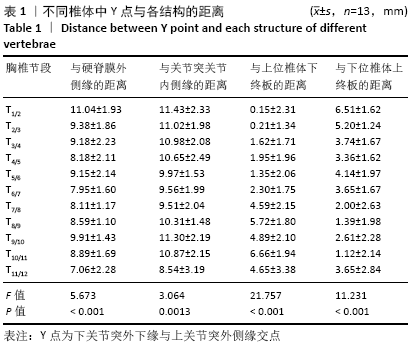
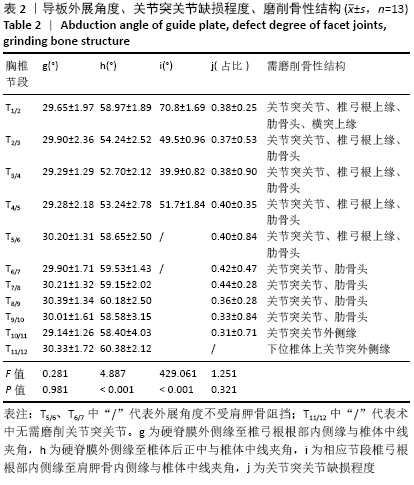
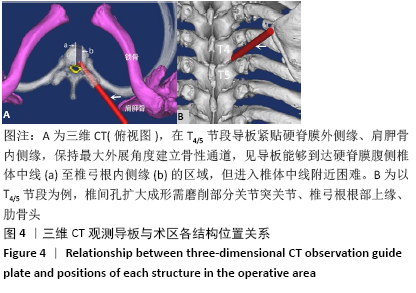
[1] OLTULU I, CIL H, ULU MO, et al. Clinical outcomes of symptomatic thoracic disk herniations treated surgically through minimally invasive lateral transthoracic approach. Neurosurg Rev. 2019;42(4):885-894.
[2] WOOD KB, GARVEY TA, GUNDRY C, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the thoracic spine. Evaluation of asymptomatic individuals. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77:1631-1638.
[3] ROELZ R, SCHOLZ C, KLINGLER JH, et al. Giant central thoracic disc herniations: surgical outcome in 17 consecutive patients treated by mini-thoracotomy. Eur Spine J. 2016;25:1443-1451.
[4] DALBAYRAK S, YAMAN O, OZTÜRK K, et al. Transforaminal approach in thoracal disc pathologies: transforaminal microdiscectomy technique. Minim Invasive Surg. 2014;2014:301945.
[5] STILLERMAN CB, CHEN TC, COULDWELL WT, et al. Experience in the surgical management of 82 symptomatic herniated thoracic discs and review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 1998;88(4):623-633.
[6] XIAOBING Z, XINGCHEN L, HONGGANG Z, et al. “U” route transforaminal percutaneous endoscopic thoracic discectomy as a new treatment for thoracic spinal stenosis. Int Orthop. 2019;43(4):825-832.
[7] ROSS JS, PEREZ-REYES N, MASARYK TJ, et al. Thoracic disk herniation: MR imaging. Radiology. 1987;165(2):511-515.
[8] Rogers MA, Crockard HA. Surgical treatment of the symptomatic herniated thoracic disk. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;300:70-78.
[9] WAGNER R, TELFEIAN AE, IPRENBURG M, et al. Transforaminal Endoscopic Foraminoplasty and Discectomy for the Treatment of a Thoracic Disc Herniation. World Neurosurg. 2016;90:194-198.
[10] OPPENLANDER ME, CLARK JC, KALYVAS J, et al. Surgical management and clinical outcomes of multiple- level symptomatic herniated thoracic discs. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;19(6):774-783.
[11] LUBELSKI D, ABDULLAH KG, STEINMETZ MP, et al. Lateral extracavitary, costotransversectomy,and transthoracic thoracotomy approaches to the thoracic spine:review of techniques and complications. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(4):222-232.
[12] ZHAO Y, WANG Y, XIAO S, et al. Transthoracic approach for the treatment of calcified giant herniated thoracic discs. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(11):2466-2473.
[13] HUR JW, KIM JS, SEUNG JH. Full-endoscopic interlaminar discectomy for the treatment of a dorsal migrated thoracic disc herniation: Case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(22):e15541.
[14] DEVIREN V, KUELLING FA, POULTER G, et al. Minimal invasive anterolateral transthoracic transpleural approach:a novel technique for thoracic disc herniation. A review of the literature,description of a new surgical technique and experience with first 12 consecutive patients. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2011;24(5):E40-E48.
[15] ROSENTHAL D. Endoscopic approaches to the thoracic spine. Eur Spine J. 2000;9 (Suppl 1):S8-S16.
[16] WAIT SD, FOX DJ JR, KENNY KJ, et al. Thoracoscopic resection of symptomatic herniated thoracic discs: clinical results in 121 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37:35-40.
[17] 杨俊松,楚磊,王永峰,等.经皮脊柱内镜在治疗胸椎管狭窄症中的应用研究[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2019,8(2):98-104.
[18] 刘越,徐宝山,吉宁,等.经皮椎间孔镜技术治疗胸椎间盘突出症的初步体会[J].天津医药,2017,45(2):121-124.
[19] BARTELS RH, PEUL WC. Mini-thoracotomy or thoracoscopic treatment for medially located thoracic herniated disc? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32:E581-E584.
[20] BILSKY MH. Transpedicular approach for thoracic disc herniations. Neurosurg Focus. 2000;9(4):e3.
[21] FESSLER RG, STURGILL M. Review: complications of surgery for thoracic disc disease. Surg Neurol. 1998;49:609-618.
[22] YOSHIHARA H, YONEOKA D. Comparison of in-hospital morbidity and mortality rates between anterior and nonanterior approach procedures for thoracic disc herniation. Spine (PhilaPa 1976). 2014;39:E728-E733.
[23] RUETTEN S, HAHN P, OEZDEMIR S, et al. Full-endoscopic uniportal decompression in disc herniations and stenosis of the thoracic spine using the interlaminar,extraforaminal,or transthoracic retropleural approach. J Neurosurg Spine. 2018;29(2):157-168.
[24] Jho HD. Endoscopic microscopic transpedicular thoracic discectomy: Technical note. J Neurosurg. 1997;87(1):125-129.
[25] BAE J, CHACHAN S, SHIN SH, et al. Percutaneous Endoscopic Thoracic Discectomy in the Upper and Midthoracic Spine: A Technical Note. Neurospine. 2019;16(1):148-153.
[26] RUETTEN S, HAHN P, OEZDEMIR S, et al. Operation of Soft or Calcified Thoracic Disc Herniations in the Full-Endoscopic Uniportal Extraforaminal Technique. Pain Physician. 2018;21(4):E331-E340.
[27] LIU W, YAO L, LI X, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic thoracic discectomy via posterolateral approach: A case report of migrated thoracic disc herniation. Medicine(Baltimore). 2019;98(41):e17579.
[28] CHOI KY, EUN SS, LEE SH, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic thoracic discectomy; transforaminal approach. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2010;53:25-28.
[29] YEUNG AT, TSOU PM. Posterolateral endoscop-icexcision for lumbar disc herniation:Surgical tech- Nique,outcome,and complications in 307 consecutive cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(7):722-731.
[30] HOOGLAND T, SCHUBERT M, MIKLITZ B, et al. Transfo-raminal posterolateral endoscopic dis-cectomy with or without the combination of a low-dose chymopa-pain:a prospective randomized study in 280 consecutive cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(24):890-897.
[31] 袁恒,张西峰,张琳,等.脊柱内镜下治疗胸腰段椎间盘突出的临床疗效[J].实用骨科杂志,2018,24(8):733-736.
[32] AN B, LI XC, ZHOU CP, et al. Percutaneous full endoscopic posterior decompression of thoracic myelopathy caused by ossification of the ligamentum flavum. Eur Spine J. 2019;28(3):492-501.
[33] DEBNATH UK, MCCONNELL JR, SENGUPTA DK, et al. Results of hemivertebrectomy and fusion for symptomatic thoracic disc herniation. Eur Spine J. 2003;12:292-299.
[34] ODA I, ABUMI K, LÜ D, et al. Biomechanical role of the posterior elements, costovertebral joints, and rib cage in the stability of the thoracic spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21:1423-1429.
[35] AL-MAHFOUDH R, MITCHELL PS, WILBY M, et al. Management of Giant Calcified Thoracic Disks and Description of the Trench Vertebrectomy Technique. Global Spine J. 2016;6(6):584-591.
|