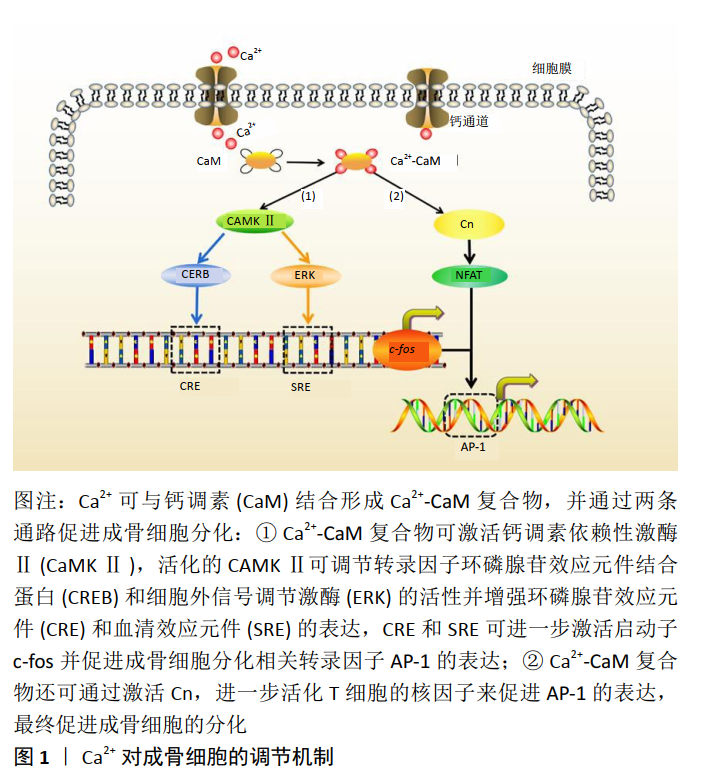
[1] ROBERTS TT, ROSENBAUM AJ. Bone grafts, bone substitutes and orthobiologics: the bridge between basic science and clinical advancements in fracture healing. Organogenesis. 2012;8(4):114-124.
[2] ZHENG ZW, CHEN YH, WU DY, et al. Development of an Accurate and Proactive Immunomodulatory Strategy to Improve Bone Substitute Material-Mediated Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. Theranostics. 2018; 8 (19):5482-5500.
[3] KANG H J, MAKKAR P, PADALHIN AR, et al. Comparative study on biodegradation and biocompatibility of multichannel calcium phosphate based bone substitutes. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;110:110694.
[4] GILEV MV, BAZARNY VV, VOLOKITINA EA, et al. Laboratory Monitoring of Bone Tissue Remodeling after Augmentation of Impression Intraarticular Fracture with Different Types of Bone Graft. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2019;167(5):681-684.
[5] UDA Y, AZAB E, SUN N, et al. Osteocyte Mechanobiology. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2017;15(4):318-325.
[6] CLAPHAM D E. Calcium signaling. Cell. 2007;131(6):1047-1058.
[7] BOOTMAN MD. Calcium signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012;4(7):a011171.
[8] MAENO S, NIKI Y, MATSUMOTO H, et al. The effect of calcium ion concentration on osteoblast viability, proliferation and differentiation in monolayer and 3D culture. Biomaterials. 2005;26(23):4847-4855.
[9] KAWANO S, SHOJI S, ICHINOSE S, et al. Characterization of Ca(2+) signaling pathways in human mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Calcium. 2002;32(4):165-174.
[10] WANG X, ZHANG Y, JI W, et al. Categorising bone defect hematomas - Enhance early bone healing. Med Hypotheses. 2018;113:77-80.
[11] YANG Y, XIAO Y. Biomaterials Regulating Bone Hematoma for Osteogenesis. Adv Healthc Mater.2020;e2000726.
[12] VITI F, LANDINI M, MEZZELANI A, et al. Osteogenic Differentiation of MSC through Calcium Signaling Activation: Transcriptomics and Functional Analysis. PLoS One. 2016;11(2):e0148173.
[13] YE G, GUAN H, KARUSH J, et al. Effects of Ca2+-activated potassium and inward rectifier potassium channel on the differentiation of endothelial progenitor cells from human peripheral blood. Mol Biol Rep. 2014; 41(5):3413-3423.
[14] BERRIDGE MJ, LIPP P, BOOTMAN MD. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000;1(1):11-21.
[15] KAWANO S, OTSU K, KURUMA A, et al. ATP autocrine/paracrine signaling induces calcium oscillations and NFAT activation in human mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Calcium. 2006;39(4):313-324.
[16] YE B. Ca2+ oscillations and its transporters in mesenchymal stem cells. Physiol Res. 2010;59(3):323-329.
[17] CHEN H, TANG QL, WU XY, et al. Differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells into germ-like cells in mouse seminiferous tubules. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(1):819-828.
[18] HEI H, GAO J, DONG J, et al. BK Knockout by TALEN-Mediated Gene Targeting in Osteoblasts: KCNMA1 Determines the Proliferation and Differentiation of Osteoblasts. Mol Cells. 2016;39(7):530-535.
[19] TAO R, LAU CP, TSE HF, et al. Regulation of cell proliferation by intermediate-conductance Ca2+-activated potassium and volume-sensitive chloride channels in mouse mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008;295(5):C1409-1416.
[20] PCHELINTSEVA E, DJAMGOZ MBA. Mesenchymal stem cell differentiation: Control by calcium-activated potassium channels. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(5):3755-3768.
[21] AQUINO-MARTíNEZ R, ANGELO AP, PUJOL FV. Calcium-containing scaffolds induce bone regeneration by regulating mesenchymal stem cell differentiation and migration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):265.
[22] DIRCKX N, VAN HUL M, MAES C. Osteoblast recruitment to sites of bone formation in skeletal development, homeostasis, and regeneration. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2013;99(3):170-191.
[23] NAKAMURA S, MATSUMOTO T, SASAKI J, et al. Effect of calcium ion concentrations on osteogenic differentiation and hematopoietic stem cell niche-related protein expression in osteoblasts. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(8):2467-2473.
[24] LEI Q, LIN D, HUANG WX, et al. [Effects of calcium ion on the migration and osteogenic differentiation of human osteoblasts]. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018;36(6):602-608.
[25] JUNG GY, PARK YJ, HAN JS. Effects of HA released calcium ion on osteoblast differentiation. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21(5):1649-1654.
[26] CARY R L, WADDELL S, RACIOPPI L, et al. Inhibition of Ca²⁺/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 stimulates osteoblast formation and inhibits osteoclast differentiation. J Bone Miner Res. 2013;28(7): 1599-1610.
[27] LIU W, LE CC, WANG D, et al. Ca(2+)/CaM/CaMK signaling is involved in cadmium-induced osteoclast differentiation. Toxicology. 2020;441: 152520.
[28] ZAYZAFOON M, FULZELE K, MCDONALD JM. Calmodulin and calmodulin-dependent kinase IIalpha regulate osteoblast differentiation by controlling c-fos expression. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(8):7049-7059.
[29] KUKUSHKIN AN, ABRAMOVA MV, SVETLIKOVA SB, et al. Downregulation of c-fos gene transcription in cells transformed by E1A and cHa-ras oncogenes: a role of sustained activation of MAP/ERK kinase cascade and of inactive chromatin structure at c-fos promoter. Oncogene. 2002; 21(5):719-730.
[30] WAGNER EF. Functions of AP1 (Fos/Jun) in bone development. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002;61 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):ii40-42.
[31] BABU RL, NAVEEN KUMAR M, PATIL RH, et al. Effect of estrogen and tamoxifen on the expression pattern of AP-1 factors in MCF-7 cells: role of c-Jun, c-Fos, and Fra-1 in cell cycle regulation. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;380(1-2):143-151.
[32] ZAYZAFOON M. Calcium/calmodulin signaling controls osteoblast growth and differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 2006;97(1):56-70.
[33] MANOLAGAS SC. Birth and death of bone cells: basic regulatory mechanisms and implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 2000;21(2):115-137.
[34] BOYLE WJ, SIMONET WS, LACEY DL. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 2003;423(6937):337-342.
[35] TAKAYANAGI H, KIM S, TANIGUCHI T. Signaling crosstalk between RANKL and interferons in osteoclast differentiation. Arthritis Res. 2002;4 Suppl 3 (Suppl 3):S227-232.
[36] 李平,马超, 李小娇,等. 钙离子信号在破骨细胞中作用的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节外科,2011,4(5):417-421.
[37] CHENG X, HOOKWAY ES, KASHIMA T, et al. The role of calcium and nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) in human osteoclast formation and resorption. Calcif Tissue Int. 2015;96(1):73-79.
[38] SHIN MM, KIM YH, KIM SN, et al. High extracellular Ca2+ alone stimulates osteoclast formation but inhibits in the presence of other osteoclastogenic factors. Exp Mol Med. 2003;35(3):167-174.
[39] MENTAVERRI R, YANO S, CHATTOPADHYAY N, et al. The calcium sensing receptor is directly involved in both osteoclast differentiation and apoptosis. FASEB J. 2006;20(14):2562-2564.
[40] BOUDOT C, SAIDAK Z, BOULANOUAR A K, et al. Implication of the calcium sensing receptor and the Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway in the extracellular calcium-mediated migration of RAW 264.7 osteoclast precursor cells. Bone. 2010;46(5):1416-1423.
[41] NGUYEN LH, ANNABI N, NIKKHAH M, et al. Vascularized bone tissue engineering: approaches for potential improvement. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2012; 18 (5): 363-382.
[42] LIU Y, CHAN JK, TEOH SH. Review of vascularised bone tissue-engineering strategies with a focus on co-culture systems. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;9(2):85-105.
[43] MOCCIA F, TANZI F, MUNARON L. Endothelial remodelling and intracellular calcium machinery. Curr Mol Med. 2014;14(4):457-480.
[44] MOCCIA F, BERRA-ROMANI R, TANZI F. Update on vascular endothelial Ca(2+) signalling: A tale of ion channels, pumps and transporters. World J Biol Chem. 2012;3(7):127-158.
[45] PINTO MC, KIHARA AH, GOULART VA, et al. Calcium signaling and cell proliferation. Cell Signal. 2015;27(11):2139-2149.
[46] PINTON P, GIORGI C, SIVIERO R, et al. Calcium and apoptosis: ER-mitochondria Ca2+ transfer in the control of apoptosis. Oncogene. 2008;27(50):6407-6418.
[47] WESTERLUND AM, DELEMOTTE L. Effect of Ca2+ on the promiscuous target-protein binding of calmodulin. PLoS Comput Biol. 2018;14(4): e1006072.
[48] TOUSSAINT F, CHARBEL C, BLANCHETTE A, et al. CaMKII regulates intracellular Ca²⁺ dynamics in native endothelial cells. Cell Calcium. 2015;58(3):275-285.
[49] KAHL CR, MEANS AR. Regulation of cell cycle progression by calcium/calmodulin-dependent pathways. Endocr Rev. 2003;24(6):719-736.
[50] LI XX, LIU YM, LI YJ, et al. High glucose concentration induces endothelial cell proliferation by regulating cyclin-D2-related miR-98. J Cell Mol Med. 2016;20(6):1159-1169.
[51] HUI S, CHOI J, ZAIDI S, et al. Peptide-mediated disruption of calmodulin-cyclin E interactions inhibits proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and neointima formation. Circ Res. 2011;108(9):1053-1062.
[52] JIN Y, MUHL L, BURMAKIN M, et al. Endoglin prevents vascular malformation by regulating flow-induced cell migration and specification through VEGFR2 signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19(6):639-652.
[53] ANGHELESCU VM, NECULAE I, DINCA O, et al. Inflammatory-Driven Angiogenesis in Bone Augmentation with Bovine Hydroxyapatite, B-Tricalcium Phosphate, and Bioglasses: A Comparative Study. J Immunol Res. 2018;2018:9349207.
[54] KUMAGAI H, MAKIHARA T, FUNAYAMA T, et al. Angiogenesis and new bone formation in novel unidirectional porous beta-tricalcium phosphate: a histological study. J Artif Organs. 2019;22(4):294-299.
[55] KUSUMBE AP, RAMASAMY SK, ADAMS RH. Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. 2014; 507(7492):323-328.
[56] RATHER HA, JHALA D, VASITA R. Dual functional approaches for osteogenesis coupled angiogenesis in bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;103:109761.
[57] PIKUŁA M, LANGA P, KOSIKOWSKA P, et al. Stem cells and growth factors in wound healing. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2015;69: 874-885.
[58] WALSH DP, RAFTERY RM, CHEN G, et al. Rapid healing of a critical-sized bone defect using a collagen-hydroxyapatite scaffold to facilitate low dose, combinatorial growth factor delivery. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(10):1843-1853.
[59] LUGINBUEHL V, ZOIDIS E, MEINEL L, et al. Impact of IGF-I release kinetics on bone healing: a preliminary study in sheep. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013;85(1):99-106.
[60] WU M, CHEN G, LI Y P. TGF-β and BMP signaling in osteoblast, skeletal development, and bone formation, homeostasis and disease. Bone Res. 2016;4:16009.
[61] LADDHA AP, KULKARNI YA. VEGF and FGF-2: Promising targets for the treatment of respiratory disorders. Respir Med. 2019;156:33-46.
[62] CAPLAN AI, CORREA D. PDGF in bone formation and regeneration: new insights into a novel mechanism involving MSCs. J Orthop Res. 2011; 29(12):1795-1803.
[63] NESBITT WS, GIULIANO S, KULKARNI S, et al. Intercellular calcium communication regulates platelet aggregation and thrombus growth. J Cell Biol. 2003;160(7):1151-1161.
[64] MARTíNEZ CE, SMITH PC, PALMA ALVARADO VA. The influence of platelet-derived products on angiogenesis and tissue repair: a concise update. Front Physiol. 2015;6:290.
[65] CAVALLO C, ROFFI A, GRIGOLO B, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma: The Choice of Activation Method Affects the Release of Bioactive Molecules. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:6591717.
[66] GARNER AL, FRELINGER AL, 3RD, GERRITS AJ, et al. Using extracellular calcium concentration and electric pulse conditions to tune platelet-rich plasma growth factor release and clotting. Med Hypotheses. 2019; 125:100-105.
[67] WANG M, TAN J, MIAO Y, et al. Role of Ca²⁺ and ion channels in the regulation of apoptosis under hypoxia. Histol Histopathol. 2018;33(3): 237-246.
[68] ECHEVERRI LF, HERRERO MA, LOPEZ JM, et al. Early stages of bone fracture healing: formation of a fibrin-collagen scaffold in the fracture hematoma. Bull Math Biol. 2015;77(1):156-183.
[69] KOLAR P, SCHMIDT-BLEEK K, SCHELL H, et al. The early fracture hematoma and its potential role in fracture healing. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2010;16(4):427-434.
[70] WANG X, FRIIS T, GLATT V, et al. Structural properties of fracture haematoma: current status and future clinical implications. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;11(10):2864-2875.
[71] SHIU HT, GOSS B, LUTTON C, et al. Controlling whole blood activation and resultant clot properties by carboxyl and alkyl functional groups on material surfaces: a possible therapeutic approach for enhancing bone healing. J Mater Chem B. 2014;2(20):3009-3021.
[72] WEISEL JW, LITVINOV RI. Mechanisms of fibrin polymerization and clinical implications. Blood. 2013;121(10):1712-1719.
[73] SISSON K, ZHANG C, FARACH-CARSON MC, et al. Fiber diameters control osteoblastic cell migration and differentiation in electrospun gelatin. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;94(4):1312-1320.
[74] O’KEEFE RJ. Fibrinolysis as a Target to Enhance Fracture Healing. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(18):1776-1778.
[75] BADAMI AS, KREKE MR, THOMPSON MS, et al. Effect of fiber diameter on spreading, proliferation, and differentiation of osteoblastic cells on electrospun poly(lactic acid) substrates. Biomaterials. 2006;27(4): 596-606.
[76] DAS S, JHINGRAN R, BAINS VK, et al. Socket preservation by beta-tri-calcium phosphate with collagen compared to platelet-rich fibrin: A clinico-radiographic study. Eur J Dent. 2016;10(2):264-276.
[77] COLLET J P, PARK D, LESTY C, et al. Influence of fibrin network conformation and fibrin fiber diameter on fibrinolysis speed: dynamic and structural approaches by confocal microscopy. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20(5):1354-1361.
[78] PETERS A, SCHELL H, BAIL HJ, et al. Standard bone healing stages occur during delayed bone healing, albeit with a different temporal onset and spatial distribution of callus tissues. Histol Histopathol. 2010;25(9): 1149-1162.
[79] CAMERON JA, MILNER DJ, LEE JS, et al. Employing the biology of successful fracture repair to heal critical size bone defects. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2013;367:113-132.
[80] MEHTA M, SCHELL H, SCHWARZ C, et al. A 5-mm femoral defect in female but not in male rats leads to a reproducible atrophic non-union. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(1):121-129.
[81] LUGOVSKOĬ EV, GRITSENKO PG, KOMISARENKO SV. [Molecular mechanisms of the polymerization of fibrin and the formation of its three-dimensional network]. Bioorg Khim. 2009;35(4):437-456.
[82] WEISEL JW, LITVINOV RI. Fibrin Formation, Structure and Properties. Subcell Biochem. 2017;82:405-456.
[83] KAMIJO T, MUKAI S, TAIRA C, et al. γD318Y fibrinogen shows no fibrin polymerization due to defective “A-a” and “B-b” interactions, whereas that of γK321E fibrinogen is nearly normal. Thromb Res. 2019;182: 150-158.
[84] REMIJN JA, LOUNES KC, HOGAN KA, et al. Mutations on fibrinogen (gamma 316-322) are associated with reduction in platelet adhesion under flow conditions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;936:444-448.
[85] IKEDA M, KOBAYASHI T, ARAI S, et al. Recombinant γT305A fibrinogen indicates severely impaired fibrin polymerization due to the aberrant function of hole ‘A’ and calcium binding sites. Thromb Res. 2014;134(2): 518-525.
[86] BRENNAN SO, DAVIS RL, MOSESSON MW, et al. Congenital hypodysfibrinogenaemia (Fibrinogen Des Moines) due to a gamma320Asp deletion at the Ca2+ binding site. Thromb Haemost. 2007;98(2):467-469.
[87] ALEMAN MM, BYRNES JR, WANG JG, et al. Factor XIII activity mediates red blood cell retention in venous thrombi. J Clin Invest. 2014;124(8): 3590-3600.
[88] WANG X, LUO Y, YANG Y, et al. Alteration of clot architecture using bone substitute biomaterials (beta-tricalcium phosphate) significantly delays the early bone healing process. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6(48):8204-8213.
[89] CHOO T, MARINO V, BARTOLD PM. Effect of PDGF-BB and beta-tricalcium phosphate (beta-TCP) on bone formation around dental implants: a pilot study in sheep. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013;24(2): 158-166.
[90] DUVAL C, ALLAN P, CONNELL SD, et al. Roles of fibrin alpha- and gamma-chain specific cross-linking by FXIIIa in fibrin structure and function. Thromb Haemost. 2014;111(5):842-850.
[91] VASILYEVA A, YURINA L, INDEYKINA M, et al. Oxidation-induced modifications of the catalytic subunits of plasma fibrin-stabilizing factor at the different stages of its activation identified by mass spectrometry. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2018;1866(8):875-884.
[92] PROTOPOPOVA A D, RAMIREZ A, KLINOV DV, et al. Factor XIII topology: organization of B subunits and changes with activation studied with single-molecule atomic force microscopy. J Thromb Haemost. 2019; 17(5):737-748.
[93] HETHERSHAW EL, CILIA LA CORTE AL, DUVAL C, et al. The effect of blood coagulation factor XIII on fibrin clot structure and fibrinolysis. J Thromb Haemost. 2014;12(2):197-205.
[94] MUSZBEK L, BERECZKY Z, BAGOLYZ, et al. Factor XIII: a coagulation factor with multiple plasmatic and cellular functions. Physiol Rev. 2011; 91(3):931-972. |