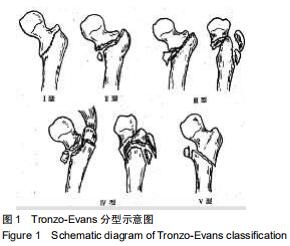
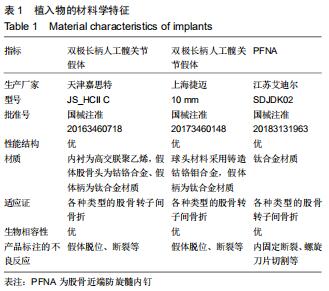
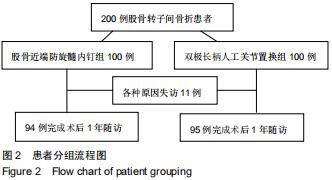
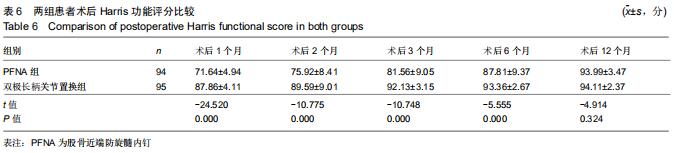
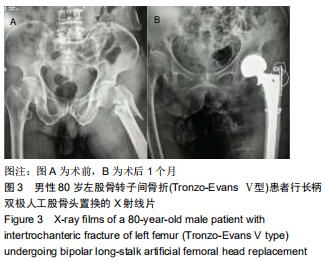
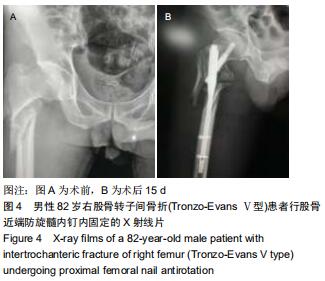
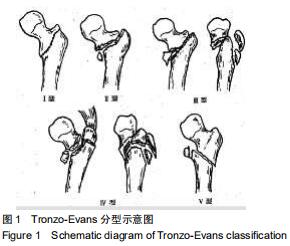
|
[1] 陈孝平,汪建平,赵继宗,等.外科学[M].9版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2018: 661.
[2] 姬晨妮,陈伟,朱燕宾,等.京津唐地区1583例老年股骨转子间骨折流行病学特征分析[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2015,1(1):45-49.
[3] YOON BH, BAEK JH, KIM MK, et al. Poor prognosis in elderly patients who refused surgery because of economic burden and medical problem after hip fracture. J Korean Med Sci. 2013;28(9):1378-1381.
[4] LI K, ZHENG Y. Internal fixation versus conservative treatment for elderly patients with a trochanteric hip fracture in conjunction with post-stroke hemiplegia. Injury. 2016;47(10):2169-2172.
[5] DAUGAARD CL, JØRGENSEN HL, RIIS T, et al. Is mortality after hip fracture associated with surgical delay or admission during weekends and public holidays? A retrospective study of 38,020 patients. Acta Orthop. 2012;83(6):609-613.
[6] 王志,汤健,华兴一.InterTan髓内钉与股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年性股骨粗隆间骨折的Meta分析[J].安徽医学,2018,39(2):136-140.
[7] FAIRAG R, ABDULJABBAR FH, PAGE A, et al. Are Cephalomedullary Nail Guides Accurate? A Case Report of an Unexpected Complication After Nailing an Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2018;9:2151458518757797.
[8] HÉLIN M, PELISSIER A, BOYER P, et al. Does the PFNA™ nail limit impaction in unstable intertrochanteric femoral fracture? A 115 case-control series. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(1):45-49.
[9] HU YG, HAN L, FANG WL, et al. Comparison of anatomical locking plate and Gamma nail for the treatment of intertrochanteric fracture with external wall fractures. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2016;29(6):496-501.
[10] YU W, ZHANG X, ZHU X, et al. Proximal femoral nails anti-rotation versus dynamic hip screws for treatment of stable intertrochanteric femur fractures: an outcome analyses with a minimum 4 years of follow-up. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17:222.
[11] 戴文涛,吴建雄,程小勇,等.远端固定生物型假体的人工股骨头置换术治疗高龄股骨粗隆间骨折的体会[J].北京医学,2017,39(4):436-437.
[12] 董建彬,王智勇,芦浩,等.内固定术与髋关节置换术治疗股骨粗隆间骨折疗效的Meta分析[J].中国骨伤,2015,28(3):245-251.
[13] 孙贵耀,乔晓光,张雪华.老年股骨粗隆间骨折的治疗研究进展[J].医学综述,2014,20(21):3894-3896.
[14] 王立刚,陈晓东,朱俊峰,等.老年人股骨粗隆间骨折的治疗进展[J].临床与病理杂志,2016,36(5):695-701.
[15] 张轩轩,李宝丰,章莹,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉与髋关节置换术治疗高龄股骨粗隆间骨折Meta分析[J].实用医学杂志,2019,35(6):903-907.
[16] 陈明初.人工股骨头置换治疗高龄股骨转子间骨折内固定失效[J].临床骨科杂志,2017,20(1):79.
[17] ÖZKAYIN N, OKÇU G, AKTUĞLU K. Intertrochanteric femur fractures in the elderly treated with either proximal femur nailing or hemiarthroplasty: A prospective randomised clinical study. Injury. 2015;46 Suppl 2:S3-8.
[18] FICHMAN SG, MÄKINEN TJ, SAFIR O, et al. Arthroplasty for unstable pertrochanteric hip fractures may offer a lower re-operation rate as compared to cephalomedullary nailing. Int Orthop. 2016;40(1):15-20.
[19] SUN D, PARK BS, JANG GI, et al. The fixation method according to the fracture type of the greater trochanter in unstable intertrochanteric fractures undergoing arthroplasty. Hip Pelvis. 2017;29(1):62-67.
[20] 黄绍东,韦玮,卢显威,等.PFNA近端锁定板和人工股骨头置换术对高龄骨质疏松性股骨粗隆间骨折患者围术期指标髋功能恢复及下肢静脉血栓的影响[J].河北医学,2019,25(2):241-245.
[21] 刘阳,彭昊,黄冠予,等.人工股骨头置换术治疗老年患者不稳定型股骨粗隆间骨折[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2019,16(4):63-67.
[22] 康兵文,肖波,王森.PFNA与骨水泥加长柄人工股骨头置换治疗高龄骨质疏松性股骨转子间骨折的比较研究[J].创伤外科杂志,2019,21(10): 766-770.
[23] 周亚东,朱华章.人工股骨头置换与股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定治疗高龄股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(8): 846-848.
[24] LI Y, ZHAO WB, WANG DL, et al. Treatment of osteoporotic intertrochanteric fractures by zoledronic acid injection combined with proximal femoral nail anti-rotation. Chin J Traumatol. 2016;19(5): 259-263.
[25] YU W, ZHANG X, WU R, et al. The visible and hidden blood loss of Asia proximal femoral nail anti-rotation and dynamic hip screw in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures of elderly high- risk patients: a retrospective comparative study with a minimum 3 years of follow-up. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016,17:269.
[26] MA KL, WANG X, LUAN FJ, et al. Proximal femoral nails antirotation, Gamma nails, and dynamic hip screws for fixation of intertrochanteric fractures of femur: A meta-analysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014; 100(8):859-866.
[27] 谢峰,周怡利,徐明灯,等.加长柄人工股骨头置换术治疗高龄不稳定股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019,34(12): 1288-1289.
[28] 陶钧,许克庆,吴成玉,等.生物型长柄人工股骨头置换术治疗90岁以上Evans Ⅲ-Ⅳ型股骨粗隆间骨折22例[J].安徽医药,2020,24(2):275-280.
[29] 李明东,王丹,高星,等.手术方式和手术时间对老年髋部骨折术后深静脉血栓发生率的影响[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2017,6(5):375-378.
[30] LU XD, WANG B, XU W, et al. Comparison of calcar replacement arthroplasty and Intertan nail in treatment of intertrochanteric fracture in the aged. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.2016,96(31):2466-2471.
[31] LIM JW, NG GS, JENKINS RC, et al. Total hip replacement for neck of femur fracture: Comparing outcomes with matched elective cohort. Injury. 2016,47(10):2144-2148.
[32] COOMBER R, PORTEOUS M, HUBBLE MJW, et al. Total hip replacement for hip fracture: Surgical techniques and concepts. Injury. 2016;47(10):2060-2064.
[33] 朱爱祥.PFNA与人工股骨头置换术治疗老年不稳定型股骨粗隆间骨折的临床价值分析[J].中国实用医药,2018,13(34):76-78.
[34] 杨福成,张向敏,张朝阳,等.PFNA与加长柄人工股骨头置换治疗高龄股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效比较[J].实用骨科杂志,2016,22(11):1031-1034.
[35] 沈波,焦竞,勘武生.人工关节置换与内固定术治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的Meta分析[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2014,43(5):586-594.
[36] 程锐,曾少鞠,谢伟雄,等.PFNA术与人工股骨头置换术治疗股骨粗隆间骨折的效果对比分析[J].中国医药科学,2019,9(4):240-243.
[37] 陈洋伟,乔玲玉,李艺贤.人工股骨头置换术结合快速康复理念治疗高龄不稳定型股骨转子间骨折的效果观察[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2019, 19(60):339-340.
[38] 巩栋.生物型人工股骨头置换与股骨近端抗旋髓内钉治疗高龄不稳定型转子间骨折的回顾性研究和Meta分析[D].兰州:甘肃中医药大学,2019.
[39] 杨朝君,孙智文,张爱民,等.人工股骨头置换术结合快速康复理念治疗高龄不稳定型股骨转子间骨折的临床效果[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版), 2018,13(4):253-259.
[40] 孙卫平.加长柄人工股骨头置换治疗高龄不稳定型股骨转子间骨折[C]. 全军骨科学会创伤骨科分会.第三届全军创伤骨科学术大会论文集.全军骨科学会创伤骨科分会:中国骨与关节损伤杂志社,2015:93-94.
[41] 殷勇,杨静.股骨柄假体人工半髋关节置换治疗高龄股骨转子间骨折[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2018,12(2):174-178.
[42] 柳椰,邬波,马旭,等.人工髋关节置换治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的临床研究[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2019,39(7):1041-1043.
[43] 孙启才,茹选良,钱志钢,等.髋关节置换术治疗老年股骨转子间骨折内固定失败的中期随访[J].中国骨伤,2017,30(7):591-596.
[44] 吴建军.半髋关节置换与防旋型股骨近端髓内钉治疗高龄不稳定型股骨粗隆间骨折的临床效果观察[J].临床研究,2020,28(1):117-119.
[45] 付玉平,李宏伟,王帅,等.关节置换和股骨近端髓内钉治疗高龄股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效研究[J].中国医科大学学报,2017,46(12):1092-1094+1100.
|