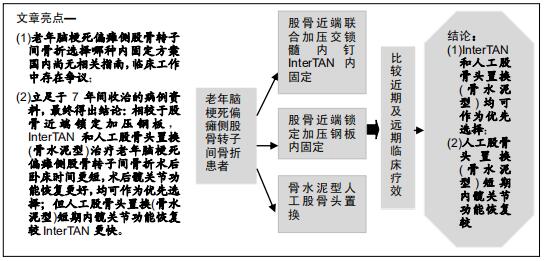
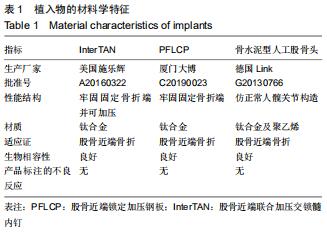
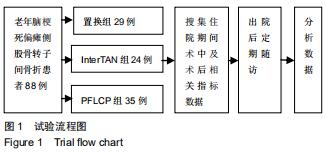
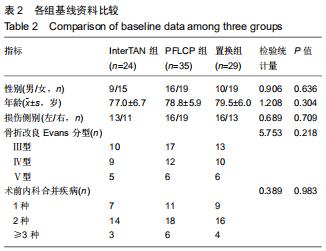
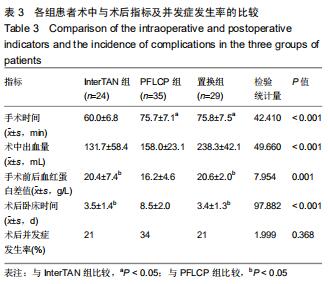
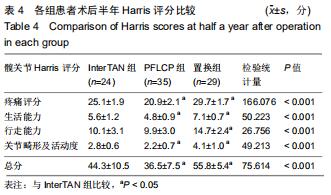
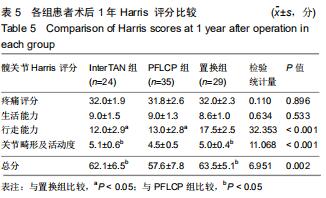
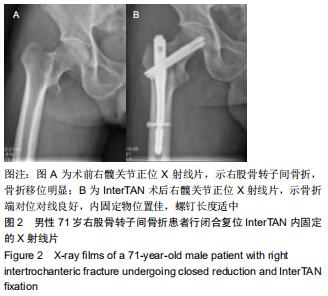
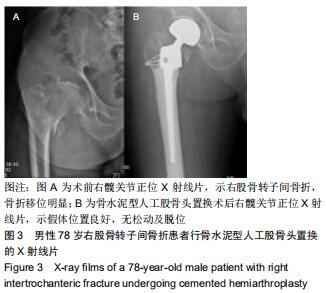
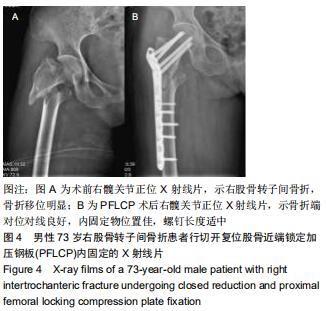
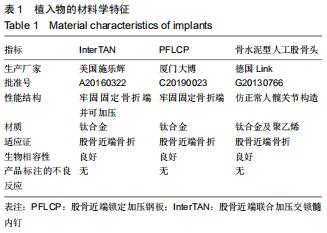
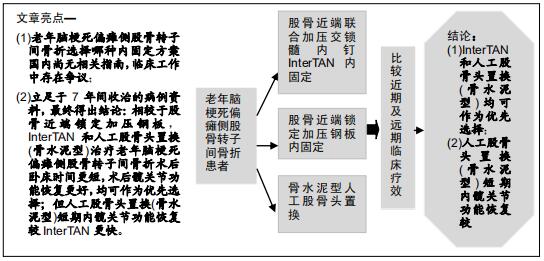
|
[1] TUCKER A, DONNELLY KJ, ROWAN C, et al. Is the best plate a nail? A review of 3230 unstable intertrochanteric fractures of the proximal femur. J Orthop Trauma.2018;32(2):53-60.
[2] HIRAGAMI K, ISHII J. Embedding the lateral end of the lag screw within the lateral wall in the repair of reverse obliquity intertrochanteric femur fracture. J Int Med Res. 2018;46(3): 1103-1108.
[3] YOO JI, HA YC, LIM JY, et al. Early Rehabilitation in Elderly after Arthroplasty versus Internal Fixation for Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures of Femur: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Korean Med Sci.2017; 32(5):858-867.
[4] SIK CW, HOON AJ, JOON-HYUK K, et al. Cementless bipolar hemiarthroplasty for unstable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients. Clin Orthop Surg.2010;2(4): 221-226.
[5] PARKER MJ, CAWLEY S. Sliding hip screw versus the Targon PFT nail for trochanteric hip fractures: a randomised trial of 400 patients. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(9):1210-1215.
[6] HUI Z, ZENG X, NAN Z, et al. INTERTAN nail versus proximal femoral nail antirotation-Asia for intertrochanteric femur fractures in elderly patients with primary osteoporosis. J Int Med Res. 2007; 45(4):1297-1309.
[7] SHAH MD, KAPOOR CS, SONI RJ, et al. Evaluation of outcome of proximal femur locking compression plate (PFLCP) in unstable proximal femur fractures. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2017; 8(4): 308-312.
[8] 张擎柱,樊琪,尹雪莲,等.三种植入物治疗老年脑梗死偏瘫侧股骨转子间骨折的比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(24):3805-3811.
[9] 万乾,杨小华,张擎柱,等.骨水泥型人工股骨头置换与股骨近端防旋髓内钉置入治疗老年脑梗死患者偏瘫侧股骨转子间骨折的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(35):5590-5595.
[10] 万乾,张擎柱,张义,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉与锁定加压钢板治疗老年脑梗死偏瘫侧股骨转子间骨折的疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(11):1411-1416.
[11] HARS M, TROMBETTI A. Body composition assessment in the prediction of osteoporotic fractures. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2017;29(4):394-401.
[12] SMITH É, COMISKEY C, CARROLL Á. Prevalence of and risk factors for osteoporosis in adults with acquired brain injury. Ir J Med Sci. 2016;185(2):473-481.
[13] MARZOLINI S, MCILROY W, TANG A, et al. Predictors of low bone mineral density of the stroke-affected hip among ambulatory individuals with chronic stroke. Osteoporos Int. 2014;25(11): 2631-2638.
[14] NIU E, YANG A, HARRIS AH, et al. Which Fixation Device is Preferred for Surgical Treatment of Intertrochanteric Hip Fractures in the United States? A Survey of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(11):3647-3655.
[15] ZHANG H, ZENG X, ZHANG N, et al. INTERTAN nail versus proximal femoral nail antirotation-Asia for intertrochanteric femur fractures in elderly patients with primary osteoporosis.J Int Med Res. 2017;45(4): 1297-1309.
[16] SANDERS D, BRYANT D, TIESZER C, et al. A Multi-Centre Randomized Control Trial Comparing A Novel Intramedullary Device (InterTAN) Versus Conventional Treatment (Sliding Hip Screw) Of Geriatric Hip Fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2016;31(1): 1-8.
[17] 潘垚,陈云丰,章伟,等. InterTan髓内钉治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的失败原因分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2014,16(8):674-678.
[18] 虎群盛,姜自伟,黄枫. 股骨粗隆间骨折髓内钉固定相关问题的研究进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2016, 8(11):1004-1008.
[19] VISTE A, PERRY KI, TAUNTON MJ, et al. Proximal femoral replacement in contemporary revision total hip arthroplasty for severe femoral bone loss: a review of outcomes. Bone Joint J.2017;99-B(3):325-329.
[20] KOVALAK E, ERMUTLU C, ATAY T, et al. Management of unstable pertrochanteric fractures with proximal femoral locking compression plates and affect of neck-shaft angle on functional outcomes. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2017;8(3):209-214.
[21] 季烈峰,陈巨坤,徐丁,等. 股骨近端防旋髓内钉与解剖锁定钢板治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2014,16(8): 727-730.
[22] 孙奇,童培建,徐斌斌,等. 老年股骨粗隆间骨折术后一年死亡率及其危险因素分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2013,15(5):371-376.
[23] 吴强,王欣,杨旭,等.股骨粗隆间骨折围手术期隐性失血的性别差异研究[J].中华骨科杂志, 2017, 37(1):31-35.
[24] 危杰,王军,高明,等.老年髋部骨折围手术期失血量的分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2015,17(2):104-107.
[25] LORICH DG, GELLER DS, NIELSON JH. Osteoporotic pertrochanteric hip fractures: management and current controversies. Instr Course Lect. 2004; 53(2):441-454.
[26] ESEN E, DUR H, ATAOĞLU MB, et al. Evaluation of proximal femoral nail-antirotation and cemented, bipolar hemiarthroplasty with calcar replacement in treatment of intertrochanteric femoral fractures in terms of mortality and morbidity ratios. Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi. 2017;28(1):35-40.
[27] REINDL R, HARVEY EJ, BERRY GK, et al. Intramedullary versus extramedullary fixation for unstable intertrochanteric fractures: a prospective randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(23):1905-1912.
[28] KLEWENO C, MORGAN J, REDSHAW J, et al. Short versus long cephalomedullary nails for the treatment of intertrochanteric hip fractures in patients older than 65 years. J Orthop Trauma. 2014; 28(7):391-397.
[29] 杨力,孙奇,易立明,等.人工股骨头置换与髓内固定治疗脑卒中后老年股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2013, 15(5): 397-401.
|