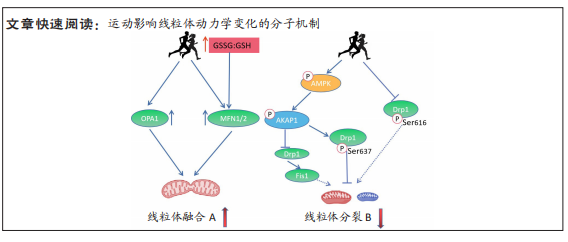
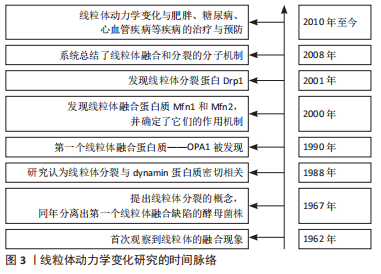
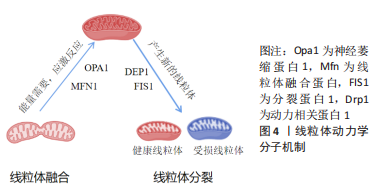
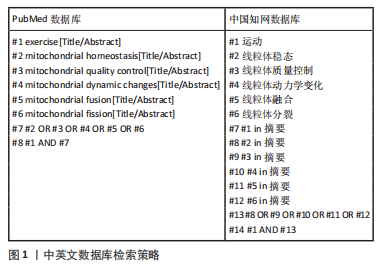
[1] 杨茂君.你的心头也有星辰大海——带你领略呼吸的奥秘[J].科学通报, 2017,62(35):4077-4082.
[2] MURATA D, ARAI K, IIJIMA M, et al. Mitochondrial division, fusion and degradation. J Biochem. 2020;167(3):233-241.
[3] CHAN DC. Mitochondrial dynamics and its involvement in disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 2020;15:235-259.
[4] GIACOMELLO M, PYAKUREL A, GLYTSOU C, et al. The cell biology of mitochondrial membrane dynamics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(4):204-224.
[5] VAN DER BLIEK AM, SHEN Q, KAWAJIRI S. Mechanisms of mitochondrial fission and fusion. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5(6):a011072.
[6] YI X, GUO W, SHI Q, et al. SIRT3-Dependent mitochondrial dynamics remodeling contributes to oxidative stress-induced melanocyte degeneration in vitiligo. Theranostics. 2019;9(6):1614-1633.
[7] ZHANG T, WU P, ZHANG JH, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid alleviates oxidative stress-based apoptosis via improving mitochondrial dynamics in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2018;38(7):1413-1423.
[8] KLUGE MA, FETTERMAN JL, VITA JA. Mitochondria and endothelial function. Circ Res. 2013;112(8):1171-1188.
[9] NG MYW, WAI T, SIMONSEN A. Quality control of the mitochondrion. Dev Cell. 2021;56(7):881-905.
[10] PERNAS L, SCORRANO L. Mito-morphosis: mitochondrial fusion, fission, and cristae remodeling as key mediators of cellular function. Annu Rev Physiol. 2016;78:505-531.
[11] MEMME JM, ERLICH AT, PHUKAN G, et al. Exercise and mitochondrial health. J Physiol. 2021;599(3):803-817.
[12] 舒田.运动干预增龄骨骼肌的线粒体UPR机制研究[D].天津:天津体育学院,2020.
[13] 陈茉,文颖娟,赵欢,等.中医药调控线粒体质量控制治疗糖尿病心肌病研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(21):242-250.
[14] HAILESELASSIE B, JOSHI AU, MINHAS PS, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction mediated through dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) propagates impairment in blood brain barrier in septic encephalopathy. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):36.
[15] ZHAO G, CAO K, XU C, et al. Crosstalk between mitochondrial fission and oxidative stress in paraquat-induced apoptosis in mouse alveolar type II cells. Int J Biol Sci. 2017;13(7):888-900.
[16] YOULE RJ, VAN DER BLIEK AM. Mitochondrial fission, fusion, and stress. Science. 2012;337(6098):1062-1065.
[17] CHAN DC. Mitochondrial fusion and fission in mammals. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:79-99.
[18] COHEN MM, TARESTE D. Recent insights into the structure and function of Mitofusins in mitochondrial fusion. F1000Res. 2018;7:F1000 Faculty Rev-1983.
[19] KOSHIBA T, DETMER SA, KAISER JT, et al. Structural basis of mitochondrial tethering by mitofusin complexes. Science. 2004;305(5685):858-862.
[20] LI D, WANG J, JIN Z, et al. Structural and evolutionary characteristics of dynamin-related GTPase OPA1. PeerJ. 2019;7:e7285.
[21] RAFELSKI SM. Mitochondrial network morphology: building an integrative, geometrical view. BMC Biol. 2013;11:71.
[22] KALIA R, WANG RY, YUSUf A, et al. Structural basis of mitochondrial receptor binding and constriction by DRP1. Nature. 2018;558(7710):401-405.
[23] LIU R, CHAN DC. The mitochondrial fission receptor Mff selectively recruits oligomerized Drp1. Mol Biol Cell. 2015;26(24):4466-4477.
[24] MEARS JA, LACKNER LL, FANG S, et al. Conformational changes in Dnm1 support a contractile mechanism for mitochondrial fission. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011;18(1):20-26.
[25] LEE JE, WESTRATE LM, WU H, et al. Multiple dynamin family members collaborate to drive mitochondrial division. Nature. 2016;540(7631):139-143.
[26] SHARMA A, SMITH HJ, YAO P, et al. Causal roles of mitochondrial dynamics in longevity and healthy aging. EMBO Rep. 2019;20(12):e48395.
[27] TONDERA D, CZAUDERNA F, PAULICK K, et al. The mitochondrial protein MTP18 contributes to mitochondrial fission in mammalian cells. J Cell Sci. 2005;118(Pt 14):3049-3059.
[28] YU R, LIU T, JIN SB, et al. MIEF1/2 orchestrate mitochondrial dynamics through direct engagement with both the fission and fusion machineries. BMC Biol. 2021;19(1):229.
[29] 刘刚,门运政,童旭辉,等.线粒体融合与裂变在右美托咪定减轻小鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤中的作用及其机制[J].南方医科大学学报,2020,40(4): 463-468.
[30] HU C, HUANG Y, LI L. Drp1-Dependent mitochondrial fission plays critical roles in physiological and pathological progresses in mammals. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(1):144.
[31] BAK DW, WEERAPANA E. Cysteine-mediated redox signalling in the mitochondria. Mol Biosyst. 2015;11(3):678-697.
[32] TYUMENTSEV MA, STEFANOVA NA, MURALEVA NA, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction as a predictor and driver of alzheimer’s disease-like pathology in OXYS rats. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;63(3):1075-1088.
[33] WILLEMS PH, ROSSIGNOL R, DIETEREN CE,et al. Redox homeostasis and mitochondrial dynamics. Cell Metab. 2015;22(2):207-218.
[34] 赵永才.运动干预骨骼肌、心肌线粒体动力学研究现状——心肌线粒体动力学研究展望[J].体育科学,2016,36(11):75-81+96.
[35] HERZIG S, LONG F, JHALA US, et al. CREB regulates hepatic gluconeogenesis through the coactivator PGC-1. Nature. 2001;413(6852):179-183.
[36] JI LL, WU E, THOMAS DP. Effect of exercise training on antioxidant and metabolic functions in senescent rat skeletal muscle. Gerontology. 1991;37(6):317-325.
[37] 胡萌.线粒体融合分裂在有氧运动改善自发性高血压大鼠心功能中的作用及机制研究[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2021.
[38] TARPEY MD, DAVY KP, MCMILLAN RP, et al. Skeletal muscle autophagy and mitophagy in endurance-trained runners before and after a high-fat meal. Mol Metab. 2017;6(12):1597-1609.
[39] ARRIBAT Y, BROSKEY NT, GREGGIO C, et al. Distinct patterns of skeletal muscle mitochondria fusion, fission and mitophagy upon duration of exercise training. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2019;225(2):e13179.
[40] AXELROD CL, FEALY CE, MULYA A, et al. Exercise training remodels human skeletal muscle mitochondrial fission and fusion machinery towards a pro-elongation phenotype. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2019;225(4):e13216.
[41] BUSQUETS-CORTÉS C, CAPÓ X, MARTORELL M, et al. Training and acute exercise modulates mitochondrial dynamics in football players’ blood mononuclear cells. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2017;117(10):1977-1987.
[42] LITTLE JP, GILLEN JB, PERCIVAL ME, et al. Low-volume high-intensity interval training reduces hyperglycemia and increases muscle mitochondrial capacity in patients with type 2 diabete. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2011;111(6):1554-1560.
[43] PERRY CG, LALLY J, HOLLOWAY GP, et al. Repeated transient mRNA bursts precede increases in transcriptional and mitochondrial proteins during training in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 2010;588(Pt 23):4795-4810.
[44] JU JS, JEON SI, PARK JY, et al. Autophagy plays a role in skeletal muscle mitochondrial biogenesis in an endurance exercise-trained condition. J Physiol Sci. 2016;66(5):417-430.
[45] FEALY CE, MULYA A, LAI N, et al. Exercise training decreases activation of the mitochondrial fission protein dynamin-related protein-1 in insulin-resistant human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985). 20141;117(3):239-245.
[46] DING H, JIANG N, LIU H, et al. Response of mitochondrial fusion and fission protein gene expression to exercise in rat skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1800(3):250-256.
[47] 刘慧君. 过氧化氢、Ca~(2+)对骨骼肌线粒体移动和动态变化的调节[D].北京:中国人民解放军军事医学科学院,2010.
[48] 于滢.一次大负荷运动对大鼠骨骼肌线粒体分布和功能影响及针刺干预作用[D].北京:北京体育大学,2015.
[49] CARTONI R, LÉGER B, HOCK MB, et al. Mitofusins 1/2 and ERRalpha expression are increased in human skeletal muscle after physical exercise. J Physiol. 2005;567(Pt 1):349-358.
[50] KRUSE R, PEDERSEN AJ, KRISTENSEN JM, et al. Intact initiation of autophagy and mitochondrial fission by acute exercise in skeletal muscle of patients with Type 2 diabetes. Clin Sci (Lond). 2017;131(1):37-47.
[51] MOORE TM, ZHOU Z, COHN W, et al. The impact of exercise on mitochondrial dynamics and the role of Drp1 in exercise performance and training adaptations in skeletal muscle. Mol Metab. 2019;21:51-67.
[52] 刘晓然,于滢,王蕴红,等.大负荷运动对大鼠骨骼肌线粒体融合和分裂蛋白的影响[J].首都体育学院学报,2016,28(02):167-171.
[53] 漆正堂.骨骼肌线粒体对不同训练方式的适应及其基因应答机制的研究[D].上海:华东师范大学,2009.
[54] 孙卫东,丁虎,刘晓然,等.骨骼肌线粒体对细胞能量需求的快速应答: mfn1/2与fis1基因在急性运动中的动态表达[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2008,27(5):544-550.
[55] 娄旭佳,阮蓉,金其贯,等.白藜芦醇干预运动性疲劳模型大鼠线粒体动力学的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(17):2625-2630.
[56] 白胜超. 一次大负荷离心运动后骨骼肌线粒体分裂的机制及针刺干预研究[D].北京:北京体育大学,2018.
[57] 白胜超,陈圣菊,尚画雨等.针刺干预对大鼠离心运动性骨骼肌损伤后线粒体分裂的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2020,39(11):878-887.
[58] VEERANKI S, GIVVIMANI S, KUNDU S, et al. Moderate intensity exercise prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy associated contractile dysfunction through restoration of mitochondrial function and connexin 43 levels in db/db mice. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016;92:163-173.
[59] 刘涛. 运动对慢性心衰心肌线粒体功能、生物合成与融合分裂的调节作用[D].北京:北京体育大学,2009.
[60] 陶小平,彭雄辉.一次大负荷跑台运动后大鼠心肌能量代谢及线粒体形态动力学的变化研究[J].北京体育大学学报,2014,37(3):64-70.
[61] SCHOEPE M, SCHREPPER A, SCHWARZER M, et al. Exercise can induce temporary mitochondrial and contractile dysfunction linked to impaired respiratory chain complex activity. Metabolism. 2012;61(1):117-126.
[62] TONDERA D, GRANDEMANGE S, JOURDAIN A, et al. SLP-2 is required for stress-induced mitochondrial hyperfusion. EMBO J. 2009;28(11):1589-1600.
[63] PASTORE N, VAINSHTEIN A, KLISCH TJ, et al. TFE3 regulates whole-body energy metabolism in cooperation with TFEB. EMBO Mol Med. 2017;9(5):605-621.
[64] NAVARRO A, BOVERIS A. Brain mitochondrial dysfunction in aging: conditions that improve survival, neurological performance and mitochondrial function. Front Biosci. 2007;12:1154-1163.
[65] 李百侠.线粒体分裂融合与转运在运动预防AD中的机制研究[D].上海:华东师范大学,2020.
[66] KOU X, LI J, LIU X, et al. Swimming attenuates d-galactose-induced brain aging via suppressing miR-34a-mediated autophagy impairment and abnormal mitochondrial dynamics. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017;122(6):1462-1469.
[67] 欧秀伶,于宝明,孙剑.运动对高脂饮食性肥胖大鼠棕色脂肪组织线粒体形态和动力学的影响及可能机制的研究[J].山东体育学院学报,2013, 29(1):70-73.
[68] 钱帅伟,孙易,漆正堂,等.运动对线粒体稳态调控机制的研究述评——基于运动介导TFEB调节线粒体质量控制的关键机制探讨[J].体育科学, 2020,40(2):70-82.
[69] TOYAMA EQ, HERZIG S, COURCHET J, et al. AMP-activated protein kinase mediates mitochondrial fission in response to energy stress. Science. 2016;351 (6270):275-281.
[70] ZHANG CS, LIN SC. AMPK promotes autophagy by facilitating mitochondrial fission. Cell Metab. 20168;23(3):399-401.
[71] 张坦,孙易,丁树哲.运动介导AMPK调控线粒体质量控制的机制研究进展[J].中国体育科技,2018,54(6):97-102. |