[1] FERSON ND, UHL AM, ANDREW JS. Piezoelectric and Magnetoelectric Scaffolds for Tissue Regeneration and Biomedicine: A Review. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2021;68(2):229-241.
[2] RAJABI AH, JAFFE M, ARINZEH TL. Piezoelectric materials for tissue regeneration: A review. Acta Biomater. 2015;24:12-23.
[3] SAFAVI AS, SENDERA A, HAGHIGHIPOUR N, et al. The Role of Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Fields on Mesenchymal Stem Cells Differentiation: A Systematic Review. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2022;19(6):1147-1160.
[4] PAOLUCCI T, PEZZI L, CENTRA AM, et al. Electromagnetic Field Therapy: A Rehabilitative Perspective in the Management of Musculoskeletal Pain - A Systematic Review. J Pain Res. 2020;13:1385-1400.
[5] HU H, YANG W, ZENG Q, et al. Promising application of Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields (PEMFs) in musculoskeletal disorders. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110767.
[6] 李天乐,卢倩,苗辉,等.低频脉冲电磁场对骨骼相关疾病的生物学效应研究进展[J].医学研究杂志,2022,51(7):7-10.
[7] ROSSO F, BONASIA DE, MARMOTTI A, et al. Mechanical Stimulation (Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields “PEMF” and Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy “ESWT”) and Tendon Regeneration: A Possible Alternative. Front Aging Neurosci. 2015;7:211.
[8] SCHUERMANN D, MEVISSEN M. Manmade Electromagnetic Fields and Oxidative Stress-Biological Effects and Consequences for Health. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(7):3772.
[9] CIFRA M, APOLLONIO F, LIBERTI M, et al. Possible molecular and cellular mechanisms at the basis of atmospheric electromagnetic field bioeffects. Int J Biometeorol. 2021;65(1):59-67.
[10] NIMPF S, KEAYS DA. Myths in magnetosensation. iScience. 2022;25(6): 104454.
[11] DEL SEPPIA C, GHIONE S, LUSCHI P, et al. Pain perception and electromagnetic fields. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2007;31(4):619-642.
[12] PENG L, FU C, WANG L, et al. The Effect of Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields on Angiogenesis. Bioelectromagnetics. 2021;42(3):250-258.
[13] YAO C, ZHAO L, PENG R. The biological effects of electromagnetic exposure on immune cells and potential mechanisms. Electromagn Biol Med. 2022; 41(1):108-117.
[14] PANAGOPOULOS DJ, KARABARBOUNIS A, YAKYMENKO I, et al. Human‑made electromagnetic fields: Ion forced‑oscillation and voltage‑gated ion channel dysfunction, oxidative stress and DNA damage (Review). Int J Oncol. 2021; 59(5):92.
[15] WANG F, LIU Y, DU C, et al. Current Strategies for Real-Time Enzyme Activation. Biomolecules. 2022;12(5):599.
[16] The classic: Fundamental aspects of fracture treatment by Iwao Yasuda, reprinted from J. Kyoto Med. Soc., 4:395-406, 1953. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1977;(124):5-8.
[17] D’ALESSANDRO D, RICCI C, MILAZZO M, et al. Piezoelectric Signals in Vascularized Bone Regeneration. Biomolecules. 2021;11(11):1731.
[18] CALIOGNA L, MEDETTI M, BINA V, et al. Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields in Bone Healing: Molecular Pathways and Clinical Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(14):7403.
[19] MARTINI F, PELLATI A, MAZZONI E, et al. Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Signaling in the Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Induced by Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(6):2104.
[20] VARANI K, VINCENZI F, PASQUINI S, et al. Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Stimulation in Osteogenesis and Chondrogenesis: Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Implications. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(2):809.
[21] 赵琳.低频脉冲电磁场治疗骨质疏松的机制及临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(8):1210-1216.
[22] IBRAHIM MS, KHAN MA, NIZAM I, et al. Peri-operative interventions producing better functional outcomes and enhanced recovery following total hip and knee arthroplasty: an evidence-based review. BMC Med. 2013;11:37.
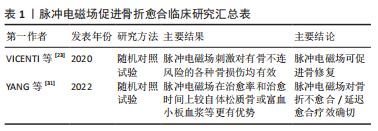
[23] VICENTI G, BIZZOCA D, SOLARINO G, et al. The role of biophysical stimulation with pemfs in fracture healing: from bench to bedside. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020;34(5 Suppl. 1):131-135.
[24] NICKSIC PJ, DONNELLY DT, HESSE M, et al. Electronic Bone Growth Stimulators for Augmentation of Osteogenesis in In Vitro and In Vivo Models: A Narrative Review of Electrical Stimulation Mechanisms and Device Specifications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:793945.
[25] VARANI K, VINCENZI F, RAVANI A, et al. Adenosine Receptors as a Biological Pathway for the Anti-Inflammatory and Beneficial Effects of Low Frequency Low Energy Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields. Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:2740963.
[26] MOHAMMADKHAH M, MARINKOVIC D, ZEHN M, et al. A review on computer modeling of bone piezoelectricity and its application to bone adaptation and regeneration. Bone. 2019;127:544-555.
[27] GRIFFIN XL, COSTA ML, PARSONS N, et al. Electromagnetic field stimulation for treating delayed union or non-union of long bone fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(4):CD008471.
[28] DAISH C, BLANCHARD R, FOX K, et al. The Application of Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields (PEMFs) for Bone Fracture Repair: Past and Perspective Findings. Ann Biomed Eng. 2018;46(4):525-542.
[29] BAHNEY CS, ZONDERVAN RL, ALLISON P, et al. Cellular biology of fracture healing. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(1):35-50.
[30] CALIOGNA L, BINA V, BRANCATO AM, et al. The Role of PEMFs on Bone Healing: An In Vitro Study. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(22):14298.
[31] YANG J, ZHANG X, LIANG W, et al. Efficacy of adjuvant treatment for fracture nonunion/delayed union: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):481.
[32] SISKEN BF, WALKER J, ORGEL M. Prospects on clinical applications of electrical stimulation for nerve regeneration. J Cell Biochem. 1993;51(4): 404-409.
[33] TANDON B, BLAKER JJ, CARTMELL SH. Piezoelectric materials as stimulatory biomedical materials and scaffolds for bone repair. Acta Biomater. 2018; 73:1-20.
[34] 王震,张岩,朱彦丞,等.骨髓炎辅助治疗的研究进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2016,18(12):1064-1068.
[35] DÍAZ-DEL CERRO E, VIDA C, MARTÍNEZ DE TODA I, et al. The use of a bed with an insulating system of electromagnetic fields improves immune function, redox and inflammatory states, and decrease the rate of aging. Environ Health. 2020;19(1):118.
[36] BAYIR E, BILGI E, ŞENDEMIR-ÜRKMEZ A, et al. The effects of different intensities, frequencies and exposure times of extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields on the growth of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli O157:H7. Electromagn Biol Med. 2015;34(1):14-18.
[37] 李旭纲,陈一心,邱旭升.低能量脉冲电磁场对金黄色葡萄球菌生长的影响及其与抗生素的协同抑菌作用[J].中国医学物理学杂志,2021, 38(10):1294-1298.
[38] WANG T, YANG L, JIANG J, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields: promising treatment for osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2019;30(2):267-276.
[39] 张璟岚,张滨婧,陈艺菲,等.磁场对间充质干细胞成骨的生物学效应[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(1):145-151.
[40] BRILL AL, EHRLICH BE. Polycystin 2: A calcium channel, channel partner, and regulator of calcium homeostasis in ADPKD. Cell Signal. 2020;66:109490.
[41] HE Y, YANG M, CHEN Z, et al. Effect of polycystin2 on differentiation and maturation of osteoblasts promoted by low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2022;38(3):1159-1172.
[42] 肖豪,刘静,周君.脉冲电磁场治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(8):1266-1271.
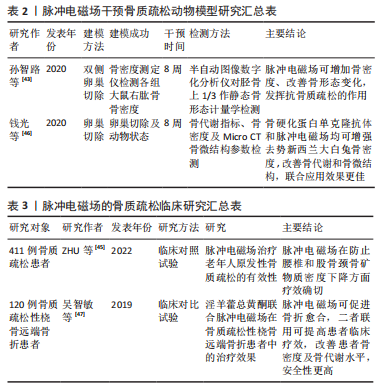
[43] 孙智路,尹剑,黄开亮,等.脉冲电磁场抗骨质疏松作用及对Smurf1表达的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(8):1093-1097.
[44] 刘勇华,涂萍,吴和平.脉冲电磁场辅助治疗原发性骨质疏松症疗效分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(3):275-278.
[45] ZHU S, LI Y, WANG L, et al. Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields May Be Effective for the Management of Primary Osteoporosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2022;30:321-328.
[46] 钱光,余月明,董有海,等.脉冲电磁场磁疗与骨硬化蛋白单克隆抗体联合干预绝经后新西兰大白兔骨代谢和骨微结构的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(20):3130-3134.
[47] 吴智敏,吴明,胡关彪,等.淫羊藿总黄酮联合低频脉冲电磁场治疗骨质疏松性桡骨远端骨折[J].中国新药与临床杂志,2019,38(11):665-668.
[48] 李兰,周君.骨关节炎的物理治疗进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2019, 25(8):918-921.
[49] WANG T, XIE W, YE W, et al. Effects of electromagnetic fields on osteoarthritis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;118:109282.
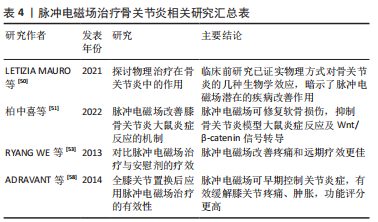
[50] LETIZIA MAURO G, SCATURRO D, GIMIGLIANO F, et al. Physical Agent Modalities in Early Osteoarthritis: A Scoping Review. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57(11):1165.
[51] 柏中喜,方兴刚,马龙祥,等.脉冲电磁场通过Wntβ-catenin信号通路改善膝骨关节炎大鼠炎症反应的机制[J].中国医学物理学杂志,2022, 39(5):617-622.
[52] LI S, YU B, ZHOU D, et al. Electromagnetic fields for treating osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;(12):CD003523.
[53] RYANG WE S, KOOG YH, JEONG KI, et al. Effects of pulsed electromagnetic field on knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013;52(5):815-824.
[54] 向小娜,余曦,刘岩,等.富血小板血浆与脉冲电磁场联合应用治疗骨关节炎:理论与临床研究的进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(30): 4868-4874.
[55] 郑晓芬.骨关节炎发病机制和治疗的最新进展[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(20):3255-3262.
[56] ALRAWASHDEH W, ESCHWEILER J, MIGLIORINI F, et al. Effectiveness of total knee arthroplasty rehabilitation programmes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Rehabil Med. 2021;53(6):jrm00200.
[57] FRANKLIN PD, LI W, AYERS DC. The Chitranjan Ranawat Award: functional outcome after total knee replacement varies with patient attributes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(11):2597-2604.
[58] ADRAVANTI P, NICOLETTI S, SETTI S, et al. Effect of pulsed electromagnetic field therapy in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: a randomised controlled trial. Int Orthop. 2014;38(2):397-403.
[59] GARVING C, JAKOB S, BAUER I, et al. Impingement Syndrome of the Shoulder. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2017;114(45):765-776.
[60] GALACE DE FREITAS D, MARCONDES FB, MONTEIRO RL, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic field and exercises in patients with shoulder impingement syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014;95(2):345-352.
[61] ROSS CL, ANG DC, ALMEIDA-PORADA G. Targeting Mesenchymal Stromal Cells/Pericytes (MSCs) With Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) Has the Potential to Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2019;10:266.
[62] AL-JABRI T, TAN JYQ, TONG GY, et al. The role of electrical stimulation in the management of avascular necrosis of the femoral head in adults: a systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):319.
[63] HINES JT, JO WL, CUI Q, et al. Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: an Updated Review of ARCO on Pathogenesis, Staging and Treatment. J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(24):e177.
[64] 洪志楠,何伟,魏秋实,等.股骨头坏死物理治疗的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(23):2160-2164.
[65] EWURUM CH, GUO Y, PAGNHA S, et al. Surgical Navigation in Orthopedics: Workflow and System Review. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1093:47-63.
[66] BLYTH MJ, SMITH JR, ANTHONY IC, et al. Electromagnetic navigation in total knee arthroplasty-a single center, randomized, single-blind study comparing the results with conventional techniques. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(2):199-205.
[67] MIHALIČ R, ZDOVC J, MOHAR J, et al. Electromagnetic navigation system for acetabular component placement in total hip arthroplasty is more precise and accurate than the freehand technique: a randomized, controlled trial with 84 patients. Acta Orthop. 2020;91(6):675-681.
[68] 李军,詹俊锋,许新忠,等.一种新型导航系统在胫骨髓内钉远端锁钉应用中的评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(27):4342-4347.
[69] CHAN DS, BURRIS RB, ERDOGAN M, et al. The insertion of intramedullary nail locking screws without fluoroscopy: a faster and safer technique. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(7):363-366. |