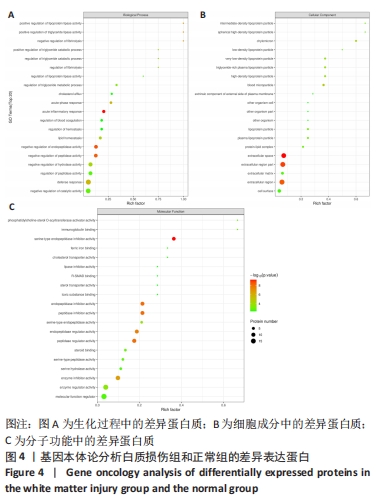
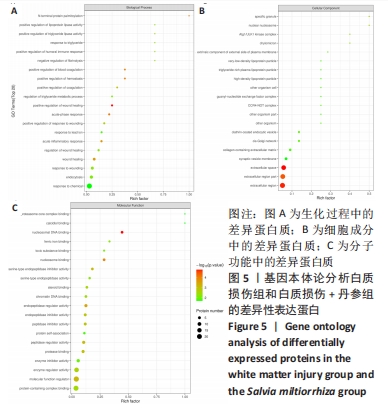
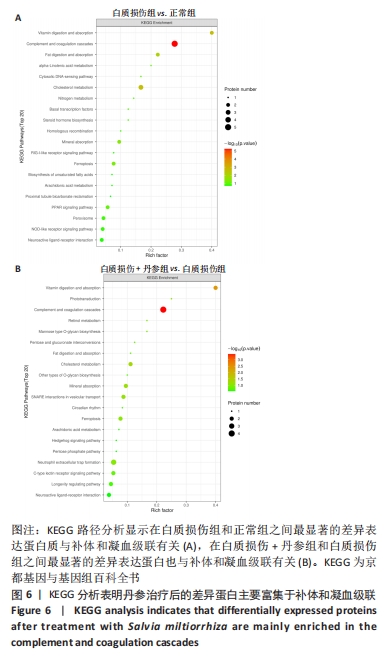
[1] LIU S, ZHANG X, LIU Y, et al. Early application of caffeine improves white matter development in very preterm infants. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2020;281:103495.
[2] LIU L, OZA S, HOGAN D, et al. Global, regional, and national causes of under-5 mortality in 2000-15: an updated systematic analysis with implications for the Sustainable Development Goals. Lancet. 2016;388: 3027-3035.
[3] SONG J, SUN H, XU F, et al. Recombinant human erythropoietin improves neurological outcomes in very preterm infants. Ann Neurol. 2016;80:24-34.
[4] SONG J, XU F, WANG L, et al. Early amplitude-integrated electroencephalography predicts brain injury and neurological outcome in very preterm infants. Sci Rep. 2015;5:13810.
[5] AGUT T, ALARCON A, CABAÑAS F, et al. Preterm white matter injury: ultrasound diagnosis and classification. Pediatr Res. 2020;87:37-49.
[6] BACK SA, LUO NL, BORENSTEIN NS, et al. Late oligodendrocyte progenitors coincide with the developmental window of vulnerability for human perinatal white matter injury. J Neurosci. 2001;21:1302-1312.
[7] KHWAJA O, VOLPE JJ. Pathogenesis of cerebral white matter injury of prematurity. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2008; 93:F153-F161.
[8] CHEN X, GUO J, BAO J, et al. The anticancer properties of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (Danshen): a systematic review. Med Res Rev. 2014; 34:768-794.
[9] CHUA YT, ANG XL, ZHONG XM, et al. Interaction between warfarin and Chinese herbal medicines. Singapore Med J. 2015;56:11-18.
[10] LIU J, SHEN HM, ONG CN. Salvia miltiorrhiza inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG(2) cells. Cancer Lett. 2000;153:85-93.
[11] LI ZM, XU SW, LIU PQ. Salvia miltiorrhizaBurge (Danshen): a golden herbal medicine in cardiovascular therapeutics. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39:802-824.
[12] KIM MS, BANG JH, LEE J, et al. Salvia miltiorrhiza extract protects white matter and the hippocampus from damage induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015;15:415.
[13] STUMPF C, FAN Q, HINTERMANN C, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of danshen on human vascular endothelial cells in culture. Am J Chin Med. 2013;41:1065-1077.
[14] SONG YH, LIU Q, LV ZP, et al. Protection of a polysaccharide from Salvia miltiorrhiza, a Chinese medicinal herb, against immunological liver injury in mice. Int J Biol Macromol. 2008;43:170-175.
[15] SU CY, MING QL, RAHMAN K, et al. Salvia miltiorrhiza: Traditional medicinal uses, chemistry, and pharmacology. Chin J Nat Med. 2015; 13:163-182.
[16] HAN JY, FAN JY, HORIE Y, et al. Ameliorating effects of compounds derived from Salvia miltiorrhiza root extract on microcirculatory disturbance and target organ injury by ischemia and reperfusion. Pharmacol Ther. 2008;117:280-295.
[17] HARAUZ G, LADIZHANSKY V, BOGGS JM. Structural polymorphism and multifunctionality of myelin basic protein. Biochemistry. 2009;48: 8094-8104.
[18] VASSALL KA, BAMM VV, HARAUZ G. MyelStones: the executive roles of myelin basic protein in myelin assembly and destabilization in multiple sclerosis. Biochem J. 2015;472:17-32.
[19] SU X, YUAN H, BAI Y, et al. Clobetasol Attenuates White Matter Injury by Promoting Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cell Differentiation. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2020;55:188-196.
[20] BALDASSARRO VA, STANZANI A, GIARDINO L, et al. Neuroprotection and neuroregeneration: roles for the white matter. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(11):2376-2380.
[21] CHEN J, ZUO S, WANG J, et al. Aspirin promotes oligodendrocyte precursor cell proliferation and differentiation after white matter lesion. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014;6:7.
[22] SHARP J, FRAME J, SIEGENTHALER M, et al. Human embryonic stem cell-derived oligodendrocyte progenitor cell transplants improve recovery after cervical spinal cord injury. Stem Cells. 2010;28:152-163.
[23] RUS H, NICULESCU F. The complement system in central nervous system diseases. Immunol Res. 2001;24:79-86.
[24] ASANO S, HAYASHI Y, IWATA K, et al. Microglia-Astrocyte Communication via C1q Contributes to Orofacial Neuropathic Pain Associated with Infraorbital Nerve Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:6834.
[25] LI M, SUN C, XUE S, et al. Complement protein levels in serum astrocyte-derived exosomes are associated with cognitive impairment in obstructive sleep apnea. J Clin Sleep Med. 2023;19:727-739.
[26] RUS HG, KIM LM, NICULESCU FI, et al. Induction of C3 expression in astrocytes is regulated by cytokines and Newcastle disease virus. J Immunol. 1992;148:928-933.
[27] GASQUE P, FONTAINE M, MORGAN BP. Complement expression in human brain. Biosynthesis of terminal pathway components and regulators in human glial cells and cell lines. J Immunol. 1995;154: 4726-4733.
[28] SAEZ-CALVERAS N, BREWSTER AL, STUVE O. The validity of animal models to explore the pathogenic role of the complement system in multiple sclerosis: A review. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022;15:1017484.
[29] ASAVAPANUMAS N, TRADTRANTIP L, VERKMAN AS. Targeting the complement system in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2021;21(8):1073-1086.
[30] SHIRAZI Y, RUS HG, MACKLIN WB, et al. Enhanced degradation of messenger RNA encoding myelin proteins by terminal complement complexes in oligodendrocytes. J Immunol. 1993;150:4581-4590.
[31] WREN DR, NOBLE M. Oligodendrocytes and oligodendrocyte/type-2 astrocyte progenitor cells of adult rats are specifically susceptible to the lytic effects of complement in absence of antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989;86:9025-9029.
[32] TATOMIR A, RAO G, BOODHOO D, et al. Histone Deacetylase SIRT1 Mediates C5b-9-Induced Cell Cycle in Oligodendrocytes. Front Immunol. 2020;11:619.
|