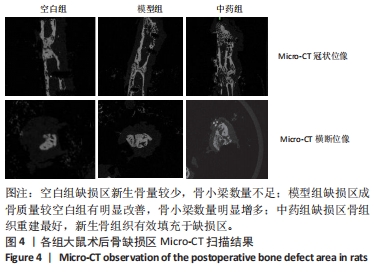
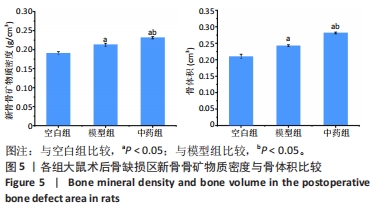
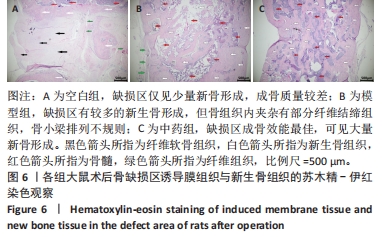
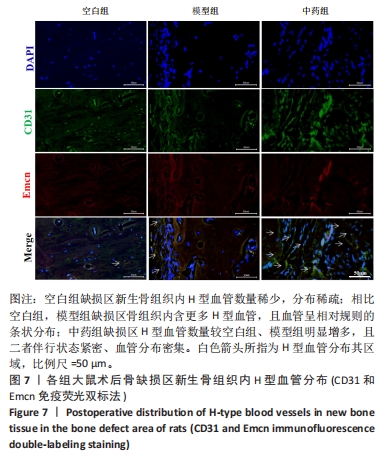
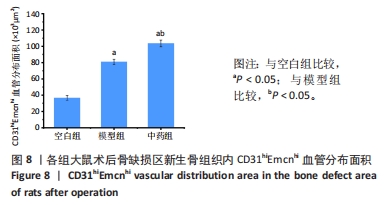
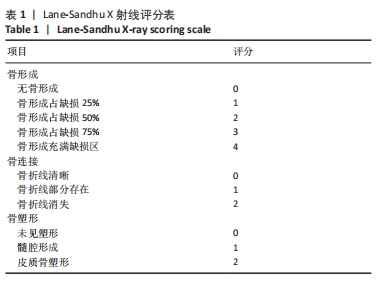
结果与结论:①X射线片显示,空白组缺损区骨折线清晰,仅有少量骨痂形成;模型组缺损区可见不连续皮质骨,骨缺损区仍存在;中药组缺损区充满新生骨组织,骨髓腔与部分皮质骨形成,骨折线消失。②Micro-CT扫描显示,空白组缺损区新生骨量较少,模型组缺损区骨小梁数量明显增多,中药组大量新生骨组织填充于骨缺损区。③苏木精-伊红染色显示,空白组缺损区仅见少量新骨形成,成骨质量较差;模型组缺损区有较多的新骨形成,但骨组织内夹杂有部分纤维结缔组织;中药组缺损区可见大量新骨形成,成骨质量最佳。④CD31/Emcn免疫荧光双标染色显示,空白组骨缺损区新生骨组织内H型血管数量稀少、分布稀疏;相比空白组,模型组骨缺损区骨组织内含更多H型血管,血管呈相对规则的条状分布;中药组骨缺损区H型血管数量最多,并且血管分布密集。⑤结果表明,骨碎补总黄酮可通过上调H型血管表达增强成血管-成骨作用,提高大鼠股骨Masquelet诱导膜模型成骨效能、促进骨重建。
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-4570-5162(曾志奎)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: