中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (10): 1521-1527.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2237
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
种植义齿相对位置对食物嵌塞影响的有限元分析
庞国宝1,2,赵 凝1,2,安美文1,2
- 1太原理工大学生物医学工程学院,山西省太原市 030024;2山西省材料强度与结构冲击重点实验室,山西省太原市 030024
Effect of relative position of planting denture on interdental food impaction: finite element analysis
Pang Guobao1, 2, Zhao Ning1, 2, An Meiwen1, 2
- 1College of Biomedical Engineering, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, Shanxi Province, China; 2Shanxi Key Laboratory of Material Strength and Structural Impact, Taiyuan 030024, Shanxi Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
食物嵌塞:是指在咀嚼过程中咬合压力将食物碎片楔入两颗相邻牙齿牙间隙的现象。食物嵌塞可分为垂直型和水平型,垂直型食物嵌塞是指食物碎片从𬌗面的垂直方向上嵌入牙间隙内,水平型食物嵌塞是指食物碎片被唇、舌的压力挤入牙间隙内。
种植义齿:是指经手术方法在口腔牙齿缺失区域牙槽骨内植入采用金属、陶瓷等人工材料制成的类似于牙根形态的种植体,即人工牙根,待其成活且形成骨结合后再在上端制作修复体完成种植义齿的修复。
背景:种植义齿是一种固位、支持、稳定功能都很出色的牙修复体,但其种植后的塞牙现象是困扰广大牙列缺损患者的一个普遍现象。
目的:应用有限元分析法针对食物嵌塞这一问题进行生物力学数值模拟分析,给出种植义齿的相对宽度、相对高度、相对角度对食物嵌塞影响的定量关系。
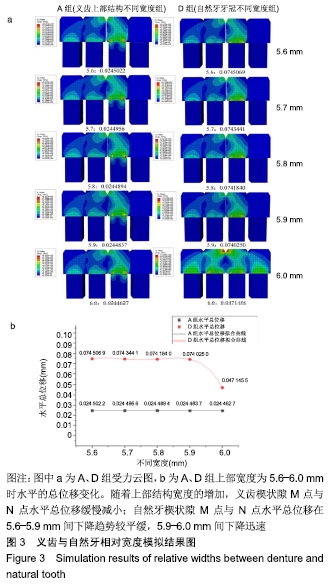
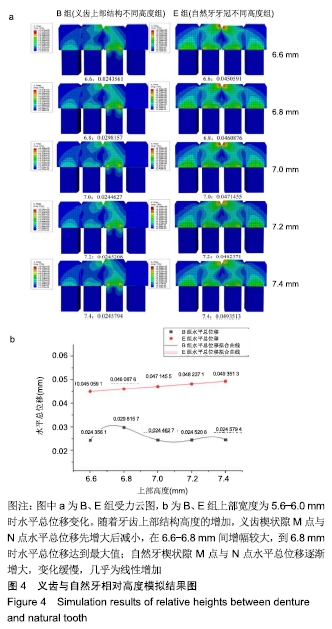
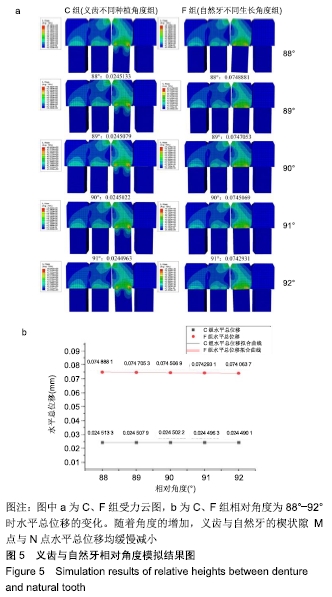
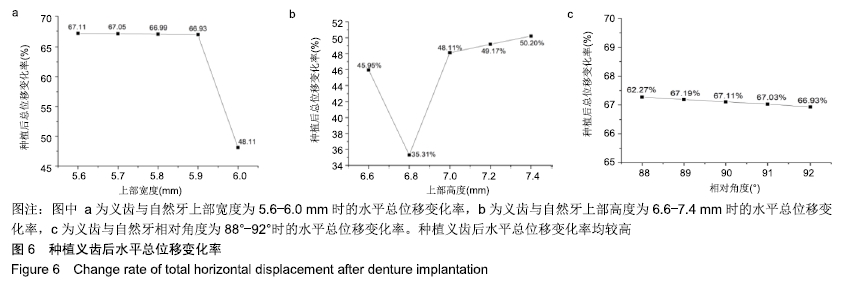
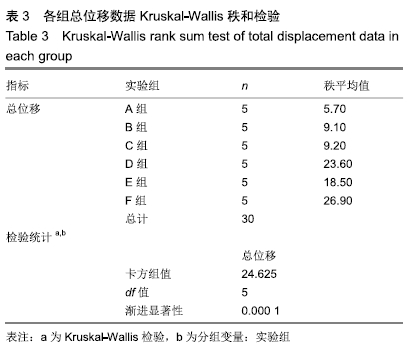
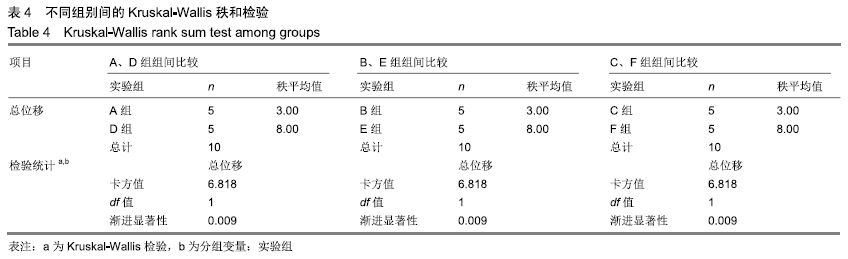
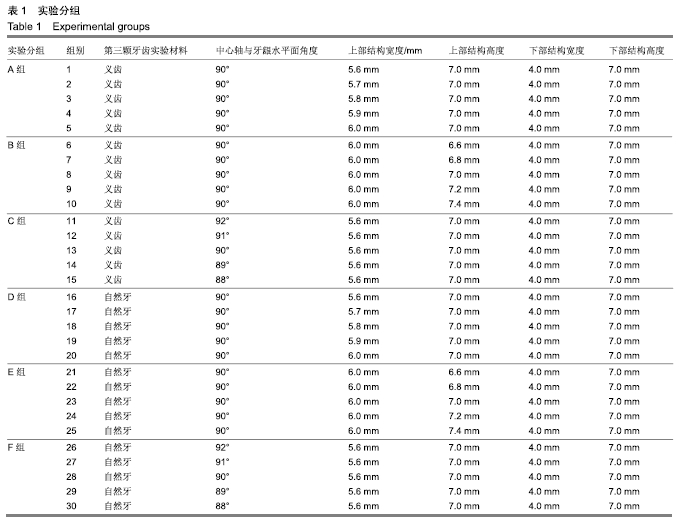
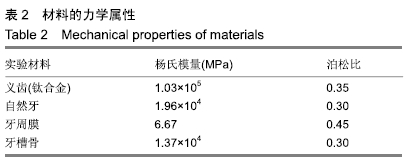
方法:为研究种植义齿相对牙齿在不同宽度、高度、角度情况下对食物嵌塞的影响,设计了义齿上部结构不同宽度组(分5个亚组:5.6,5.7,5.8,5.9,6.0 mm)、义齿上部结构不同高度组(分5个亚组:6.6,6.8,7.0,7.2,7.4 mm)、义齿不同种植角度组(分5个亚组:92°、91°、90°、89°、88°)、自然牙牙冠不同宽度组(分5个亚组:5.6,5.7,5.8,5.9,6.0 mm)、自然牙牙冠不同高度组(分5个亚组:6.6,6.8,7.0,7.2,7.4 mm)、自然牙不同生长角度组(分5个亚组:92°、91°、90°、89°、88°)4颗牙齿局部牙列模型,每个亚组通过改变第3个牙齿部件的相对位置来设计,其余条件相同。对所有牙列模型进行食物嵌塞数值模拟,并分析牙齿受力形变情况,比较各组间受力前后牙间隙宽度曲线。
结果与结论:①随着种植义齿上部结构宽度的增加,义齿受力后水平总位移缓慢减少;当上部结构宽度为5.9-6.0 mm间时,自然牙受力变形后牙间隙迅速减小,此时种植义齿对食物嵌塞的影响趋近于自然牙情况下的食物嵌塞状况;②当义齿上部结构高度低于邻牙时,随着该义齿上部结构高度的增加,受力后牙间隙先增大后减小;当义齿低于邻牙且高度在6.8-7.0 mm之间时,受力后牙间隙迅速减小;③义齿受力前后水平总位移随着种植角度的增加缓慢减小;④结果表明为减小食物嵌塞现象,种植义齿与邻牙间隙应小于0.05 mm,种植义齿上部结构高度应低于邻牙0.2 mm左右,种植角度应约等于90°。
ORCID: 0000-0001-6562-4699(庞国宝)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: