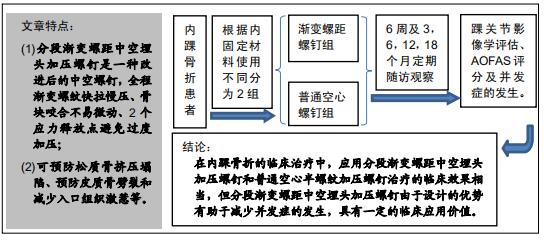
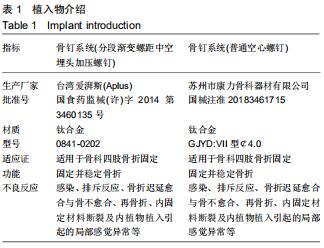
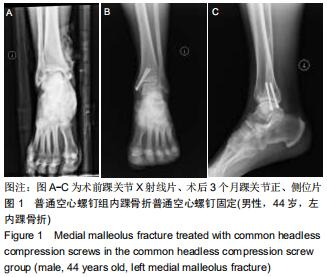
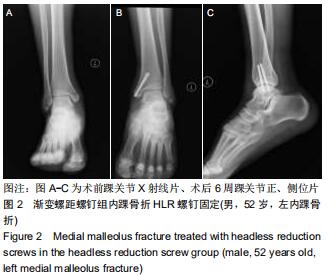
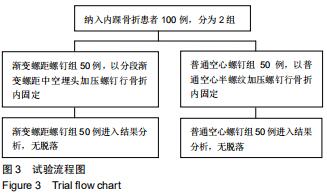
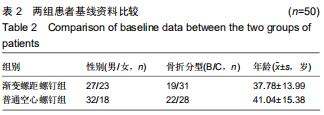
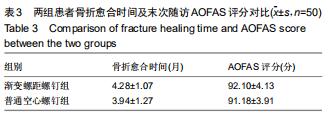
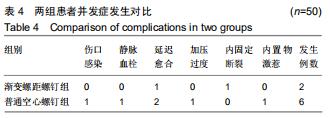
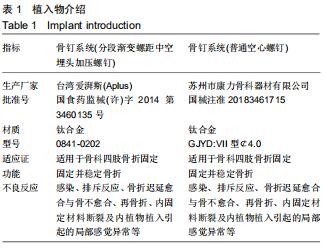
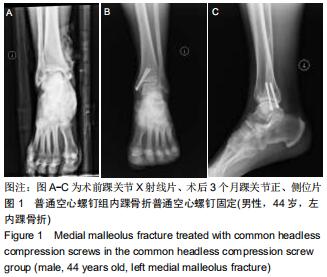
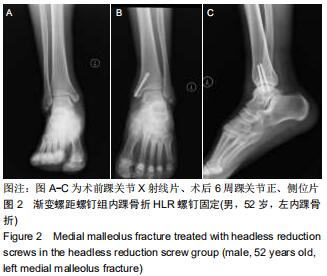
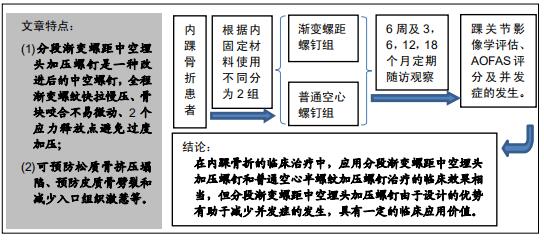
|
[1] WHITE TO, CARTER TH. Ankle fractures: facts and fiction. Bone Joint J. 2018;7(4):3-8.
[2] AITKEN SA, JOHNSTON I, JENNINGS AC, et al. An evaluation of the Herscovici classification for fractures of the medial malleolus. Foot Ankle Surg. 2017;23:317-320.
[3] KUSNEZOV NA , EISENSTEIN ED, DIAB N, et al. Medial malleolar fractures and associated deltoid ligament disruptions: current management controversies. Orthopedics. 2017;40(2):e216-e222.
[4] HERSCOVICI D JR, SCADUTO JM, INFANTE A. Con-servative treatment of isolated fractures of the medial malleolus. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89:89-93.
[5] KITAOKA HB, ALEXANDER IJ, ADELAAR RS, et al. Clinical rating systems for the ankle-hindfoot, midfoot, hallux, andlesser toes. Foot Ankle Int. 1994;15(7):349-353.
[6] 陈孝平,汪建平.外科学[M]:北京:人民卫生出版社,2013: 634-635.
[7] 侯树勋.现代创伤骨科学[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2002:1255.
[8] DAVIDOVITCH RI, EGOL KA. The medial malleolus osteoligamentous complex and its role in ankle fractures. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2009;67(4):318-324.
[9] BROCKWELL J, YEUNG Y, GRIFFITH JF. Stress fractures of the foot and ankle. Sports Med Arthrosc. 2009;17(3):149-159.
[10] KOPP F. Traumatic peroneal dislocation with medial malleolus fracture: a case report. Foot Ankle Int. 2008;29(7): 756-758.
[11] LAREAU CR, BARITEAU JT, PALLER DJ, et al. Contribution of the medial malleolus to tibiotalar joint contact characteristics. Foot Ankle Spec. 2015;8:23-28.
[12] ALLURI RK, TAN EW. Indications, postoperative management, and advances in ankle fracture fixation. Tech Foot Ankle.2018; 17(3):105-114.
[13] TANG J, HU JF, GUO WC, et al. Research and application of absorbable screw in orthopedics: a clinical review comparing PDLLA screw with metal screw in patients with simple medial malleolus fracture. Chin J Traumatol. 2013;16(1):27-30.
[14] KHURANA S, KARIA R, EGOL KA. Operative treatment of nonunion following distal fibula and medial malleolar ankle fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2013;34(3):365-371.
[15] 汪国栋,孟乘飞,陈磊,等.改良关节镜前内侧入路有限切开内固定治疗内踝移位骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2015,17(6):539-540,
[16] 陈雁西,俞光荣.踝关节骨折的治疗策略与数字化临床路径[J].中华骨科杂志,2011,31(3):275-284.
[17] PAKARINEN HJ, FLINKKIL TE, OHTONEN PP, et al. Stability criteria for nonoperative ankle fracture management. Foot Ankle Int. 2011;32(2):141-147.
[18] CARTER TH, OLIVER WM, GRAHAM C, et al. Medial malleolus: operative or non-operative (MOON) trial protocol - a prospective randomised controlled trial of operative versus non-operative management of associated medial malleolus fractures in unstable fractures of the ankle. Trials. 2019;20(1):565.
[19] MCKENNA PB, O'SHEA K, BURKE T. Less is more: lag screw only fixation of lateral malleolar fractures Paul B. Int Orthop. 2007;31(4):497-502.
[20] 叶超,洪建军,郑亦静,等.经皮微创内固定技术(MIPO)治疗踝关节骨折的疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2014,29(8): 788-790.
[21] LIN CC, LIN KJ, CHEN WC, et al. Larger screw diameter may not uarantee greater pullout strength for headless screws: a biomechanical study. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2017;24;62(3): 257-261.
[22] LIN CC, LIN KP, HUANG CC, et al. Partially threaded headless screw may benefit adequate interfragmentary compression and reduced driving torque for small bone fixation. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2018;26(1):1-6.
[23] HART A, HARVEY EJ, LEFEBVRE LP, et al. Insertion profiles of 4 headless compression screws. J Hand Surg Am. 2013;38: 1728-1734.
[24] BARNES H, CANNADA LK, WATSON JT. A clinical evaluation of alternative fixation techniques for medial malleolus fractures. Injury. 2014;45:1365-1367.
[25] RICCI WM, TORNETTA P, BORRELLI J JR. Lag screw fixation of medial malleolar fractures: a biomechanical, radiographic, and clinical comparison of unicortical partially threaded lagscrews and bicortical fully threaded lag screws. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26:602-606.
[26] SAINI P, AGGRAWAL A, MEENA S, et al. Miniarthrotomy assisted percutaneous screw fixation for displaced medial malleolus fractures a novel technique. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2014;5:252-256.
[27] MANDEL J, BEHERY O, NARAYANAN R, et al. Single- vs 2-screw lag fixation of the medial malleolus in unstable ankle fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2019;40(7):790-796.
[28] BUCKLEY R, KWEK E, DUFFY P, et al. Single-screw fixation compared with double screw fixation for treatment of medial malleolar fractures: a prospective randomized trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2018;32(11):548-553.
[29] SHAH Y, SYED T, MYSZWESKI T, et al. Comparison of outcome following either one or two screws for medial malleolar fracture fixation. Injury Extra. 2009;40(10):223-224.
[30] DEMILL SL, BUSSEWITZ BW, PHILBIN TM. Injury to the Posterior Tibial Tendon After Open Reduction Internal Fixation of the Medial Malleolus. Foot Ankle Spec. 2015;8(5):360-363.
[31] FEMINO JE, GRUBER BF, KARUNAKAR MA. Safe zone for the placement of medial malleolar screws. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(1):133-138.
[32] GIORDANO V, GOMES AF, AMARAL NP, et al. Preventing surgical complications: a survey on surgeons' perception of intra-articular malleolar screw misplacement in a cadaveric study. Patient Saf Surg. 2011;5(1):24.
|