中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (35): 5718-5726.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1482
• 组织构建循证医学 evidence-based medicine in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
抗阻运动对2型糖尿病糖脂代谢异常患者干预效果的系统综述和Meta分析
梁 敏1,王海牛2,黄 鹏2,朱玮华2,李顺昌1
- (1运动医学与健康研究所,成都体育学院,四川省成都市 610041;2运动医学与健康学院,成都体育学院,四川省成都市 610041)
Systematic review and meta-analysis of effect of resistance exercise on glucose and lipid metabolism disorder in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients
Liang Min1, Wang Hainiu2, Huang Peng2, Zhu Weihua2, Li Shunchang1
- (1Institute of Sports Medicine and Health, 2College of Sports Medicine and Health, Chengdu Sport University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
抗阻运动:抗阻运动是对抗阻力的负重训练方法。通过抗阻训练可改善体成分、增加肌肉力量、改善胰岛素抵抗,是降低2型糖尿病患者糖脂指标的有效方法。抗阻运动要选择大肌肉动作,多关节运动,同时兼顾身体的均衡性。抗阻运动的负荷评价方法有心率、最大摄氧量、代谢当量、主观疲劳程度等,长期坚持中高强度的抗阻训练将获得更好的降糖脂效益。目前,抗阻运动大量运用于临床并得到了显著的效果,针对不同的患者提供不同的运动方案。
2型糖尿病:在医学上糖尿病按病因学划分为4种类别,包括1型糖尿病、2型糖尿病、妊娠期糖尿病及其他类型糖尿病,但其中2型糖尿病增长较为迅速且90%的患者都是属于2型糖尿病,糖尿病一直是普遍关注的健康话题,因此预防和治疗是当务之急。
.jpg)
文题释义:
抗阻运动:抗阻运动是对抗阻力的负重训练方法。通过抗阻训练可改善体成分、增加肌肉力量、改善胰岛素抵抗,是降低2型糖尿病患者糖脂指标的有效方法。抗阻运动要选择大肌肉动作,多关节运动,同时兼顾身体的均衡性。抗阻运动的负荷评价方法有心率、最大摄氧量、代谢当量、主观疲劳程度等,长期坚持中高强度的抗阻训练将获得更好的降糖脂效益。目前,抗阻运动大量运用于临床并得到了显著的效果,针对不同的患者提供不同的运动方案。
2型糖尿病:在医学上糖尿病按病因学划分为4种类别,包括1型糖尿病、2型糖尿病、妊娠期糖尿病及其他类型糖尿病,但其中2型糖尿病增长较为迅速且90%的患者都是属于2型糖尿病,糖尿病一直是普遍关注的健康话题,因此预防和治疗是当务之急。
摘要
背景:抗阻运动已被证实有利于改善2型糖尿病患者的糖脂代谢,但抗阻运动的运动方式、强度、频率,以及与不同运动形式的有效结合还需要更深入的探索和证实。
目的:评价抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者糖脂代谢紊乱的干预效果。
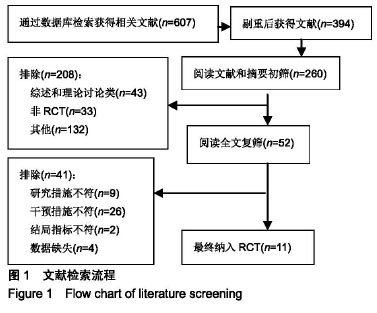
方法:检索 PubMed、FMRS、EMbase、The Cochrane Library、中国知网、万方等数据库,搜集抗阻运动干预2型糖尿病的相关RCTs(研究对象分为空白对照组、有氧对照组、抗阻组),检索时限设定为建库至2018年12月,同时追溯检索纳入文献的参考文献。由2名研究者按纳入和排除标准筛选文献并提取有效数据,进行质量评价。采用RevMan 5.3软件对最终纳入的文献数据进行Meta分析。
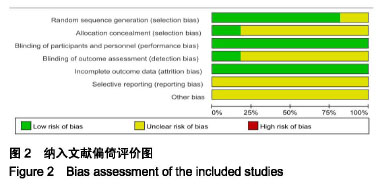
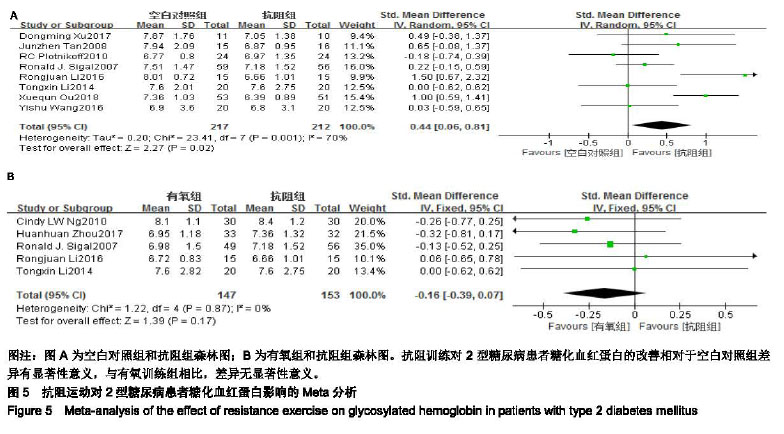
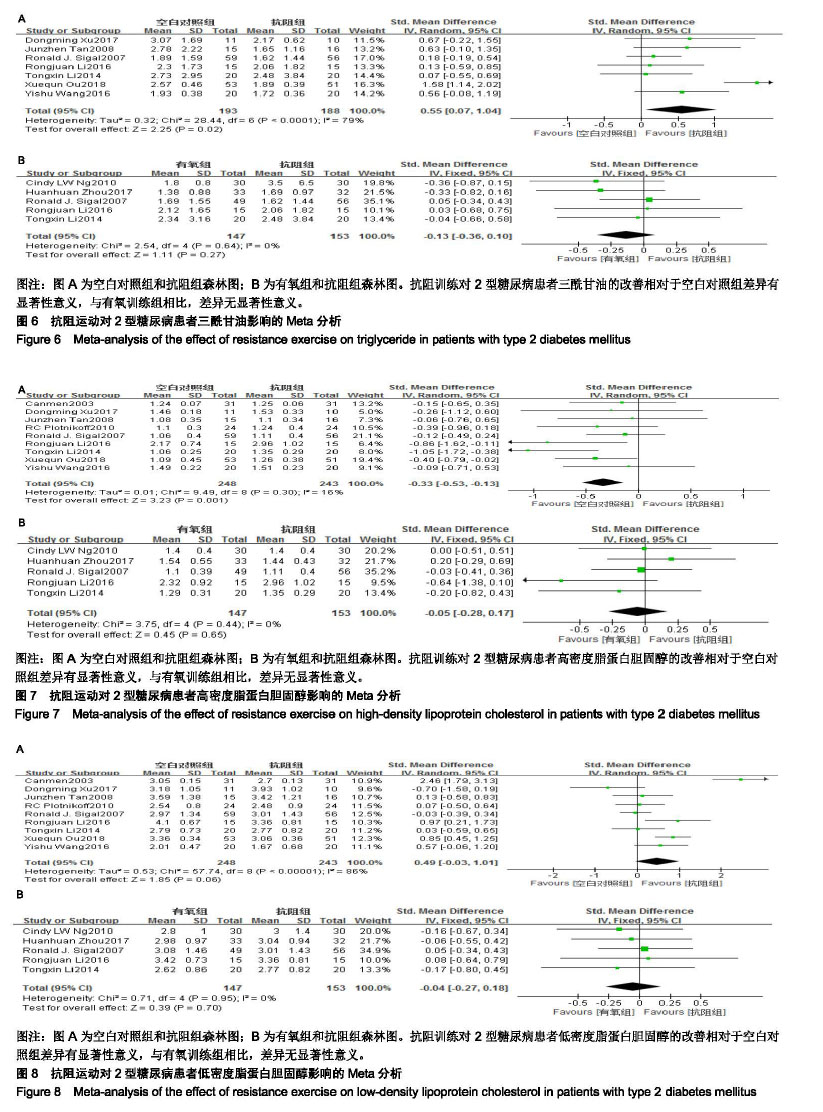
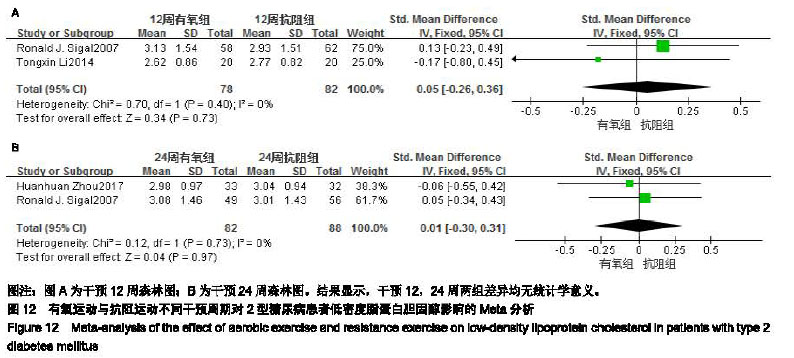
结果与结论:①最终纳入11篇随机对照试验,所有文献的选择性报告和其他偏倚风险两项评估均为不清楚,但整体文献质量处于中等偏上;②Meta分析结果显示进行抗阻运动组在改善空腹血糖[SMD=0.84,95%CI(0.39,1.29),P=0.000 2]、糖化血红蛋白[SMD=0.44,95%CI(0.06,0.81),P=0.02]、三线甘油[SMD=0.55,95%CI(0.07,1.04),P=0.02]、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇[SMD=-0.33,95%CI(-0.53,-0.13),P=0.001]、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇[SMD=0.49,95%CI(-0.03,1.01),P=0.06]具有显著效果;③抗阻运动组均优于空白对照组,与有氧运动组相比较无显著性差异;④结果显示抗阻运动有利于改善2型糖尿病患者糖脂代谢水平,可以作为糖尿病运动治疗的重要组成部分。
背景:抗阻运动已被证实有利于改善2型糖尿病患者的糖脂代谢,但抗阻运动的运动方式、强度、频率,以及与不同运动形式的有效结合还需要更深入的探索和证实。
目的:评价抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者糖脂代谢紊乱的干预效果。
方法:检索 PubMed、FMRS、EMbase、The Cochrane Library、中国知网、万方等数据库,搜集抗阻运动干预2型糖尿病的相关RCTs(研究对象分为空白对照组、有氧对照组、抗阻组),检索时限设定为建库至2018年12月,同时追溯检索纳入文献的参考文献。由2名研究者按纳入和排除标准筛选文献并提取有效数据,进行质量评价。采用RevMan 5.3软件对最终纳入的文献数据进行Meta分析。
结果与结论:①最终纳入11篇随机对照试验,所有文献的选择性报告和其他偏倚风险两项评估均为不清楚,但整体文献质量处于中等偏上;②Meta分析结果显示进行抗阻运动组在改善空腹血糖[SMD=0.84,95%CI(0.39,1.29),P=0.000 2]、糖化血红蛋白[SMD=0.44,95%CI(0.06,0.81),P=0.02]、三线甘油[SMD=0.55,95%CI(0.07,1.04),P=0.02]、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇[SMD=-0.33,95%CI(-0.53,-0.13),P=0.001]、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇[SMD=0.49,95%CI(-0.03,1.01),P=0.06]具有显著效果;③抗阻运动组均优于空白对照组,与有氧运动组相比较无显著性差异;④结果显示抗阻运动有利于改善2型糖尿病患者糖脂代谢水平,可以作为糖尿病运动治疗的重要组成部分。
中图分类号:



.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
抗阻运动:抗阻运动是对抗阻力的负重训练方法。通过抗阻训练可改善体成分、增加肌肉力量、改善胰岛素抵抗,是降低2型糖尿病患者糖脂指标的有效方法。抗阻运动要选择大肌肉动作,多关节运动,同时兼顾身体的均衡性。抗阻运动的负荷评价方法有心率、最大摄氧量、代谢当量、主观疲劳程度等,长期坚持中高强度的抗阻训练将获得更好的降糖脂效益。目前,抗阻运动大量运用于临床并得到了显著的效果,针对不同的患者提供不同的运动方案。#br#
2型糖尿病:在医学上糖尿病按病因学划分为4种类别,包括1型糖尿病、2型糖尿病、妊娠期糖尿病及其他类型糖尿病,但其中2型糖尿病增长较为迅速且90%的患者都是属于2型糖尿病,糖尿病一直是普遍关注的健康话题,因此预防和治疗是当务之急。
#br#
文题释义:#br#
抗阻运动:抗阻运动是对抗阻力的负重训练方法。通过抗阻训练可改善体成分、增加肌肉力量、改善胰岛素抵抗,是降低2型糖尿病患者糖脂指标的有效方法。抗阻运动要选择大肌肉动作,多关节运动,同时兼顾身体的均衡性。抗阻运动的负荷评价方法有心率、最大摄氧量、代谢当量、主观疲劳程度等,长期坚持中高强度的抗阻训练将获得更好的降糖脂效益。目前,抗阻运动大量运用于临床并得到了显著的效果,针对不同的患者提供不同的运动方案。#br#
2型糖尿病:在医学上糖尿病按病因学划分为4种类别,包括1型糖尿病、2型糖尿病、妊娠期糖尿病及其他类型糖尿病,但其中2型糖尿病增长较为迅速且90%的患者都是属于2型糖尿病,糖尿病一直是普遍关注的健康话题,因此预防和治疗是当务之急。