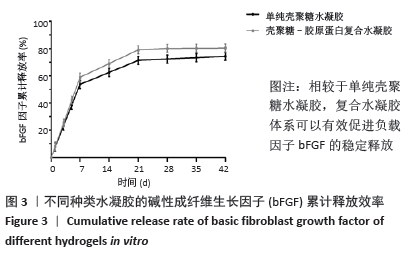
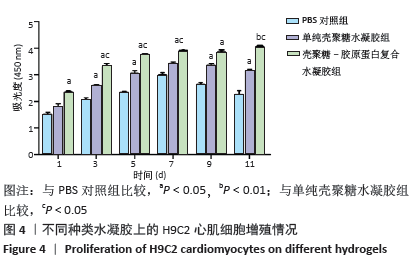
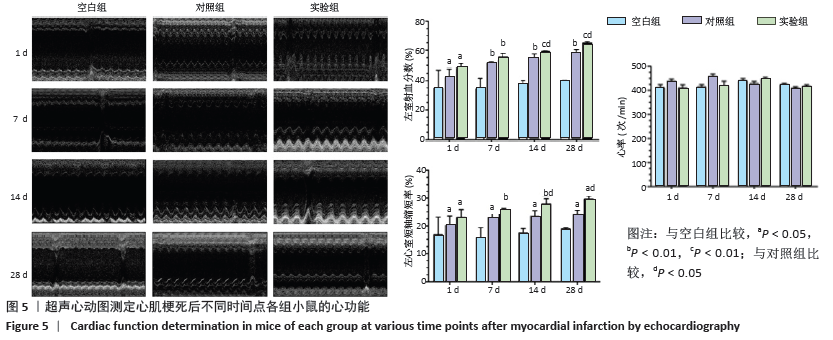
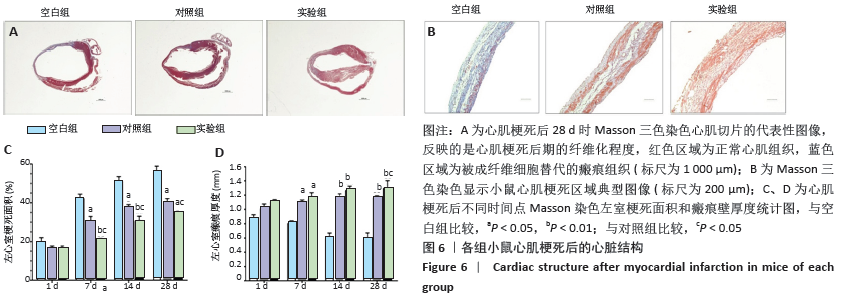
[1] BENJAMIN EJ, VIRANI SS, CALLAWAY CW, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2018 update:a report from the American heart association.Circulation. 2018;137(12):e67-e492.
[2] GONZÁLEZ A, SCHELBERT EB, DÍEZ J, et al. Myocardial interstitial fibrosis in heart failure:biological and translational perspectives. Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71(15):1696-1706.
[3] BLACKBURN NJ, SOFRENOVIC T, KURAITIS D, et al. Timing underpins the benefits associated with injectable collagen biomaterial therapy for the treatment of myocardial infarction. Biomaterials. 2015;39:182-192.
[4] YANAMANDALA M, ZHU W, GARRY DJ, et al. Overcoming the roadblocks to cardiac cell therapy using tissue engineering. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017; 70(6):766-775.
[5] FUJITA B, ZIMMERMANN WH. Myocardial tissue engineering strategies for heart repair: current state of the art. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2018;27(6):916-920.
[6] SALUDAS L, PASCUAL-GIL S, PRÓSPER F, et al. Hydrogel based approaches for cardiac tissue engineering. Int J Pharm. 2017;523(2): 454-475.
[7] SARKAR B, NGUYEN PK, GAO W, et al. Angiogenic self-assembling peptide scaffolds for functional tissue regeneration. Biomacromolecules. 2018; 19(9):3597-3611.
[8] ALKAN M, MADANIEH R, SHAH NN, et al. Regenerative stem cell therapy optimization via tissue engineering in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2017;8(4):515-526.
[9] PARK J, ANDERSON CW, SEWANAN LR, et al. Modular design of a tissue engineered pulsatile conduit using human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Acta Biomater. 2019;S1742-7061(19): 30695-30696.
[10] JOHNSON TA, SINGLA DK. Therapeutic application of adult stem cells in the heart. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1553:249-264.
[11] ZHANG S, LIU Y, ZHANG X, et al. Prostaglandin E2 hydrogel improves cutaneous wound healing via M2 macrophages polarization.Theranostics. 2018;8(19):5348-5361.
[12] XUE H, HU L, XIONG Y, et al. Quaternized chitosan-Matrigel-polyacrylamide hydrogels as wound dressing for wound repair and regeneration. Carbohydr Polym. 2019;226:115302.
[13] JACKMAN C, LI H, BURSAC N. Long-term contractile activity and thyroid hormone supplementation produce engineered rat myocardium with adult-like structure and function. Acta Biomater. 2018;78:98-110.
[14] XU B, LI Y, DENG B, et al. Chitosan hydrogel improves mesenchymal stem cell transplant survival and cardiac function following myocardial infarction in rats. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13(2):588-594.
[15] SHU Y, HAO T, YAO F, et al. RoY- peptide-modified chitosan-based hydrogel to improve angiogenesis and cardiac repair under hypoxia. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(12):6505-6517.
[16] SHI C, ZHAO Y, YANG Y, et al. Collagen-binding VEGF targeting the cardiac extracellular matrix promotes recovery in porcine chronic myocardial infarction. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(2):356-363.
[17] ZHU H, JIANG X, LI X, et al. Intramyocardial delivery of VEGF165 via a novel biodegradable hydrogel induces angiogenesis and improves cardiac function after rat myocardial infarction.Heart Vessels. 2016; 31(6):963-975.
[18] KRETZSCHMAR K, POST Y, BANNIER-HÉLAOUËT M, et al. Profiling proliferative cells and their progeny in damaged murine hearts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115(52):E12245-E12254.
[19] TANG J, LI Y, HUANG X, et al. Fate mapping of Sca1(+) cardiac progenitor cells in the adult mouse heart. Circulation. 2018;138(25):2967-2969.
[20] WU Q, ZHAN J, PU S, et al. Influence of aging on the activity of mice Sca-1+CD31- cardiac stem cells. Oncotarget. 2017;8(1):29-41.
[21] LIU H, PAUL C, XU M. Optimal environmental stiffness for stem cell mediated ischemic myocardium repair. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1553: 293-304.
[22] WHITE SL, HIRTH R, MAHÍLLO B, et al. The global diffusion of organ transplantation: trends, drivers and policy implications. Bull World Health Organ. 2014;92(11):826-835.
[23] JUMABAY M, MATSUMOTO T, YOKOYAMA S, et al. Dedifferentiated fat cells convert to cardiomyocyte phenotype and repair infarcted cardiac tissue in rats. Mol Cell Cardiol. 2009;47(5):565-575.
[24] HONG KU, BOLLI R. Cardiac stem cell therapy for cardiac repair.Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2014;16(7):324.
[25] CHAUDHURI R, RAMACHANDRAN M, MOHARIL P, et al. Biomaterials and cells for cardiac tissue engineering:Current choices. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;79:950-957.
[26] WANG W, TAN B, CHEN J, et al. An injectable conductive hydrogel encapsulating plasmid DNA-eNOs and ADSCs for treating myocardial infarction. Biomaterials. 2018;160:69-81.
[27] LEIJTEN J, SEO J, YUE K, et al. Spatially and temporally controlled hydrogels for tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng R Rep. 2017;119:1-35.
[28] ROBERTS DE, SCHER AM. Effect of tissue anisotropy on extracellular potential fields in canine myocardium in situ. Circ Res. 1982;50(3): 342-351.
[29] KOUTSOPOULOS S. Self-assembling peptide nanofiber hydrogels in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: Progress, design guidelines, and applications. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(4): 1002-1016.
[30] MATHIEU M, BARTUNEK J, OUMEIRI BE, et al. Cell therapy with autologous bone marrow mononuclear stem cells is associated with superior cardiac recovery compared with use of nonmodified mesenchymal stem cells in a canine model of chronic myocardial infarction. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009;138(3):646-653.
[31] QIU Y, PARK K.Environment-sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;53(3):321-339.
[32] XIONG ZH, WEI J, LU MQ, et al. Protective effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosomes on preserving the morphology and angiogenesis of placenta in rats with preeclampsia. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;9(105):1240-1247.
[33] ANGERT D, BERRETTA RM, KUBO H, et al. Repair of the injured adult heart involves new myocytes potentially derived from rResident cardiac stem cells. Circ Res. 2011;108(10):1226-1237.
[34] SOOD N, BHARDWAJ A, MEHTA S, et al. Stimuli-responsive hydrogels in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Drug Deliv. 2016;23(3):758-780.
[35] CUI Z, NI NC, WU J, et al. Polypyrrole-chitosan conductive biomaterial synchronizes cardiomyocyte contraction and improves myocardial electrical impulse propagation. Theranostics. 2018;8(10):2752-2764.
[36] LU J, DAI QM, MA GS, et al. Erythropoietin attenuates cardiac dysfunction in rats by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2017;31(4):367-379. |