中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (11): 1772-1779.doi: 10.12307/2023.964
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
脊髓损伤后细胞焦亡调控机制及治疗策略
尚文雅1,任亚锋2,李 冰2,韦慧麟1,张芝兰1,黄晓萌1,黄 靖1
- 1河南中医药大学,河南省郑州市 450046;2河南中医药大学第一附属医院,河南省郑州市 450000
-
收稿日期:2023-01-10接受日期:2023-02-11出版日期:2024-04-18发布日期:2023-07-27 -
通讯作者:任亚锋,主任医师,硕士生导师,河南中医药大学第一附属医院,河南省郑州市 450000 -
作者简介:尚文雅,女,2000 年生,河南省许昌市人,汉族,河南中医药大学在读硕士。 -
基金资助:河南省中医管理局国家中医临床研究基地科研专项课题(2018JDZX010),项目负责人:任亚锋;河南省中医药科学研究专项课题(20-21ZY2164),项目参与人:任亚锋;河南省中医药科学研究专项课题(2021JDZY022),项目负责人:任亚锋
Regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic strategies for pyroptosis after spinal cord injury
Shang Wenya1, Ren Yafeng2, Li Bing2, Wei Huilin1, Zhang Zhilan1, Huang Xiaomeng1, Huang Jing1
- 1Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2023-01-10Accepted:2023-02-11Online:2024-04-18Published:2023-07-27 -
Contact:Ren Yafeng, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Shang Wenya, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:National TCM Clinical Research Base Scientific Research Special Project of Henan Provincial TCM Administration, No. 2018JDZX010 (to RYF); Special Project of Henan Provincial TCM Scientific Research, No. 20-21ZY2164 (to RYF [project participant]); Special Project of Henan Provincial TCM Scientific Research, No. 2021JDZY022 (to RYF)
摘要:
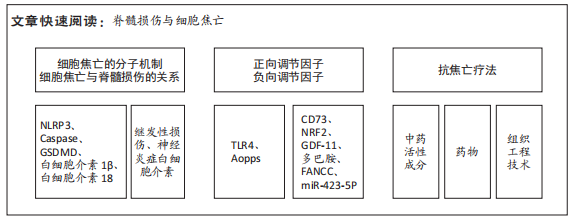
文题释义:
细胞焦亡:是一种以促炎活性为特征的程序性细胞死亡,由半胱氨酸蛋白酶(Caspase-1/4/5/11)激活,并由Gasdermin家族介导,导致细胞裂解死亡,释放炎性细胞内容物,加剧炎症反应,与脊髓损伤后继发性损伤阶段的发展密切相关。脊髓损伤:可引起严重的运动和感觉障碍,显著降低患者的生活质量和预期寿命,减轻继发性神经元死亡和改善存活神经元功能被认为是脊髓损伤治疗的关键策略。由于其发病机制复杂,目前尚无有效的治疗脊髓损伤药物。
背景:调节细胞死亡和神经炎症是治疗脊髓损伤的两个重要途径,细胞焦亡是一种与神经炎症密切相关的程序性死亡模式,针对性靶向抑制脊髓损伤后焦亡,是一项有前景的治疗策略。
目的:归纳细胞焦亡在脊髓损伤中的分子机制、正负向调节因子及治疗策略的研究进展。方法:以“spinal cord injury,pyroptosis,nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3(NLRP3),Caspase,Gasdermin D(GSDMD),IL-1β,IL-18”为检索词,在PubMed和Web of Science数据库进行检索,最终纳入93篇英文文献。
结果与结论:①作为新发现的程序性死亡方式,细胞焦亡已被证实在脊髓损伤后继发性损伤阶段起重要作用。②在脊髓损伤后细胞焦亡的调节因子中,CD73、NRF2、GDF-11、多巴胺、FANCC和miR-423-5P可抑制细胞焦亡,TLR4和Aopps可促进细胞焦亡。③在治疗策略方面,中药活性成分丹皮酚、雷公藤红素、桦木酸、胡椒碱、山奈酚、喜树碱,各种细胞来源的外泌体,药物二甲双胍、拓扑替康、锂、锌和一氧化碳释放分子3能有效抑制焦亡,减轻脊髓继发性损伤,但这些药物的毒副反应和具体剂量有待深入研究。④细胞焦亡加重脊髓损伤的具体分子机制仍知之甚少,非经典途径及其他炎性小体的作用值得进一步探索。⑤目前脊髓损伤后焦亡的研究仅停留在动物实验阶段,尚无相关临床研究,且无批准的靶向治疗药物。⑥细胞焦亡在脊髓损伤后的应用具有巨大潜能,未来需继续研究其具体调控机制,为脊髓损伤的治疗提供新的作用靶点。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9626-8017(尚文雅)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
尚文雅, 任亚锋, 李 冰, 韦慧麟, 张芝兰, 黄晓萌, 黄 靖. 脊髓损伤后细胞焦亡调控机制及治疗策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(11): 1772-1779.
Shang Wenya, Ren Yafeng, Li Bing, Wei Huilin, Zhang Zhilan, Huang Xiaomeng, Huang Jing. Regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic strategies for pyroptosis after spinal cord injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1772-1779.
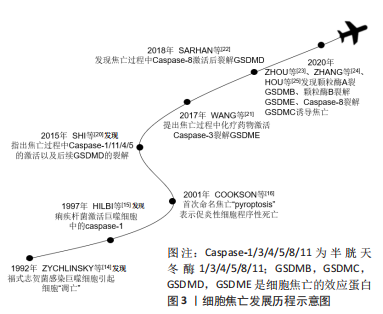
2.1.1 细胞焦亡的发展历程 研究者们对于细胞焦亡的研究要迟于其他类型的细胞死亡,其可以追溯到1992年,ZYCHLINSKY等[14]首次在报告中指出,革兰阴性菌福氏志贺菌在感染小鼠的巨噬细胞或人的单核细胞后,会导致细胞“凋亡”;紧接着,HILBI等[15]发现痢疾杆菌能激活人单核细胞中的Caspase-1并释放成熟的白细胞介素1β。起初,人们认为这是细胞凋亡,随着研究进一步深入,于2001年发现这种巨噬细胞的死亡虽然是由细菌感染所引起,但与凋亡不同,并将其定义为依赖caspase1的程序性坏死[16]。长期以来,焦亡被定义为病原体或毒素刺激巨噬细胞后,由Caspase-1介导的单核细胞死亡,但研究发现Gasdermin家族中的蛋白在针对特定细菌的反应中起着更为重要的作用,因此,细胞死亡命名委员会于2018年更新了对焦亡的定义,建议将其定义为细胞程序性死亡的形式之一,严重依赖于Gasdermin家族蛋白质形成的质膜孔,通常(但不总是)是依赖炎性半胱氨酸蛋白酶激活的结果[17]。细胞焦亡发展历程见图3。
2.1.2 细胞焦亡的分子机制 细胞焦亡的发生涉及多个分子,是个复杂的病理过程,查阅大量文献后总结有:炎性小体包括核苷酸结合寡聚化结构域样受体蛋白(nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor pyrin domain containing,NLRP)1、NLRP3、黑素瘤缺乏因子2(absent in melanoma2,AIM2);半胱天冬酶(Caspase)家族如Caspase-1/3/4/5/8/11;Gasdermin 家族包括GSDMB,GSDMC,GSDMD和GSDME;促炎因子包括白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18等,其中研究最广泛,最具特征性的炎性小体是NLRP3。NLRP3蛋白复合物由3部分组成,第一部分是NLRP3支架;第二部分是PYCARD适配器,通常称为凋亡相关斑点样蛋白,其有两个结构域,分别为与pro-Caspase-1相互作用的Caspase激活和募集结构域(CARD),以及在炎性小体中与相同结构域协同作用的pyrin结构域(PYD);第三部分是效应蛋白
pro-Caspase-1[18]。此外,白细胞介素1家族是炎症反应中重要的信号分子,也是被充分研究的半胱天冬酶的底物,与焦亡密切相关[19]。目前研究有限,焦亡的具体组分尚未完全发掘,亟待进一步的研究。
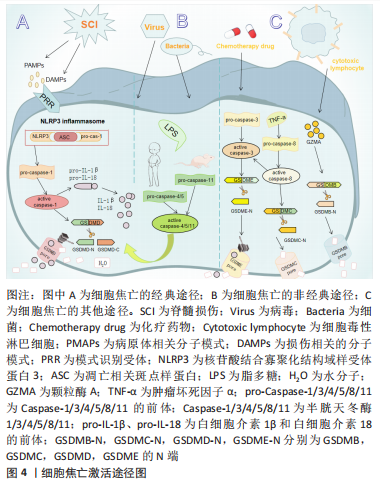
细胞焦亡的基本特征是具有促炎活性,导致膜完整性丧失,细胞溶解和炎症[20-25]。目前公认的细胞焦亡激活途径有3种。①经典途径:NLRP3炎性小体广泛研究于该途径。在脊髓损伤中,NLRP3的激活需要两个不同的分子模式,第一个信号是病原体相关分子模式,如脊髓损伤后脊髓小胶质细胞反应性被触发,第二个信号是损伤相关分子模式,如三磷酸腺苷,它们可以被模式识别样受体所识别,组装成有活性的炎性小体,进而激活无活性的pro-Caspase-1,促进成熟的Caspase-1裂解GSDMD并产生GSDMD的N端,将白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18的前体加工成成熟的细胞因子,由于GSDMD的N端具有膜造孔活性,其在细胞膜上形成直径10-15 nm的孔隙,破坏细胞内外渗透压平衡,水分子进入细胞引起肿胀,从而导致细胞膜破裂,胞浆内容物释放,实现焦亡[26]。②非经典途径:由小鼠的Caspase-11与人类Caspase-4/5所介导,研究表明,Caspase-11与Caspase-4/5序列的相似程度为60%,且三者均为细胞内脂多糖的受体,可以直接识别并激活脂多糖,将GSDMD裂解成N端和C端两个片段,GSDMD的N端在细胞膜上形成孔隙,激活和释放成熟的白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18[27]。③细胞焦亡的其他途径:在GSDME含量高的癌症和正常细胞中,某些化疗药物可以通过Caspase-3裂解GSDME引起焦亡;在肿瘤坏死因子α的刺激下,Caspase-8可以裂解GSDMC产生GSDMC的N端,引起焦亡;细胞毒性淋巴细胞中颗粒酶A可以通过裂解GSDMB引起焦亡[28],但这些途径是否与脊髓损伤相关尚未得到研究,见图4。
2.1.3 细胞焦亡与其他程序性死亡的联系 大量的研究证据表明,程序性死亡是脊髓损伤后的一个重要过程,其与细胞坏死有所区别。程序性死亡是由一系列基因表达事件介导的活性细胞死亡,包括凋亡、坏死、自噬、铁死亡、焦亡和副凋亡,它可以消除不必要的和受损的细胞,代表一种防御机制[29]。有趣的是,各种程序性死亡类型间并非独立,在标志物、发病时程及部位等存在串扰,且无法确定哪一种死亡类型占主导作用。细胞自噬与焦亡间可通过多种细胞器形成复杂的交互网络,脊髓损伤后,受损的线粒体导致活性氧的大量积累,诱导NLRP3炎性小体的激活,从而激活Caspase-1,成熟的Caspase-1一方面引起细胞焦亡,另一方面直接切割β干扰素TIR结构域衔接蛋白(TIR-domain containing adaptor inducing interferon-β,TRIF),减弱TRIF/Toll样受体4(Toll-like receptor4,TLR4)信号通路诱导的细胞自噬[30]。同时,细胞自噬可以清除受损线粒体内的活性氧、炎性因子等,从而负向调节NLRP3的激活,抑制焦亡[31]。同样,溶酶体破裂释放组织蛋白酶B,一方面直接激活NLRP3引起细胞焦亡,另一方面通过激活unc51样自噬激活激酶1负向调节自噬。
目前已有多位学者验证了通过促进脊髓损伤后自噬通量的恢复来减轻细胞焦亡、调节机体功能的药物。此外,细胞凋亡与焦亡间也存在一定的联系[32]。在阅读关于脊髓损伤后焦亡的细胞实验研究发现,在评估大鼠焦亡时,除常见的细胞焦亡标志物外,通常也会采用TUNEL检测法来检测细胞凋亡情况。人们对细胞凋亡和焦亡间的联系多体现于Caspase家族,如细胞凋亡的重要标志物Caspase-3可以使GSDMD失活从而抑制焦亡,但也可以使GSDME裂解促进焦亡[33];Caspase-8既可以裂解GSDMD、GSDME引起细胞焦亡,也可以引起细胞凋亡[34];Caspase-1是细胞焦亡经典途径中的重要分子,而在缺乏焦亡相关蛋白底物时,它也可以引发凋
亡[35]。综上,各种程序性死亡类型间的相互作用机制值得进一步研究。

2.2 脊髓损伤后焦亡的负向调节因子
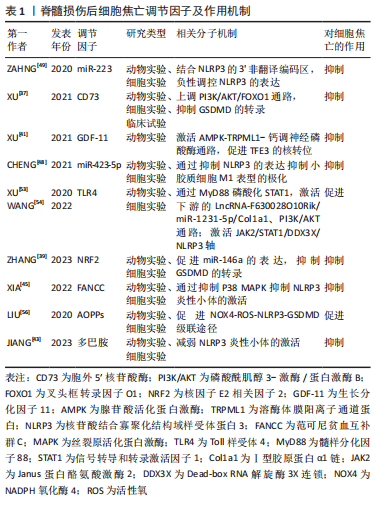
2.2.1 胞外5′核苷酸酶(Ecto-5′-nucleotidase,CD73) CD73是一种糖基磷脂酰肌醇锚定的细胞表面蛋白,被认为是细胞外腺苷生成的限速酶,在腺苷系统中起核心作用[36]。XU等[37]首先验证了脊髓损伤与细胞焦亡的关系,发现脊髓损伤患者外周血的NLRP3/GSDMD蛋白表达水平要高于正常患者,且线性回归分析证实该表达与损伤程度呈正相关,表明细胞焦亡可以加重脊髓损伤;他们又敲除脊髓损伤小鼠的CD73基因,发现细胞焦亡程度部分被抑制。此外,他们还使用了氧糖剥夺模型模拟细胞焦亡微环境,探讨CD73的作用机制,结果显示,CD73通过磷酸酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(Phosphoinositide 3-kinases/proteinkinase B,PI3K/Akt)信号通路在调控叉头框转录因子O1转录水平上抑制GSDMD的表达,从而抑制小胶质细胞焦亡。这提示CD73是抑制脊髓损伤后焦亡的潜在因子之一。
2.2.2 核因子E2相关因子2(nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2,NRF2) NRF2已被证实在脊髓损伤患者中下调,其过表达有利于维持小胶质细胞稳态,减少细胞死亡和氧化应激损伤,促进脊髓功能修复[38]。ZHANG等[39]发现NRF2过表达在体内外均可减轻细胞焦亡,先前有证据表示,miR-146a可减轻脊髓损伤后炎症反应,而NRF2促进miR-146a的转录。因此,作者猜测miR-146a可能是NRF2的下游基因,他们将miR-146a抑制剂转染入脂多糖和三磷酸腺苷处理的大鼠小胶质细胞中,发现由NRF2过表达引起的细胞焦亡的抑制作用被解除。同样,GSDMD的过表达也可以阻断NRF2抑制焦亡的作用。综上,NRF2与miR-146a启动子结合,促进miR-146a的表达,继而靶向GSDMD的转录,这可能是NRF2负向调节细胞焦亡的作用机制。
2.2.3 生长分化因子11(recombinant growth differentiation factor 11,GDF-11) GDF-11属于转化生长因子β超家族,是一种抗衰老因子,可影响脑缺血损伤后神经的再生与发育,发挥神经保护作用[40]。XU等[41]探讨了GDF-11促进脊髓损伤后功能恢复的机制,分析了焦亡、自噬、坏死间的关系,发现经GDF-11处理后的脊髓损伤小鼠,其NLRP3、Caspase-1、GSDMD表达和受体相互作用蛋白激酶1、3阳性神经元密度降低而腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶(adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase,AMPK)、TFE3表达增加;进一步研究表明,运用自噬抑制剂3-甲基腺嘌呤后,这一变化被逆转。说明GDF-11可能通过促进TFE3的核转位,促进自噬,抑制焦亡和坏死,保护受损脊髓。
2.2.4 多巴胺 是一种存在于脑中的神经递质,它是神经和免疫系统之间的化学信使,可以调节NLRP3依赖性的神经炎症[42]。JIANG等[43]报道在雌性脊髓损伤小鼠模型中,腹腔注射多巴胺可以促进脊髓损伤后运动功能的恢复,减轻NLRP3炎性小体的激活和炎性因子水平,减少神经元的丢失和细胞焦亡,可能是减轻脊髓损伤后继发性损害的新途径。
2.2.5 范可尼贫血互补群C(Fanconi anemia,complementation group C,FANCC) FANCC是FA基因家族中的一员,参与某些炎症反应,研究发现FANCC缺陷的小鼠对脂多糖诱导的感染性休克反应更为强烈[44]。XIA等[45]将激活的小胶质细胞与神经元体外共培养,模拟小胶质细胞炎症反应诱导的神经元凋亡,发现FANCC过表达可抑制小胶质细胞焦亡,进而降低神经元凋亡。此外,他们于脊髓损伤造模前1周将敲掉FANCC的短发夹RNA腺相关病毒载体注射入小鼠尾静脉,发现这些小鼠的神经胶质瘢痕形成增加,髓鞘破坏严重,轴突生长受到更严重的抑制。但目前尚不清楚介导脊髓损伤后焦亡和神经元凋亡的具体调控因子或靶点,以及是否存在上游调控因子影响FANCC的表达,未来需要更深入的研究。
2.2.6 微小RNAs(microRNAs,miRNAs) miRNAs是一种非编码的单链RNA分子,其长度为22-24个核苷酸,广泛参与DNA转录后调控[46],最近研究表明,一些miRNAs的表达可能影响神经发生、神经元分化和神经发育,脊髓损伤后也存在miRNAs的异常转录调控,如miR-423,miR-223,miR-31和miR-96等[47]。CHENG等[48]建立大鼠脊髓损伤模型,收集损伤中心两侧各0.25 cm样本进行RNA测序,采用基因本体和京都基因和基因组百科全书数据库确定信号通路的富集,分析miRNAs的差异表达。根据结果,作者筛选出了一种有希望的miRNA (miR-423-5p),发现其在脊髓损伤后表达下降,且在第7天达到最低,并确定了miR-423-5p和NLRP3间的直接靶向关系,其可抑制NLRP3炎性小体的激活,抑制炎症反应。基于以上结果,日后可以进一步研究miR-423-5p与细胞焦亡间的关系,探讨其是否可以作为潜在的焦亡抑制剂,用于脊髓损伤的治疗。
miR-223也是与炎症密切相关的miRNAs之一。但miR-223在脊髓损伤中的作用至今仍有争议,以往相关研究中既有有益结果,也有有害结果。有研究者认为,miR-223在应对脊髓损伤后神经炎症中发挥了积极作用。ZAHNG等[49]研究证明,急性脊髓损伤期大鼠miR-223水平增高,而miR-223的过表达可以改善大鼠脊髓结构,减轻炎症反应,改善神经系统功能;同样,体外小胶质细胞中过表达的miR-223也可抑制脂多糖诱导的炎症。然而,其他研究人员持有不同的观点。有研究发现miR-223-3P对其下游分子靶点E3泛素连接酶WD-40域蛋白7具有反向调节作用,而该分子可通过调节氧化应激、炎症反应、细胞凋亡和焦亡修复大鼠受损脊髓[50]。先前LIU等[51]也曾报道阻断miR-223可抑制脊髓损伤小鼠的神经元丢失,促进功能恢复。因此,miR-223在脊髓损伤中的潜在作用及机制尚不完全清楚,关于它是否可以作为焦亡的负向调节因子有待进一步研究。

2.3 脊髓损伤后焦亡的正向调节因子
2.3.1 Toll样受体4(Toll Like Receptor 4,TLR4) TLR4是天然免疫应答中的一个关键角色,参与各种神经系统疾病中神经炎症的启动,作为损伤和病原体相关模式的模式识别样受体,已有研究证明TLR4在细胞焦亡中起重要作用[52]。XU等[53]发现LNCRNA-F630028O10RIK显著提高了脊髓损伤后小鼠小胶质细胞中焦亡和炎症相关基因的表达水平。有趣的是,脊髓损伤后TLR4被激活,而TLR4的缺失在体内外均下调了LNCRNA-F630028O10RIK及其下游因子,通过抑制焦亡促进了脊髓损伤后运动功能恢复,此外,lncRNA-F630028O10Rik的过表达消除了由TLR4缺失引起的抗焦亡作用。因此,lncRNA-F630028O10Rik是TLR4诱导脊髓损伤后细胞焦亡的重要媒介。
同样,WANG等[54]发现,TLR4与双糖链蛋白多糖相互作用,可以激活脊髓损伤后Janus蛋白酪氨酸激酶2/信号转导与转录激活因子1通路,共同促进Dead-box RNA解旋酶3X连锁(DEAD-box RNA helicase 3 X-linked,DDX3X)的表达,这也进一步加剧了NLRP3诱导的小胶质细胞焦亡。他们还认为DDX3X在脊髓损伤后表达增加,抑制DDX3X在体外能减轻NLRP3的激活和小胶质细胞的焦亡,表明DDX3X也是脊髓损伤后调节小胶质细胞焦亡的潜在靶点,但他们并未探讨DDX3X对NLRP3炎性小体激活的具体调控作用。总之,以上结果表明TLR4可以作为脊髓损伤后焦亡的正向调节因子,通过多种途径激发小胶质细胞的焦亡。
2.3.2 晚期氧化蛋白产物(adanced oxidation protein products,AOPPs) AOPPs是一种新型氧化应激标志物,许多研究表明血浆AOPPs的形成和积累是炎症的重要介质,也是活性氧的激活剂[55],脊髓损伤后血浆、脑脊液和脊髓中的蛋白质易被氯化氧化剂氧化形成AOPPs。LIU等[56]发现脊髓损伤后1 d,大鼠血浆、脑脊液及脊髓中AOPPs含量均显著升高,第3天达高峰,后开始下降。AOPPs预处理的小胶质细胞通过激活NADPH氧化酶引发活性氧的过度生成,引起p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38,mitogen activated protein kinase,p38 MAPK)和c-Jun氨基末端激酶(c-Jun N-terminal kinase,JNK)磷酸化,触发核转录因子kB p65核转位,进而诱导小胶质细胞中NLRP3炎性小体、Caspase-1的激活和GSDMD的裂解,导致细胞焦亡。因此,抑制AOPPs的表达可能为减轻脊髓损伤的细胞焦亡提供新的思路。

文章将脊髓损伤后细胞焦亡调节因子及作用机制归纳如下,见表1。
2.4 脊髓损伤后的抗焦亡疗法
2.4.1 中药活性成分治疗 目前,中药活性成分在抑制脊髓损伤后细胞焦亡中显示出优越的效果,具有广阔的应用前景。丹皮酚是芍药提取物中的主要活性成分,ZHAO等[57]将丹皮酚溶液通过腹腔注射入脊髓损伤大鼠体内,结合体外实验,发现丹皮酚可能通过TLR4/髓样分化因子88/核转录因子kB(P65)信号通路促进M2小胶质细胞的极化,抑制NLRP3炎性小体的形成和细胞焦亡。雷公藤红素是第一个从雷公藤根皮中分离出来的天然产物,DAI等[58]发现雷公藤红素对细胞焦亡的抑制作用可能部分受抑制核因子kB信号通路以调节脊髓小胶质细胞NLRP3炎性小体的激活,并通过减少肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β等炎性因子的释放来缓解炎症反应。此外,雷公藤红素还可以降低脊髓小胶质细胞(特别是M1小胶质细胞)的活化。
桦木酸是一种萃取于白桦树的五环三萜类化合物,WU等[59]发现桦木酸通过AMPK-哺乳动物类雷帕霉素靶蛋白-调节转录因子EB信号通路恢复脊髓损伤后的自噬通量,从而诱导有丝吞噬,消除活性氧的积累,最终抑制细胞焦亡,改善脊髓损伤的预后。同样,在另一项研究中,ZHANG等[60]也展示了细胞自噬、焦亡、氧化应激和炎症之间的联系,且探讨了胡椒碱对它们的影响。胡椒碱是从黑胡椒中提取的一种天然活性生物碱,作者发现胡椒碱可以通过增强自噬从而减轻脊髓损伤后神经炎症、氧化应激和焦亡,促进脊髓功能的恢复,而这一现象可以被自噬抑制剂3-甲基腺嘌呤所逆转。
山奈酚存在于西兰花、柚子及卷心菜等膳食中,以往的研究表明在神经炎症模型中,山奈酚可以抑制小胶质细胞介导的炎症反应[61]。LIU等[62]首次报道了山奈酚在脊髓损伤中的病理生理机制,结果发现山奈酚可减轻脊髓损伤后小胶质细胞活化介导的氧化应激,促进神经功能恢复。接着,用脂多糖结合三磷酸腺苷在体外引起小胶质细胞活化,发现山奈酚通过抑制NADPH氧化酶4的表达减少活性氧的产生,抑制p38 MAPK和JNK的磷酸化,进而抑制核转录因子kB(p65)核转位,下调焦亡途径的关键蛋白和炎性因子表达,抑制焦亡。
喜树碱是一种拓扑异构酶1(topoisomerase1,TOP1)抑制剂,从喜树树皮和枝干分离所得[63]。TOP1是哺乳动物细胞中的一种必需酶,已被证明与先天免疫应答有关,是调节炎症和自身免疫的潜在靶点[64]。JIANG等[65]发现喜树碱可以降低脊髓损伤小鼠体内TOP1的水平,减少中性粒细胞的数量和神经元的丢失,抑制NLRP3炎性小体的激活,从而抑制脊髓损伤后细胞焦亡,促进小鼠运动功能的恢复。由此可见,一些中药活性成分通过抑制脊髓损伤后细胞焦亡来保护受损脊髓,促进实验动物运动功能的恢复,日后研究应以这些中药单体为中心,寻找可能的中药复方来抑制细胞焦亡,调控神经炎症,并探寻其具体作用机制,为脊髓损伤提供新的治疗策略。
文章将抑制脊髓损伤后细胞焦亡的中药活性成分及作用机制相关研究作一汇总,见表2。

2.4.2 组织工程技术 国际神经修复学会和中国神经修复学会指南均提出细胞治疗作为脊髓损伤的治疗选择[66]。间充质干细胞具有分化为神经元的潜力,可间接触发内源性存活信号通路,抑制脊髓损伤后炎症反应,促进轴突再生和髓鞘形成,减轻星形胶质瘢痕和组织空洞的形成,修复受损脊髓功能[67]。然而,间充质干细胞移植可能会引起组织免疫排斥反应、致畸和肿瘤等副反应,同时也伴随着干细胞移植后死亡率高等问题。目前,一个有趣的观点认为间充质干细胞还可以通过传递外泌体来促进脊髓损伤的恢复,而外泌体主要通过携带蛋白质、DNA片段、RNAs和脂质等物质来发挥作用[68],各种细胞来源的外泌体均可抑制脊髓损伤后脊髓微环境的炎症反应,降低程序性死亡水平,抑制星形胶质细胞的激活,促进小胶质细胞从M1向M2转化,从而促进脊髓神经功能恢复[69-70]。
SHENG等[71]将miRNA-22负载于间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体中,观察其对脊髓损伤大鼠炎症反应的抑制作用,结果发现其能抑制炎性因子的释放和GSDMD的表达,抑制小胶质细胞焦亡的发生;此外,负载miRNA-22的外泌体显示出比单独外泌体更高的抑制焦亡的能力。在这项研究中,作者发现间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体和miRNA-22联合应用可进一步抑制脊髓损伤后的神经炎症反应,改善大鼠受损的神经功能。ZHOU等[72]发现骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体能改善脊髓损伤大鼠髓鞘排列,减少髓鞘丢失,降低Caspase-1表达,减少周细胞焦亡,提高周细胞存活率,改善血脊髓屏障完整性,加速运动功能恢复。同样,ZHAO等[73]利用微阵列检测筛选出骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体中一种非编码环状RNA circ_003564,发现骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体可减少细胞焦亡标志物的表达,促进脊髓损伤大鼠的功能恢复,其作用可被circ_003564敲除减弱,在体外,当骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体和神经元共培养时,其可通过递送circ_003564减弱神经元焦亡。
此外,M2小胶质细胞来源的外泌体在脊髓损伤的治疗中也显示出良好的前景。小胶质细胞是脊髓微环境的组成成分之一,根据脊髓微环境状态的不同,小胶质细胞可以发生各种形态和功能变化,最终分化为促炎性小胶质细胞(M1)和抗炎性小胶质细胞(M2),二者处于动态平衡的状态[74]。ZHOU等[75]发现M2小胶质细胞外泌体比M0小胶质细胞外泌体更能促进脊髓损伤小鼠的功能行为恢复,其可通过miR-672-5P抑制AIM2的活性,进而调节AIM2/ASC/Caspase-1信号级联,抑制脊髓损伤后神经元的焦亡。外泌体作为脊髓损伤后新兴的治疗策略,探讨其在细胞焦亡中调控作用机制,能够为脊髓损伤的防治开拓新的领域。
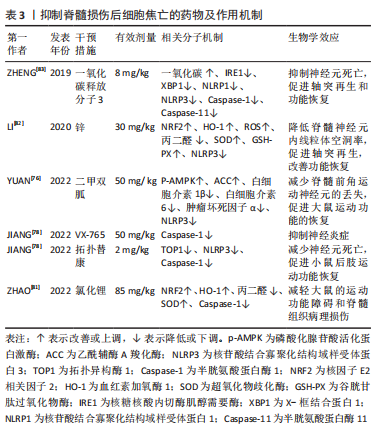
2.4.3 药物治疗 近年来,国内外有大量的研究报道了抑制脊髓损伤后细胞焦亡的药物,并重点探讨其作用机制。二甲双胍是治疗神经系统疾病的候选药物之一,最近一项研究发现二甲双胍通过激活磷酸化的AMPK及其下游蛋白乙酰辅酶A羧化酶来抑制NLRP3炎症小体的激活,抑制脊髓损伤后神经元焦亡和炎症反应[76]。拓扑替康是一种半合成水溶性衍生物,能够穿过血脑屏障,与喜树碱一样,它是一种TOP1抑制剂[77]。JIANG等[78]报道拓扑替康在体内外均可降低脊髓损伤后TOP1和Caspase-1的水平,抑制NLRP3炎性小体的激活和焦亡,降低炎性因子水平和中性粒细胞数量,提示在特定剂量和持续时间内拓扑替康对神经的保护作用可能与抑制Caspase-1依赖性的焦亡有关。此外,他们还探讨了高选择性的小分子Caspase-1抑制剂VX-765对焦亡的影响,发现VX-765通过抑制Caspase-1抑制脊髓损伤介导的神经元焦亡和炎症。
已有研究证实,锂对谷氨酸诱导的兴奋性毒性、缺血诱导的神经元损伤和其他神经退行性疾病具有神经保护作用[79]。但先前一项临床试验显示,经锂治疗后脊髓损伤患者没有显著改善[80],ZHAO等[81]认为这项研究侧重于脊髓损伤慢性期,而不是评估治疗更有效的早期阶段,因此他们验证了锂在治疗脊髓损伤急性期方面的作用,发现在脊髓损伤大鼠中,腹腔注射氯化锂可以通过NRF2/血红素加氧酶1信号通路抑制Caspase-1的表达、减少氧化应激反应,抑制焦亡和减轻炎症,这个过程可以被NRF2抑制剂全反式维甲酸所逆转。有趣的是,LI等[82]发现锌也可通过NRF2/血红素加氧酶1信号通路抑制脊髓损伤后NLRP3炎症小体的激活,发挥抗焦亡作用。
大量研究证据表明,一氧化碳在脊髓损伤中具有显著的抗炎作用。ZHENG等[83]探讨了一氧化碳在脊髓损伤动物模型中抑制细胞焦亡及炎性小体信号通路的潜在药理作用,他们发现在大鼠脊髓损伤和体外缺氧缺糖的原代神经元模型中,核糖核酸内切酶肌醇需要酶及其下游的X-框结合蛋白被激活,伴随着NLRP1、NLRP3炎性小体产生和焦亡活动增加,而外源性给予一氧化碳释放分子3(一种经典的一氧化碳供体),可以增加脊髓组织内一氧化碳含量,抑制神经元肌醇依赖酶1磷酸化,下调焦亡标志物和炎性因子的表达,减轻脊髓损伤后神经元死亡,是一种有希望的治疗策略。此外,还有一些靶向焦亡组分的药物正在研究中,如靶向NLRP3炎性小体的MCC950、CY-09、Bay11-7082、OLT1177、曲尼司特和格列本脲等[84-89];靶向Caspase-1、VX-740、AC-YVAD-CMK等[90-91];靶向GSDMD的坏死磺胺和Ac-FLTD-CMK等[92-93]。但是对于这些药物的潜在毒性以及不同给药方式是否对疗效有影响的研究较少,且这些药物的半数致死量、半数有效量、剂量反应曲线仍需在不同的动物和细胞模型中进一步研究,这对未来在临床上的应用至关重要。

文章将抑制脊髓损伤后细胞焦亡的药物相关研究作一汇总,见表3。
| [1] SAADOUN S, PAPADOPOULOS MC. Targeted perfusion therapy in spinal cord trauma. Neurotherapeutics. 2020;17(2):511-521. [2] LU Y, YANG J, WANG X, et al. Research progress in use of traditional Chinese medicine for treatment of spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;127:110136. [3] FAN YD, ZHU ML, GENG D, et al. The study on pathological mechanism and solution method for spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(13):4063-4068. [4] LI F, WANG H, CHEN H, et al. Mechanism of ferroptosis and its role in spinal cord injury. Front Neurol. 2022;13:926780. [5] PARK CS, LEE JY, CHOI HY, et al. Protocatechuic acid improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury by attenuating blood-spinal cord barrier disruption and hemorrhage in rats. Neurochem Int. 2019;124:181-192. [6] LIN S, MEI X. Role of NLRP3 inflammasomes in neuroinflammation diseases. Eur Neurol. 2020;83(6):576-580. [7] LI F, WANG H, CHEN H, et al. Mechanism of ferroptosis and its role in spinal cord injury. Front Neurol. 2022;13:926780. [8] LI H, ZHANG X, QI X, et al. Icariin inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neuronal apoptosis after spinal cord injury through modulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15(2):277-286. [9] ZHU J, FU Y, TU G. Role of Smad3 inhibitor and the pyroptosis pathway in spinal cord injury. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(2):1675-1681. [10] TITOLO P, FUSINI F, ARRIGONI C, et al. Combining nerve and tendon transfers in tetraplegia: a proposal of a new surgical strategy based on literature review. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2019;29(3):521-530. [11] LIN Y, LI C, LI J, et al. NEP1-40-modified human serum albumin nanoparticles enhance the therapeutic effect of methylprednisolone against spinal cord injury. J Nanobiotechnology. 2019;17(1):12. [12] FAILLI V, KOPP MA, GERICKE C, et al. Functional neurological recovery after spinal cord injury is impaired in patients with infections. Brain. 2012;135(Pt 11):3238-3250. [13] WANG H, LIU C, MEI X, et al. Berberine attenuated pro-inflammatory factors and protect against neuronal damage via triggering oligodendrocyte autophagy in spinal cord injury. Oncotarget. 2017;8(58):98312-98321. [14] ZYCHLINSKY A, PREVOST MC, SANSONETTI PJ. Shigella flexneri induces apoptosis in infected macrophages. Nature. 1992;358(6382):167-169. [15] Hilbi H, Chen Y, Thirumalai K, et al. The interleukin 1beta-converting enzyme, caspase 1, is activated during Shigella flexneri-induced apoptosis in human monocyte-derived macrophages. Infect Immun. 1997;65(12):5165-5170. [16] COOKSON BT, BRENNAN MA. Pro-inflammatory programmed cell death. Trends Microbiol. 2001;9(3):113-114. [17] GALLUZZI L, VITALE I, AARONSON SA, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25(3):486-541. [18] ZHOU X, YANG Y, WU L, et al. Brilliant blue g inhibits inflammasome activation and reduces disruption of blood-spinal cord barrier induced by spinal cord injury in rats. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:6359-6366. [19] LU F, LAN Z, XIN Z, et al. Emerging insights into molecular mechanisms underlying pyroptosis and functions of inflammasomes in diseases. J Cell Physiol. 2020; 235(4):3207-3221. [20] SHI J, ZHAO Y, WANG K, et al. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature. 2015;526(7575):660-665. [21] WANG Y, GAO W, SHI X, et al. Chemotherapy drugs induce pyroptosis through caspase-3 cleavage of a gasdermin. Nature. 2017;547(7661):99-103. [22] SARHAN J, LIU BC, MUENDLEIN HI, et al. Caspase-8 induces cleavage of gasdermin D to elicit pyroptosis during Yersinia infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018; 115(46):E10888-E10897. [23] ZHOU Z, HE H, WANG K, et al. Granzyme A from cytotoxic lymphocytes cleaves GSDMB to trigger pyroptosis in target cells. Science. 2020;368(6494):eaaz7548. [24] ZHANG Z, ZHANG Y, XIA S, et al. Gasdermin E suppresses tumour growth by activating anti-tumour immunity. Nature. 2020;579(7799):415-420. [25] HOU J, ZHAO R, XIA W, et al. PD-L1-mediated gasdermin C expression switches apoptosis to pyroptosis in cancer cells and facilitates tumour necrosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22(10):1264-1275. [26] LAMKANFI M, DIXIT VM. Mechanisms and functions of inflammasomes. Cell. 2014;157(5):1013-1022. [27] SHI J, GAO W, SHAO F. Pyroptosis: gasdermin-mediated programmed necrotic cell death. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017;42(4):245-254. [28] YANG B, ZHONG W, GU Y, et al. Emerging mechanisms and targeted therapy of pyroptosis in central nervous system trauma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:83211. [29] SHI Z, YUAN S, SHI L, et al. Programmed cell death in spinal cord injury pathogenesis and therapy. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(3):e12992. [30] LAI M, YAO H, SHAH SZA, et al. The NLRP3-Caspase 1 inflammasome negatively regulates autophagy via TLR4-TRIF in prion peptide-infected microglia. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;10:116. [31] ZHAO S, LI X, WANG J, et al.The role of the effects of autophagy on NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory nervous system diseases. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:657478. [32] QI X, MAN SM, MALIREDDI RK, et al. Cathepsin B modulates lysosomal biogenesis and host defense against Francisella novicida infection. J Exp Med. 2016;213(10): 2081-2097. [33] ROGERS C, FERNANDES-ALNEMRI T, MAYES L, et al.Cleavage of DFNA5 by caspase-3 during apoptosis mediates progression to secondary necrotic/pyroptotic cell death. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14128. [34] CHEN KW, DEMARCO B, HEILIG R, et al. Extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis activate pannexin-1 to drive NLRP3 inflammasome assembly. EMBO J. 2019;38(10):e101638. [35] TAABAZUING CY, OKONDO MC, BACHOVCHIN DA. Pyroptosis and apoptosis pathways engage in bidirectional crosstalk in monocytes and macrophages. Cell Chem Biol. 2017;24(4):507-514.e4. [36] RESTA R, YAMASHITA Y, THOMPSON LF. Ecto-enzyme and signaling functions of lymphocyte CD73. Immunol Rev. 1998;161:95-109. [37] XU S, WANG J, ZHONG J, et al. CD73 alleviates GSDMD-mediated microglia pyroptosis in spinal cord injury through PI3K/AKT/Foxo1 signaling. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(1):e269. [38] LV R, DU L, ZHANG L, ZHANG Z. Polydatin attenuates spinal cord injury in rats by inhibiting oxidative stress and microglia apoptosis via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Life Sci. 2019;217:119-127. [39] ZHANG D, MAO F, WANG S, et al. Role of transcription factor Nrf2 in pyroptosis in spinal cord injury by regulating GSDMD. Neurochem Res. 2023;48(1):172-187. [40] ZHAO Y, WANG LH, PENG A, et al. The neuroprotective and neurorestorative effects of growth differentiation factor 11 in cerebral ischemic injury. Brain Res. 2020;1737:146802. [41] XU Y, HU X, LI F, et al. GDF-11 protects the traumatically injured spinal cord by suppressing pyroptosis and necroptosis via TFE3-mediated autophagy augmentation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:8186877. [42] MISHRA A, SINGH S, TIWARI V, et al. Dopamine D1 receptor agonism induces dynamin related protein-1 inhibition to improve mitochondrial biogenesis and dopaminergic neurogenesis in rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Behav Brain Res. 2020;378:112304. [43] JIANG W, HE F, DING G, et al. Dopamine inhibits pyroptosis and attenuates secondary damage after spinal cord injury in female mice. Neurosci Lett. 2023; 792:136935. [44] SEJAS DP, RANI R, QIU Y, et al. Inflammatory reactive oxygen species-mediated hemopoietic suppression in Fancc-deficient mice. J Immunol. 2007;178(8): 5277-5287. [45] XIA M, LI X, YE S, et al. FANCC deficiency mediates microglial pyroptosis and secondary neuronal apoptosis in spinal cord contusion. Cell Biosci. 2022;12(1):82. [46] SHI Y, ZHAO X, HSIEH J, et al. MicroRNA regulation of neural stem cells and neurogenesis. J Neurosci. 2010;30(45):14931-1496. [47] WANG Y, YUAN Y, GAO Y, et al. MicroRNA-31 regulating apoptosis by mediating the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/protein kinase B signaling pathway in treatment of spinal cord injury. Brain Dev. 2019;41(8):649-661. [48] CHENG J, HAO J, JIANG X, et al. Ameliorative effects of miR-423-5p against polarization of microglial cells of the M1 phenotype by targeting a NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;99:108006. [49] ZHANG M, WANG L, HUANG S, et al. MicroRNA-223 targets NLRP3 to relieve inflammation and alleviate spinal cord injury. Life Sci. 2020;254:117796. [50] ZHANG H, YANG T. FBXW7alpha promotes the recovery of traumatic spinal cord. Curr Mol Med. 2020;20(6):494-504.[51] LIU D, HUANG Y, JIA C, et al. Administration of antagomir-223 inhibits apoptosis, promotes angiogenesis and functional recovery in rats with spinal cord injury. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015;35(4):483-491. [52] ZHONG Y, WU S, YANG Y, et al. LIGHT aggravates sepsis-associated acute kidney injury via TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(20):11936-11948. [53] XU S, WANG J, JIANG J, et al. TLR4 promotes microglial pyroptosis via lncRNA-F630028O10Rik by activating PI3K/AKT pathway after spinal cord injury. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(8):693. [54] WANG J, ZHANG F, XU H, et al. TLR4 aggravates microglial pyroptosis by promoting DDX3X-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation via JAK2/STAT1 pathway after spinal cord injury. Clin Transl Med. 2022;12(6):e894. [55] CRISTANI M, SPECIALE A, SAIJA A, et al. Circulating advanced oxidation protein products as oxidative stress biomarkers and progression mediators in pathological conditions related to inflammation and immune dysregulation. Curr Med Chem. 2016;23(34):3862-3882. [56] LIU Z, YAO X, JIANG W, et al. Advanced oxidation protein products induce microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via MAPKs-NF-κB signaling pathway and pyroptosis after secondary spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1): 90. [57] ZHAO H, WANG X, LIU S, et al. Paeonol regulates NLRP3 inflammasomes and pyroptosis to alleviate spinal cord injury of rat. BMC Neurosci. 2022;23(1):16. [58] DAI W, WANG X, TENG H, et al. Celastrol inhibits microglial pyroptosis and attenuates inflammatory reaction in acute spinal cord injury rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;66:215-223. [59] WU C, CHEN H, ZHUANG R, et al. Betulinic acid inhibits pyroptosis in spinal cord injury by augmenting autophagy via the AMPK-mTOR-TFEB signaling pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(4):1138-1152. [60] ZHANG H, WU C, YU DD, et al. Piperine attenuates the inflammation, oxidative stress, and pyroptosis to facilitate recovery from spinal cord injury via autophagy enhancement. Phytother Res. 2022. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7625. [61] LI WH, CHENG X, YANG YL, et al. Kaempferol attenuates neuroinflammation and blood brain barrier dysfunction to improve neurological deficits in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats. Brain Res. 2019;1722:146361. [62] LIU Z, YAO X, SUN B, et al. Pretreatment with kaempferol attenuates microglia-mediate neuroinflammation by inhibiting MAPKs-NF-κB signaling pathway and pyroptosis after secondary spinal cord injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;168: 142-154. [63] POMMIER Y. Topoisomerase I inhibitors: camptothecins and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(10):789-802. [64] HO JSY, MOK BW, CAMPISI L, et al, Parameswaran S. TOP1 inhibition therapy protects against SARS-CoV-2-induced lethal inflammation. Cell. 2021;184(10): 2618-2632.e17. [65] JIANG W, HE F, DING G, et al. Topoisomerase 1 inhibition modulates pyroptosis to improve recovery after spinal cord injury. FASEB J. 2022;36(6):e22294. [66] HUANG H, YOUNG W, SKAPER S, et al. International association of neurorestoratology and the Chinese association of neurorestoratology. clinical neurorestorative therapeutic guidelines for spinal cord injury (IANR/CANR version 2019). J Orthop Translat. 2019;20:14-24. [67] KHODABANDEH Z, MEHRABANI D, DEHGHANI F, et al. Spinal cord injury repair using mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow in mice: a stereological study. Acta Histochem. 2021;123(5):151720. [68] DILSIZ N. Hallmarks of exosomes. Future Sci OA. 2021;8(1):FSO764. [69] JIANG D, GONG F, GE X, et al. Neuron-derived exosomes-transmitted miR-124-3p protect traumatically injured spinal cord by suppressing the activation of neurotoxic microglia and astrocytes. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020;18(1):105. [70] LIU W, RONG Y, WANG J, et al. Exosome-shuttled miR-216a-5p from hypoxic preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells repair traumatic spinal cord injury by shifting microglial M1/M2 polarization. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):47. [71] SHENG Y, ZHOU X, WANG J, et al. MSC derived EV loaded with miRNA-22 inhibits the inflammatory response and nerve function recovery after spinal cord injury in rats. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(21):10268-10278. [72] ZHOU Y, WEN LL, LI YF, et al. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protect the injured spinal cord by inhibiting pericyte pyroptosis. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(1):194-202. [73] ZHAO Y, CHEN Y, WANG Z, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosome attenuates inflammasome-related pyroptosis via delivering circ_003564 to Improve the recovery of spinal cord injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(11):6771-6789. [74] BROCKIE S, HONG J, FEHLINGS MG. The role of microglia in modulating neuroinflammation after spinal cord injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(18):9706. [75] ZHOU Z, LI C, BAO T, et al. Exosome-shuttled miR-672-5p from anti-inflammatory microglia repair traumatic spinal cord injury by inhibiting AIM2/ASC/Caspase-1 signaling pathway mediated neuronal pyroptosis. J Neurotrauma. 2022;39(15-16): 1057-1074. [76] YUAN Y, FAN X, GUO Z, et al. Metformin protects against spinal cord injury and cell pyroptosis via AMPK/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2022;2022:3634908. [77] ZHENG G, ZHAN Y, WANG H, et al. Carbon monoxide releasing molecule-3 alleviates neuron death after spinal cord injury via inflammasome regulation. EBioMedicine. 2019;40:643-654. [78] JIANG W, HE F, DING G, et al. Topotecan reduces neuron death after spinal cord injury by suppressing Caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis. Mol Neurobiol. 2022; 59(10):6033-6048. [79] HAUPT M, BÄHR M, DOEPPNER TR. Lithium beyond psychiatric indications: the reincarnation of a new old drug. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(12):2383-2387. [80] YANG ML, LI JJ, SO KF, et al. Efficacy and safety of lithium carbonate treatment of chronic spinal cord injuries: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Spinal Cord. 2012;50(2):141-146. [81] ZHAO YJ, QIAO H, LIU DF, et al. Lithium promotes recovery after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(6):1324-1333. [82] LI D, TIAN H, LI X, et al. Zinc promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury by activating Nrf2/HO-1 defense pathway and inhibiting inflammation of NLRP3 in nerve cells. Life Sci. 2020;245:117351. [83] ZHENG G, ZHAN Y, WANG H, et al. Carbon monoxide releasing molecule-3 alleviates neuron death after spinal cord injury via inflammasome regulation. EBioMedicine. 2019;40:643-654. [84] XU X, YIN D, REN H, et al. Selective NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor reduces neuroinflammation and improves long-term neurological outcomes in a murine model of traumatic brain injury. Neurobiol Dis. 2018;117:15-27. [85] FAN X, MA W, ZHANG Y, et al. P2X7 Receptor (P2X7R) of Microglia Mediates Neuroinflammation by Regulating (NOD)-Like Receptor Protein 3 (NLRP3) Inflammasome-Dependent Inflammation After Spinal Cord Injury. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e925491. [86] IRRERA N, VACCARO M, BITTO A, et al. BAY 11-7082 inhibits the NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathways and protects against IMQ-induced psoriasis. Clin Sci (Lond). 2017;131(6):487-498.[87] MARCHETTI C, SWARTZWELTER B, GAMBONI F, et al. OLT1177, a β-sulfonyl nitrile compound, safe in humans, inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome and reverses the metabolic cost of inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018; 115(7):E1530-E1539. [88] HUANG Y, JIANG H, CHEN Y, et al. Tranilast directly targets NLRP3 to treat inflammasome-driven diseases. EMBO Mol Med. 2018;10(4):e8689. [89] SHAO H, HUANG L, DUAN S, et al. Glyburide attenuates ozone-induced pulmonary inflammation and injury by blocking the NLRP3 inflammasome. Environ Toxicol. 2020;35(8):831-839. [90] CORNELIS S, KERSSE K, FESTJENS N, et al. Inflammatory caspases: targets for novel therapies. Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(4):367-385. [91] LI XQ, YU Q, FANG B, et al. Knockdown of the AIM2 molecule attenuates ischemia-reperfusion-induced spinal neuronal pyroptosis by inhibiting AIM2 inflammasome activation and subsequent release of cleaved caspase-1 and IL-1β. Neuropharmacology. 2019;160:107661. [92] RATHKEY JK, ZHAO J, LIU Z, et al. Chemical disruption of the pyroptotic pore-forming protein gasdermin D inhibits inflammatory cell death and sepsis. Sci Immunol. 2018;3(26):eaat2738. [93] YANG J, LIU Z, WANG C, et al. Mechanism of gasdermin D recognition by inflammatory caspases and their inhibition by a gasdermin D-derived peptide inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(26):6792-6797. |
| [1] | 周邦瑜, 李 杰, 阮玉山, 耿福能, 李绍波. 美洲大蠊研粉干预脊髓半横断大鼠运动功能和自噬蛋白Beclin-1的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1223-1228. |
| [2] | 曾凡卓, 李雨欣, 孙嘉晨, 谷欣阳, 文 山, 田 鹤, 梅晰凡. 脊髓损伤模型小胶质细胞的高效移植替换策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1007-1014. |
| [3] | 刘 涛, 张文凯, 马子谦, 张 焱, 陈学明. 利鲁唑干预脊髓损伤大鼠小胶质细胞中NLRP3炎性小体的活化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1036-1042. |
| [4] | 陈泽鹏, 侯永辉, 陈树东, 侯 宇, 林定坤. 牛磺熊去氧胆酸干预缺糖缺氧条件下脊髓神经元的凋亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 528-534. |
| [5] | 刘志杨, 傅泽铤, 夏 雨, 丁海丽. 运动性骨骼肌损伤中时钟基因BMAL1与MyoD的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 510-515. |
| [6] | 徐子涵, 毕耘枫, 李 江, 张宗亮, 宋 晨, 董 捷, 刘 冬. 重复磁刺激S3神经根联合M1区治疗脊髓损伤后尿潴留[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(11): 1719-1723. |
| [7] | 袁长深, 廖书宁, 李 哲, 官岩兵, 吴思萍, 胡 琪, 梅其杰, 段 戡. N6-甲基腺苷相关调节因子与骨关节炎:生物信息学和实验验证分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(11): 1724-1729. |
| [8] | 郑明魁, 薛晨晖, 关晓明, 马 迅. 人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体降低脊髓损伤后血脊髓屏障的通透性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 50-55. |
| [9] | 赵权威, 李 辉, 刘大男, 龚才伟, 陈 龙. 达格列净减轻氧化低密度脂蛋白诱导的内皮细胞焦亡和功能障碍[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 80-85. |
| [10] | 龙清熙, 张萍淑, 刘 青, 欧 亚, 张丽丽, 元小冬. 单细胞RNA测序揭示星形胶质细胞的异质性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 139-146. |
| [11] | 何宛俞, 程乐平. 干细胞移植修复脊髓损伤的策略与进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [12] | 郭淑慧, 杨晔, 江杨洋, 许建文. 神经源性膀胱miRNA-mRNA调控网络的筛选与验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [13] | 杨九杰, 李 治, 王树杰, 田 野, 赵 伟. 神经电生理监测硬脊膜切开减压治疗急性脊髓损伤过程中脊髓的功能变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1232-1236. |
| [14] | 郝柳芳, 段红梅, 王子珏, 郝 飞, 郝 鹏, 赵 文, 高钰丹, 杨朝阳, 李晓光. 转基因小鼠脊髓损伤后室管膜细胞的时空动态变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 883-889. |
| [15] | 李晓寅, 杨晓青, 陈淑莲, 李正超, 王梓琪, 宋 震, 朱达仁, 陈旭义. 胶原/丝素蛋白支架联合神经干细胞治疗创伤性脊髓损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 890-896. |
在临床上,原发性损伤导致神经元立即死亡,无法治疗,而继发性损伤被认为是修复受损神经元的决定性因素[7]。预防继发性损伤常用的手段主要为外科手术结合大剂量的甲基强的松龙,手术治疗能有效地为受损脊髓减压,及时清除局部刺激,稳定病情[8-10];术后使用甲基强的松龙可以减少继发性的氧化应激和炎症反应来改善手术对脊髓的损伤[11]。但大剂量的甲基强的松龙存在不良反应,如肺炎、败血症、血栓栓塞、股骨头坏死,且其对患者的神经恢复疗效甚微[12],在使用过程中仍有争议,目前仍没有一种治疗方法能达到理想的效果。因此,开展脊髓损伤的病理学研究以及开发副反应少的治疗方法是非常必要的。在继发性损伤的病理生理事件中,调节细胞死亡和神经炎症是两个重要的治疗途径[13]。近年来,大批学者将目光投向脊髓损伤后细胞焦亡的研究,设想通过抑制过度神经炎症,减少细胞死亡,防止继发性损伤扩展到周围组织,尽可能抑制进行性组织损伤,为进一步的神经修复和再生创造条件,抑制焦亡调节的细胞死亡成为近期治疗脊髓损伤的新策略。尽管有大量文献对焦亡的机制和功能进行了研究,但对焦亡如何参与脊髓损伤以及如何改善脊髓损伤后的焦亡尚不清楚。
文章在以往研究基础上重点探讨了细胞焦亡在脊髓损伤中的具体应用领域及其局限性,详细阐述了细胞焦亡分子机制及与其他程序性死亡间的联系,归纳了脊髓损伤后促进焦亡与抑制焦亡的因子,从中药活性成分、组织工程技术和药物3方面分类总结了最新靶向脊髓损伤后焦亡的治疗策略,并讨论了它们是如何作为潜在的神经保护治疗起作用的。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2022年12月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2012年1月至2022年12月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed和Web of Science数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 包括“spinal cord injury,pyroptosis,nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3(NLRP3),Caspase,Gasdermin D(GSDMD),IL-1β,IL-18”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著和综述。
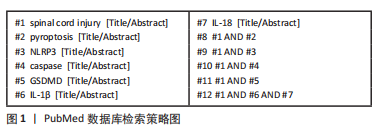
1.1.6 检索策略 以PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图1。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①介绍细胞焦亡相关分子机制的文献;②细胞焦亡与脊髓损伤有关的文献;③细胞焦亡中相关蛋白或细胞因子与脊髓损伤有关的文献;④同一领域选择最新或在权威杂志发表的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 排除研究主题与此综述相关性较低及重复性文献。
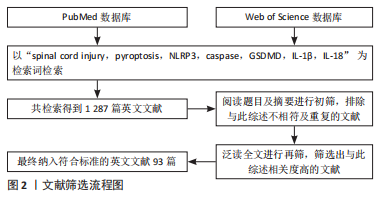
1.3 文献质量评估及数据提取 共检索到1 287篇文献,依照纳排标准进行筛选,最终纳入93篇相关度高的英文文献进行综述,其中PubMed数据库79篇,Web of Science数据库14篇。文献筛选流程,见图2。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 以往综述在脊髓损伤中细胞焦亡的研究多处在其本身分子机制上,单方面探讨了抑制细胞焦亡的因子,关注靶向抑制细胞焦亡某一组分的药物,而没有深入探讨其对脊髓损伤病理的影响。该综述在此基础上详细阐述了细胞焦亡与其他程序性死亡间的联系,重点探讨了细胞焦亡在脊髓损伤中的具体应用领域及其优缺点。此外,除常规药物外,还归纳了最新用于抑制焦亡的组织工程技术如外泌体、干细胞和非编码RNA等,以及有希望的中药活性成分,期待为更好地理解脊髓损伤发病机制和寻求新的治疗方法提供思路。
3.3 综述的局限性 近年来,对脓毒症和肿瘤等多种疾病中细胞焦亡的研究已逐渐为人所知。然而,关于焦亡在脊髓损伤中的作用以及相关干预措施的研究仍较少,内容不够深入。且由于篇幅限制,文章未能将现存所有调节因子及抗焦亡疗法列举论述,此外,文章未关注细胞焦亡的上游分子机制,也没有提到靶向上游组分如Pannexin-1通道、P2X7及组织蛋白酶B等的治疗方法。
3.4 综述的重要意义 文章详细综述了细胞焦亡在脊髓损伤后继发性损伤阶段作用机制的相关研究,归纳了正、负向调节因子和有前景的抗焦亡疗法,以期学者看到细胞焦亡存在的巨大潜能,进而为脊髓损伤的诊断、治疗提供新的思路。通过促进负向调节因子如CD73、NRF2、GDF-11、多巴胺、FANCC及miR-423-5P的表达,抑制正向调节因子如TLR4、AOPPs的表达,可以有效抑制脊髓损伤后细胞焦亡,为神经元和髓鞘修复创造有利的脊髓微环境。接下来可以围绕这些调节因子及干预措施进行实质性的临床研究。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 目前关于脊髓损伤后焦亡的研究仍处于起步阶段,未来可以从以下几方面入手:①脊髓损伤病理机制的复杂性使得其不能只归结于某种单一细胞死亡类型的抑制或激活,可以开发针对多种程序性死亡方式的特异性联合治疗;②脊髓损伤后神经元、小胶质细胞、星形胶质细胞、少突胶质细胞均可出现焦亡,多项研究仅关注某单一细胞的影响,日后可探讨神经元与胶质细胞间的焦亡是否存在串扰;③研究细胞焦亡各个组分间是否存在相互作用;④研究脊髓损伤后细胞焦亡的上游机制,寻找从源头抑制焦亡的方法;⑤除常规治疗外,是否可以采取直接敲除焦亡相关蛋白Gasdermin家族的方式来抑制细胞焦亡;⑥积极开展临床试验,探究在临床上脊髓损伤患者是否具有一致的变化,焦亡标志物是否可以作为诊断和评价脊髓损伤预后的生物标志物;⑦充分发挥中医药优势,开发有希望的中药复方。
总之,细胞焦亡与脊髓损伤的关系值得深入研究,目前的实验药物有很大的希望,这为脊髓损伤的救治提供了有前景的候选方案。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
细胞焦亡:是一种以促炎活性为特征的程序性细胞死亡,由半胱氨酸蛋白酶(Caspase-1/4/5/11)激活,并由Gasdermin家族介导,导致细胞裂解死亡,释放炎性细胞内容物,加剧炎症反应,与脊髓损伤后继发性损伤阶段的发展密切相关。脊髓损伤:可引起严重的运动和感觉障碍,显著降低患者的生活质量和预期寿命,减轻继发性神经元死亡和改善存活神经元功能被认为是脊髓损伤治疗的关键策略。由于其发病机制复杂,目前尚无有效的治疗脊髓损伤药物。
近年来,大批学者将目光投向脊髓损伤后细胞焦亡的研究,设想通过抑制过度神经炎症,减少细胞死亡,防止继发性损伤扩展到周围组织,尽可能抑制进行性组织损伤,为进一步的神经修复和再生创造条件,抑制焦亡调节的细胞死亡成为近期治疗脊髓损伤的新策略。尽管有大量文献对焦亡的机制和功能进行了研究,但对焦亡如何参与脊髓损伤以及如何改善脊髓损伤后的焦亡尚不清楚。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||