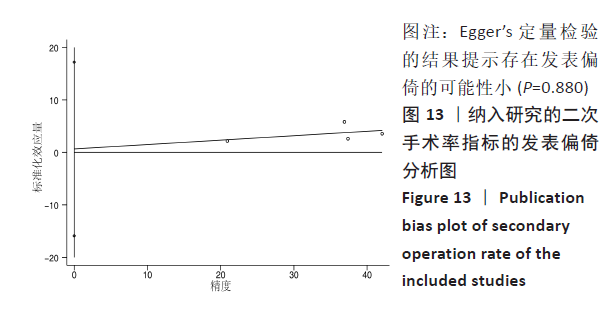
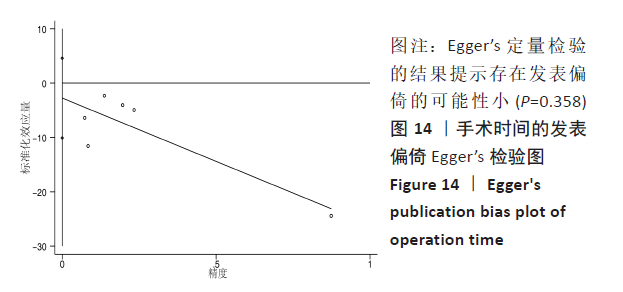
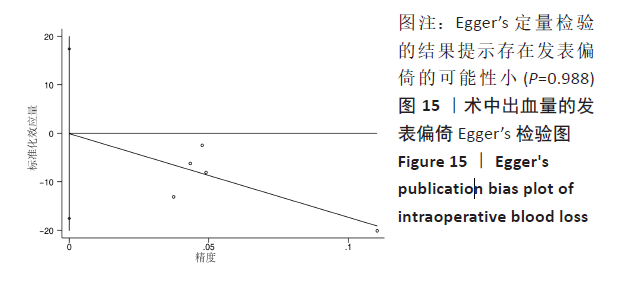
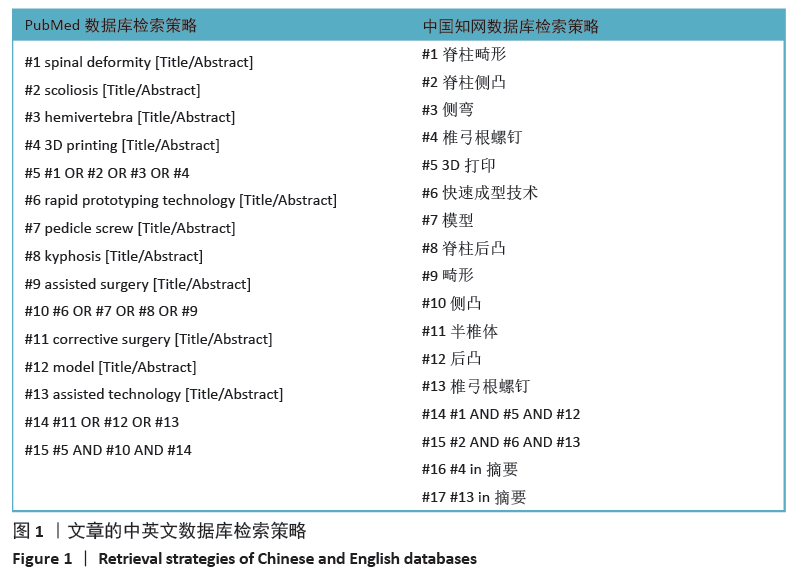
[1] MOKE L, OVERBERGH T, SEVERIJNS P, et al. The transverse gravitational deviation index, a novel gravity line-related spinal parameter, relates to balance control and health-related quality of life in adults with spinal deformity. Spine. 2020;45(1): E25-E36.
[2] SIU TL, ROGERS JM, LIN K, et al. Custom-made titanium 3-dimensional printed interbody cages for treatment of osteoporotic fracture-related spinal deformity. World Neurosurg. 2018;111:1-5.
[3] CHEUNG ZB, SELVERIAN S, CHO BH, et al. Idiopathic scoliosis in Children and adolescents: emerging techniques in surgical treatment. World Neurosurg. 2019; 130:e737-e742.
[4] XUN FX, CANAVESE F, XU HW, et al. Dynamic 3D reconstruction of thoracic cage and abdomen in children and adolescents with scoliosis: preliminary results of optical reflective motion analysis assessment. J Pediatr Orthop. 2020;40(4):196-202.
[5] PASHA S, CAHILL PJ, FLYNN JM, et al. Relationships between the axial derotation of the lower instrumented vertebra and uninstrumented lumbar curve correction: radiographic outcome in Lenke 1 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis with a minimum 2-year follow-up. J Pediatr Orthop. 2018;38(4): e194-e201.
[6] CHEN X, CAI H, ZHANG G, et al. The construction of the scoliosis 3D finite element model and the biomechanical analysis of PVCR orthopaedy. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020;27(2):695-700.
[7] PASHA S, FLYNN J. Data-driven classification of the 3D spinal curve in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis with an applications in surgical outcome prediction. Sci Rep. 2018; 8(1):1-10.
[8] BOHL MA, ZHOU JJ, MOONEY MA, et al. The Barrow Biomimetic Spine: effect of a 3-dimensional-printed spinal osteotomy model on performance of spinal osteotomies by medical students and interns. J Spine Surg. 2019;5(1):58.
[9] GADIYA A, SHAH K, NAGAD P, et al. A Technical note on making patient-specific pedicle screw templates for revision pediatric kyphoscoliosis surgery with sublaminar wires in situ. J Orthop Case Rep. 2019;9(1):82.
[10] CLIFTON W, VLASAK A, DAMON A, et al. Freehand C2 pedicle screw placement: surgical anatomy and operative technique. World Neurosurg. 2019;132:113.
[11] TAKAHATA M, YAMADA K, AKIRA I, et al. A novel technique of cervical pedicle screw placement with a pilot screw under the guidance of intraoperative 3D imaging from C-arm cone-beam CT without navigation for safe and accurate insertion. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(11):2754-2762.
[12] ZHAO Z, LIU Z, HU Z, et al. Improved accuracy of screw implantation could decrease the incidence of post-operative hydrothorax? O-arm navigation vs. free-hand in thoracic spinal deformity correction surgery. Int Orthop. 2018;42(9):2141-2146.
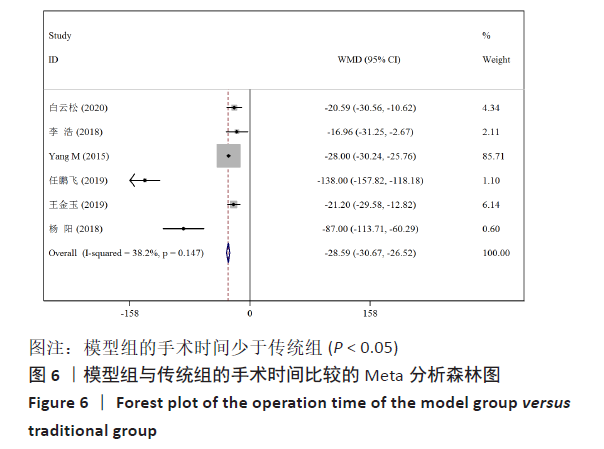
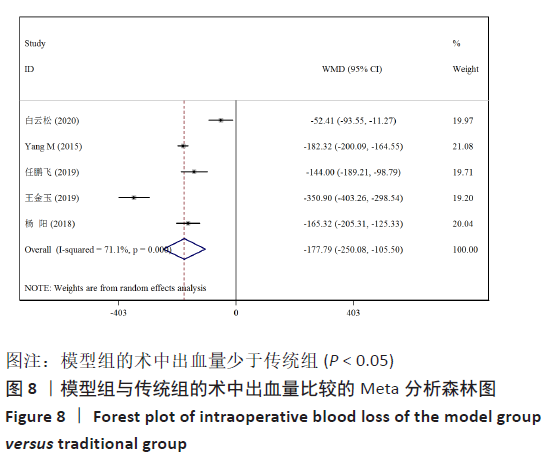
[13] YANG M, LI C, LI Y, et al. Application of 3D rapid prototyping technology in posterior corrective surgery for Lenke 1 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients. Medicine. 2015;94(8):e582.
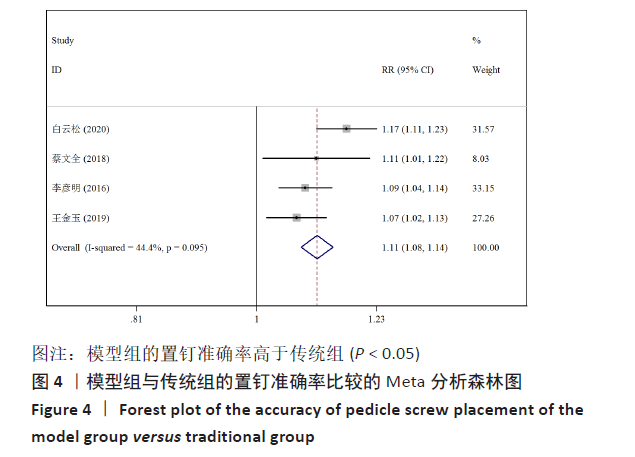
[14] 任鹏飞,矫健航,张善勇,等.3D打印脊柱后凸模型体外模拟截骨在脊柱后凸畸形矫形手术的应用效果分析[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2019,12(6):410-413.
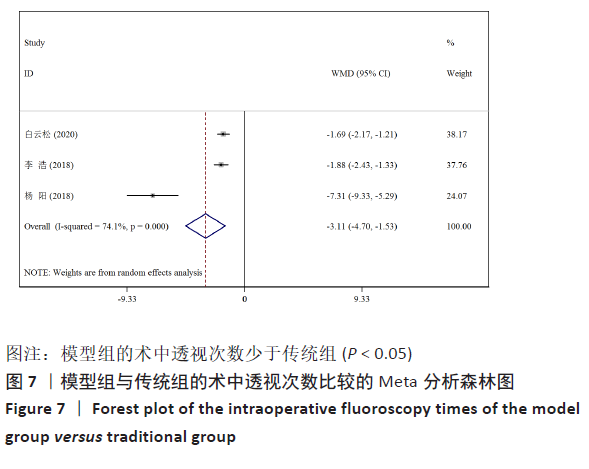
[15] 李浩,张学军,祁新禹,等.3D打印技术辅助手术治疗儿童重度脊柱侧凸的应用研究[J]. 临床小儿外科杂志,2018,17(9): 654-658.
[16] 李彦明,李明,张国友,等.3D打印在脊柱侧凸矫形中的应用初探[J].第二军医大学学报,2016,37(2):231-235.
[17] 杨阳,刘林,薛文,等.3D打印技术在重度僵硬性脊柱侧后凸畸形截骨矫形治疗中的辅助作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(31):4959-4964.
[18] 王金玉,周政纲,王思哲,等.3D打印技术在经椎弓根椎体截骨术治疗脊柱后凸畸形中的应用[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(5):496-498.
[19] 白云松,张学军,曹隽,等.3D打印模型在儿童先天性脊柱侧凸治疗中的应用研究[J]. 临床小儿外科杂志,2020,19(2): 115-119.
[20] 蔡文全,姚瑞翔,宿玉玺,等.3D打印技术在儿童先天性脊柱半椎体手术治疗中的应用研究[J].临床小儿外科杂志, 2018,17(4):259-262.
[21] ZEDEN JP, MÜLLER JU, EL REFAEE EAM, et al. Neuronavigation and 3D fluoroscopy-guided lag screw reduction and osteosynthesis for traumatic spondylolistheses of the axis: a path worth exploring? Neurosurgical focus. 2017;43(2):E2.
[22] LIN JD, TAN LA, WEI C, et al. The posterior superior iliac spine and sacral laminar slope: key anatomical landmarks for freehand S2-alar-iliac screw placement. J Neurosurg Spine. 2018;29(4):429-434.
[23] ELTES PE, KISS L, BARTOS M, et al. Geometrical accuracy evaluation of an affordable 3D printing technology for spine physical models. J Clin Neurosci. 2020;72:438-446.
[24] KIM WK, KIM T, LEE S, et al. 3D-printing-based open repair of extensive thoracoabdominal aorta in severe scoliosis. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019;31(1): 61-63.
[25] SONG P, HU C, PEI X, et al. Dual modulation of crystallinity and macro-/microstructures of 3D printed porous titanium implants to enhance stability and osseointegration. J Mater Chem B. 2019;7(17):2865-2877.
[26] SKOV ST, BÜNGER C, LI H, et al. Lengthening of magnetically controlled growing rods caused minimal pain in 25 children: pain assessment with FPS-R, NRS, and r-FLACC. Spine Deform. 2020;8(4):763-770.
[27] YUAN T, JIA G, YANG L, et al. Occipitocervical fusion combined with 3-dimensional navigation and 3-dimensional printing technology for the treatment of atlantoaxial dislocation with basilar invagination: a case report. Medicine. 2020;99(5):e18983.
[28] ACAROGLU E, DOANY M, CETIN E, et al. Correction of rotational deformity and restoration of thoracic kyphosis are inversely related in posterior surgery for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Med Hypotheses. 2019; 133:109396.
[29] CECCHINATO R, BERJANO P, ZERBI A, et al. Pedicle screw insertion with patient-specific 3D-printed guides based on low-dose CT scan is more accurate than free-hand technique in spine deformity patients: a prospective, randomized clinical trial. Eur Spine J. 2019;28(7):1712-1723.
[30] RAJASEKARAN S, BHUSHAN M, AIYER S, et al. Accuracy of pedicle screw insertion by AIRO® intraoperative CT in complex spinal deformity assessed by a new classification based on technical complexity of screw insertion. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(9): 2339-2347.
[31] BOHL MA, MCBRYAN S, NAKAJI P, et al. Development and first clinical use of a novel anatomical and biomechanical testing platform for scoliosis. J Spine Surg. 2019;5(3):329.
[32] TAN LA, YERNENI K, TUCHMAN A, et al. Utilization of the 3D-printed spine model for freehand pedicle screw placement in complex spinal deformity correction. J Spine Surg. 2018;4(2):319.
[33] GIROD PP, HARTMANN S, KAVAKEBI P, et al. Asymmetric pedicle subtractionosteotomy (aPSO) guided by a 3D-printed model to correct a combined fixed sagittal and coronal imbalance. Neurosurg Rev. 2017;40(4):689-693.
[34] CHEN PC, CHANG CC, CHEN HT, et al. The accuracy of 3D printing assistance in the spinal deformity surgery. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:7196528. |