中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (3): 384-390.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0597
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
人参皂苷Rg1干预非酒精性脂肪肝模型大鼠肝细胞的凋亡
肖 阳1,侯云鹤2,尹 鑫3,康 凤3,李树德2,杨世昆4,陶建平1
- (1昆明医科大学第二附属医院麻醉科,云南省昆明市 650000;2昆明医科大学生物化学与分子生物学系,云南省昆明市 650500;3昆明医科大学2016级医学实验技术班,云南省昆明市 650500;4昆明医科大学第一附属医院移植科,云南省昆明市 650000)
Ginsenoside Rg1 protects against hepatocyte apoptosis in a rat model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Xiao Yang1, Hou Yunhe2, Yin Xin3, Kang Feng3, Li Shude2, Yang Shikun4, Tao Jianping1
- (1Department of Anesthesiology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650000, Yunnan Province, China; 2Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 32016 Medical Experimental Technology Class, Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China; 4Department of Organ Transplantation, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650000, Yunnan Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
人参皂苷Rg1:人参皂苷Rg1是人参和三七中共有的主要活性成分,具有抗炎症、抗纤维化和神经保护作用等功能。有研究表明,人参皂苷Rg1有可通过抑制氧化应激导致的细胞凋亡,从而达到治疗效果。
非酒精性脂肪肝:非酒精性脂肪肝包括单纯性非酒精性脂肪肝、非酒精性脂肪肝炎以及进一步发展的肝硬化和肝细胞癌。从形态学角度,非酒精性脂肪肝主要表现为以肝小叶出现弥漫性肝细胞脂肪变性的特征。临床表现为轻度无明显症状,中度甚至重度可出现肝区隐痛、全身乏力、腹泻等表现。
文题释义:
人参皂苷Rg1:人参皂苷Rg1是人参和三七中共有的主要活性成分,具有抗炎症、抗纤维化和神经保护作用等功能。有研究表明,人参皂苷Rg1有可通过抑制氧化应激导致的细胞凋亡,从而达到治疗效果。
非酒精性脂肪肝:非酒精性脂肪肝包括单纯性非酒精性脂肪肝、非酒精性脂肪肝炎以及进一步发展的肝硬化和肝细胞癌。从形态学角度,非酒精性脂肪肝主要表现为以肝小叶出现弥漫性肝细胞脂肪变性的特征。临床表现为轻度无明显症状,中度甚至重度可出现肝区隐痛、全身乏力、腹泻等表现。
.jpg) 文题释义:
人参皂苷Rg1:人参皂苷Rg1是人参和三七中共有的主要活性成分,具有抗炎症、抗纤维化和神经保护作用等功能。有研究表明,人参皂苷Rg1有可通过抑制氧化应激导致的细胞凋亡,从而达到治疗效果。
非酒精性脂肪肝:非酒精性脂肪肝包括单纯性非酒精性脂肪肝、非酒精性脂肪肝炎以及进一步发展的肝硬化和肝细胞癌。从形态学角度,非酒精性脂肪肝主要表现为以肝小叶出现弥漫性肝细胞脂肪变性的特征。临床表现为轻度无明显症状,中度甚至重度可出现肝区隐痛、全身乏力、腹泻等表现。
文题释义:
人参皂苷Rg1:人参皂苷Rg1是人参和三七中共有的主要活性成分,具有抗炎症、抗纤维化和神经保护作用等功能。有研究表明,人参皂苷Rg1有可通过抑制氧化应激导致的细胞凋亡,从而达到治疗效果。
非酒精性脂肪肝:非酒精性脂肪肝包括单纯性非酒精性脂肪肝、非酒精性脂肪肝炎以及进一步发展的肝硬化和肝细胞癌。从形态学角度,非酒精性脂肪肝主要表现为以肝小叶出现弥漫性肝细胞脂肪变性的特征。临床表现为轻度无明显症状,中度甚至重度可出现肝区隐痛、全身乏力、腹泻等表现。摘要
背景:人参皂苷Rg1可以减轻氧化应激并且抑制细胞凋亡,是三七和人参共有的有效活性成分。
目的:分析人参皂苷Rg1对非酒精性脂肪性肝病大鼠模型肝细胞凋亡的抑制作用及分子机制。
方法:SD大鼠40只,适应性喂养2周后随机分成4组(n=10),分别为空白对照组,模型对照组,人参皂苷Rg1低剂量组,人参皂苷Rg1高剂量组。空白对照组正常饮食,模型对照组高脂高糖饮食22周,人参皂苷Rg1组高脂高糖饮食14周后加用Rg1灌胃治疗8周。用显色法检测血清中氧化应激指标,苏木精-伊红染色观察肝组织病理形态变化,油红染色观察肝组织的脂滴,TUNEL染色观察肝细胞的凋亡情况。通过Q-PCR从mRNA水平检测肝脏组织中Bax、Bcl-2、Caspase-3的表达情况。通过免疫组织化学、Western Blotting从蛋白质水平检测肝脏组织中的凋亡关键因子Bax、Bcl-2、Procaspase-3、Caspase-3 cleavage p17表达情况。
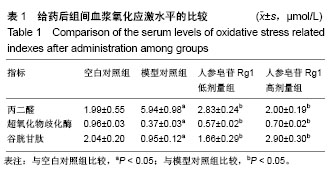
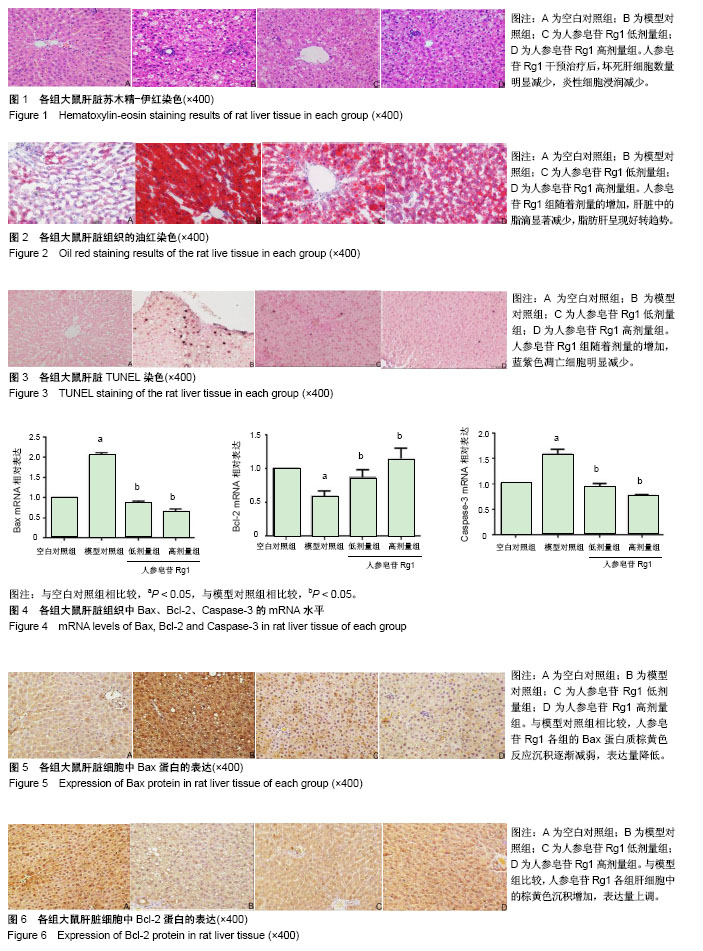
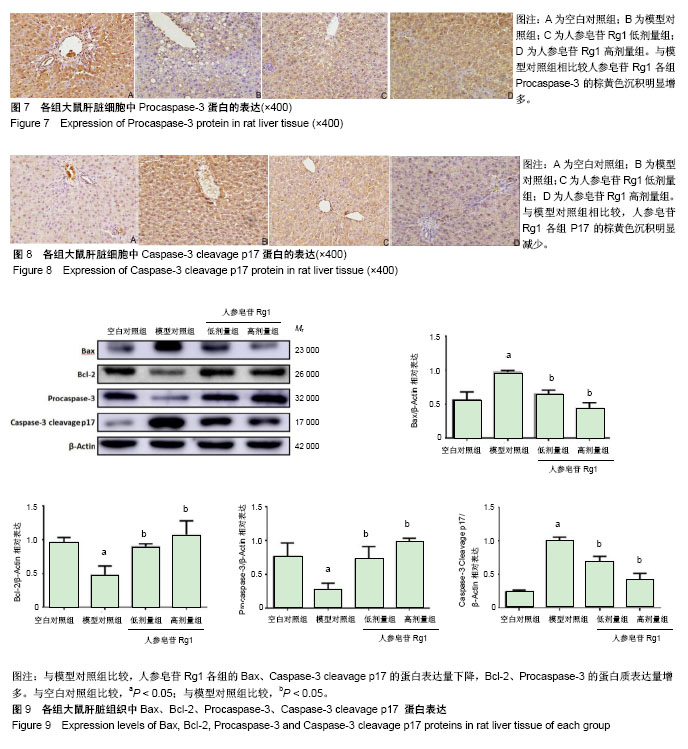
结果与结论:①苏木精-伊红染色:与空白对照组比较,模型组肝脏细胞排列紊乱出现大量脂肪空泡并且大量炎性细胞浸润,与模型对照组相比,人参皂苷Rg1组肝细胞排列形态逐渐恢复正常脂肪空泡减少以及炎性细胞浸润减少;②油红染色:与模型对照组比较,人参皂苷Rg1组肝细胞脂滴明显减少,并且随着Rg1的浓度升高而降低;③TUNEL染色:与模型对照组比较,人参皂苷Rg1组的凋亡程度明显降低;④显色法检测:与模型对照组比较,人参皂苷Rg1组与模型组比较,谷胱甘肽、超氧化物歧化酶升高(P < 0.05),丙二醛降低(P < 0.05);⑤与模型对照组比较,人参皂苷Rg1组Bax、Caspase-3的mRNA表达降低(P < 0.05),Bcl-2 mRNA表达升高(P < 0.05);⑥与模型对照组比较,人参皂苷Rg1组的Bax,Caspase-3 cleavage p17的蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05),Bcl-2、Procaspase-3的蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05),存在一定的剂量依赖性;⑦结果表明,人参皂苷Rg1可能通过减轻氧化应激,抑制非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠模型的肝细胞凋亡,从而缓解非酒精性脂肪肝的进展。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-4527-7252(肖阳)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
人参皂苷Rg1:人参皂苷Rg1是人参和三七中共有的主要活性成分,具有抗炎症、抗纤维化和神经保护作用等功能。有研究表明,人参皂苷Rg1有可通过抑制氧化应激导致的细胞凋亡,从而达到治疗效果。
非酒精性脂肪肝:非酒精性脂肪肝包括单纯性非酒精性脂肪肝、非酒精性脂肪肝炎以及进一步发展的肝硬化和肝细胞癌。从形态学角度,非酒精性脂肪肝主要表现为以肝小叶出现弥漫性肝细胞脂肪变性的特征。临床表现为轻度无明显症状,中度甚至重度可出现肝区隐痛、全身乏力、腹泻等表现。
文题释义:
人参皂苷Rg1:人参皂苷Rg1是人参和三七中共有的主要活性成分,具有抗炎症、抗纤维化和神经保护作用等功能。有研究表明,人参皂苷Rg1有可通过抑制氧化应激导致的细胞凋亡,从而达到治疗效果。
非酒精性脂肪肝:非酒精性脂肪肝包括单纯性非酒精性脂肪肝、非酒精性脂肪肝炎以及进一步发展的肝硬化和肝细胞癌。从形态学角度,非酒精性脂肪肝主要表现为以肝小叶出现弥漫性肝细胞脂肪变性的特征。临床表现为轻度无明显症状,中度甚至重度可出现肝区隐痛、全身乏力、腹泻等表现。