[1] SCHEER JK, FAKURNEJAD S, LAU D, et al. Results of the 2014 SRS Survey on PJK/PJF: a report on variation of select srs member practice patterns, treatment indications, and opinions on classification development. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40: 829-840.
[2] CAMMARATA M, AUBIN CE, WANG X, et al. Biomechanical risk factors for proximal junctional kyphosis: a detailed numerical analysis of surgical instrumentation variables. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39: E500-507.
[3] GLATTES RC, BRIDWELL KH, LENKE LG, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis in adult spinal deformity following long instrumented posterior spinal fusion: incidence, outcomes, and risk factor analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30: 1643-1649.
[4] KIM YJ, BRIDWELL KH, LENKE LG, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis in adult spinal deformity after segmental posterior spinal instrumentation and fusion: minimum five-year follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33: 2179-2184.
[5] FERRERO E, BOCAHUT N, LEFEVRE Y, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis in thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: risk factors and compensatory mechanisms in a multicenter national cohort. Eur Spine J. 2018; 27: 2241-2250.
[6] LIU FY, WANG T, YANG SD, et al. Incidence and risk factors for proximal junctional kyphosis: a meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2016; 25: 2376-2383.
[7] KIM HJ, BRIDWELL KH, LENKE LG, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis results in inferior SRS pain subscores in adult deformity patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 38: 896-901.
[8] MARUO K, HA Y, INOUE S, et al. Predictive factors for proximal junctional kyphosis in long fusions to the sacrum in adult spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38: E1469-1476.
[9] YAGI M, AKILAH KB, BOACHIE-ADJEI O. Incidence, risk factors and classification of proximal junctional kyphosis: surgical outcomes review of adult idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36: E60-68.
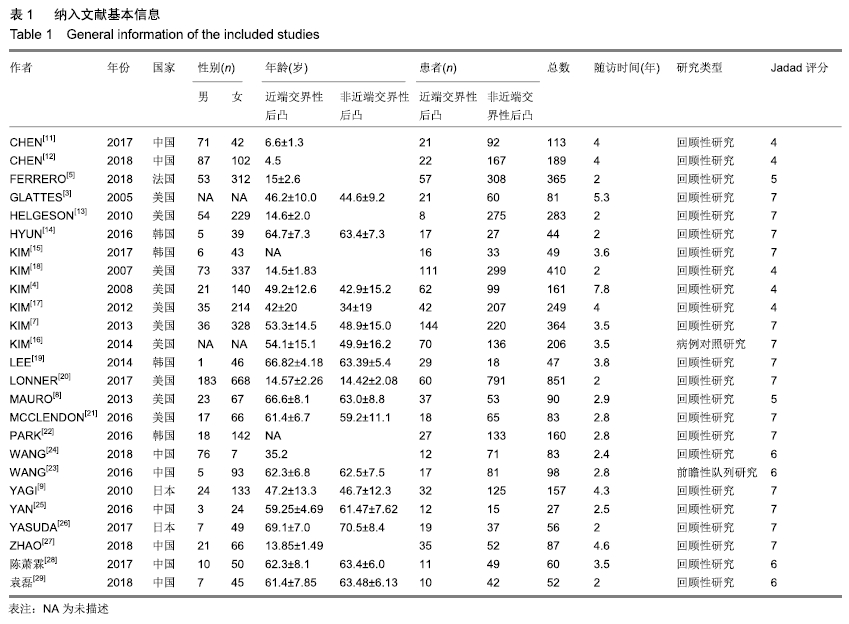
[10] JADAD AR, MOORE RA, CARROLL D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996; 17: 1-12.
[11] CHEN X, CHEN ZH, QIU Y, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis after posterior spinal instrumentation and fusion in young children with congenital scoliosis: a preliminary report on its incidence and risk factors. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42: E1197-1203.
[12] CHEN X, XU L, QIU Y, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and evolution of proximal junctional kyphosis after posterior hemivertebra resection and short fusion in young children with congenital scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018; 43: 1193-1200.
[13] HELGESON MD, SHAH SA, NEWTON PO, et al. Evaluation of proximal junctional kyphosis in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis following pedicle screw, hook, or hybrid instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35: 177-181.
[14] HYUN SJ, KIM YJ, RHIM SC. Patients with proximal junctional kyphosis after stopping at thoracolumbar junction have lower muscularity, fatty degeneration at the thoracolumbar area. Spine J. 2016;16: 1095-1101.
[15] KIM DK, KIM JY, KIM DY, et al. Risk factors of proximal junctional kyphosis after multilevel fusion surgery: more than 2 years follow-up data. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2017;60: 174-180.
[16] KIM HJ, BRIDWELL KH, LENKE LG, et al. Patients with proximal junctional kyphosis requiring revision surgery have higher postoperative lumbar lordosis and larger sagittal balance corrections. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39: E576-580.
[17] KIM HJ, YAGI M, NYUGEN J, et al. Combined anterior-posterior surgery is the most important risk factor for developing proximal junctional kyphosis in idiopathic scoliosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470: 1633-1639.
[18] KIM YJ, LENKE LG, BRIDWELL KH, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis after 3 different types of posterior segmental spinal instrumentation and fusions: incidence and risk factor analysis of 410 cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32: 2731-2738.
[19] LEE JH, KIM JU, JANG JS, et al. Analysis of the incidence and risk factors for the progression of proximal junctional kyphosis following surgical treatment for lumbar degenerative kyphosis: minimum 2-year follow-up. Br J Neurosurg. 2014;28: 252-258.
[20] LONNER BS, REN Y, NEWTON PO, et al. Risk factors of proximal junctional kyphosis in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis-the pelvis and other considerations. Spine Deform. 2017;5: 181-188.
[21] MCCLENDON J JR, SMITH TR, SUGRUE PA, et al. Spinal implant density and postoperative lumbar lordosis as predictors for the development of proximal junctional kyphosis in adult spinal deformity. World Neurosurg. 2016;95: 419-424.
[22] PARK SJ, LEE CS, CHUNG SS, et al. Different risk factors of proximal junctional kyphosis and proximal junctional failure following long instrumented fusion to the sacrum for adult spinal deformity: survivorship analysis of 160 patients. Neurosurgery. 2017;80: 279-286.
[23] WANG H, MA L, YANG D, et al. Incidence and risk factors for the progression of proximal junctional kyphosis in degenerative lumbar scoliosis following long instrumented posterior spinal fusion. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95: e4443.
[24] WANG T, ZHAO Y, LIANG Y, et al. Risk factor analysis of proximal junctional kyphosis after posterior osteotomy in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2018; 29: 75-80.
[25] YAN P, BAO H, QIU Y, et al. Mismatch Between Proximal Rod Contouring and Proximal Junctional Angle: A Predisposed Risk Factor for Proximal Junctional Kyphosis in Degenerative Scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017; 42: E280-e287.
[26] YASUDA T, HASEGAWA T, YAMATO Y, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis in adult spinal deformity with long spinal fusion from T9/T10 to the ilium. J Spine Surg. 2017; 3: 204-211.
[27] ZHAO J, YANG M, YANG Y, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis following correction surgery in the Lenke 5 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patient. J Orthop Sci. 2018;23: 744-749.
[28] 陈萧霖,曾岩,陈仲强,等.退变性腰椎侧凸后路长节段固定融合术后近端交界性后凸的危险因素分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2017,27(7):612-621.
[29] 袁磊,陈萧霖,曾岩,等.退变性腰椎侧凸患者椎旁肌退变与术后近端交界性后凸的相关性研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2018,28(5):425-433.
[30] 赵师州,钱邦平,邱勇.强直性脊柱炎胸腰椎后凸畸形截骨矫形术后近端交界性后凸的危险因素与临床意义[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2018, 28(8): 675-681.
[31] LAU D, CLARK AJ, SCHEER JK, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis and failure after spinal deformity surgery: a systematic review of the literature as a background to classification development. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014; 39: 2093-2102.
[32] O'LEARY PT, BRIDWELL KH, LENKE LG, et al. Risk factors and outcomes for catastrophic failures at the top of long pedicle screw constructs: a matched cohort analysis performed at a single center. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34: 2134-2139.
[33] KEBAISH KM, MARTIN CT, O'BRIEN JR, et al. Use of vertebroplasty to prevent proximal junctional fractures in adult deformity surgery: a biomechanical cadaveric study. Spine J. 2013;13: 1897-1903.
[34] BRIDWELL KH, LENKE LG, CHO SK, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis in primary adult deformity surgery: evaluation of 20 degrees as a critical angle. Neurosurgery. 2013;72: 899-906.
[35] ANNIS P, LAWRENCE BD, SPIKER WR, et al. Predictive factors for acute proximal junctional failure after adult deformity surgery with upper instrumented vertebrae in the thoracolumbar spine. Evid Based Spine Care J. 2014; 5: 160-162.
[36] HA Y, MARUO K, RACINE L, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis and clinical outcomes in adult spinal deformity surgery with fusion from the thoracic spine to the sacrum: a comparison of proximal and distal upper instrumented vertebrae. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;19: 360-369.
[37] ZHU Z, TANG NL, XU L, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in Chinese girls. Nat Commun. 2015; 6: 8355.
[38] HART RA, PRENDERGAST MA, ROBERTS WG, et al. Proximal junctional acute collapse cranial to multi-level lumbar fusion: a cost analysis of prophylactic vertebral augmentation. Spine J. 2008;8: 875-881.
[39] 郑波,王飞,张志成,等.近端交界性后凸的危险因素分析[J].中国康复理论与实践,2017, 23(5): 607-611.
[40] BRIDWELL KH, GLASSMAN S, HORTON W, et al. Does treatment (nonoperative and operative) improve the two-year quality of life in patients with adult symptomatic lumbar scoliosis: a prospective multicenter evidence-based medicine study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34: 2171-2178.
[41] MASEVNIN S, PTASHNIKOV D, MICHAYLOV D, et al. Risk factors for adjacent segment disease development after lumbar fusion. Asian Spine J. 2015; 9: 239-244.
|